Penile Implant Surgery
in Hyderabad, India |
Types & Cost
At PACE Hospitals, regain your sexual health and confidence with our advanced penile implant surgery, tailored to address erectile dysfunction. Our dedicated Urologists and cutting-edge technology ensure exceptional care and optimal results.
Request an appointment for Penile implant surgery
Penile implant surgery appointment
Thank you for contacting us. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
PACE Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Thank you for contacting us. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
PACE Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Protect Your Health:
People residing in Hyderabad who are looking for Penile implant surgery
near me' can schedule an appointment online at PACE Hospitals by completing the form above titled
'Request an Appointment for Penile implant surgery' or can call our appointment desk at
04048486868.
Things to Remember When Visiting the Hospital:
- Please remember to bring your previous medical records. This will help our doctors understand your medical history and provide the best possible care.
Penile implant definition
A penile implant, also known as a penile prosthesis, is a surgically inserted device that helps patients achieve an erection. Penile implants are used to treat conditions such as erectile dysfunction (ED) and Peyronie’s disease.
Advanced surgical skills and expertise are essential for urologists and surgeons to evaluate patients for candidacy, choose the best type of implant, and to perform the treatment safely and efficiently. During the surgical procedure, inflatable or malleable implants are inserted into the penis to help with erections, to restore sexual function, and to improve the patient's quality of life.
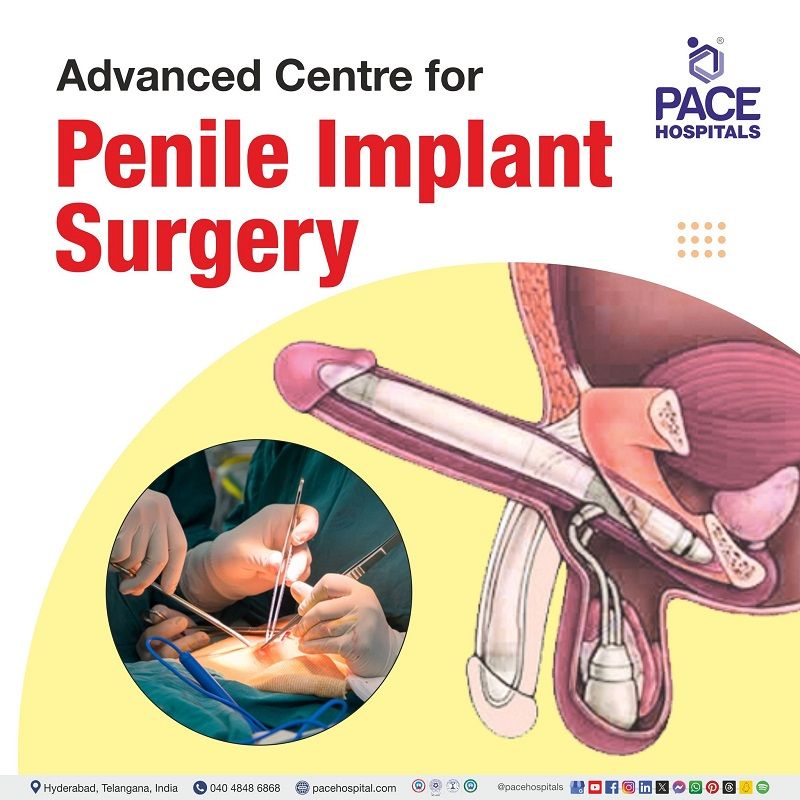
There are two (2) types of penile prosthesis implants, and they include the following:
- Inflatable penile implant
- Single-piece device
- Two-piece device
- Three-piece device
- Non-inflatable penile implant
Inflatable penile prosthesis (IPP)
The objective of the IPP is to stimulate a normal penile erection. It consists of two cylinders placed into the corpora cavernosa and connected to a pump. The cylinders are filled with sterile normal saline, stimulating the corpora cavernosa blood filling during a physiologic erection when the pump is squeezed and released many times (recycling).
- Single-piece IPP: In the middle of the 1980s, two different one-piece IPPs were introduced: the AMS Hydroflex prosthesis (American Medical Systems, Minnetonka, MN, USA) and the Flexi-Flate implant from Surgitek (Surgitek, Racine, WI, USA).
- Two-piece IPP: Frein and Mentor Corporation developed and marketed a two-piece hydraulic implant known as the "GFS prosthesis" (which stands for girth, flaccidity, and simplicity) in the late 1980s. Ambicor, a two-piece prefilled and pre-connected IPP made up of two cylinders and a silicon elastomer pump, became available by AMS in the 1990s.
- Three-piece IPP: Scott and associates developed the IPP's initial three-piece prototype. Although the first prototype was introduced in 1972, the AMS company made several technological and design advancements in cylinders between 1973 and 1990. A competing three-piece inflatable implant, the Mentor Alpha-1 IPP, was introduced by Mentor Corporation to the AMS penile prostheses in 1982. Additionally, the Coloplast Titan IPP has benefited from several innovative modifications that have enhanced the device's functionality, reliability, and durability.
Non-inflatable penile prosthesis (non-IPP)
These may be known as semi-rigid rods or malleable prostheses. Typically, this device consists of two rods covered in a silicone or polyurethane jacket or a spiral wire core or silicone substance. The American Medical Systems (AMS) 600 Spectra (Minnetonka, MN, USA) and Coloplast Genesis (Minneapolis, MN, USA) are the most commercially successful malleable prosthesis implants.
Penile implant Indications
Several urological diseases can be effectively managed with penile implant surgery. Below are some of the indications of penile implant surgery:
- Erectile dysfunction: Guidelines from the American Urological Association and the European Urological Association indicate that if more conservative treatments for erectile dysfunction (ED), such as phosphodiesterase inhibitors, vacuum erection devices, and intracavernosal injections, have failed, a penile implant may be placed.
- Peyronie disease: Peyronie's disease is a common condition that causes sexual dysfunction, psychological distress, and penile deformity. The penile implant is the recommended treatment for PD/ED men who need a consistent erection with no impact on their baseline penile sensation, urination, ejaculation, or orgasm.
- Severe psychogenic impotence: The inability to consistently achieve or sustain an erection that is needed for sexual performance mainly or entirely due to psychological or interpersonal reasons is known as psychogenic erectile dysfunction.
- Prolonged priapism >24 hours: Penile implant insertion can be considered immediately for cases lasting more than 24 hours and more than 36 hours, as well as for patients who are refractory to distal shunt techniques. To preserve penile length, patients with prolonged ischemic priapism may be acceptable for immediate placement of a penile implant.
- Gender-affirming surgery:
It was found that prosthesis placement is beneficial in addition to gender-affirming surgery. However, following a phalloplasty, placing a penile implant can be a complex surgical procedure with a significant risk of complications.
Contraindications of Penile Implant
The penile implant is not recommended in cases of recurring urinary infections or in conditions where immunosuppressive medications, spinal cord injuries, poorly managed diabetes, or other conditions may increase the risk of local infections. Below are some of the other contraindications of penile implant:
- Active infection: When there is an active infection anywhere in the body, especially in the urinary tract or genitals, a penile implant may not be used.
- Not willing for revised surgery: Patients who are unwilling to undergo implant surgery again, if necessary, are not suitable for a penile implant.
- Unresolved urination problems: A penile implant is not recommended in people with unresolved urinary issues, such as increased postvoid residual urine volume caused by a neurogenic bladder or obstruction of the bladder outlet.
- Comorbidities: Patients with significant comorbidities—mainly cardiovascular—who may find it challenging to be involved in sexual activity are not suitable for penile implants.
- Patients with low motivation: Patients should not undergo penile implants if they are low motivated or have wrong expectations.
Advantages of Penile implant
Penile implant surgery has shown to be a safe and successful choice for men with severe erectile dysfunction (ED), providing a long-lasting treatment for recovering sexual function despite certain risks. Below are some of the advantages of penile implant surgery:
- Penile implants offer a high rate of patient satisfaction.
- Penile implants are more spontaneous than prescribed medications.
- They usually have a functional prosthetic life of seven to ten years.
- Penile implants are provided with a controlled duration of erection.
- Penile implants appear ordinary and unnoticeable.
- Penile implants have a strong enough erection to allow for penetration, enabling the patient to end their sexual activity.
- The penile implant hardens the penis. The average patient experiences an erection 30 seconds after beginning to pump the device.
- Using an injectable or tablet form is not necessary for a penile implant.
Penile Implant Surgery steps
The urology team follows the below steps for performing penile implant surgery:
Before Penile Implant surgery
- Urologists usually perform penile implant surgery in hospitals or surgical centers. Most penile implant patients undergo an assessment by the surgeon to understand the reason for their erectile dysfunction and to estimate the risk associated with surgery.
- After patients have decided that a penile implant may be an appropriate choice, the doctor helps them understand the process, the risks and possible complications, and the best type of implant.
- Patients need to follow the surgeon's advice for taking medications both before and after the surgical procedure. Urologists frequently advise patients not to take any medicines that may change the function of platelets in the blood or raise the risk of bleeding during the two weeks before and after penile implant surgery.If a patient takes any medications that increase the risk of the surgery, the surgeon checks with the medications and provides alternatives.
- To lower the risk of infection, the surgeon may advise taking an antibiotic-infused soap bath three nights before the surgical procedure. Patients need to avoid shaving the surgical site by themselves.
During Penile Implant surgery
- Usually, an anesthesiologist administers either spinal or general anesthetic during penile implant surgery.
- Antibiotics may be given to the patient a few hours before surgery to lower the chance of infection.
- Urine is drained from the bladder by inserting a catheter, a tube through the urethra. Urinary catheters are usually removed within the first 24 hours following surgery.
- The surgeon will make an incision in the lower abdomen, at the base of the penis, or beneath the head of the penis.
- Next, the surgeon stretches the spongy tissues of the penis that would usually fill with blood during an erection. The two hollow chambers known as the corpora cavernosa contain this tissue.
- The surgeon will select the appropriate implant size and insert the cylinders inside the penis after flushing the area with an antibiotic solution to prevent infection.
- If the surgeon decides to implant a two-piece inflatable device, the pump and valve mechanism are inserted inside the scrotum. For a three-piece device, the surgeon will create an internal incision to implant a fluid reservoir beneath the abdominal wall.
- After the device is positioned, the surgeon will sew the incisions closed.
After Penile implant surgery
- After 48 hours of surgery, the majority of men go home.
- To avoid infection, patients need to take antibiotics as prescribed by the surgeon.
- Patients need to wear loose-fitting clothes and underwear after the procedure. It is essential for men who use an inflatable device to ensure that the scrotal pump remains in place as they heal.
- After surgery, most men can return to intense physical activity in about a month. Depending on their type of implant and the surgeon's advice, people can resume sexual activity four to six weeks after surgery.
Penile implant problems
There may be certain complications with the penile implant. They are rare. However, they tend to happen sometimes. Below are some of the complications of penile implant:
- Infection: Of 100 patients receiving an implant for the first time, 1 to 3 have an infection. If the surgery is repeated, infection is more likely. If it becomes infected, the implant will need to be removed. Though they can happen up to a year after surgery, infections typically happen within the first eight weeks after the surgery.
- Scrotal hematoma: Scrotal, lower abdominal, and inner thigh edema and bruises are seen. Blood accumulation can result in significant swelling. To help avoid this, the surgeon will place a scrotal support after surgery, which resembles a jockstrap.
- Penile implant failure: The device fails early. About two out of every 100 people who receive implants have this. Early after surgery, the pump or cylinders may stop functioning. The device will need to be replaced if this occurs.
- Second surgery: Within the first ten years following implant placement, 15 to 20 out of every 100 patients will require another surgery. This is a result of the device breakdown.
- Autoinflation: The device may inflate on its own. Usually, some effort is required for this to occur. To avoid this during surgery, doctors take considerable precautions. Even with the best measures, it might nevertheless happen in certain situations. Those individuals who have undergone surgery for prostate cancer or who are overweight are more likely to experience this.
- Erosion: The implant eventually penetrates the skin. It is more likely to occur if patients have had an infection. It may be necessary to remove the implant.
- Migration: It refers to the dislocation of the implant. This may require additional surgery.
- Reduced penile length: Penile shortening may occur as a result of the penile implant surgery or may have been caused by trauma, scarring, post-priapism corporal fibrosis, radiation, or surgery in the past.
- Postoperative urinary retention: The inability to urinate while having a full bladder following surgery is known as postoperative urine retention. It is a common complication affecting patients after penile implant surgery.
Questions that the patients can ask the healthcare team about penile implant surgery?
- When can I go home?
- What kind of pain can I expect?
- When can I go back to work?
- When can I start exercising again?
- What can I eat and drink after penile implant surgery?
- Could this procedure have any long-term effects?
- How long will it take for my wound to heal?
- When am I allowed to drive again?
- Do I need any further treatment?
- How long after the surgery can I resume sexual activities?
- Do I need to replace the penile implant after some years?
- When do I need to see my doctor again?
History of Penile implant Surgery
- The “os penis” was created by Bogoras in 1936 and Frumkin in 1943 by implanting resected ribs into the dorsal part of the penis. These were the first reported attempts to reconstruct the penis to provide rigidity for intercourse.
- In 1948, Bergman and associates published a report on the use of a rib graft for rigidity in the plastic reconstruction of an amputated penis. Despite having intercourse, the grafted rib was completely absorbed in a few years.
- Scardino in 1950 and Goodwin and Scott in 1952 both reported the placement of acrylic penile splints.
- In 1960, Beheri incised the tunica albuginea to place paired polyethylene rods into the corpus cavernosum and used dilators to create tunnels within. Later, he announced that his prosthesis had been successful in treating 700 patients of erectile dysfunction in various categories.
- At the same time, Sayegh and Loeffler started using perforated acrylic implants between the corpora cavernosa.
- Lash and associates later used a similar prosthesis in the surgical treatment of Peyronie's disease.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs) on Penile implant Surgery
How long is pain after penile implant?
Following the implantation of an inflated penile prosthesis (IPP), postoperative pain is normal and may last for up to six weeks. In addition, there is a subset of chronic penile prosthesis pain that is comparable to chronic post-surgical pain (CPSP), which is characterized by pain that develops at least two months following surgery without an obvious cause.
How long do penile implants last?
After the placement of an inflated penile prosthesis (IPP), long-term follow-up data revealed that nearly half of the devices remained effective 20 years after the initial penile implant, with 60% of patients reporting high levels of satisfaction and satisfactory quality of life results.
How long is the recovery for a penile implant?
For the insertion of penile implants, local anesthetic has been used, but most patients get spinal or general anesthesia and depart the same day or after a 23-hour stay. While postoperative pain varies in intensity and length, most patients experience some localized discomfort lasting up to four or six weeks after surgery.
Is penile implant surgery reversible?
Since penile implant surgery is an irreversible procedure, the patient would not be able to get an erection with Intracavernosal injection (ICI) or oral therapy if the patient decided to have the implant removed.
Is a penile implant better than injections?
Because of the high patient-initiated dropout rate, however, the majority of clinicians consider intracavernosal injection as a palliative treatment for erectile dysfunction. In contrast, penile prosthesis provide a more long-term solution to erectile dysfunction.
What is penile implant surgery?
A surgical procedure called penile prosthesis implantation is used to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) in patients who are not responding to other types of treatment. Implants that are inflatable or malleable are inserted into the penis during the surgery to help patients achieve erections, restore their sexual function, and enhance their quality of life.
Are penile implants safe?
Yes, penile implants are safe for individuals suffering from erectile dysfunction (ED), and the inflatable penile prosthesis (IPP) remains a great choice due to its high overall satisfaction rates and low risk of complications.
Can penile implants increase penile size?
For a majority of patients, penile implant surgery maintains the usual size rather than increasing the penile size when compared to the preoperative stretched measure. Males with inflatable prostheses are expected to experience a greater increase in length compared to those with implants that are malleable.
Can you ejaculate with a penile implant?
Despite having lost or significantly reduced erectile function, most men were still able to ejaculate and have an orgasm before surgery. There's no effect on ejaculation or orgasmic functioning following the implantation of a prosthetic device.
What do penile implants look like?
Before the implant is inserted into the patient's body, it resembles two heavy-duty oval balloons. Depending on the type of penile implant, the balloons may attach to a plastic reservoir, a valve, or tubing.
How does a penile implant work?
During the penile implant surgery, implants that are inflatable or malleable are inserted into the penis to help patients achieve erections, restore their sexual function, and enhance their quality of life. Hence penile implant procedure is used to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) in those patients who are unresponsive to other forms of treatment.
What is a semi-rigid penile implant?
Semi-rigid rods or malleable prostheses are alternative names for non-inflatable penile prostheses (non-IPPs). Since IPP provides penile stiffness and flaccidity that closely resembles a normal penile erectile function, it is seen to be a better option than a malleable prosthesis.
What is the average age for penile implant surgery?
Over 45 is the average age of men with penile implants. On the other hand, younger men who are unable to get an erection due to health problems could find the process helpful.
Can a penile implant be redone?
In most cases, it is advised to remove destroyed penile implants as soon as possible. Nevertheless, during preoperative assessments and surgical investigation, patients without symptoms of sepsis, local infection, or necrosis may have their destroyed implants saved and re-implanted.
What is the latest penile implant technology?
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Boston Scientific's novel Tactra flexible penile prosthesis in April 2019. The prosthesis has a Nitinol nickel-titanium alloy core protected by a special dual-layer silicone shell.
Our Locations
Metro Pillar Number C1772, Beside Avasa Hotel, Hitech City Road, Near HITEC City Metro Station, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Mythri Nagar, Beside South India Shopping Mall, Hafeezpet, Madeenaguda, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
040 4848 6868
Payment in advance for treatment at PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, Telangana, India (Pay in INR ₹)
For Bank Transfer:-
- Bank Name: HDFC
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.50200028705218
IFSC Code: HDFC0000545 - Bank Name: STATE BANK OF INDIA
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.62206858997
IFSC Code: SBIN0020299
Scan QR Code by Any Payment App (GPay, Paytm, Phonepe, BHIM, Bank Apps, Amazon, Airtel, Truecaller, Idea, Whatsapp etc).

CONTACT US
Call: +914048486868
WhatsApp: +918977889778
Email: info@pacehospitals.in
FOLLOW US
SUBSCRIBE
Subscribe to our newsletter and stay updated with the latest health information.
Subscribe to PACE Hospitals' Public Newsletter
Thank you for subscribing to PACE Hospitals' Newsletter. Stay updated with the latest health information.
Oops, there was an error. Please try again submitting your details.
ABOUT US
QUICK LINKS
Disclaimer
General information on healthcare issues is made available by PACE Hospitals through this website (www.pacehospital.com), as well as its other websites and branded social media pages. The text, videos, illustrations, photographs, quoted information, and other materials found on these websites (here by collectively referred to as "Content") are offered for informational purposes only and is neither exhaustive nor complete. Prior to forming a decision in regard to your health, consult your doctor or any another healthcare professional. PACE Hospitals does not have an obligation to update or modify the "Content" or to explain or resolve any inconsistencies therein.
The "Content" from the website of PACE Hospitals or from its branded social media pages might include any adult explicit "Content" which is deemed exclusively medical or health-related and not otherwise. Publishing material or making references to specific sources, such as to any particular therapies, goods, drugs, practises, doctors, nurses, other healthcare professionals, diagnoses or procedures is done purely for informational purposes and does not reflect any endorsement by PACE Hospitals as such.


