Best Polypectomy Surgery in Hyderabad, India | Procedure & Cost
PACE Hospitals is recognized as the best hospital for polypectomy surgery in Hyderabad, Telangana, India, with a focus on patient safety, precision, and long-term relief from polys. Our highly experienced gastroenterologists, ENT specialists, and surgeons specialize in safe and effective minimally invasive endoscopic techniques, ensuring reduced pain, faster recovery, and excellent outcomes.
At PACE Hospitals, we specialize in advanced polypectomy procedures, including colorectal, gastric, and nasal polypectomy, to safely remove polyps from the digestive tract, nasal passages, and other affected areas. This procedure effectively addresses symptoms such as unexplained bloating, abdominal pain, bleeding, chronic nasal congestion, difficulty breathing, irregular bowel movements, and persistent stomach discomfort, improving overall health and quality of life.
Quick Navigation
Book an appointment for Polypectomy Procedure
Polypectomy Surgery appointment
Why Choose PACE Hospitals for Polypectomy surgery?
State-of-the-Art Facilities, Advanced Endoscopic Techniques
Team of the Best Gastroenterologists & Surgeons in Hyderabad
Precision & Safe Polyps Removal with 99.9% Success Rate
Affordable & Cost-effective Polypectomy Procedure
What is Polypectomy Surgery?
Polypectomy surgery
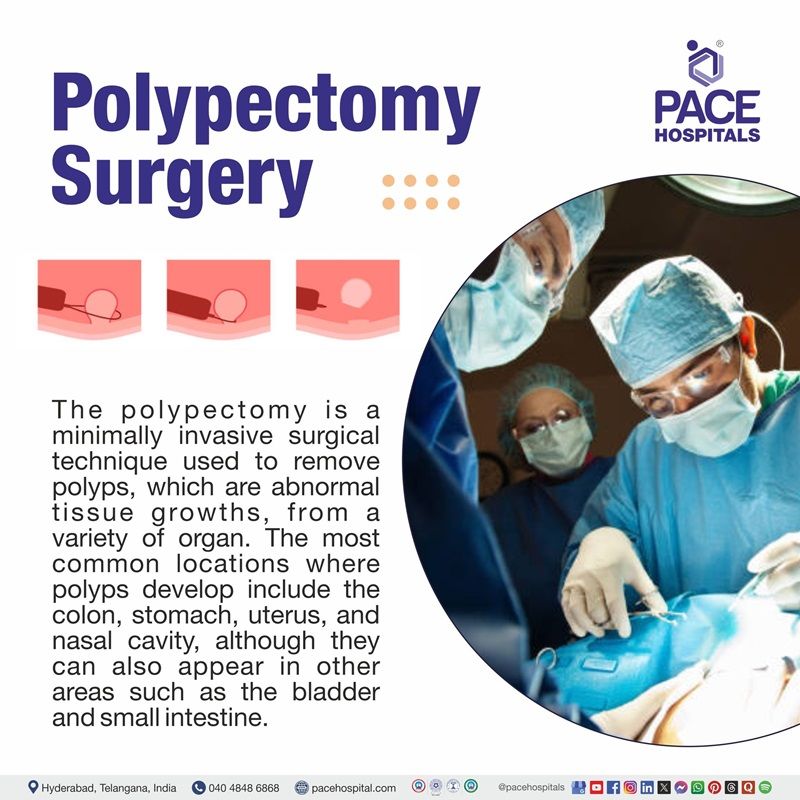
Polypectomy is a minimally invasive surgical technique used to remove polyps, which are abnormal tissue growths, from a variety of organs. The most common locations where polyps develop include the colon, stomach, uterus, and nasal cavity, although they can also appear in other areas such as the bladder and small intestine.
Polypectomy meaning
Polypectomy helps in removing benign, precancerous, or malignant growths while performing an endoscopy or colonoscopy. This surgical procedure depends on the size, morphology, and location of the polyp. It cuts down malignancy risks, reduces symptoms, and helps in accurate histopathological diagnosis, making it a vital part of cancer prevention and symptomatic relief.
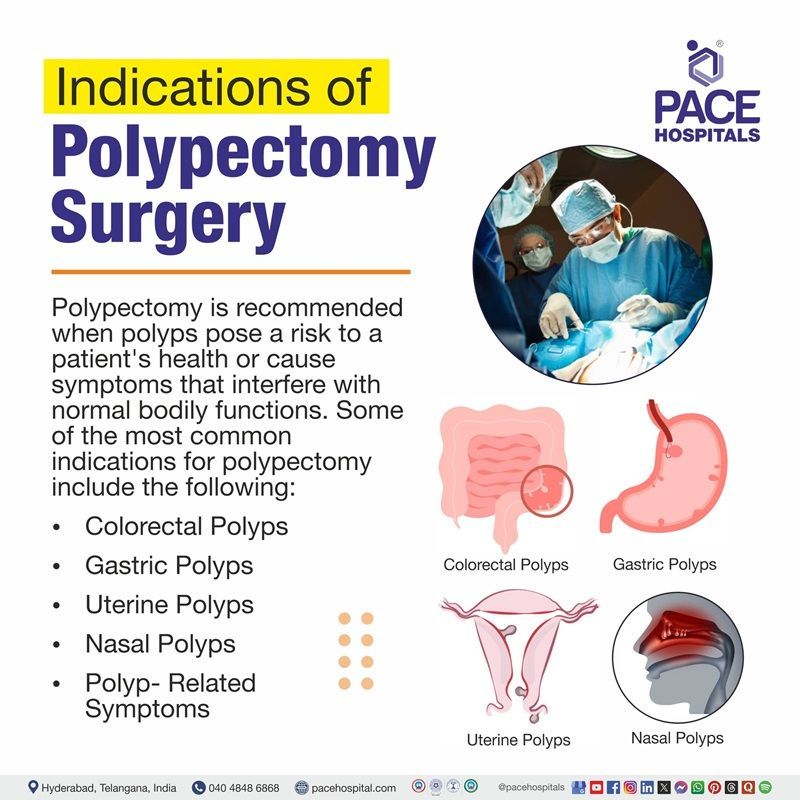
When is a polypectomy indicated?
Polypectomy is recommended when polyps pose a risk to a patient's health or cause symptoms that interfere with normal bodily functions. Some of the most common indications for polypectomy include the following:
1. Colorectal Polypectomy
Colorectal polyps are commonly found during screening colonoscopy, especially in individuals over 50 or with a family history of colorectal cancer. They can be adenomatous, hyperplastic, inflammatory, or serrated. Large, irregular, or dysplastic polyps pose a higher cancer risk and require removal.
2, Gastric Polypectomy
These are growths in the stomach lining, often detected in an upper endoscopy. While some remain benign, adenomatous polyps can become cancerous. Symptoms include bleeding, discomfort, nausea, or obstruction. Polypectomy is performed to prevent malignancy and relieve symptoms.
3. Hysteroscopic Polypectomy
Uterine polyps form in the endometrial lining, often affecting reproductive-age and postmenopausal women. They cause abnormal bleeding, heavy periods, or infertility. While usually benign, some may become cancerous, especially in older women, making polypectomy necessary.
4. Nasal Polypectomy
Nasal polyps are soft, noncancerous growths linked to chronic inflammation, allergies, or asthma. Symptoms include nasal congestion, breathing difficulties, anosmia, and sinus infections. Endoscopic polypectomy restores airflow, improving respiratory function and reducing infections.
5. Cervical Polypectomy
A cervical polypectomy is a procedure to remove a polyp from the cervix. It's usually done in a clinic during a pelvic exam
6. Polyp- Related Symptoms
Polypectomy is recommended for unexplained rectal bleeding, altered bowel habits, persistent pain, bloating, or chronic nasal congestion. Removing polyps relieves symptoms and allows histopathological examination to assess malignancy risk, guiding further treatment if necessary.
Contraindications for Polypectomy
Although polypectomy is a safe and effective procedure, certain medical conditions and factors may prevent its immediate execution. In such cases, alternative treatments or additional medical interventions may be necessary.
- Bleeding Disorders: Patients with uncontrolled bleeding disorders or those taking anticoagulants are at an increased risk of excessive bleeding during and after the procedure. If polypectomy is necessary, anticoagulation therapy may need to be temporarily adjusted under medical supervision to ensure a safe outcome.
- Invasive Malignancies: If a polyp is suspected to be an invasive carcinoma, simple endoscopic removal may not be sufficient. In such cases, surgical resection (e.g., colectomy for colorectal cancer or gastrectomy for gastric cancer) may be required to ensure complete tumor removal.
- Severe Inflammation or Infection: Patients with active inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) flares, acute diverticulitis, or severe infections in the gastrointestinal tract have a higher risk of perforation or excessive bleeding during polypectomy. In such situations, the procedure is typically delayed until the inflammation resolves.
- Large Sessile or Deeply Infiltrating Polyps: Certain large sessile polyps (flat, broad-based growths) or deeply infiltrating polyps may not be amenable to endoscopic resection. Instead, these cases may require surgical excision to make sure that complete removal is done and reduce the risk of complications.
- Poor Patient Health Status: Patients with severe cardiovascular, respiratory, or systemic illnesses may not tolerate the procedure well, particularly if general anesthesia or deep sedation is required. A detailed risk-benefit assessment should be conducted before proceeding with polypectomy in such individuals.
Polypectomy Procedure
Before the procedure
Proper preoperative preparation of the patient is important to make sure that the procedure is safe and effective in the patient. This preoperative steps required may differ based on the polyp type being removed and its location in the body.
Pre-Procedure Assessment
- Prior to the polypectomy procedure, patients might undergo a thorough medical checkup to estimate their overall health status and eligibility for the polypectomy procedure. The evaluation includes the details below:
- A detailed medical history, including any previous polypectomies, history of gastrointestinal disorders, or past surgeries.
- A review of family history, particularly regarding colorectal cancer, gastric cancer, or hereditary polyposis syndromes.
- A list of current medications, especially anticoagulants, antiplatelets, NSAIDs, and diabetic medications, which may require temporary adjustments.
- Assessment for allergies, particularly to anesthetic agents or contrast dyes.
Bowel Preparation (For Colorectal and Gastric Polypectomy)
For polyps in the colon or stomach, patients are required to undergo bowel cleansing to ensure clear visualization during the procedure. This typically includes:
- A liquid diet (clear fluids only) for 24–48 hours before the procedure.
- Administration of laxatives or bowel cleansing agents such as polyethylene glycol (PEG) solutions to clear the colon.
- Fasting for 6–12 hours before the procedure to minimize the risk of aspiration during sedation.
Medication Adjustments
Certain medications may increase the risk of bleeding or interact with anesthesia. Therefore, physicians may recommend:
- Temporarily stopping blood thinners with appropriate bridging therapy, if necessary.
- Adjusting diabetic medications to prevent hypoglycemia, especially if fasting is required.
- Avoiding NSAIDs and herbal supplements that may contribute to increased bleeding risk.
Consent and Counseling
Before the procedure, the physician explains:
- The reason for the polypectomy and its potential benefits.
- The risks involved, including bleeding, infection, and perforation.
- Possible alternative treatments if polypectomy is not advisable.
- The need for histopathological examination of the removed polyp to assess for malignancy.
- Post-procedure recovery expectations and follow-up requirements.
Patients are required to provide informed consent before the procedure can proceed.
During the Procedure
The detailed procedure of polypectomy upon the completion of preoperative assessment is as mentioned below:
Patient Positioning
The patient is positioned according to the site of the polyp:
- Left lateral position for colorectal polypectomy during a colonoscopy.
- Supine position for gastric or uterine polypectomy.
- Semi-reclined position for nasal polypectomy using an endoscope.
Sedation or Anesthesia
Depending on the complexity of the procedure, different levels of sedation may be used:
- Local anesthesia for nasal or minor gastrointestinal polypectomies.
- Conscious sedation (e.g., midazolam, fentanyl) for colorectal and gastric polypectomy.
- General anesthesia for extensive procedures or in cases where patient cooperation is difficult.
Insertion of the Endoscope
A flexible endoscope is introduced into the targeted area:
- Colonoscope for colorectal polyps.
- Gastroscope for gastric polyps.
- Hysteroscope for uterine polyps.
- Nasal endoscope for nasal polypectomy.
The endoscope provides high-definition visualization of the polyp and the surrounding tissue.
Polyp Removal Technique
The suitable technique is selected based on the size, location, and morphology of the polyp:
- Cold forceps or snare for small polyps (<10 mm).
- Hot snare polypectomy for larger polyps (>10 mm), with electrocautery to reduce bleeding.
- Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) for sessile or flat polyps, using fluid injection to lift the polyp.
- Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for deep or complex polyps, ensuring complete removal.
Hemostasis Management
To prevent or control bleeding, various hemostatic techniques may be employed, such as:
- Electrocautery (coagulation mode) to cauterize blood vessels.
- Endoscopic clips to close any visible blood vessels.
- Hemostatic sprays or gels in cases of persistent bleeding.
Specimen Retrieval and Histopathology
The removed polyp is collected using retrieval baskets, suction, or endoscopic nets and sent to the laboratory for histopathological examination. This helps determine whether the polyp is benign, precancerous, or malignant.
Post Polypectomy (After the procedure)
Upon successful completion of the procedure, postoperative care includes the following:
Post-Procedure Monitoring
After the procedure, the patient is monitored for any immediate complications, including:
- Bleeding, which may require additional hemostatic measures.
- Perforation, which, although rare, may require surgical intervention.
- Sedation-related effects, such as dizziness or nausea.
- Most patients are discharged within a few hours, unless complications arise.
Dietary Recommendations
After polypectomy, dietary guidelines depend on the site of the procedure:
- Colorectal or gastric polypectomy: A soft diet is recommended initially, avoiding spicy, fatty, and high-fiber foods for 24–48 hours.
- Uterine or nasal polypectomy: No specific dietary restrictions, but adequate hydration is advised.
Activity Restrictions
Patients should avoid strenuous activities, heavy weightlifting, and excessive bending for at least 24–48 hours after the procedure to reduce the risk of bleeding or strain on the operated site.
Follow-Up Appointments
Follow-up is essential to:
- Review the histopathology report to determine if further treatment is needed.
- Plan for repeat surveillance endoscopy/colonoscopy based on polyp type and patient risk factors.
- Assess for symptom recurrence or complications.
Warning Signs to Report
Patients are instructed to seek medical attention if they experience:
- Severe or persistent abdominal pain.
- Excessive rectal bleeding or melena (black, tarry stools).
- High fever or chills, indicating possible infection.
- Dizziness or fainting, suggestive of blood loss.
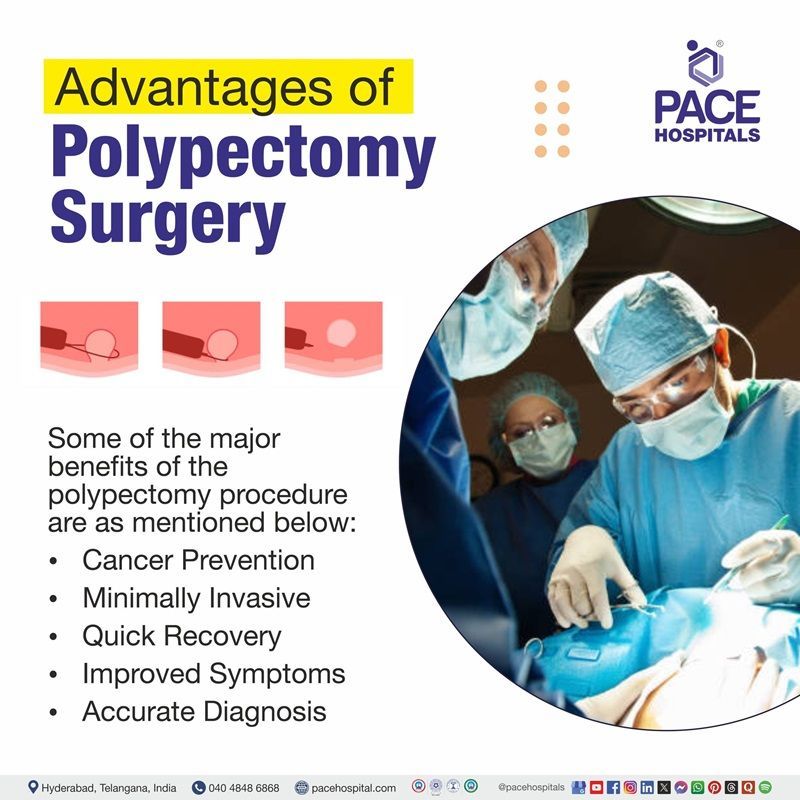
Advantages of Polypectomy
Some of the major benefits of the polypectomy procedure are as mentioned below:
- Cancer Prevention: Polypectomy helps in removing precancerous polyps, significantly reducing the risk of colorectal, gastric, or uterine cancer.
- Minimally Invasive: As the polypectomy procedure is minimally invasive, it avoids open surgery while achieving effective polyp removal.
- Quick Recovery: Post-procedure, most of the patients return to normal activities within 24–48 hours.
- Improved Symptoms: Polypectomy helps in resolving issues like rectal bleeding, nasal obstruction, or abnormal uterine bleeding.
- Accurate Diagnosis: This procedure enables histopathological analysis to detect malignancies early.
Polypectomy Complications
While polypectomy is generally safe, complications can occur:
- Bleeding: The polypectomy procedure can sometimes lead to bleeding that can be immediate or delayed, often controlled with endoscopic interventions.
- Perforation: Perforation is very rare but serious, especially in large polyp resections, sometimes requiring surgical repair.
- Infection: Infection can occur occasionally at the removal site, necessitating antibiotic treatment.
- Post-Polypectomy Syndrome: This is a rare condition causing fever and localized inflammation due to mucosal injury.
- Incomplete Resection: Some polyps may require repeat procedures for complete removal.
Life After the Polypectomy Procedure
- Recovery: Most patients experience mild bloating or discomfort but recover quickly.
- Dietary Adjustments: Patients recovering from colorectal polypectomy should consume fiber-rich foods and stay hydrated.
- Regular Screening: Follow-up colonoscopy or endoscopy is advised based on polyp type and recurrence risk.
- Lifestyle Modifications: A healthy diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking/alcohol can help prevent polyp recurrence.
Polypectomy Cost in Hyderabad, India
Polypectomy Surgery Cost in Hyderabad, India varies from ₹8,000 to ₹65,000 (US$95 to US$750). The final cost of Polyps Removal Surgery depends on various factors, including the polyp location, surgeon’s expertise, hospital facilities, required diagnostic procedures, type of anesthesia, medications, post-surgical care and insurance coverage.
| Type of Polypectomy | Estimated Cost (₹) |
|---|---|
| Nasal Polypectomy | ₹8,000 – ₹28,000 |
| Colorectal Polypectomy | ₹20,000 – ₹35,000 |
| Gastric Polypectomy | ₹18,000 – ₹48,000 |
| Rectal Polyp Excision | ₹16,000 – ₹65,000 |
At PACE Hospitals, we offer advanced polypectomy surgery at an affordable cost with expert specialists and state-of-the-art technology. Our team ensures safe and minimally invasive procedures for the removal of polyps from the colon, stomach, and nasal passages, helping patients recover quickly with minimal discomfort.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Polypectomy surgery
What is a polypectomy, and why is it performed?
A polypectomy is a minimally invasive procedure to remove polyps from the colon, stomach, uterus, or nasal cavity. It helps prevent cancer, manage symptoms like bleeding and obstruction, and is usually performed during an endoscopy or colonoscopy using specialized tools.
What are the risks associated with polypectomy?
Risks include bleeding, perforation, infection, and post-polypectomy syndrome. Bleeding may occur immediately or later. Perforation is rare but serious. Most complications are managed with endoscopic intervention, while severe cases may require surgical repair or additional medical care.
How soon can I resume normal activities after a polypectomy?
Most patients resume normal activities within 24 hours, but strenuous exercise and heavy lifting should be avoided for a week. Those with large polyp removals may need additional rest. Following dietary and activity restrictions can prevent complications like delayed bleeding.
Can polyps grow back after a polypectomy?
A removed polyp does not regrow, but new polyps can develop over time. Regular surveillance, a healthy diet, exercise, and avoiding smoking and alcohol help reduce the risk of recurrence. Patients with prior polyps should adhere to recommended follow-up screenings.
How can I reduce my risk of developing polyps in the future?
Adopt a fiber-rich diet, exercise regularly, avoid smoking and excessive alcohol, and maintain a healthy weight. Regular screenings, especially for high-risk patients, help detect and remove polyps early, reducing the risk of progression to cancer.
Are all polyps cancerous or dangerous?
Not all polyps are cancerous. Some remain benign, while others may be precancerous or malignant. Larger, irregular, or villous polyps have a higher risk of cancer. Regular screening and histopathological examination help determine whether a polyp requires further medical attention.
How do doctors detect polyps before recommending a polypectomy?
Polyps are detected using colonoscopy, endoscopy, hysteroscopy, or nasal endoscopy. Additional imaging techniques like CT colonography or MRI may be used when direct visualization is not feasible. These techniques help identify polyps early, ensuring timely removal and reducing cancer risks.
Is polypectomy painful?
Polypectomy is usually painless, as it’s performed under local anesthesia, conscious sedation, or general anesthesia. Some patients may experience mild bloating, cramping, or soreness, but these symptoms are temporary and can be managed with simple pain relievers if needed.
How long does a polypectomy procedure take?
The duration depends on polyp size and location. Small polyps take 5–10 minutes, medium-sized ones take 10–20 minutes, and larger or complex polyps may take up to 60 minutes. Advanced techniques like EMR or ESD may require more time for complete removal.
Do I need to stay overnight in the hospital after a polypectomy?
Polypectomy is usually an outpatient procedure, and most patients go home the same day. However, overnight observation may be required for large polyp removal, bleeding complications, or patients with pre-existing health conditions requiring close monitoring.
What should I eat after a polypectomy?
For colorectal or gastric polypectomy, a soft, low-fiber diet is recommended for 24–48 hours. Avoid spicy, fried, or high-fiber foods. After uterine or nasal polypectomy, normal eating can resume, though avoiding irritants is advised for comfort.
When should I get my next colonoscopy or endoscopy after a polypectomy?
Follow-up depends on polyp type, size, and pathology. Precancerous polyps require repeat colonoscopy in 3–5 years, while benign polyps may only need surveillance every 5–10 years. Your doctor will recommend an appropriate screening interval.
What happens if a polyp is found to be cancerous after removal?
If a polyp is cancerous, further evaluation is needed to determine if additional surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation is required. In some cases, complete polyp removal is curative, but advanced cases may need more treatment.
Can I take my regular medications after a polypectomy?
Most medications can be resumed immediately. However, blood thinners (e.g., warfarin, aspirin) may need temporary discontinuation to reduce bleeding risk. Always consult your doctor before restarting medications, especially if taking anticoagulants or diabetes medications.
Can pregnant women undergo a polypectomy?
Polypectomy can be safely performed during pregnancy if necessary, such as for symptomatic or suspicious polyps. However, elective procedures are often delayed until after delivery, unless they pose an immediate health risk to the mother or the baby.
How should I prepare for a polypectomy?
Preparation depends on the polyp’s location. For colorectal polypectomy, bowel cleansing with laxatives or enemas is required. Patients may also need to fast for 6–12 hours and adjust medications like blood thinners or diabetes drugs before the procedure.
Is sedation required for a polypectomy?
Sedation is commonly used for comfort and relaxation. Colonoscopy and gastric polypectomy often require conscious or deep sedation, while uterine and nasal polypectomy may be performed with local anesthesia or mild sedation, depending on the complexity.
Can polypectomy cause long-term digestive problems?
Polypectomy rarely causes long-term digestive issues. Some patients experience temporary bloating, mild cramping, or altered bowel habits, which resolve within a few days. Rare complications like scarring or incomplete removal may require further evaluation or treatment.
Can I drive myself home after a polypectomy?
No, due to sedation effects like drowsiness and impaired judgment, patients should arrange for someone to drive them home. It’s advised to avoid driving, operating machinery, or making important decisions for at least 24-hour post-procedure.
What are the symptoms of complications after a polypectomy?
Warning signs include severe abdominal pain, persistent bleeding, fever, dizziness, vomiting, or black stools. These may indicate bleeding, infection, perforation, or post-polypectomy syndrome. Seek immediate medical attention if any of these symptoms occur.



