Gynaecology Hospital in Hyderabad for all Gynecological Diseases and Treatment
PACE Hospitals is one of the
Best Gynaecology Hospital in Hyderabad, Telangana, India, providing comprehensive patient-centric treatment for all gynaecological diseases and disorders. The team of experienced and skilled gynaecologist, obstetrician and gynaecology surgeons have wide expertise in managing all types of common and critical women's health conditions, including:
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD), Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
- Vaginosis, Candidiasis, Vulvovaginitis, HPV
- Menstrual Disorders, Menopause-related Issues
- Endometriosis, Uterine Fibroids, Ovarian Cysts,
- Breast Lump, Breast Cyst
- Pelvic Organ Prolapse, Pelvic Pain, Preeclampsia
- Anaemia in Pregnancy, Ectopic pregnancy
- Placenta Previa, Placenta Accreta
- Sexually transmitted infections (STI)
Why choose PACE Hospitals for Gynecology Treatment?
Comprehensive Gynaecological Care
Providing treatment to a wide range of gynaecology diseases and disorders including PCOS, PCOD, Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, Menstrual Disorders, Ovarian Cysts, Uterine Fibroids, Endometriosis, Ectopic Pregnancy and more.
Advanced State-of-the-art Facility
Equipped with advanced and latest diagnostic equipment, robotic and minimally invasive surgical facilities for all types of gynecological diseases and treatment.
Skilled & Experienced
OB-Gynaecologist
Team of experienced gynaecology doctor, obstetrician, obstetrician gynaecologist and gynecology surgeon with vast experience in minimally invasive procedures.
Advanced Centre for Gynecological Disease Treatment in Hyderabad, Telangana

The Gynaecology Department at PACE Hospitals is one of the best gynecologist hospital in Hyderabad, Telangana, India. The department is led by a team of experienced gynaecology doctors, obstetricians and gynaecology surgeons, who are highly skilled and have expertise in addressing all types of women's health issues, from regular gynaecological examinations to minimally invasive surgical procedures for complex gynaecological conditions, ensuring the highest standards of gynaecological care. The Gynaecological treatment care at PACE Hospitals is aimed at providing comprehensive, personalized, evidence-based treatments for conditions such as menstrual disorders, fertility issues, pregnancy care, and complex surgeries with a focus on patients receiving the highest quality care with a comfortable, compassionate and supportive environment.
The Department of Gynaecology at PACE Hospitals is equipped with state-of-the-art and cutting-edge facilities, making it one of the
top gynecology hospitals in Hyderabad, Telangana, India. We offer a wide range of gynaecological treatments, from preventive care to specialized procedures. Our advanced diagnostic facilities enable our gynaecology specialists to perform diagnostic and minimally invasive procedures for complex disorders with utmost precision, ensuring reduced recovery times, minimal scarring, and less post-operative pain.
Our Counselling Clinic to improve Women's Health
3,12,338
98,538
684
2011
Best Gynaecology Doctor in Hyderabad | Top OB-Gynaecologist
Team of the best gynecology doctors in Hyderabad, Telangana, India, specializes in managing all kinds of Gynecological Diseases and Treatment. They are skilled in examining and treating a wide array of regular and critical women's health conditions, including menstrual irregularities, hormonal imbalance, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), high-risk pregnancies, menopausal complications, uterine fibroids, ovarian cysts, endometriosis, cervical abnormalities, infertility, breast-related issues and more. The specialized team of obstetrician gynecologist and gynaecology surgeons are highly skilled and apt with the latest and advanced treatment modalities, and minimally invasive procedures to cater for the utmost treatment care with precision, minimal complications and a high success rate.
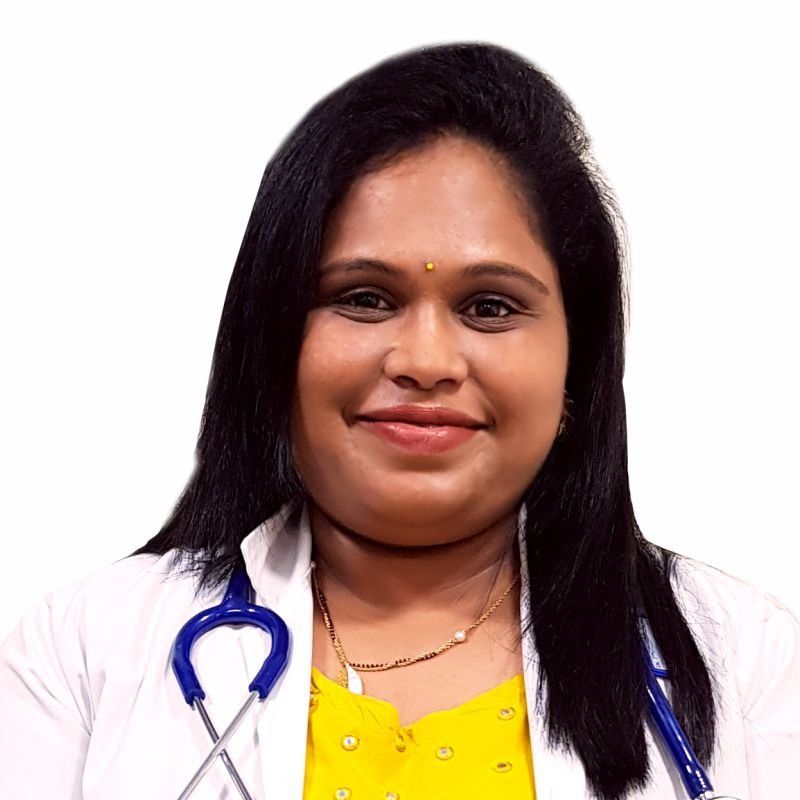
Dr. Mugdha Bandawar
MBBS, DGO, FMAS, DMAS (Diploma in Minimal Access Surgery)
Experience: 10+ years
Obstetrician, Gynecologist, Laparoscopic Surgeon and Infertility Consultant
Consultation Details
Timing:
Mon to Sat - 9 am to 6 pm
Location:
PACE Hospitals, Hitech City
Gynaecological Diseases and Conditions Explained by Drs
Need Help?
Struggling with common gynaecological concerns like heavy menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia), severe menstrual pain (dysmenorrhea), menstruation absence (amenorrhea), irregular menstruation, hormonal imbalances, pelvic pain, pelvic inflammatory disease, gynaecological infections, pain in the breast, sexually transmitted infections, menopause-related symptoms or seeking treatment for complex gynaecological disorders like uterine fibroids, ovarian cysts, endometriosis, breast cyst, breast lump, ectopic pregnancy, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), polycystic ovarian disease (PCOD), pelvic organ prolapse, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), Asherman’s syndrome, we offer evidence-based solutions tailored to your needs with high success rate.
What we treat?
We have expertise in the treatment and management of a wide array of gynaecological diseases and disorders affecting women's reproductive health conditions. From everyday women's health conditions like menstrual disorders, Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), pelvic pain, Breast Pain, Nipple Discharge, Breast lumps and gynaecological infections to complex and critical conditions like uterine fibroids, ovarian cysts, endometriosis, ectopic pregnancy, Uterine Prolapse, Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS), Breast Cyst, our team of gynaecologist, obstetrician and gynaecology surgeons is committed to providing the compassionate, patient-centric comprehensive solutions for women's reproductive health.

Patient Testimonials
Gynaecological Diagnostic Test & Procedures
We provide comprehensive and cutting-edge diagnostic and procedural treatment tailored to women's healthcare needs. Our advanced and latest screening approach and diagnostic procedures like pelvic ultrasound, colposcopy, hysteroscopy and endometrial biopsy examine critical conditions like uterine fibroids, ovarian cysts, endometriosis and reproductive health disorders, resulting in the early detection and precise evaluation, enabling our gynaecologist and obstetrician to make an informed decision to proceed with the appropriate treatment approach.

1. Pelvic Examination: Pelvic examination is the process performed to collect information about the pelvic area, which includes vulva, vagina, cervix, uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes; it is done to look for signs of diseases or infections. Gynaecologists commonly perform this test to detect sexually transmitted infections (STI’s), yeast infections, and bacterial vaginosis. It includes visual external examination, manual examination, speculum exam, pap test and rectal exam.
2. Blood Tests: Women can undergo various blood tests that provide valuable insights into their health. These tests measure specific hormones in a woman's body associated with pregnancy. Blood tests can identify the pregnancy and measure hormone levels (FSH, LH, oestrogen, progesterone, TSH, prolactin), providing valuable information about a woman's overall reproductive health and well-being. These tests can also diagnose specific types of sexually transmitted diseases (chlamydia, HIV, herpes, gonorrhoea, syphilis), often combined with urine tests to confirm, which can be critical in identifying and treating these infections.
3. Urine Examinations: A urinalysis is the most common diagnostic test conducted to examine the urine to detect and measure various compounds through physical, chemical, and microscopic tests and to assess many different aspects of health with a urine sample. It is performed to check protein and sugars.it is performed to confirm kidney problems, diabetes and preeclampsia, urinary tract infections and liver problems.
4. Pelvic Laparoscopy: Pelvic laparoscopy a minor invasive procedure is performed to examine and treat the abnormalities of the uterus, ovaries, cervix, and fallopian tubes in the pelvic area. Conditions treated include endometriosis, chronic pelvic pain, pelvic inflammatory disease and cancers. It includes inserting the instrument into the abdomen by making small incisions. That instrument is called a laparoscope, which contains a thin device with an attached camera and light to visualize the organs.
5. Pelvic Ultrasound: A pelvic ultrasound is a diagnostic test that utilizes sound waves to make images of the organs inside the pelvis that are used to examine the organs and structures within the pelvis, such as the uterus, cervix, fallopian tubes, vagina and ovaries of the female. It allows the visuals of the pelvic organs. Ultrasound uses a transducer which places on the pelvic skin using the conductive gel.
6. Transvaginal Ultrasound: An ultrasound test identifies abnormalities using high-frequency sound waves to create (provide) pictures of internal organs. A transvaginal ultrasound, or endovaginal ultrasound, is used to examine the pelvis organs such as the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, cervix and vagina.
It differs from a regular pelvic ultrasound where it involves the insertion of an ultrasound probe that measures approximately 2–3 inches into the vaginal canal. With this probe, the internal organs can be examined in detail, allowing healthcare professionals to diagnose and treat various medical conditions.
7. Pap Test: It is also called a pap smear test, a screening procedure to assess cervical cancer. It identifies the presence of precancerous or cancerous cells. It can determine the changes in the cells on the opening of the uterus, called the cervix. This test is usually performed by inserting a metal or plastic tool named a speculum into the vagina to open and widen the vagina walls. Gynaecologist uses a swab to take cell samples from the cervix and send it for laboratory evaluation.
8. Human papillomavirus (HPV) Test: The procedures involved in HPV and PAP tests share some similarities. HPV, capable of causing alterations in cervical cells, can be detected through an HPV test. This test can be conducted solely or in combination with a pap test in an approach known as co-testing.
10. Hysteroscopy: Hysteroscopy is a diagnostic procedure used to inspect the inside of the uterus (womb). This procedure involves using a hysteroscope, a thin instrument with a camera and light located at the end. It can be passed into the patient's uterus through the vagina and cervix. The camera can send images (inside the uterus) to the monitor, which is observed by the gynaecologist.
11. Mammogram: It is an X-ray examination of the woman’s breast. It is used to identify and diagnose (find) the breast problems such as pain, lump or nipple discharge and even in asymptomatic women. This procedure identifies breast cancers, benign tumours and cysts before gynaecologists detect them by touch.
12. Colposcopy: Colposcopy is a diagnostical procedure containing a magnifying instrument with a light called a colposcope (which magnifies the images), used to examine the vulva, vagina and cervix. This instrument is placed into the vagina to open it, and a microscope is used to see the cervix and vaginal walls more clearly. A gynaecologist may take tissue samples for lab evaluation if any abnormal areas are identified.
13. Endometrial Biopsy: Gynaecologists may perform a procedure called endometrial biopsy to examine the abnormalities of the uterus and to diagnose the diseases such as endometrial cancer, fertility and abnormal uterine bleeding. During the process, a thin, flexible tube called a pipelle (consisting of a small tube inside) will be inserted through the opening of the cervix and into the uterus. The gynaecologist moves the pipelle back and forth to get a biopsy (tissue) sample from the uterus for laboratory evaluation.
14. Amniocentesis: Amniocentesis is a test that is performed during pregnancy to examine if the pregnant woman's baby has potential genetic or chromosomal abnormalities such as Edward's, Down's, or Patau's syndromes. This process involves extracting a small sample of amniotic fluid from the area surrounding the developing fetus within the uterus. It can be performed between the 15th and 20th weeks of pregnancy. Through this screening process, obstetricians can determine the risk for specific medical conditions, allowing for early intervention and treatment if necessary.
15. Breast Biopsy: A breast biopsy is a procedure of taking (removing) a small piece of tissue from the breast for further laboratory evaluation. It uses a biopsy needle to remove a sample of tissue, or may be removed during surgery. It is done to confirm that cancer or other abnormal cells are present in the breast.
16. Cervical Biopsy: A cervical biopsy is a gynaecological procedure performed to remove (take out) a tissue sample from the cervix to test for the presence of abnormal or precancerous or cancer cells and send it for lab evaluation. The test is performed when abnormalities are found during a pelvic exam or pap test. There are different methods for performing a cervical biopsy, such as colposcopic, cone and endocervical curettage.
17. Hysterosalpingogram: Hysterosalpingogram is an X-ray imaging technique to examine potential causes of pregnancy problems or infertility in women. It uses X-rays to provide a picture of the fallopian tubes and uterus. It can detect scar tissue, structural abnormalities, fibroids, tumours, polyps, or blockages in the tubes. An obstetrician-gynaecologist may recommend this procedure if a patient has had difficulty conceiving or has experienced multiple miscarriages.
Gynaecological Procedures Performed:
1. Hysterectomy:
A
hysterectomy is a surgical process involving removing the woman's womb (uterus). It is a common treatment for various reproductive system problems such as abnormal uterine bleeding, chronic pelvic pain, fibroids, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, womb cancer or fallopian tube cancer. After the procedure, the woman cannot menstruate or become pregnant.
2. Myomectomy: Myomectomy is a minor surgical procedure to remove uterine fibroids from the uterus. Fibroids are benign (non-cancerous) muscle cells that grow inside or outside the uterus. During the procedure, the gynaecologist removes the fibroids while preserving healthy tissue in the uterus to enable pregnancy in the future. It is the best choice if someone wants to conceive in future. Laparoscopic Myomectomy, Abdominal myomectomy, and Hysteroscopic myomectomy are the types of myomectomies.
3. Caesarean Section: Caesarean section is also called C-Section. It is a surgical delivery of the baby by making an incision (cut) in the abdomen and uterus of the mother. It should be performed when the vaginal (normal) delivery of the mother is either unsafe or not possible and when the baby is at risk. Some conditions that may require a caesarean birth include foetal size, abnormal foetal heart rate, foetal position, placenta problems, diabetes, high blood pressure, or HIV infection in the mother.
4. Endometrial Ablation: Endometrial ablation is a minimally invasive procedure that destroys the endometrial tissue lining of the uterus to treat abnormal uterine bleeding. It can be caused by several reasons, such as hormonal changes, fibroids and polyps in the uterus. It is typically recommended for women who don't wish to become pregnant in the future. Gynaecologists don't make any incisions (cuts). Instead, they use a thin tool inserted through the vagina to reach the uterus and destroy the uterine lining.
5. Ovarian Cystectomy: Ovarian cystectomy is a surgical procedure for removing ovarian cysts. Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that are common and disappear on their own. This procedure may recommend when the cysts are large, causing pain and are not going away. Gynaecologists remove ovarian cysts using laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy (makes a small incision in the abdomen to send tool named a laparoscope and uses surgical instruments to remove cysts by making another small incision) and open cystectomy (laparotomy – the surgeon makes a large incision to remove the cyst).
6. Tubal Ligation: Tubal ligation is an effective and permanent surgical procedure to prevent pregnancy. It involves blocking, cutting, or sealing the fallopian tubes (creates a connection of ovaries to the uterus). By doing so, the procedure stops the fertilization of eggs and their transportation to the uterus, effectively preventing pregnancy. One of the benefits of the process is that it does not affect menstruation, and women can continue to experience their regular menstrual cycles after the procedure. Overall, tubal ligation is a safe and reliable method of birth control that provides long-term benefits for women who wish to avoid pregnancy.
7. Cervical Cerclage: Cervical cerclage is the surgical procedure performed by closing the cervix at the time of pregnancy or before the pregnancy to prevent premature birth. It is typically recommended for women with a weak or problematic cervix or those at risk of early labour. Obstetricians can stitch the cervix during this procedure to prevent preterm labour, and the stitches are removed either during delivery or after 37 weeks of pregnancy.
8. Cervix Cryrocautery: Cryocautery is a fast and effective method of temporarily freezing the cervix using a metal probe for 1-2 minutes. This freezing can treat mild abnormal cervical cells and excessive vaginal discharge or bleeding during sex. It promotes the growth of thicker and tougher tissue, which leads to less bleeding during sex or less production of vaginal discharge. A speculum is used to open the cervical area for clear visibility. Then the gynaecologist places a cold metal probe on the cervix for up to 1 to 2 mins. It may cause menstrual-type pain.
9. Loop Electrosurgical Excision procedure (LEEP): LEEP is an interventional procedure that uses a heated wire loop attached to the electric current to remove abnormal or precancerous cells and abnormal layers of tissue from the lower genital tract of females, including the vagina and cervix. Gynaecologists may use a colposcope along with this procedure to see the cervix clearly and diagnose and treat precancerous cells to prevent cervical cancer and conditions such as polyps and genital warts. It is typically performed if a gynaecologist suspects vaginal or cervical problems during a pelvic or PAP exam.
10. Elective Abortion: Abortion is a common medical procedure for terminating a pregnancy, which can be done through medication or surgery. Over the world, one in four pregnancies ends in absorption. Elective abortion is widely practised and generally considered safe. However, late-term abortions can result in severe complications such as miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, and sterility.
11. Dilation and Curettage: Dilation and curettage (D&C) is a minimally invasive surgical procedure to remove tissue from the uterus. It treats conditions such as miscarriage, abnormal uterine bleeding, and leftover tissue after an abortion. During the process, the gynaecologist dilates (expands) the cervix using a laminaria stick and then uses a curette (a suction or scraping device) to remove or clean out the tissue from the uterus and send it to the lab for further evaluation to check for any abnormalities.
12. Vulvectomy: A vulvectomy is a medical procedure typically performed to remove cancerous or precancerous cells found on the vulva (contains inner and outer labia as well as the clitoris). Patients undergoing this procedure can expect a thorough consultation with their healthcare provider to discuss the risks and benefits of the surgery, as well as any possible side effects or complications that may arise. Ultimately, vulvectomy is an essential medical intervention that can help to avoid the spread of cancerous cells and improve a patient's overall health and well-being.
13. Uterine Fibroid Embolization: Uterine Artery Embolization, or Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE), is a procedure to treat or reduce the size of symptomatic uterine fibroids (shrink non-cancerous tumours in the uterus) by blocking the blood supply. Monitoring through fluoroscopy (a form of real-time x-ray), the embolic agents (agents for blocking blood flow) are delivered to the uterus to treat the fibroids. The duration of recovery and hospitalization are minimal as this procedure is not a major surgery. Uterine artery embolization is also a safe and reliable procedure for postpartum haemorrhage (blood loss by the mother during birth).
14. Oophorectomy: Oophorectomy is a surgical procedure that involves removing one or both ovaries. It is also known as ovary removal surgery (ovariectomy). Removal of one ovary is called unilateral oophorectomy, while removal of both ovaries is called bilateral oophorectomy. This procedure can help prevent ovarian cancer, endometriosis, and pelvic inflammatory disease.
There are different types of oophorectomy procedures, including prophylactic oophorectomy, a preventive surgery to avoid the risk of getting cancers, and salpingo-oophorectomy, which involves removing one or both ovaries and fallopian tubes. Partial oophorectomy consists in removing one or both ovaries.
15. External Cephalic Version: It is a procedure of turning the baby from the breech (feet) position to the down (head)position. It is done when the baby's feet (breech position) present at the opening of the uterus, making vaginal delivery difficult. This procedure is usually safe, but some risks are rarely associated, such as alteration in the baby's heartbeat, placenta tearing and preterm labour.
16. Pelvic Floor Repair (Colporrhaphy): Colporrhaphy refers to surgical repair of the pelvic organ prolapse, such as prolapsed bladder or rectum. Pelvic organ prolapse occurs when the bladder, bowel, top of the vagina, or uterus slips down and bulges into the vagina from its normal position. It is a minor surgical procedure to repair and strengthen the vaginal wall after a prolapse. During this procedure, a cut is made near the vaginal entrance, after which the gynaecological surgeon repairs and restructures the weakened tissue. Laparoscopic colposuspension is a minor surgical technique that provides a safe method of reconstructing the pelvic floor without needing a large abdominal incision or other surgeries, including vaginal mesh and hysterectomy.
17. Episiotomy: Episiotomy is a surgical procedure where a cut (incision) is made between the vaginal opening and anus, known as the perineum, to allow the baby to come out more easily. This procedure may be done to prevent tearing of the perineal tissue. It is usually recommended when the mother is exhausted from pushing for several hours, when there is a risk to the baby's health, or when the baby's heartbeat is increasing. It may also be recommended to avoid the risk when the mother has heart disease.
18. Laparoscopic Tubal Recanalization: Tying fallopian tubes is called tubal ligation, and it is a permanent process to prevent pregnancy, but laparoscopic tubal recanalization can reverse it. The woman can become pregnant, depending on the ovaries' age and functioning. This is performed by making an incision at the abdomen, using a laparoscope to view the fallopian tubes. Then the gynaecology surgeon unties the tied fallopian tubes and reattaching them. A highly skilled professional is needed to perform this procedure.
19. Hysteroscopic Polypectomy: Hysteroscopic polypectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the endometrial (uterine) polyps by preserving the womb (uterus). Uterine polyps are small fleshy growths that can form along the inner lining of the uterus (endometrium). These polyps are common, but rarely do they become cancerous. It is performed for endometrial biopsy and to remove the polyps. An extended thin scope attached with a light, a camera, and surgical instruments called a hysteroscopic resectoscope is inserted into the vagina and cervix into the uterus to remove the tissue. The gynaecologist utilizes an electrosurgical wire loop on the resectoscope to remove polyps or fibroids.
20. IUD Insertions: IUD abbreviates as intrauterine device, a minor procedure that includes insertion of T-shaped device into the uterus to prevent pregnancy by stopping sperm cells reaching and fertilising eggs. It is most effective among various forms of reversible birth control. The gynaecologist will perform a pelvic examination with the help of fingers before inserting a speculum to view the inner side of the vagina. The IUD will be placed inside the uterus with the help of special instrument and speculum will be removed after successful IUD placement.
Surgeries Performed
230+
Laparoscopic Myomectomy
780+
Laparoscopic Ovarian Cysts Removal
830+
Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
380+
Laparoscopic Tubal Recanalisation
780+
Laparoscopic Tubal Ligation
620+
Laparoscopic Adenomyomectomy
1640+
Diagnostic Hysteroscopy
540+
Hysteroscopic Polypectomy
Health and Diseases Information

Why choose PACE Hospitals?
- A Multi-Super Speciality Hospital.
- NABH, NABL, NBE & NABH - Nursing Excellence accreditation.
- State-of-the-art Liver and Kidney transplant centre.
- Empanelled with all TPA’s for smooth cashless benefits.
- Centralized HIMS (Hospital Information System).
- Computerized health records available via website.
- Minimum waiting time for Inpatient and Outpatient.
- Round-the-clock guidance from highly qualified gynaecologists.
- Standardization of ethical medical care.
- 24X7 Outpatient & Inpatient Pharmacy Services.
- State-of-the-art operation theatres.
- Intensive Care Units (Surgical and Medical) with ISO-9001 accreditation.