Best Brain Aneurysm Treatment in Hyderabad, India
PACE Hospitals is recognized as the best hospital for brain aneurysm treatment in Hyderabad, Telangana, India, committed to delivering world-class neurovascular care. Our multidisciplinary team of expert neurosurgeons, interventional radiologists, and critical care specialists ensures advanced treatment and excellent recovery outcomes. We offer cutting-edge minimally invasive and surgical procedures, including endovascular coiling, surgical clipping, flow diversion stents, rehabilitation & post-treatment care, 24/7 emergency stroke & aneurysm care – immediate intervention for critical cases.
A brain aneurysm is a weakened area in a blood vessel in the brain that bulges, potentially leading to rupture, brain haemorrhage, or stroke. At PACE Hospitals, we specialize in advanced brain aneurysm treatments, ensuring minimally invasive & advanced surgical techniques for faster recovery, state-of-the-art neuro ICU & advanced imaging for accurate diagnosis, personalized care plans tailored to each patient’s condition.
Book an appointment for Brain Aneurysm Treatment
Brain Aneurysm Treatment appointment
Why Choose PACE Hospitals for Brain Aneurysm Treatment?

State-of-the-Art Neuro ICU & Advanced Imaging
Best Neurosurgeons in Hyderabad, India
24/7 Emergency Stroke & Aneurysm Care
Affordable & Reliable Minimally Invasive & Advanced Surgical Techniques
The evaluation of brain aneurysm is based on imaging studies, which help the neurosurgeon to conclude the diagnosis. The brain aneurysm treatment is subject to the size, location, and rupturing of it. As earlier the patient improves from the initial brain injury, the faster the recovers from brain aneurysm.
The neurosurgeon considers the following factors before selecting the appropriate tests to diagnose pelvic inflammatory disease.
- The presented signs and symptoms of brain aneurysm
- Age, family history and general health of the suspected patient
- Medical history and medication history.
- The results of previous medical tests
Brain aneurysm diagnosis
Based on the above information (symptoms, age, family history, medical history, etc.), a neurosurgeon advises the following tests to diagnose the aneurysm and determine if blood has leaked into the space between the skull bone and the brain:
- Computed tomography (CT) scan
- Computed tomography angiography (CTA)
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI):
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA)
- Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA)
- Cerebral angiogram
- Ultrasonography
- Nuclear imaging
- Lumbar puncture
- Cerebrospinal fluid analysis
Computed tomography (CT) scan
- A CT scan is typically the initial test that will be selected by a neurosurgeon when a subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH) is suspected.
- It is a painless and fast test that uses X-rays to create two-dimensional images or slices of the brain and skull to diagnose blood in the brain. As mentioned above, it is often suggested as the first test to identify a rupture.
- In around 90% of patients, a high-quality CT scan without contrast can diagnose rupture and bleeding (SAH) within the first 48 hours after symptoms start.
- The location and extent (amount of blood) of the aneurysm (if present) in the subarachnoid space (between the brain and the surrounding membrane) can give clues about where it has ruptured.
- Finding an aneurysm near the area of the most significant bleeding on the scan supports the diagnosis and helps guide further treatment decisions.
- A CT scan is helpful for patients with multiple aneurysms. In addition to identifying and locating these vascular issues, this scan can also reveal other unexpected conditions, such as arteriovenous malformations (abnormal tangles of blood vessels), bleeding within brain tissue, or fluid buildup in the brain (hydrocephalus).
- Furthermore, these scans can provide information about how much blood is present in spaces around the brain, helping the neurosurgeon predict the possibility of complications.
Computed tomography angiography (CTA)
- CTA is a non-invasive test that injects a contrast dye into the patient's vein. This is followed by a CT (Computed tomography) scan, which produces detailed pictures of blood flow in the brain's arteries.
- This test is a fast and painless scan that shows the size, location, and shape of an unruptured or ruptured aneurysm. Neurosurgeons often prefer this test to examine blood vessels in the brain and determine whether blood has leaked into the brain.
- During the process, the patient lies on a table that slides into a CT scanner, which looks like a large ring. Occasionally, a contrasted dye can be injected to visualise the blood vessels clearly on an X-ray; a series of X-rays are taken to assess the arteries, look for abnormalities, and look for a possible aneurysm in the blood vessels.
- This process produces sharper, more detailed pictures of blood flow in the brain arteries. Images from CT angiography (CTA) are quick to obtain and can be rotated, providing clear views of the brain's blood vessels relative to the skull base. This capability helps surgeons plan procedures effectively.
- Some studies have shown that CTA is highly sensitive, accurately detecting aneurysms in 77% to 97% of patients, and specific, with accuracy ranging from 87% to 100%, making it reliable in clinical practice.
- However, it may not always recognise the lesions involving the carotid artery at the base of the skull or within the cavernous sinuses filled with contrast dye.
- Besides, there are concerns about the high radiation doses associated with CT scans, especially for patients who require frequent imaging. These factors must be considered when deciding on diagnostic imaging for patients with suspected intracranial aneurysms.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
An MRI is a non-invasive imaging examination that uses computer-generated radio waves and a magnetic field to create detailed two-dimensional (2D) anatomical pictures (images) of the brain and can determine if there is any rupture that causes bleeding in the brain.
Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA)
- Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) delivers clear images of the brain arteries. It will show an aneurysm's size, location, and shape and helps detect intracranial aneurysms in both symptomatic and asymptomatic patients.
- It is a sensitive (effective) method for detecting an aneurysm in symptomatic patients who have a high risk (i.e., patients with polycystic renal disease and those with one or more first-order family members with documented cerebral aneurysms).
- During this test, the patient will be placed on an examination table that slides into a magnetic resonance scanner. The blood vessels are imaged to identify a brain aneurysm and detect brain aneurysms larger than 3-5mm.
- MR angiography (MRA) has been used for about twenty years (two decades) as an imaging technique to detect aneurysms in patients who are not in urgent condition but show symptoms that suggest they might have one or who have a family history of aneurysms.
Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA)
- This test gives detailed images of the blood vessels in the brain to identify a problem with blood flow. It involves inserting a small, thin tube called a catheter into an artery in the leg and directing it to the blood vessels in the brain. The contrast dye will be injected through the catheter to take X-ray images.
- Some researchers claim that CTA (computed tomography angiography) can now replace DSA (digital subtraction angiography) or catheter angiography as the best method to find brain aneurysms in cases of rupture, bleeding and sudden severe headaches (SAH).
- This judgment is based on the fact that CTA can be performed quickly (fast) as part of a routine CT scan, making it safer since no catheters are inserted into blood vessels, lowering the risk of complications.
- However, most experts still consider DSA the gold standard for examining blood flow in the brain and aneurysms.
- DSA is effective because it provides detailed images needed to measure aneurysms accurately. This is crucial for planning treatments like surgery or using endovascular methods. DSA also helps monitor changes over time by comparing images, which is essential for follow-up care after treatment.
Cerebral angiogram
It is the most reliable test for diagnosing cerebral aneurysms, as it allows the neurosurgeon to examine the brain's blood flow and blood vessels.
In this test, the patient lies on an X-ray table. Afterwards, a catheter (a small tube) is inserted into the patient's leg and directed into each blood vessel in the neck that goes to the brain. Contrast dye is also injected through the catheter before X-ray images are taken to find blockages in arteries in the neck or the brain and detect any weak spots in an artery, such as an aneurysm.
This examination can help detect aneurysm's size, shape, and exact location and determine the cause of brain bleeding.
Ultrasonography
- Transcranial Doppler (TCD) ultrasonography is a non-invasive technique used in patients with bleeding in the subarachnoid space (subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH) to detect vasospasm (sudden constriction of a blood vessel) in the arteries inside the skull.
- TCD ultrasonography can track changes in the velocity of blood flow over time in patients with subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH). These changes may reveal worsening conditions, helping neurosurgeons to choose specific treatments.
Nuclear imaging
- Some large (giant) aneurysms in the cavernous segment of the internal carotid artery may be treated by blocking the artery.
- Before deciding on this treatment, surgeons determine whether the brain has enough reserve to handle the blood flow loss from the carotid artery and assess this using an endovascular balloon occlusion test, which is an endovascular procedure in which a balloon is temporarily inflated in an artery, to temporarily block the artery while monitoring cerebral blood flow with (single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), a nuclear imaging test that displays how blood flows to tissues and organs) scans.
- Patients who tolerate the test without significant areas of reduced blood flow may be the considered candidates for carotid artery occlusion treatment.
Lumbar puncture
- A lumbar puncture involves inserting a thin needle into the lower part of the patient spine to collect a sample of CSF.
- This puncture can be used in about 5% of patients in whom cranial CT shows no abnormalities despite symptoms or history suggesting bleeding (subarachnoid haemorrhage).
- If the patient's cerebrospinal fluid seems bloody and doesn't clear up even after draining more fluid, this indicates blood has leaked into the space around the brain.
- The presence of xanthochromia, a yellowish discolouration of the cerebrospinal fluid, represents the presence of bilirubin from the breakdown of haemoglobin and is even more definitive (conclusive evidence) than a high red-cell count in the cerebrospinal fluid.
- In cases where bleeding occurs more than 12 hours before a lumbar puncture, the CSF may appear yellow due to haemoglobin breakdown products.
- In contrast, if the blood in the CSF is fresh, like from a recent traumatic spinal tap, it won't cause this yellow discolouration. This difference helps neurosurgeons distinguish between a haemorrhage that occurred some time ago versus recent trauma or bleeding.
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis
- This analysis estimates the various components in cerebrospinal fluid, which protects and cushions the brain and spinal cord.
- A neurosurgeon often collects the CSF by performing a lumbar puncture (spinal tap), in which a thin needle is inserted into the individual's lower back (lumbar spine). A small amount of fluid is removed and examined to detect any bleeding around the brain. If bleeding is identified in a given sample, additional tests are required to detect the exact cause of the bleeding.
- Patients with any ongoing new neurologic deficit who have no response to medical therapies (conservative treatment) should undergo urgent catheter angiography to confirm the presence of vasospasm (sudden constriction of a blood vessel), followed by angioplasty of the narrowed vessels or intraarterial administration of smooth-muscle relaxants.
- Balloon angioplasty and antispasmodic agents result in angiographically confirmed arterial dilatation in a high percentage of patients (90 to 98 per cent).
✅Differential diagnosis of brain aneurysm
A differential diagnosis is a list of possible medical conditions or diseases that can share the same symptoms of endometriosis in a woman. Cerebral aneurysm has an extensive differential diagnosis that includes the following:
- Arteriovenous malformations: Abnormal tangle of a group of blood vessels that causes issues with the connections between arteries and veins.
- Cavernous sinus syndrome: It is a rare condition characterised by ophthalmoplegia (paralysis of the muscles within or surrounding the eye), proptosis (bulging eye), ocular and conjunctival congestion (redness and swelling of the eyes), often resulting from conditions such as infections, tumours, or vascular abnormalities.
- Cerebral venous thrombosis: A rare disorder characterised by the thrombosis of the cerebral veins and the dural sinuses, potentially causing serious neurological symptoms.
- Fibromuscular dysplasia: It is a rare condition that narrows the arteries, causing problems including aneurysm, stroke and high blood pressure
- Migraine and cluster headaches: Although they are not dangerous, cluster headaches and migraines are complex headache disorders associated with significant and sometimes alarming symptoms.
- Moyamoya disease: A rare and progressive disorder that causes blocked arteries at the base of the brain, leading to neurological symptoms such as stroke, seizures, and other symptoms
- Pituitary apoplexy: It is a rare and life-threatening clinical condition that presents acute headache, vomiting, visual impairment, and altered mental state. It occurs when there is bleeding or loss of blood flow in pituitary gland.
- Vein of Galen malformation: A rare type of blood vessel malformation (abnormality) in the brain
- Stroke - ischemic or haemorrhagic (blood clot or bleeding)
- Ischemic: It can be caused by a blood clot occurring due to the blocking of blood vessels in the brain
- Haemorrhagic: It can be caused by bleeding into the brain from a rupture (burst)of blood vessels.
✅Treatment considerations for unruptured aneurysm
A neurosurgeon may consider multiple factors when determining the best approach for treating an unruptured aneurysm, including:
- Risk of rupture
- Type, size and location of the aneurysm
- Person’s age and health
- Risk of treatment
- Family history
Brain aneurysm treatment
Treatment for a brain aneurysm can vary. The primary goal of treatment is to reduce the risk of blood flow from the aneurysm into the brain. Not all aneurysms need treatment. Healthcare professionals consider the future risk of bleeding from an aneurysm versus the risk of treatment. The following are the treatment approaches that neurosurgeons can use:
Conservative treatment
- Observation
- Medical therapy
- Antiseizure drugs (anticonvulsants)
- Calcium channel-blocking drugs
- Shunt
- Rehabilitative therapy
Surgical treatment
- Open craniotomy (surgical clipping)
- Endovascular treatment
- Artery occlusion and bypass
- Endovascular coiling or coil embolisation procedure
- Coil Embolization using an Intracranial Stent
Conservative treatment
Treatment for an aneurysm is recommended when an aneurysm has not ruptured but is large or causing symptoms. The following are the conservative treatments that a neurosurgeon can decide based on the patient's condition:
Observation: Aneurysms that are tiny, unruptured and asymptomatic may be observed with imaging examinations until the growth or symptoms necessitate surgery. Sometimes neurosurgeons recommend observation (wait and watch) by suggesting some preventive measures such as quitting smoking and alcohol and controlling high blood pressure to reduce the risk of rupture.
Medical therapy: Not all brain aneurysms require invasive treatment. If a brain aneurysm is tiny, unruptured, and not causing symptoms, the neurosurgeon instead prescribes medications to control the risk factors. High blood pressure and smoking are the main factors that have been shown to have a significant effect on aneurysm formation, growth and rupture. Anti-hypertensives, specific diet and exercise programs can be advised to control high blood pressure.
Periodic radiographic imaging, including MRA, CT scan, or computed tomographic angiography, may be recommended at intervals to monitor the size and growth of the unruptured aneurysm. Regular screening is important to monitor blood pressure and other medical conditions and recognise if the aneurysm starts to grow or is about to rupture.
The goals of further therapies for a ruptured brain aneurysm are to manage symptoms and lessen the consequences. Among these therapies are:
- Antiseizure drugs (anticonvulsants): These drugs can be prescribed to prevent seizures related to a ruptured aneurysm.
- Calcium channel-blocking drugs: The risk of stroke by vasospasm (sudden contraction of an artery) can be lessened with calcium channel-blocking drugs.
Shunt: If cerebrospinal fluid builds up (hydrocephalus) due to rupture and causes harmful pressure on surrounding brain tissue. In that case, a shunt will be surgically placed into the brain to redirect the fluid away from the brain to another location in the body.
Rehabilitative therapy: Patients who have suffered a subarachnoid haemorrhage often require physical, speech, and occupational therapy to retrieve lost function and learn to manage any permanent disability.
Surgical management (Neurosurgery)
If an aneurysm is likely to rupture, various surgical approaches can be used to divert blood flow away from the targeted aneurysm and repair the affected blood vessels in the brain. There are two main surgical approaches for a cerebral aneurysm:
Open craniotomy (surgical clipping)
- Clipping is performed by surgically removing part of the skull, which is called a craniotomy. Neurosurgeons will perform this process to repair an aneurysm by making an opening in the skull of the patient to access the brain and blood vessels. After identifying the aneurysm, the neurosurgeon carefully separates it from the surrounding brain tissues.
- A small metal clip (usually made of titanium) is used to clip the neck of the aneurysm to disconnect blood flow to it.
- These clips have spring mechanisms that allow the two "jaws" to close around both sides of the aneurysm, helping separate the aneurysm from the original (parent) blood vessel. Clips come in various sizes and shapes, and the choice of a specific clip is based on the location and size of an aneurysm.
- During this surgery, the patient is given general anaesthesia. Once the clipping process is completed, the skull is sutured back together. If there are no complications during or after this procedure, most patients stay in the hospital for 4 – 6 days and recover fully after several weeks or months.
Endovascular treatment
Artery occlusion and bypass
- If the artery is damaged or if surgical clipping is not possible, the neurosurgeon may completely block the artery with the aneurysm by grafting a small artery taken from the patient's leg to reroute the blood flow.
- The most common are coils, which are long strands of very thin, coiled wire that look like guitar strings but are flexible like telephone cords.
- The graft is a tiny artery commonly taken from the patient's leg that is attached above and below the obstructed artery so that blood flow is bypassed (rerouted) through the graft.
- This procedure can even be performed by detaching a donor artery from its normal position on one end, rerouting it to the inside of the skull, and connecting it above the blocked artery called a superficial temporal artery to the middle cerebral artery (STA-MCA) bypass.
Endovascular coiling or coil embolisation procedure
- Conversely another form of surgical approach is endovascular coiling.
- A neurosurgeon or interventional neurosurgeon inserts the catheter into an artery in the groin region and reaches the aneurysm to fill it with certain materials, such as platinum, balloons, or coils.
- The most common are coils, which are long strands of very thin, coiled wire that look like guitar strings but are flexible like telephone cords.
- These materials act as barriers to restrict the blood flow into the aneurysm.
- During a neurovascular intervention procedure, the patient lies on an X-ray table, and images are taken throughout the procedure using a machine called a fluoroscope.
- A special dye is injected through a microcatheter within the blood vessels so that the neurosurgeon can see the aneurysm inside the brain and guide medical devices to it without opening the skull.
- Using a thin guide wire, the surgeon passes detachable coils through the catheter and releases them into the aneurysm, packing several of these coils into the aneurysm one by one until it is complete.
- The coils can stay inside the aneurysm, and an embolus or clot will form around them, making it difficult for more blood to enter the aneurysm.
- The procedure is called coil embolisation because the body's natural response to the coils creates an embolus.
- If there are no side effects or complications during or after the procedure, most patients stay in the hospital for one or two days and recover fully after about a week.
- The procedure may require to be performed more than once during the patient's lifetime because aneurysms treated with this procedure (coiling) can sometimes recur.
Coil Embolization using an Intracranial Stent
- It treats large aneurysms that cannot be treated with surgery or platinum coil embolisation because they are challenging to treat with coils alone. Other endovascular treatment options for these types include placing a tiny stent, a flexible mesh tube that is the same as those placed for heart blockages, in the artery to reduce blood flow into the aneurysm.
- For instance, a wide-neck aneurysm may have such a large opening that the coils might not remain inside; they could fall back into the blood vessel and block or partly block the blood flow.
- In these cases, the neurosurgeon may insert a small stent (wire mesh tube) inside the blood vessel where the aneurysm is located.
- For a wide neck aneurysm in a coil embolisation procedure, the stent can be placed across the aneurysm neck and extends past the opening on both sides, supporting the blood vessels.
- The neurosurgeon then inserts the coils as described above, threading them between the stent's wires and into the aneurysm. The stent acts as a small scaffold to hold the coils inside the aneurysm so they will not fall back into the vessel.
Brain Aneurysm Treatment Cost in Hyderabad, India
Brain Aneurysm Treatment Cost in Hyderabad, India, ranges from ₹2,80,000 to ₹7,50,000 (US$850 to US$6580). The final treatment cost depends on various factors, including type & location of aneurysm, rupture status, treatment method (endovascular coiling, surgical clipping, or flow diversion stents), hospital stay & ICU care, medical procedures & medications, post-stroke care & rehabilitation.
| Treatment Type | Estimated Cost (₹) |
|---|---|
| Endovascular Coiling (Minimally Invasive) | ₹2,80,000 – ₹5,00,000 (US$3,200 - US$5,720) |
| Surgical Clipping (Open Surgery) | ₹3,50,000 – ₹6,50,000 (US$4,000 - US$7,450) |
| Flow Diversion Stents (For Large/Complex Aneurysms) | ₹5,25,000 – ₹9,75,000 (US$6,000 - US$11,150) |
At PACE Hospitals, we provide advanced brain aneurysm treatment in India with world-class medical care at affordable costs. To ensure hassle-free access to quality treatment, we offer cashless treatment options and accept major health insurance plans, making brain aneurysm treatment more accessible for patients. Our expert stroke specialists, 24/7 emergency care, and state-of-the-art facilities ensure the best possible recovery outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Brain Aneurysm
What are the risk factors for Brain Aneurysm?
No one factor causes brain aneurysms to form. However, some factors can be considered as main factors that increases the risk of rupture of brain aneurysm such as uncontrolled high blood pressure, smoking, certain genetic conditions, older age, family history, traumatic brain injuries, excessive alcohol consumption and prior brain aneurysms.
Can we prevent a brain aneurysm?
Prevention of the formation of a brain aneurysm and rupturing it involves maintaining the following healthy lifestyle habits such as controlling blood pressure, quitting smoking, reducing the amount of alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, having a healthy diet and lifestyle and regular screening.
Can a brain aneurysm cause sudden death?
A brain aneurysm is life-threatening if it ruptures due to the pressure on the nerves or brain tissue because of the bulging aneurysm, leading to spilling blood into the surrounding tissue ( haemorrhage). A ruptured aneurysm can cause serious health issues such as haemorrhagic stroke, brain damage, coma, and even death (rarely).
Screening of a brain aneurysm that is unruptured is only recommended for patients thought to have an increased risk of having an aneurysm that could burst or rupture at some point in the future.
Do unruptured brain aneurysms cause symptoms?
Usually, unruptured aneurysms don't cause symptoms until they grow large enough to press on the nerves and tissues inside the brain and ruptures. Small aneurysms that don’t change may not cause symptoms.
What is Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Haemorrhage?
Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Haemorrhage (SAH) is one of the major complications of a brain aneurysm, characterised by bleeding into the cerebrovascular fluid that surrounds the brain caused by the rupture of a brain aneurysm.
Usually, brain aneurysm ruptures without notice. Most patients with SAH present with a 'thunderclap' headache which is severe and sudden. Other symptoms include vision changes, reduced consciousness, sensitivity to light, neck pain or stiffness, and vomiting. Some patients experience a seizure or a fit during the bleeding. However, these symptoms may vary from one person to another.
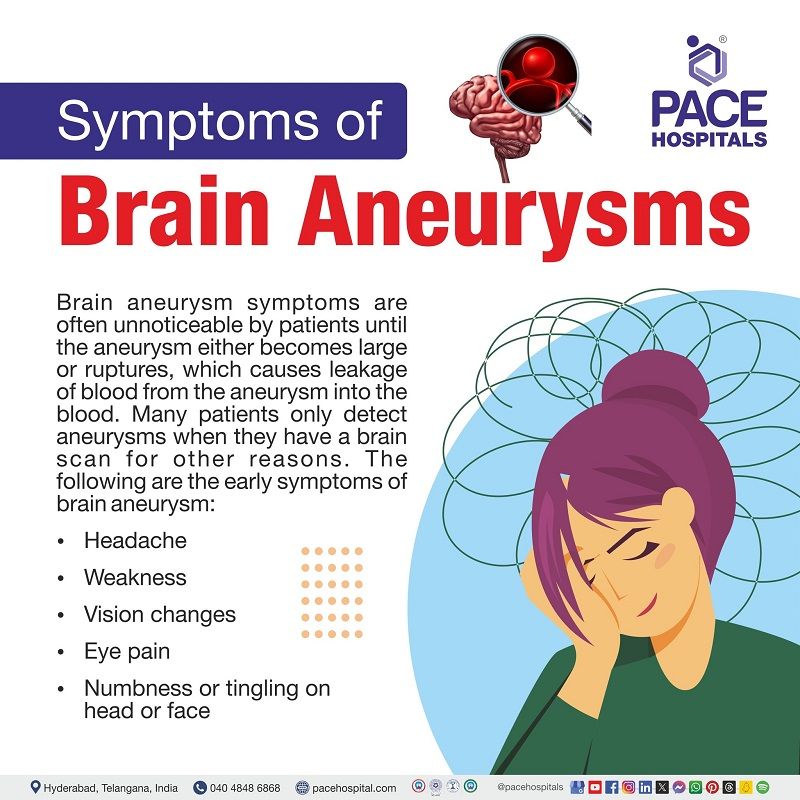
What are the symptoms of a brain aneurysm?
Unruptured aneurysms may not show symptoms, but larger ones can cause headaches, vision problems, and dizziness. A ruptured aneurysm often leads to a sudden, severe headache, nausea, seizures, loss of consciousness, or stroke-like symptoms.
What is an incidental finding of a brain aneurysm?
Most cerebral aneurysms are not noticeable until they rupture or are detected as incidental findings, usually identified during an imaging examination performed for other reasons such as routine health check-ups and other medical conditions, including head injury or unrelated symptoms. Identifying them incidentally allows the neurosurgeon to plan preventive measures to prevent rupture.
What are the signs and symptoms of a brain aneurysm?
Based on their size, some unruptured brain aneurysms may cause neurological symptoms. While smaller aneurysms may not cause symptoms, large ones may compress nerves and brain tissues, leading to rupture, resulting in chronic symptoms such as vision changes, thunderclap "headache," weakness and numbness, pain behind the eye, a dilated pupil in the eye, weakness and numbness, and one-sided facial paralysis that worsens over time.
What is the success rate of brain aneurysm treatment?
With timely intervention, the success rate is high. Minimally invasive procedures like coiling have a lower risk of complications and quicker recovery compared to open surgery. Our experienced specialists ensure the best possible outcomes.
Is brain aneurysm treatment covered by health insurance?
Yes, most health insurance plans cover brain aneurysm treatment. We assist patients in processing insurance claims and offer cashless treatment options to ease the financial burden.
How long is the recovery period after brain aneurysm treatment?
Recovery depends on the procedure performed. Patients undergoing endovascular coiling may recover within a few weeks, while those undergoing surgical clipping may require a longer recovery period of a few months with rehabilitation support.
Can a brain aneurysm be prevented?
While some risk factors are genetic, lifestyle changes like controlling high blood pressure, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, managing cholesterol, and regular health check-ups can help lower the risk of developing an aneurysm.
How is a brain aneurysm typically treated?
Treatment for an aneurysm depends on its location, size, and the presence of risk factors for a future rupture. For instance, a neurosurgeon recommends surgical management for a high-risk (rupture), large, or symptomatic aneurysm. If a brain aneurysm is tiny, unruptured, and not causing symptoms, the neurosurgeon instead prescribes medications to control the underlying risk factors to prevent the risk of rupture in future.




