Liver Elastography Test, Normal Range & Types & Cost
PACE Hospitals is the leading center for Liver Elastography and Fibroscan in Hyderabad, Telangana, India. Our expert hepatologists and gastroenterologists specialize in diagnosing and managing liver diseases, fibrosis, and cirrhosis with highly accurate, non-invasive liver stiffness assessments. Backed by advanced technology and years of clinical expertise, our doctors ensure precise evaluations and personalized treatment plans for fatty liver disease, hepatitis, and chronic liver conditions.
Quick Navigation
Book an appointment for Liver Elastography Test
Liver Elastography Fibroscan Appointment
Thank you for contacting us. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
PACE Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Oops, there was an error sending your message. Please try again later. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
PACE Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Why Choose PACE Hospitals for Liver Elastography?
State-of-the-Art Magnetic Resonance Elastography
Team of the Best Hepatologist in Hyderabad
Non-Invasive, Painless Highly Accurate Testing
Affordable & Reliable Liver Elastography Test
What is a liver elastography?
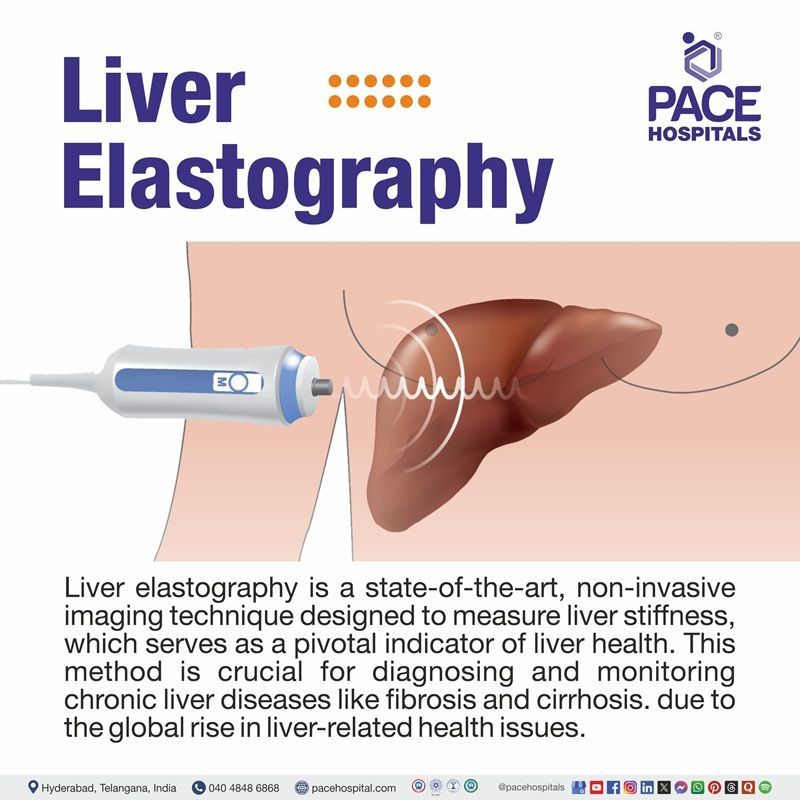
Liver elastography is a state-of-the-art, non-invasive imaging technique designed to measure liver stiffness, which serves as a pivotal indicator of liver health. This method is crucial for diagnosing and monitoring chronic liver diseases like fibrosis and cirrhosis. The healthcare team must be knowledgeable about the principles, methodologies, clinical applications, contraindications, and procedural specifics of liver elastography due to the global rise in liver-related health issues.
Principle of the liver elastography test
- The functioning of liver elastography is rooted in the understanding that liver stiffness is directly correlated with the degree of fibrosis present in the liver tissue. Fibrosis is a pathologic process that occurs as a response to persistent liver injury. The liver undergoes structural changes due to the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins, primarily collagen.
- Liver elastography measures liver stiffness, allowing the hepatologist to infer fibrosis stage without invasive procedures. This non-invasive approach reduces reliance on liver biopsies, which carry risks of complications like bleeding, infection, and discomfort for the patient. Additionally, it also quantifies the stiffness of diseased and healthy liver tissue.
Causes of liver fibrosis
Common factors that can lead to ongoing liver injury and fibrosis include:
- Hepatitis B and C: Viral infections can cause chronic liver inflammation, leading to cell damage and fibrosis if not managed properly.
- Alcohol use disorder (AUD): Alcoholic liver disease, a range of liver conditions including fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and cirrhosis, occurs due to the toxicity of alcohol, leading to inflammation and liver cell damage.
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): NAFLD, linked to metabolic syndrome, is a liver condition where excess fat accumulates in the liver without alcohol consumption, it is often seen in individuals with obesity, diabetes, or dyslipidemia, potentially leading to Non-alcoholic steato hepatitis (NASH).
- Fibrosis is a condition where healthy liver cells are replaced by scar tissue, impairing liver functionality. This buildup reduces blood flow, causing further damage. If left untreated, it can progress to severe cirrhosis, resulting in permanent scarring of the liver, leading to complications like
liver failure and increased liver cancer risk.
Types of elastography
Early detection of fibrosis and cirrhosis is crucial, as these conditions may not always present obvious symptoms. The primary types of liver elastography tests include:
Ultrasound Elastography (Transient Elastography) - FibroScan
- This technique utilizes a specialized ultrasound device to send sound waves into the liver. The device measures the velocity of the vibrations traveling through the liver tissue.
- Areas of stiffer tissue allow vibrations to travel more quickly, enabling the construction of an image that reveals regions of increased stiffness, which correlate with fibrosis.
Magnetic Resonance Elastography (MRE)
- MR Elastography is a liver imaging technique that uses MRI technology and elastography to capture mechanical vibrations, enabling the identification of fibrotic areas through detailed maps of liver stiffness variations.
Shear Wave Elastography (SWE)
- This advanced ultrasound-based technique measures the speed at which shear waves travel through the liver in real-time.
- Using standard ultrasound machines equipped with elastography software, SWE is increasingly utilized in diverse clinical environments, yielding immediate stiffness measurements that aid in patient assessment and management.
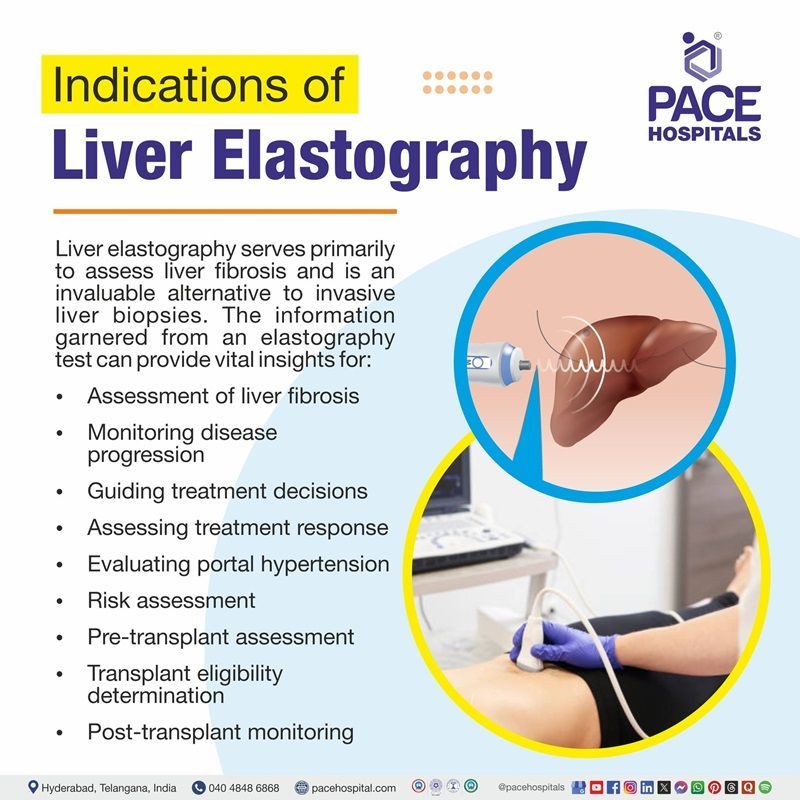
Indications of elastography
Liver elastography serves primarily to assess liver fibrosis and is an invaluable alternative to invasive liver biopsies. The information garnered from an elastography test can provide vital insights for:
- Assessment of liver fibrosis: Liver elastography is crucial for assessing fibrosis in patients with chronic liver diseases, aiding in determining disease stage and guiding antiviral therapy decisions.
- Monitoring disease progression: Elastography assessments help track liver stiffness changes over time, providing crucial information about disease progression and treatment effectiveness, especially in conditions like chronic hepatitis and NASH.
- Guiding treatment decisions: Liver elastography is crucial in managing chronic hepatitis C, identifying patients requiring more aggressive treatment based on fibrosis severity and evaluating therapy response by comparing pre- and post-treatment stiffness measurements, thus shaping the treatment strategies.
- Assessing treatment response: Post-treatment elastography is a crucial tool for assessing the effectiveness of liver disease treatments and fibrosis resolution in patients, providing real-time insights into liver stiffness, indicating the efficacy of the treatment.
- Evaluating portal hypertension: Liver stiffness measurement is crucial for assessing portal hypertension, a common complication in chronic liver disease patients. Clinicians can gauge the extent of hypertension, which often leads to additional complications.
- Risk Assessment: Identifying patients at risk for complications is crucial in managing liver conditions, allowing the doctors to implement timely intervention strategies to mitigate potential issues and improve patient outcomes.
- Pre-transplant assessment: A thorough evaluation of liver health and fibrosis levels is crucial before liver transplantation to determine a patient's suitability for the procedure.
- Transplant eligibility determination: Elastography is crucial in assessing transplant candidates, as it measures liver stiffness, ensuring only suitable individuals undergo surgery based on their liver condition, thus enhancing the chances of successful transplant outcomes.
- Post-transplant monitoring: Continuous monitoring of liver stiffness through elastography is crucial after liver transplants, as it indicates graft health and allows physicians to detect issues early, effectively manage patient recovery, and ensure the long-term success of the transplant.
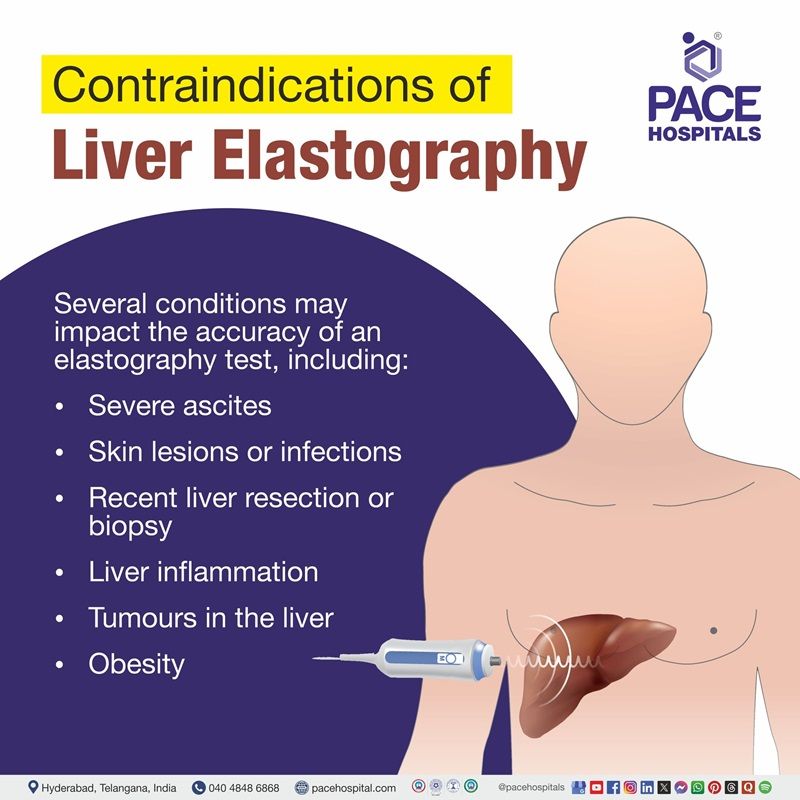
Contraindications of liver elastography
Several conditions may impact the accuracy of an elastography test, including:
- Inability to maintain position: Patients with respiratory distress or severe pain may not be suitable candidates for elastography due to potential discomfort or difficulty staying still.
- Severe ascites: Fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity can disrupt shear wave transmission, causing unreliable measurements. Addressing ascites may be necessary before elastography.
- Skin lesions or Infections: The application of a probe to a specific area may increase the risk of infection, so a thorough skin condition assessment is crucial before proceeding.
- Recent liver resection or biopsy: Patients who recently underwent liver resection or biopsy may need to delay elastography for a specific time to prevent complications and ensure more accurate results.
- Liver inflammation: The test's accuracy can be impacted by conditions like liver inflammation from illness or alcohol consumption.
- Tumours in the liver: The presence of tumors can potentially affect the accuracy of measurements taken during elastography.
- Obesity: The quality of elastography may be affected by increased body weight, making precise measurements more challenging.
Eligibility criteria for elastography testing
An elastography test may be necessary to evaluate liver fibrosis (scarring) in individuals who:
- Have liver disease and is seeking additional information from their doctor to make informed treatment decisions.
- Have Prior liver test results indicating inflammation or damage to the liver.
- Are at a higher risk of developing severe liver scarring, including those with:
- Alcohol use disorder (AUD)
- Type 2 diabetes
- Chronic hepatitis B or C
- Certain autoimmune diseases or genetic conditions
- Prolonged use of specific medications
- Show signs or symptoms associated with cirrhosis.
Liver elastography preparation
The preparation for liver elastography involves several crucial steps to guarantee patient comfort and provide accurate results.
- Patient education: Clear explanation of the procedure, including potential outcomes, is crucial for the patient.
- Procedure explanation: To provide an overview of a non-invasive procedure, its purpose, and patient expectations, addressing any concerns and emphasizing its non-invasive nature.
- Discuss results: Let patients know that the results will be reviewed in a follow-up appointment.
- Recommended fasting: Certain protocols suggest that patients fast for a few hours prior to the test. This can help reduce interference caused by food in the stomach, leading to more accurate measurements.
- Dressing comfortably: Encourage patients to wear loose-fitting clothing. This makes it easier to access the abdominal area, particularly the right upper quadrant where the probe will be positioned.
- Metal Considerations for MRE: If the test involves Magnetic Resonance Elastography (MRE), patients may need to remove all metal objects. They should inform their doctor about any implants or metal within their body, as the scanner can heat metal and potentially cause burns.
During the elastography test
The method for conducting the test varies depending on the elastography technique utilized.
Ultrasound elastography
Ultrasound elastography is typically performed by a radiology technician, a healthcare professional specifically trained in imaging tests. In some cases, a radiologist, a doctor who specializes in medical imaging, may administer the test.
The procedure for an elastography test is generally quick and follows these steps:
- The individual should remove any clothing obstructing access to the right abdomen to reveal the area over the liver.
- They will lie down on a table, where the technician will apply a special gel to the skin.
- The technician will use a wand-like device called a transducer to scan the patient's skin.
- The patient is asked to hold their breath for about 10 to 15 seconds while the device sends a series of vibrations into the liver. Although the device may pulse against the skin, it is not painful.
- The vibrations travel through the liver and reflect back to the device, which transmits the data to a computer.
- The computer then generates an image of the liver, highlighting any areas with stiff tissue or other indicators of liver disease.
Magnetic resonance elastography
Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) is a procedure performed using an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) machine. Here's what happens during an MRE:
- The patient lies on a narrow examination table.
- A technician places several small devices on the patient's lower right abdomen. One of these devices, known as a driver, emits painless vibrations into the liver, while the others transmit and receive radio waves to a connected computer.
- The table then moves into a large, tunnel-like MRI machine. The patient may experience loud sounds as the machine captures images, and earplugs or headphones might be provided to help minimize the noise.
- While inside the MRI, the patient will be instructed to hold their breath for about 10 to 15 seconds when the vibrations are being sent to the liver.
- The computer will generate images of the liver, which can reveal any scarring or other indicators of liver disease.
After the elastography test
Care following a liver elastography test is routine, but it's important to adhere to a few guidelines:
- Monitoring: Patients are usually observed for a short period post-procedure to check for any immediate adverse reactions, which typically takes place in the same clinical environment.
- Resuming normal activities: Most individuals can go back to their regular activities right after the test, as there are no specific restrictions associated with elastography.
- Follow-up appointment: Doctors usually schedule a follow-up appointment to discuss the results with patients, clarifying the significance of liver stiffness measurements and any potential steps for further management.
Advantages of liver elastography
Liver elastography presents several key benefits that improve patient care:
- Non-invasive approach: This technique allows for the assessment of liver stiffness without the need for invasive biopsies, thereby minimizing patient risk, discomfort, and potential complications typically associated with traditional liver evaluations.
- Quick and efficient: The process is relatively fast, which facilitates better patient management and throughput in outpatient clinics.
- Immediate results: Elastography provides real-time feedback, enabling doctors to make prompt decisions about patient care.
- Increased patient comfort: Most individuals undergoing the procedure report minimal to no discomfort, making it a more tolerable option for those requiring liver evaluation.
- Comprehensive insight: Beyond assessing fibrosis, liver elastography also helps evaluate the risk of complications such as portal hypertension, making it a valuable tool in the field of hepatology.
Complications of liver elastography
- Ultrasound elastography is considered to have no significant risks or complications. However, for most people, MRE may come with minimal risk
- The elastography procedure is completely non-invasive and painless, typically taking around 10 minutes to finish. While most patients with chronic liver disease can be evaluated using this test, there are certain instances where it may not be appropriate or interpretable due to the following factors:
- Localized discomfort: Some individuals may experience mild discomfort at the site where the probe was applied, though this is usually temporary and resolves quickly.
- Bruising: Rarely, localized bruising can occur, particularly in individuals with sensitive skin or blood clotting disorders.
- Infection risk: There is a slight risk of infection at the application site, especially if there are existing skin lesions. Ensuring proper hygiene and assessing the skin can help reduce this risk.
- Inflammation or Cholestasis: Factors such as inflammation or cholestasis can affect liver stiffness measurements, potentially leading to misinterpretation. It's crucial for clinicians to take the patient's overall clinical situation into account.
Liver elastography score
A radiologist will analyze the elastography images and submit the findings to the attending physician. These results will indicate the level of stiffness in the liver, which is indicative of the percentage of liver scarring (fibrosis). They will also provide information regarding any fat accumulation in the liver.
Liver elastography normal range: Liver elastography, also known as FibroScan, measures liver stiffness to assess liver disease. A higher result may indicate liver disease. The highest possible result is 75 kPa. A normal liver elastography result is between 2 and 7 kilopascals (kPa). The average normal result is 5.3 kPa.
The findings will include a fibrosis score determined by the stiffness level and its underlying cause:
- F0 to F1: Normal – indicates little to no scarring in the liver.
- F2: Moderate scarring.
- F3: Severe scarring.
- F4: Cirrhosis – very severe scarring.
- To assess fat levels in the liver, a "CAP score" is generated. This score reflects the percentage of fat present in the liver, with a normal fat content being 5% or less. Elevated levels of fat may indicate fatty liver disease, which could lead to fibrosis.
- For patients with mild to severe fibrosis and/or fatty liver disease, improvement is possible through treating the underlying cause and implementing lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes and increased physical activity.
- In cases of cirrhosis, addressing the underlying cause may prevent further deterioration of liver scarring, and effective treatment could gradually lead to some reduction in scarring.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Liver Elastography
Why is liver elastography (fibroscan) important?
Liver elastography is important because it allows for the early detection of liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and other liver diseases without the need for invasive biopsy. It helps in monitoring the progression of liver disease and determining the effectiveness of treatment options.
What conditions can liver elastography detect?
Liver elastography is mainly used to detect liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. It can also help diagnose chronic liver diseases like hepatitis B or C, fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and alcoholic liver disease by measuring the extent of liver stiffness.
Are there any risks associated with liver elastography?
Liver elastography is generally very safe and carries minimal risks. It’s a non-invasive procedure, and side effects are rare. Occasionally, patients may experience mild discomfort due to the pressure of the probe or the need to lie in a certain position during the test.
Can liver elastography help diagnose non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)?
Yes, liver elastography is effective in assessing liver stiffness and can help diagnose and monitor non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). It can be used to gauge the degree of liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD and identify those at risk for developing cirrhosis or liver-related complications.
How often should liver elastography be done?
The frequency of liver elastography depends on the individual's liver condition and the doctor's recommendations. For patients with chronic liver diseases, elastography may be repeated every 6 to 12 months to monitor disease progression or response to treatment. Your hepatologist will determine the appropriate schedule based on your condition.
What is liver elastography?
Liver elastography is a diagnostic procedure used to measure liver stiffness, which helps assess the extent of liver damage or fibrosis. This non-invasive technique uses ultrasound waves to determine the stiffness of the liver tissue, with stiffer tissue often indicating liver disease such as cirrhosis or fibrosis.
How does liver elastography work?
Liver elastography works by transmitting a painless wave through the liver using an ultrasound probe. The speed at which the wave travels through the liver is measured; faster speeds indicate stiffer tissue, which may suggest fibrosis or cirrhosis. The results are then analysed to provide a liver stiffness score.
Is liver elastography painful?
No, liver elastography is a painless procedure. It is performed using an ultrasound probe that emits vibrations to assess liver stiffness. Patients may feel slight discomfort from the pressure of the probe, but it is generally well tolerated.
How long does liver elastography take?
Liver elastography typically takes about 10-15 minutes to complete. It is a quick and non-invasive procedure, with no preparation required beyond possibly avoiding eating for a few hours prior to the test.
How accurate is liver elastography?
Liver elastography is highly accurate in assessing liver stiffness and can provide reliable information regarding the degree of fibrosis. However, factors such as obesity, inflammation, and alcohol consumption may affect its accuracy. It's typically used in conjunction with other tests for a more complete diagnosis.
How sensitive is MR elastography for liver fibrosis?
Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) is a non-invasive technique that can be highly sensitive and accurate for detecting liver fibrosis. MRE can have a sensitivity of up to 98% for detecting all stages of liver fibrosis. For advanced fibrosis (stages 3–4), MRE can have a sensitivity of up to 78%.
How to perform liver elastography?
Patients lie flat on an examination table, with a FibroScan probe placed between the ribs on the lower chest wall. Ten painless pulses are applied to the liver, recording results and generating an overall liver stiffness score.
How is liver elastography different from a liver biopsy?
Unlike a liver biopsy, which involves taking a tissue sample to examine under a microscope, liver elastography is non-invasive and uses ultrasound technology. Biopsy can be painful and carries risks such as bleeding or infection, whereas elastography is much safer and quicker.
Can liver elastography be used to monitor liver disease?
Yes, liver elastography is often used to monitor the progression of liver disease over time. It helps doctors track changes in liver stiffness, which may indicate worsening or improvement of liver fibrosis or cirrhosis and can be an important part of disease management.
Is liver elastography suitable for all patients?
While liver elastography is safe for most patients, it may not be suitable for individuals who are pregnant or have certain conditions that affect the liver’s structure, such as ascites or severe obesity. Doctors may decide to use other imaging techniques in these cases.
Can liver elastography detect liver cancer?
Liver elastography is not specifically designed to detect liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma). However, it can be useful for identifying cirrhosis, a condition that increases the risk of liver cancer. It’s often used in conjunction with other imaging tests like ultrasound or CT scans for cancer detection.
What does liver stiffness mean?
Liver stiffness refers to the rigidity or firmness of liver tissue, which increases as liver damage progresses. Healthy liver tissue is soft, but as fibrosis or cirrhosis develops, scar tissue forms, making the liver stiffer. Higher liver stiffness measurements can indicate more advanced liver disease.
Can liver elastography replace a liver biopsy?
In many cases, liver elastography can replace a biopsy as a less invasive alternative. While it provides a good estimate of liver stiffness, a biopsy may still be needed for definitive diagnosis, especially if there are concerns about specific liver diseases or for confirming the cause of liver damage.
How are liver elastography results interpreted?
Liver elastography results are typically presented as a measurement of liver stiffness in kilopascals (kPa). A higher kPa value generally indicates more severe fibrosis or cirrhosis. A lower value suggests minimal or no fibrosis. The results are then graded based on established scoring systems.
What is the normal range for liver stiffness?
The normal range for liver stiffness is usually between 2-7 kPa. However, values outside this range can suggest various degrees of fibrosis. Stiffness scores above 10-12 kPa may indicate advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis, depending on the specific scale used.
What factors can affect liver elastography results?
Factors such as obesity, excessive alcohol intake, recent meals, and inflammation may affect the accuracy of liver elastography results. In some cases, conditions like ascites or severe liver congestion may make it difficult to obtain accurate readings, necessitating additional tests or alternative methods.
How is liver elastography different from a traditional ultrasound?
While both liver elastography and traditional ultrasound use sound waves, the key difference is that elastography measures liver stiffness by transmitting shear waves, whereas traditional ultrasound focuses on the structural and visual aspects of the liver. Elastography provides quantitative information on tissue properties, not just images.
What is Fibroscan (Liver Elastography) test price in Hyderabad, Telangana?
Fibroscan test price in Hyderabad, Telangana, ranges vary from ₹3,000 to ₹15,000 (US$35 to US$175). At PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, we offer affordable fibroscan (liver elastography) tests to help diagnose liver conditions with precision and accuracy.
However, Fibroscan cost in Hyderabad may vary depending on the patient's condition, medical history, types of fibroscan (Transient Elastography (TE) – FibroScan, Shear Wave Elastography (SWE), Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) Elastography and Magnetic Resonance Elastography (MRE)), hospital facilities, diagnostic package options and any additional diagnostic tests if required (LFT, viral markers, etc.).
Our Locations
Metro Pillar Number C1772, Beside Avasa Hotel, Hitech City Road, Near HITEC City Metro Station, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Mythri Nagar, Beside South India Shopping Mall, Hafeezpet, Madeenaguda, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
040 4848 6868
Payment in advance for treatment at PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, Telangana, India (Pay in INR ₹)
For Bank Transfer:-
- Bank Name: HDFC
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.50200028705218
IFSC Code: HDFC0000545 - Bank Name: STATE BANK OF INDIA
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.62206858997
IFSC Code: SBIN0020299
Scan QR Code by Any Payment App (GPay, Paytm, Phonepe, BHIM, Bank Apps, Amazon, Airtel, Truecaller, Idea, Whatsapp etc).

CONTACT US
Call: +914048486868
WhatsApp: +918977889778
Email: info@pacehospitals.in
FOLLOW US
SUBSCRIBE
Subscribe to our newsletter and stay updated with the latest health information.
Subscribe to PACE Hospitals' Public Newsletter
Thank you for subscribing to PACE Hospitals' Newsletter. Stay updated with the latest health information.
Oops, there was an error. Please try again submitting your details.
ABOUT US
QUICK LINKS
Disclaimer
General information on healthcare issues is made available by PACE Hospitals through this website (www.pacehospital.com), as well as its other websites and branded social media pages. The text, videos, illustrations, photographs, quoted information, and other materials found on these websites (here by collectively referred to as "Content") are offered for informational purposes only and is neither exhaustive nor complete. Prior to forming a decision in regard to your health, consult your doctor or any another healthcare professional. PACE Hospitals does not have an obligation to update or modify the "Content" or to explain or resolve any inconsistencies therein.
The "Content" from the website of PACE Hospitals or from its branded social media pages might include any adult explicit "Content" which is deemed exclusively medical or health-related and not otherwise. Publishing material or making references to specific sources, such as to any particular therapies, goods, drugs, practises, doctors, nurses, other healthcare professionals, diagnoses or procedures is done purely for informational purposes and does not reflect any endorsement by PACE Hospitals as such.