Best Spine Hospital in Hyderabad, Leading Spine Surgery Hospital
PACE Hospitals is one of the
Best Spine Surgery Hospital in Hyderabad, India; providing comprehensive and evidence-based spinal cord injury treatment. The team of spine surgeon and orthopedic spine surgeon have vast experience in the latest minimally invasive techniques, laser spine surgery, and motion-preserving procedures to treat a wide spectrum of congenital, pediatric and geriatrics spinal cord injuries and abnormalities, including:
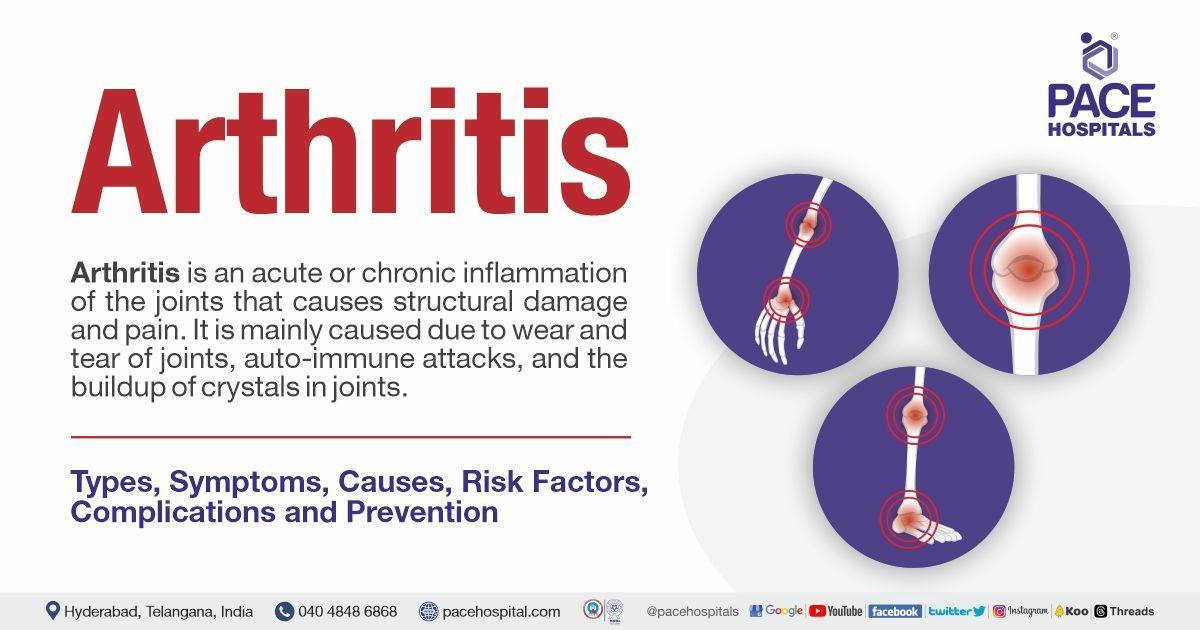
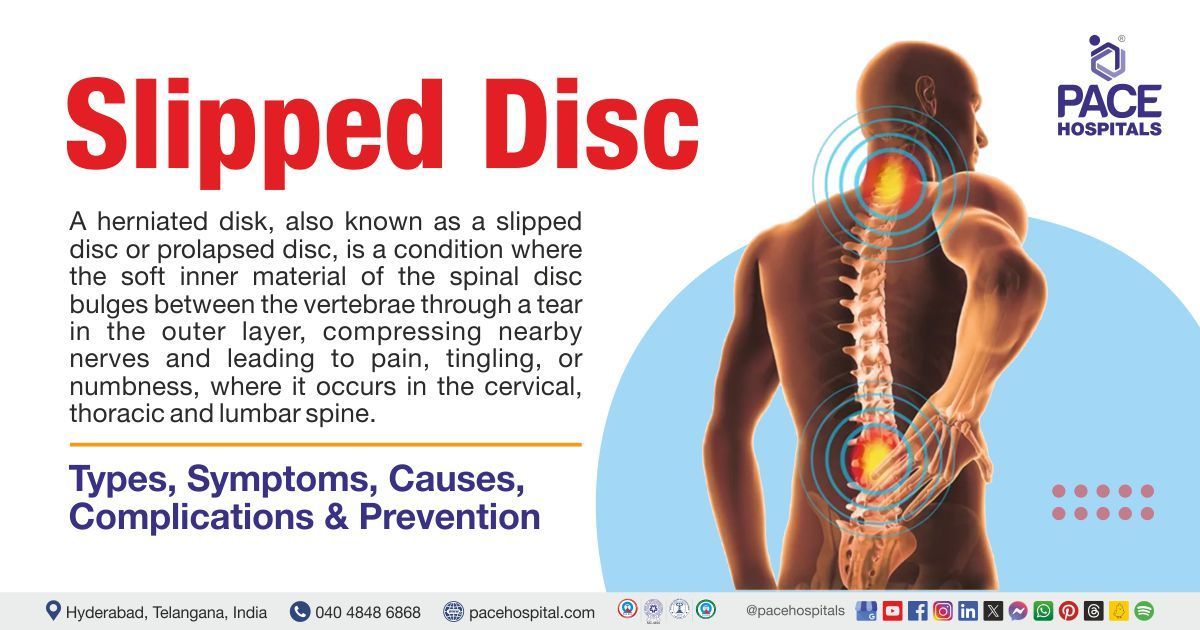
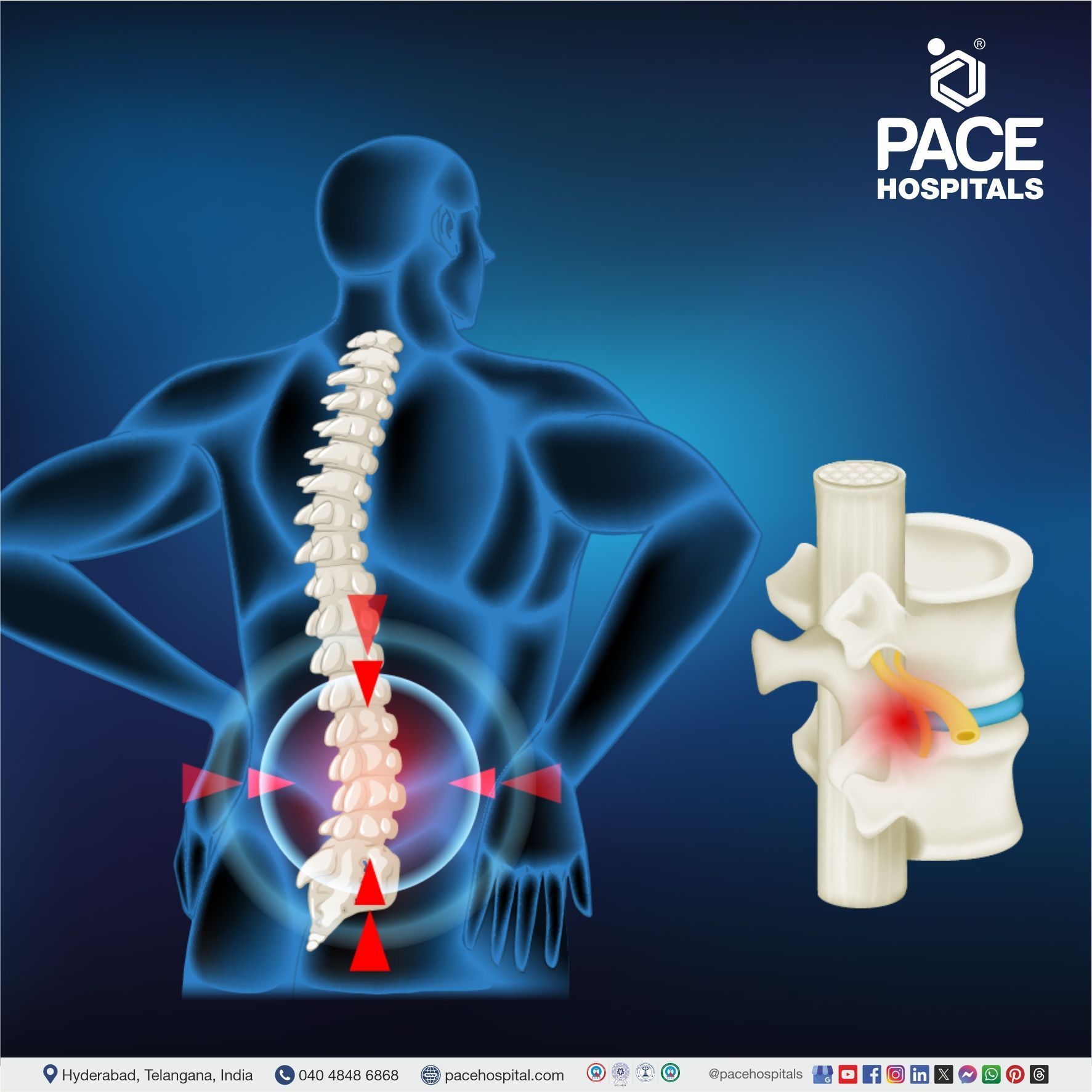
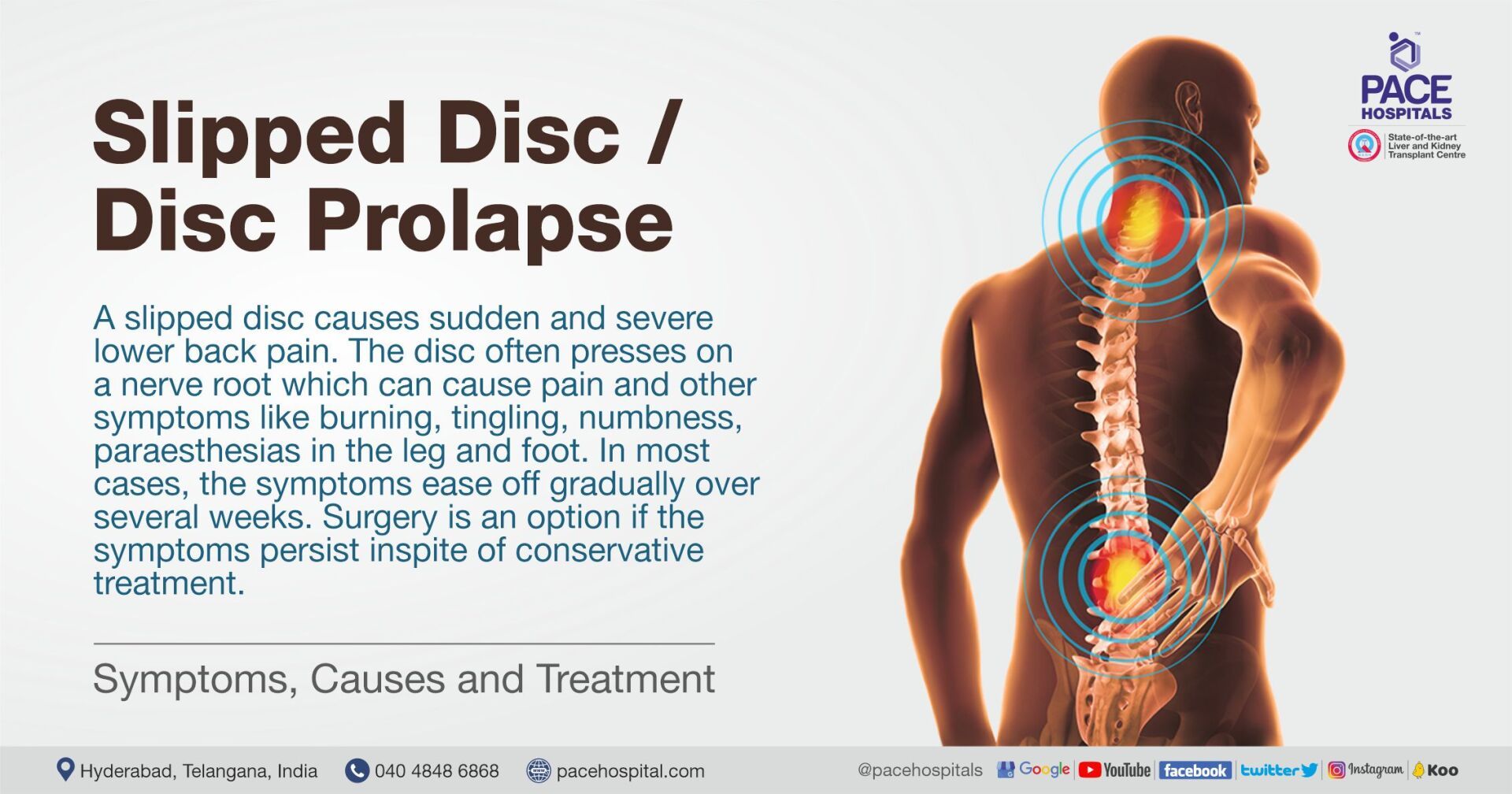
- Herniated Disc (Slipped Disc)
- Degenerative Disc Disease (DDD)
- Spondylosis (Cervical, Lumbar, or Thoracic)
- Spinal Stenosis, Sciatica (Lumbar Radiculopathy)
- Myelopathy (Cervical or Thoracic)
- Spinal Fractures (Vertebral Fractures)
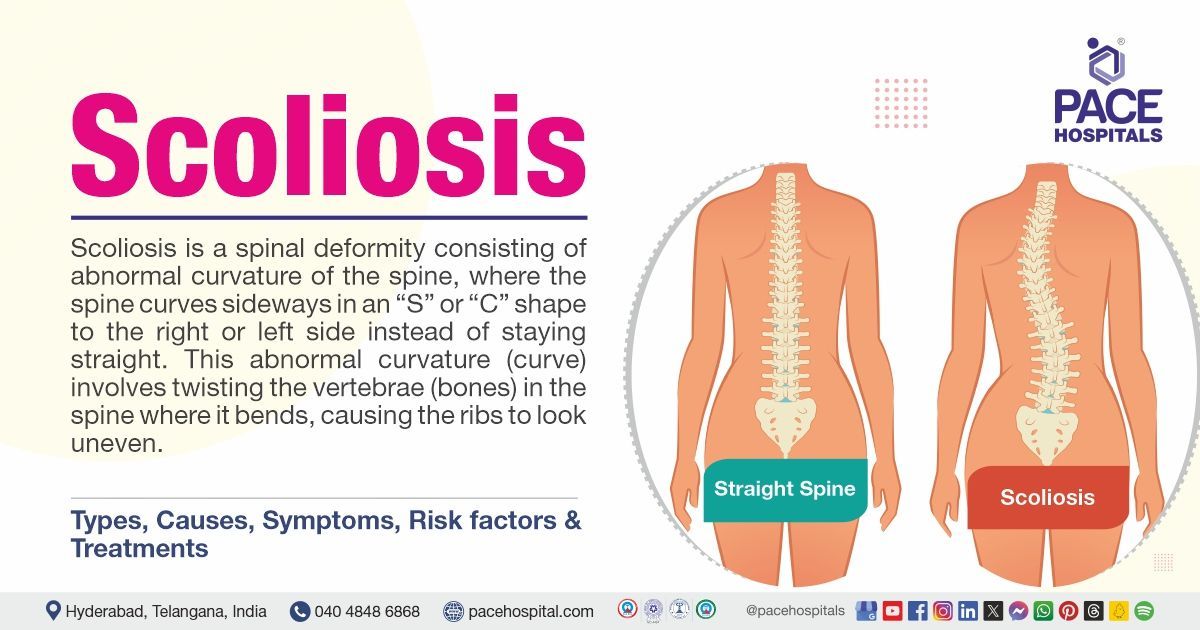
- Scoliosis, Kyphosis, Chiari Malformation
- Lordosis (Hyperlordosis), Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Spinal Osteomyelitis, Spinal Epidural Abscess
- Tuberculosis of the Spine (Pott's Disease)
- Spinal Cord Tumors, Vertebral Hemangioma
- Metastatic Spinal Cancer
Why Choose PACE Hospitals for Spine Surgery?
Comprehensive Spine Treatments for All Spinal Conditions
Providing surgical and minimally invasive treatment to wide range of spinal cord disorders including herniated discs, spinal stenosis, scoliosis, spinal fractures, sciatica and spinal tumours.
Advanced Spine Surgery Techniques - MISS, Endoscopic Procedures
Equipped with advanced and latest diagnostic equipment, robotic and minimally invasive surgical facilities for all kind of spinal cord disorders treatment.
Skilled & Experienced Spine Surgeons & Neuro-Spine Specialists
Team of experienced spine surgeon, orthopaedic spine surgeon with vast experience in advanced & latest spine surgery and minimally invasive procedures.
Best Neuro Spine Hospital in Hyderabad – Specialized Spine & Nerve Care

The Spine Surgery Department at PACE Hospitals is one of the Best Spine Hospital in Hyderabad, Telangana, India; staffed with top spine surgeon capable of managing all kinds of degenerative spine diseases, spinal infections, spinal deformities, traumatic spinal injuries, spinal realignment, scoliosis correction and osteoporosis-related fractures through advanced surgical approaches and minimally invasive techniques ensuring patient-centric effective spine care for paediatric, adult and geriatric patients suffering with spinal cord injuries or deformities.
The Department of Spine Surgery is equipped with state-of-the-art and cutting-edge diagnostic facilities, including advanced and high-resolution imaging systems (digital X-rays,
CT scans and
MRIs), EMG studies, nerve conduction studies and the latest treatment modalities, including robotic,
endoscopic spine surgery in Hyderabad and advanced rehabilitation facilities, ensuring optimal recovery and long-term relief.
3,28,338
99,825
684
2011
Best Spine Surgeon in Hyderabad | Top Neuro Spine Surgeons
A team of the best spine surgeon in Hyderabad, India, skilled in addressing a wide range of diseases and disorders affecting spinal health, they have expertise in cutting-edge minimally invasive spine surgeries like spinal fusion, laminectomy, discectomy to treat a broad spectrum of spinal cord injuries and deformities including herniated discs, spinal stenosis, scoliosis, degenerative disc disease, sciatica, kyphosis, spinal infections, Chiari Malformation, Lordosis, Ankylosing Spondylitis and more. The spinal treatment offered is compassionate and tailored to individual patients' conditions to alleviate pain, restore mobility, and improve patients' quality of life.
Dr. U L Sandeep Varma
MBBS, M.S. (General Surgery), M.Ch (Neurosurgery), Post Doctoral Fellowship in Minimal Invasive and Advanced Spine Surgery
Experience : 10+ years
Consultant Brain and Spine Surgeon
Dr. Raghuram
MBBS, DNB ORTHO, Fellowship in Joint Replacement and Arthroscopy, Fellowship in Shoulder and Upper limb, Sports medicine and Replacement
Experience : 10+ years
Orthopaedic Consultant, Trauma, Shoulder and Knee Arthroscopic Surgeon, Hip and Knee Joint Replacement Specialist
Spinal Cord Diseases and Disorder Explained by Drs
Comprehensive Spine Disorders Care - Expert Treatments & Surgery
Struggling with mobility issues, persistent back pain, numbness in your limbs, tingling, difficulty standing upright or trouble maintaining balance? You might be suffering from common spinal injuries and deformities like scoliosis, kyphosis, spinal fracture, spinal stenosis, herniated discs, or spinal infections. From common spinal cord injuries to complex Congenital, Degenerative & autoimmune disorders like Chiari Malformation, Spondylosis, Ankylosing Spondylitis, Vertebral Hemangioma, Spinal Cord Tumors and cancers, we are committed to catering evidence-based, personalized treatment plans tailored to your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Spine Surgery
What is the purpose of spine surgery?
Spine surgery is indicated to treat a wide range of spinal diseases that cause pain, instability, or neurological issues, particularly after non-surgical treatments have failed. Spine surgery normally aims to treat pain, improve function, and restore spine stability. Spine surgery may be indicated for:
• Pain relief
• Restoring function and mobility
• Preventing further nerve damage
• Correcting spinal deformities
• Restoring spinal stability
• Improving quality of life
Do you provide free online doctor consultation in India for spine surgery?
Yes, PACE Hospitals offers free online and offline doctor consultations for Teachers, Police, and Army Officials considering spine surgery. Our expert spine specialists and neurosurgeons provide personalized assessments, second opinions, and treatment guidance to help you make an informed decision about your spine health.
✅ Consult expert spine surgeons for free
✅ Evaluation of back pain & spinal conditions
✅ Medical second opinions for spine surgery
✅ Advanced facilities & cutting-edge technology
As one of the best spine hospitals in Hyderabad, Telangana, India, we utilize the latest technology and treatment strategies to deliver optimal outcomes, ensuring that our patients experience faster recovery and improved long-term results.
📞 Call: 04048486868 or 💬 WhatsApp: +918977889778. 📅 Book your free spine consultation today!
What are the different types of spine surgery, and which one is right for me?
There are various spine procedures, each designed to treat a unique spinal issue. The type of spine surgery recommended is based on the patient's diagnosis, the severity of the problem, and their overall health. The following are some typical types of spine surgeries:
• Spinal Fusion
• Laminectomy
• Discectomy
• Artificial Disc Replacement (ADR)
• Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery (MISS)
• Foraminotomy
• Kyphoplasty/Vertebroplasty
• Scoliosis Surgery
• Cervical Spine Surgery
• Spinal Decompression Surgery
What are the common spinal cord diseases for which spinal surgery is recommended?
Spinal surgery is typically recommended for a variety of spinal cord diseases and conditions that either cause significant pain or functional impairment or pose a risk of further complications if not treated. The goal of spinal surgery is to restore normal function, alleviate pain and prevent further damage to the spinal cord or nerves.
The most common spinal cord diseases for which surgery may be recommended include:
• Herniated disc (Slipped disc)
• Spinal stenosis
• Spondylolisthesis
• Degenerative disc disease
• Spinal tumors
• Trauma and spinal cord injury
• Cervical myelopathy
• Kyphosis
• Lordosis (Swayback)
• Infections of the spine (e.g., Spinal osteomyelitis, Discitis)
• Chiari malformation
• Spinal deformities (e.g., Scoliosis) etc.
Spinal surgery is usually suggested for disorders that cause severe pain, functional disability, or the possibility of progressive deterioration of the spine or spinal cord. While surgery is not always required for all spinal cord conditions, it can be an extremely successful choice when conservative treatments (such as physical therapy and drugs) do not provide relief.
What are the risks and potential complications of spine surgery?
Spine surgery, like other major surgeries, has risks and complications. While many patients achieve favourable results, it is crucial to understand the potential risks before deciding. Some of the most prevalent risks and complications of spine surgery may include infections, blood clots, nerve injuries etc.
While spine surgery has been highly successful in treating spinal disorders, it does have certain risks. Understanding these potential problems can help patients make more educated decisions about their care and increase their capacity to collaborate with their healthcare team to reduce risks during surgery.
What is the expected recovery time after spine surgery?
Recovery following spine surgery is a long process. Most patients improve significantly within three to six months. Full healing may take up to a year, especially with more complex treatments.
Following the surgeon's postoperative instructions and going to physical therapy is vital for a successful and full recovery. It is recommended to consult with the concerned spine surgeon to get personalized recovery expectations based on the procedure type and specific needs.
What kind of pain management will be provided after surgery?
To maintain comfort throughout recovery, pain treatment following spine surgery is individualized and may include a combination of drugs, therapies, and procedures. As patients recover, the approach to pain management will change to treat any persistent discomfort or rehabilitation requirements.
It is advised that the healthcare team be consulted to adjust the pain management strategy as needed to ensure the greatest possible recovery outcome.
Will I need physical therapy after surgery?
Yes, physical therapy is typically recommended after spine surgery to aid in recovery, restore mobility, and strengthen the muscles supporting your spine. The need for therapy depends on the type of surgery, your overall health, and the severity of your condition.
Benefits of Physical Therapy After Spine Surgery:
- Faster Recovery: Helps regain strength and flexibility.
- Pain Management: Reduces post-surgical discomfort and stiffness.
- Improved Mobility: Restores normal movement and function.
- Prevention of Future Issues: Strengthens muscles to prevent re-injury.
Spine surgeon and rehabilitation specialist will create a customized therapy plan based on your needs. If you're considering spinal surgery at PACE Hospitals, our expert physiotherapists ensure a smooth and safe recovery.
What are some common diagnostic tests and examinations used to assess musculoskeletal system disabilities?
Some of the common diagnostic tests and examinations performed to assess musculoskeletal system disabilities are as follows:
- X-rays
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan
- Bone Scan
- Electromyography (EMG)
- Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA:
- Ultrasound
- Arthroscopy
- Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS)
- Muscle Biopsy
- Genetic Testing
What can I do before surgery to prepare for the procedure?
Proper preparation is required for successful spine surgery and recovery. Following the surgeon's instructions, planning for assistance, and focusing on physical and mental well-being, Patients can increase their chances of a smooth operation and a good recovery.
To feel knowledgeable, secure, and prepared for the process, it is recommended to make sure that the patient and the surgeon go over every detail of the surgery.
How will my quality of life improve after spine surgery?
Spine surgery can greatly enhance the quality of life by relieving pain, increasing mobility, and restoring function. Most patients can anticipate returning to normal daily activities, improved physical and emotional health, and less dependency on pain medications.
Although recovery takes time, the long-term benefits frequently outweigh the short-term problems, and the patient may be able to resume a more active, pain-free lifestyle after surgery. The healthcare team will collaborate with the patient to optimize the outcome of the surgery and assist the patient throughout the recovery process.
What type of doctors are qualified to perform spine surgery?
Orthopaedic spine surgeons and neurosurgeons primarily perform spine surgery with considerable training in the surgical treatment of spinal cord disorders. These professionals are trained to execute various spine surgeries, from minimally invasive treatments to complicated spine repair procedures.
The choice between a neurosurgeon and an orthopaedic surgeon is frequently determined by the specific type of spinal disease, with both types of surgeons working together in some circumstances to provide comprehensive care.
How to book an appointment in the Top Spine Surgery Hospital in Hyderabad?
Anyone seeking treatment for spinal cord injuries or deformities or looking for an appointment with the best spine surgeon in the locations near Hitech City, Madhapur, Kondapur, Gachibowli, KPHB, or Kukatpally can visit the PACE Hospitals, Best Spine Care Hospital in Hyderabad and fill out the Appointment Form. They can also directly visit the hospital located near the Hi-Tech City metro station or call 04048486868 to book a hassle-free appointment.
Expert Spine Care: Advanced Treatments for Spinal Injuries & Disorders
We have expertise in the treatment and management of a wide range of spinal cord injuries and deformities through advanced minimally invasive surgeries, nerve block therapies, as well as comprehensive non-surgical therapies such as pain management, physiotherapy, and personalized rehabilitation programs. Our team of skilled and experienced spine surgeons addresses both common and complex spinal cord diseases and disorders, all aimed at restoring mobility and improving the quality of life.
As a leading spine care hospital in Hyderabad, Telangana, India, PACE Hospitals provide the highest standard of care, utilizing the latest technology and advanced techniques to treat and manage complex spinal conditions.
Google Reviews
A 64-Year Patient from Sudan with L4 L5 Disc Bulge along with Radiculopathy and Symptoms of Parkinson's Disease, treated successfully with
Minimally Invasive Lumbar Discectomy.
Spinal Cord Injury Diagnosis & Cutting-Edge Laser-Assisted Spine Surgery Techniques
At PACE Hospitals, our skilled spine surgeons are committed to evidence-based treatment by running comprehensive diagnostic tests to evaluate any injuries and deformities in the spinal cord. We proceed with appropriate treatment modalities that minimize complications, reduce hospital stay, and enhance the quality of life. Our team is proficient in advanced minimally invasive procedures, endoscopic spine surgery, and diagnostic tests like electromyography (EMG), myelography, discography, nerve conduction studies, Microdiscectomy, and robotic-assisted spine surgeries. These tests precisely analyze compression and disc abnormalities, enabling our surgeons to perform effective surgeries tailored to each patient’s needs.
As the
best hospital for spine in Hyderabad, Telangana, India, we utilize the latest technology and treatment strategies to deliver optimal outcomes, ensuring that our patients experience faster recovery and improved long-term results.

1. CT Myelogram: CT myelogram is a comprehensive imaging technique that combines computed tomography (CT) with a contrast dye injected into the spinal canal to improve visualization of the, nerve roots, spinal cord, and surrounding structures. This technique is beneficial especially for identifying spinal disorders when other imaging procedures, such as traditional X-rays or MRI, are unclear or not appropriate.
2. Electromyography (EMG): Electromyography (EMG) is a diagnostic procedure that assesses muscle electrical activity and motor neuron function. It involves inserting a needle electrode into muscle tissue to detect unusual electrical signals that may suggest nerve injury or dysfunction. EMG is used to evaluate the consequences of spinal cord damage, nerve root compression (as in radiculopathy), and conditions such as multiple sclerosis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). It aids in detecting nerve root involvement, determining the extent of motor neuron injury, and tracking the progression or recovery of muscle and nerve function. EMG gives crucial information about how spinal cord disorders affect muscle strength, nerve conduction, and motor control.
3. Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS): Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS) is a diagnostic examination that assesses the speed and strength of electrical signals passing through nerves. Electrodes are positioned on the skin over certain nerves, and a moderate electrical shock is used to induce nerve activity. NCS assesses how well electrical impulses flow along peripheral nerves (nerves outside the spinal cord), which aids in detecting nerve damage or dysfunction caused by spinal cord disorders such as radiculopathy, spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis, or diabetic neuropathy. NCS can establish whether nerve damage is caused by compression, degeneration, or inflammation by analyzing the conduction velocity and amplitude of nerve impulses, and this information can help to guide treatment options in spinal cord conditions.
4. Spinal Fluid Analysis (Lumbar Puncture or Spinal Tap): Spinal fluid analysis (also known as lumbar puncture or spinal tap) is a diagnostic procedure in which a needle is placed into the lumbar region (lower back) to collect a sample of cerebrospinal fluid, which surrounds the brain and spinal cord. This fluid is examined for abnormalities that could indicate the presence of infections, inflammation, disease processes, or neurological problems affecting the spinal cord. This test is very beneficial for detecting multiple sclerosis, spinal cord infections (such as meningitis or encephalitis), Guillain-Barré syndrome, and autoimmune conditions. CSF examination may reveal high amounts of white blood cells, protein, or the presence of unusual antibodies, providing vital information about the underlying cause of neurological symptoms and help guide treatment methods.
5. Magnetic Resonance Myelography (MRM): Magnetic Resonance Myelography (MRM) is an advanced imaging technology that uses magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and a contrast dye (often gadolinium-based) to see the spinal cord, nerve roots, and subarachnoid space. The contrast dye is introduced into the subarachnoid area either by a lumbar puncture or intravenously, and the MRI scanner generates highly detailed images of the spinal canal and nerve structures.
MRM is especially beneficial for identifying spinal cord disorders that are difficult to detect with normal MRI, such as spinal stenosis, ruptured discs, spinal cord tumors, infections, or trauma. It can detect nerve root compression, cystic lesions, and spinal canal abnormalities. MRM is frequently used when a patient is unable to undergo a regular MRI due to issues such as pacemakers or metal implants, as it enables improved visualization of the spinal cord and associated structures without the need for invasive surgery.
6. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scan: The Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scan is a specialized imaging technology that produces precise, functional images of the spinal cord and surrounding tissues. PET scans identify metabolic activity by measuring the radiation released by a small amount of radioactive tracer (often glucose or other compounds). The tracer is injected into the body and absorbed by tissues, releasing positrons that are detected by the PET scanner. The generated images show areas with significant metabolic activity, which may indicate inflammation, tumors, infection, or nerve degeneration in the spinal cord.
7. Spinal Ultrasound: Spinal ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging technology that uses sound waves with high frequency to generate real-time images of the spine and its surrounding structures, including the spinal cord. A small device known as a transducer releases sound waves and is put on the skin above the spine. The sound waves bounce off the tissues and are used to create images of the spine, allowing doctors to evaluate the spinal cord, vertebrae, ligaments, and surrounding soft tissues.
8. Cerebral Angiography: Cerebral angiography is a specialized imaging technique that employs X-rays and a contrast dye to see blood arteries in the spinal cord and brain. The contrast dye is injected into the arteries, usually by a catheter placed into the femoral artery (groin) or directly into the spinal artery. The dye improves X-ray imaging, allowing for more comprehensive visualization of the vascular structures that provide blood to the spinal cord and surrounding tissues, such as the arteries, veins, and capillaries.
9. Cerebral Spinal Fluid (CSF) Cytology and Cultures:
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Cytology and Cultures are laboratory procedures done on a sample of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collected through lumbar puncture or spinal tap. These tests analyze the composition of cells and microbial content of cerebrospinal fluid in order to detect many conditions affecting the spinal cord and brain, especially those related to infections, inflammation, or malignancies.
Spinal Surgery Procedures
1. Discectomy: Discectomy is a surgical treatment that involves removing the herniated or damaged segment of the intervertebral disc in order to relieve pressure and symptoms on the spinal nerve roots caused by lumbar disc herniation. This surgical technique is routinely performed to relieve pain, weakness, numbness, and other neurological symptoms caused by compression of the spinal nerve roots.
2. Laminectomy: Laminectomy is a procedure in which a surgeon removes a portion or all the spinal bone (lamina). This alleviates pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots caused by injury, a herniated disc, canal constriction (spinal stenosis), or tumors. A laminectomy is only considered if other medical therapies fail.
3. Laminotomy: Laminotomy is a type of spinal surgery that includes removing a section of the lamina, which is the bony part that makes up the back part of the vertebral arch in the spine. This procedure relieves the pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots caused by disorders such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or bone spurs. A laminotomy creates more space within the spinal canal, relieving pain, numbness, or weakness caused by nerve compression.
4. Lumbar spine surgery: Lumbar spine surgery is indicated to treat a variety of problems affecting the lumbar region 9lower back) of the spine, including herniated discs, spinal stenosis, degenerative disc disease, spondylolisthesis, and other spinal disorders that cause pain, numbness, or limited movement. Depending on the diagnosis, several lumbar spine procedures may be recommended.
5. Cervical spine surgery: Cervical spine surgery is used to treat the disorders that affect the cervical portion of the spine, which comprises of the seven vertebrae in the neck (C1–C7). This form of surgery is often advised when non-surgical treatments such as drugs, physical therapy, or injections have failed to alleviate symptoms such as pain, numbness, weakness, or tingling caused by spinal abnormalities in the neck.
6. Spinal cord stimulator (SCS) implantation: Spinal Cord Stimulator (SCS) Implantation is a medical procedure used to treat chronic pain, particularly when more conservative treatments (such as drugs, physical therapy, or surgery) have proven ineffective. It involves implanting a tiny device that emits electrical impulses to the spinal cord, which aids to interfere with pain signals and provides significant relief to individuals with chronic pain, particularly nerve-related pain.
7. Minimally invasive spine surgery (MISS): Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery (MISS) refers to a group of surgical methods that treat spine disorders using smaller incisions, less muscle dissection, and faster recovery times than standard open spine surgery. The aim of minimally invasive procedure is to minimize disruption to surrounding tissues, reduce post-operative pain, shorten hospital stays, and speed up recovery time.
8. Spinal Tumor Surgery: Spinal tumor surgery is a surgical treatment used to remove tumors found within or around the spine. These tumors can be primary (originating in the spine) or metastatic (spreading malignant cells throughout the body). Spinal tumor surgery is commonly used to remove the tumor, reduce pain or pressure on the spinal cord or nerves, stabilize the spine, and improve the patient's quality of life.
9. Vertebroplasty: Vertebroplasty is a minimally invasive surgical method for treating spinal compression fractures, which are usually caused by osteoporosis, trauma, or tumors. The procedure aims to stabilize the fractured vertebra, alleviate pain, and restore spinal stability.
10. Kyphoplasty: Kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive procedure that treats spinal compression fractures, which are most usually caused by osteoporosis, tumors, or trauma. It is similar to vertebroplasty but includes an additional procedure to restore the height of the damaged vertebra before injecting bone cement.
11. Foraminotomy: Foraminotomy is a procedure performed to relieve pressure on a nerve root in the spine caused by a shortened foramen (a tiny aperture through which spinal nerves exit the vertebral column). The procedure involves eliminating the bone or soft tissue surrounding the foramen to increase the space and relieve nerve compression, which can cause pain, numbness, weakness, or tingling.
12. Spinal decompression (Decompressive Surgery): Spinal decompression (Decompressive Surgery) is a procedure that is indicated to alleviate pressure on the spinal cord or nerves by removing or releasing the tissue, bone, or discs that are compressing them. This pressure can be produced by herniated discs, bone spurs, spinal stenosis, or spinal tumors, all of which can cause pain, numbness, weakness, and other neurological symptoms.
13. Artificial disc replacement: Artificial disc replacement is a surgical process that removes a damaged or degenerative spinal disc and replaces it with an artificial disc consisting of metal, plastic, or a combination of the two. The aim of artificial disc replacement is to restore normal motion to the affected region of the spine, reduce pain, and preserve spinal function, especially in cases of degenerative disc disease or other disorders that cause persistent pain or loss of spinal mobility.
14. Spinal fusion: Spinal fusion is a surgical treatment that involves combining two or more vertebrae in the spine to eliminate movement between them, hence increasing stability and lowering pain. This treatment is often performed when spinal instability or degenerative disorders produce discomfort, deformity, or neurological difficulties as a result of abnormal vertebral movement.
Patient Education and Health Blogs
Why choose PACE Hospitals?
- A Multi-Super Speciality Hospital.
- NABH, NABL, NBE & NABH - Nursing Excellence accreditation.
- State-of-the-art Liver and Kidney transplant centre.
- Empanelled with all TPAs for smooth cashless benefits.
- Centralized HIMS (Hospital Information System).
- Computerized health records available via website.
- Minimum waiting time for Inpatient and Outpatient.
- Round-the-clock guidance from highly qualified super specialist doctors, surgeons and physicians.
- Standardization of ethical medical care.
- 24X7 Outpatient & Inpatient Pharmacy Services.
- State-of-the-art operation theaters.
- Intensive Care Units (Surgical and Medical) with ISO-9001 accreditation.