Surgical Gene Therapy - Auxiliary Liver Transplantation for Rare Genetic Liver Disease
A Rare Surgery (Auxiliary Liver Transplantation) For Rare Genetic Liver Disease (Propionic Acidemia). For the first time in Telugu states, with the combined efforts of PACE Hospitals and Ankura Hospitals.
A 7-month boy suffering with rare Genetic Liver Disease called “Propionic acidemia” was referred to us (PACE Hospitals) for Liver Transplantation. Although the patient displayed no hepatological (liver-related) abnormalities, from a neurological perspective, the patient had delayed developmental milestones evident from the development of convulsions (fits) and poor head control (loss of muscle tone). The patient also displayed poor eating habits.
Paediatric Neurologist and Paediatric Gastroenterologist of Ankura hospitals evaluated the child extensively with Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) of the brain, Electroencephalogram (EEG), arterial blood gas (ABG) test, along with associated blood and genetic tests and made a diagnosis of rare metabolic liver disease called "Propionic acidemia".
What is Propionic Acidemia?
Propionic acidemia is a rare-inherited condition, a genetic autosomal-recessive inborn error of metabolism disease in which the body is unable to break down certain proteins and fats. This is due to a defect in an enzyme called Propionyl-CoA carboxylase (PCC) 24.
Propionyl-CoA Carboxylase (PCC) is a component in the tricarboxylic acid cycle responsible for mitochondrial respiration and generating energy. Reduction of Propionyl-CoA Carboxylase (PCC) can lead to an accumulation of toxic substances, which can harm the nervous system and the heart and episodes of serious illness.
Devoid of any inbuilt mechanism to eliminate the toxic buildup within the body, the prognosis of the disease could end with mental retardation and early death, usually within three years.
Due to the low incidence of propionic acidemia, expertise treatment (which usually includes liver transplantation) is very scarce, which is why the patients are usually referred to tertiary and quaternary medical centres.
Although symptomatic addressal of the prognostic life-threatening issues such as (e.g., acidosis, dehydration, seizures) may be arranged locally, the suspicion of acidemia (acid buildup in blood) is enough to transfer the patient into a facility capable of handling such rare and critical cases with a high level of expertise.
Symptoms and Signs of Propionic acidemia
The disorder presents in the early childhood period with poor feeding, vomiting, lethargy, dehydration, acidosis and lack of muscle tone (hypotonia), seizures. Without treatment, death can occur quickly, due to secondary hyperammonaemia, infection, heart damage (cardiomyopathy), brain damage and chronic kidney disease. These symptoms will become more severe whenever there are GIT infections, excessive protein intake, trauma and accidents.
Even though this is Metabolic liver disease, but they don’t present symptoms like jaundice, ascites or leg edema which are very common symptoms of chronic liver disease. Here Liver function tests are normal and liver scan also will be normal. In generally Liver does more than 2000 functions in our body. In this disorder one of liver enzyme (propionyl-CoA carboxylase) is defective and rest of liver functions were normal. In such conditions you don’t need to remove the entire liver like in regular Liver Transplantation surgery.
Scope of treatment for propionic acidemia around the globe
Being one of rare conditions, there is limited scope for propionic acidemia treatment as there is not only a scarcity of experienced personnel but also medical centres which can support the case and its treatment.
While the detection rates of propionic acidemia in Asia-Pacific could range between 0.09 and 5.05 per 1,00,000 newborns, it ranges from 0.32 to 2.20 per 1,00,000 newborns in Europe. The North American detection rates range between 0.33 per 100,000 newborns, while the highest detection rates (4.24 per 1,00,000 newborns) were seen among the Middle East and North African regions (MENA).
In world literature, nearly 70 cases underwent auxiliary liver transplantation for this condition. In India, very few cases (around 5 cases) underwent Auxiliary Liver transplantation for propionic acidemia.
Symptomatic management of Propionic acidemia
While the addressal of the underlying root cause of propionic acidemia is still under research, only symptomatic management can be provided to the patient to an extent. While the optimal management of patients with propionic acidemia (PA) is best achieved by a team of physicians with metabolic expertise and a dietician, a liver transplant could necessitate liver transplant doctors altogether.
The main aspects of propionic acidemia (PA) management include:
- Strict dietary management
- Carnitine supplementation
- Antibiotic regimen
- Ammonia scavengers
- Strict dietary management: As such, there is a Propionyl-CoA carboxylase (PCC) deficiency, leading to the build-up of toxic materials. The expertise of a dietician lies in the approval of controlled amounts of propiogenic food while also providing the patient with increased caloric intake to tackle the illness, preventing catabolism (breakdown of complex molecules in the body).
- Carnitine supplementation: Levocarnitine is a biochemical (usually produced in the liver, kidneys, etc.) that helps in the production of energy from fat into energy. It may enhance the detoxification of propionic acid, thus reducing the build-up of toxins.
- Antibiotic regimen: Intestinal bacteria (good bacteria) present in the gut are capable of producing propionate, but due to propionyl-CoA carboxylase (PCC) deficiency, propionate could prove toxic. Antibiotic therapy may be prescribed by the hepatologist to reduce the production of propionate.
- Ammonia scavengers: Hyperammonaemia (increased ammonia in the blood) is a common symptom of metabolic acidosis (acid build-up in the body) and is another toxic product build-up. Ammonia scavengers help in controlling the episodes of hyperammonaemia.
The role of liver transplantation in propionic acidemia
Metabolic decompensation (declined metabolic status leading to hypoglycaemia (low sugar in the blood), hyperammonaemia (increased ammonia in blood), and organ failure) is the final stage in propionic acidemia despite following a strict dietary and medical treatment for a 15-year survival rate of less than 50%.
Moreover, the treatment complexity, the poor long-term neurological outcomes and the frequent admissions finally cause a deficient quality of life for propionic acidemia patients and their families.
Despite the deficiency of Propionyl-CoA Carboxylase (PCC) seen in various locations of the body, the liver is the main site of action of the amino acid transamination. Thus, liver transplantation, while not a curative treatment as such, could necessarily provide at least a partial correction of the metabolic deficiency, reducing the amount of toxic build-up, minimising the risk of metabolic decompensations and improving nutrition and quality of life of propionic acidemia patients.
Nevertheless, liver transplant in such cases is a difficult but necessary option, as there have been reportedly increased rates of hepatic arterial thrombosis (clot formation in an artery in the liver) and post transplant renal dysfunction (kidney failure after transplant) are higher than in other liver transplant indications.
Auxiliary liver transplantation
Auxiliary liver transplantation has been successfully used as an alternative to whole liver transplant in some noncirrhotic inborn errors of metabolism. There are various case reports demonstrating the good outcome obtained with the utilisation of this technique in propionic acidemia patients.
The main advantage of this technique is seen in the contingency cases of donor graft failure. In case of a graft failure, the donor graft can be removed, leaving the native liver as a backup. Moreover, it leaves open the possibility of performing gene therapy in the future.
Treatment of Propionic acidemia
Medical management is dietary restriction of proteins and certain fatty foods, giving low dose long term antibiotics (metrogyl 10 days per month), L carnitine powder.
Lifelong dietary restrictions and life-threatening complications (cardiac, renal and brain) can be prevented in these children by Liver Transplantation surgery in early stage of childhood.
We at PACE Hospitals, did a new method of Liver Transplantation in this child called “Auxiliary Liver Transplantation” where the patient will have 2 livers in his body. One half of native liver will be kept in situ in the patient to take care of regular liver functions and another half of liver is taken from healthy Liver Donor which will take care of genetic liver enzyme deficiency (propionyl-CoA carboxylase).
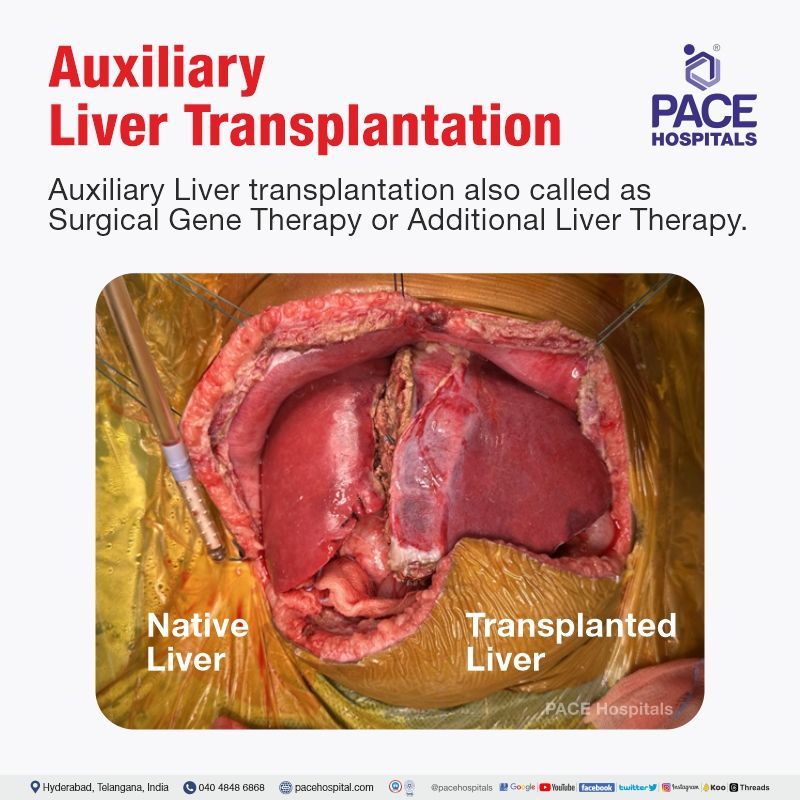
That is why this Auxiliary Liver transplantation also called as Surgical Gene Therapy or Additional Liver Therapy. In this surgery, Transplanted liver will help in production of propionic acid enzyme and his native will take care of rest of liver functions. This type of Liver transplant is technically very difficult operation. The main surgical challenges are reconstructing the blood flow and bile flow to New transplanted liver in a limited narrow space (because of persistence of half of native liver), the anaesthesia and post-operative care also very challenging because of small children, compartment syndrome and metabolic storm.
This condition is very rare described in 1in 35000 children in the USA but more common in Saudi Arabia (1 in 5000). In world literature, nearly 70 cases underwent auxiliary liver transplantation for this condition. In India very few cases (around 5 cases) underwent Auxiliary Liver transplantation for propionic acidemia.
Success Story
We at PACE Hospitals had 7 months child (7 kg child) referred for Auxiliary Liver Transplantation. Mother donated a portion of liver for his child. Here we took reduced size liver graft (Segment 2 mono segment graft) from the donor. In the child, first we removed only Left half of the liver but kept in situ of Rt lobe of liver. Segment 2 Liver mono graft taken from the mother is transplanted in left half liver space of the child. Surgery was done at PACE Hospitals, Hitech city on 25-10-2023. Surgery went for nearly 20 hours. The patient was managed in the hospital for 15 days and discharged. Now he is doing well.
First time, ANKURA group of Hospitals and PACE Hospitals doctors combinedly did this surgery successfully. This surgery is led by Dr. CH. Madhusudhan (Senior Consultant Liver Transplantation). Other team of doctors involved in this surgery are Dr. Parijath Ram Tripati (Paediatric gastroenterologist), Dr. Govind Verma (Chief Hepatologist), Dr. Phani Krishna Ravula (Liver Transplant Surgeon), Dr. Prashanth Sanghu (SGE), Dr. Sampath (Liver Intensivist), Dr. Harish (Liver Anaesthestist), Dr. BVL Narasimha Rao (Paediatrician), Dr. Pravalika Dutta (Neurologist), Dr. Rahul (Liver transplant liaison officer).
“This type of Auxiliary Liver Transplant for propionic acidemia is first time in combined Telugu states” said by Dr. CH. Madhusudhan. Many children are born with rare metabolic liver disease like Wilsons disease, Tyrosinemia, Glycogen storage disorders, PFIC, Alagille syndrome, Urea cycle defects etc and congenital birth defects Like Biliary Atresia, Liver tumours like Hepatoblastoma need liver transplantation as lifesaving procedure in them.
Sometimes permanent brain damage can be prevented if we do liver transplantation in right time of the age (before 1 year of age). This type of disorders is more prevalent in children of consanguineous marriage parents.
The reasons for low number of Pediatric Liver transplants across the India are Lack of awareness, Unaffordability, and lack of accessibility to proper treatment. The total number of Pediatric Liver Transplants in India still remains less than 150 per year despite the projected need for 3000 per year.
When children’s day, We wish every child has got right to live. We have done nearly 126 Paediatric Liver transplants till now and many were done as charity by crowdfunding. We have started public awareness programs also along with celebrities like actor Sri Vijay Devarakonda, Police official like Mr. Sajjanor during cyberabad commissioner time. Furthermore, we have also started educating the Paediatricians for the right time referral of these children for Liver Transplant in CME and conferences.
Difference between whole liver transplantation and auxiliary liver transplantation
When compared with the kidney and pancreas, the liver vasculature (network of blood vessels) is complex. This is why chronic liver disease also brings additional problems of portal hypertension (increased blood pressure in the liver), so the goal of transplantation extends beyond the range of metabolic abnormalities correction (i.e., portal pressure relief).
Orthotopic liver transplantation: Orthotopic liver transplantation (whole liver transplantation), in which the diseased host liver is replaced by the donor organ in the same anatomical position, fulfils these aims, and this procedure is now used worldwide for patients with end-stage acute or chronic liver disease.
- Severe blood loss: However, since orthotopic transplantation involves removal of the liver, it leads to severe blood loss, necessitating the use of a pump-driven system to direct venous blood from the lower half of the body and the splanchnic area (abdominal organs) to the heart.
- Disadvantage of whole liver transplantation: In the case of graft dysfunction, two results can be expected – either the death of the patient or the patient must be retransplanted immediately. The most striking disadvantage of orthotopic transplantation is in the patient with acute liver failure, whose liver might recover in time-i.e., by removing the native liver, any chance for recovery is obviated.
These considerations led to the concept of auxiliary liver transplantation.
Auxiliary liver transplantation: Auxiliary liver transplantation is the placement of healthy liver tissue in the body while leaving a part of the native liver in its place. Auxiliary liver transplantation was introduced first in patients suffering from chronic liver disease and later in those with subacute/acute liver failure and metabolic disease.
Auxiliary graft can supply the defective enzymes, and in case of any graft failure, it does not necessarily lead to the death of the recipient or require immediate retransplantation. Also, with auxiliary liver transplantation, gene therapy could be a possibility in the future.
The necessity of an auxiliary liver transplantation procedure in a metabolic liver disorder lies in the correction of metabolic defects through the grafted liver cells while the native liver cells continue to support other functions. In these cases, auxiliary liver transplantation procedures can be considered as a form of surgical gene therapy or additional liver therapy, as patients retain their native organs.
News coverage
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868