Complex Sigmoid Colon Adenocarcinoma with Urethral Fistula Treated Effectively With Cystectomy and Radical Resection
A 69 year-old female presented with stool through urethra, bleeding through urethra, and weight loss. Investigations revealed a well-differentiated adenocarcinoma of the sigmoid colon with bladder involvement. She underwent an
enbloc resection with bladder reconstruction and was discharged in stable condition with detailed post-operative care instructions.
Chief complaints
The patient presented with a chief complaint of passing stool through urethra for the past 8 months, accompanied by occasional episodes of bleeding through urethra. She also reports experiencing white discharge and burning sensation while passing urine. Additionally, there is a history of constipation persisting for the same duration. Over the past 8 months, the patient has experienced significant weight loss of approximately 20 kg.
Medical history
The patient has a medical history significant for a prior
hysterectomy. However, there are no reported comorbidities or any history of oncological conditions.
Investigations
- Colonoscopy: Circumferential ulcerated growth at 20 cm from anal verge with critical narrowing; multiple biopsies taken.
- Histopathological examination (HPE): Well-differentiated adenocarcinoma with prominent villoglandular morphology.
- PET-CT: Long segment asymmetric circumferential thickening at the rectosigmoid junction abutting the bladder base, with positive lymph nodes in the sigmoidal and perilesional areas.
- Cardiac fitness assessment: Cleared for surgery.
Diagnosis
The patient was diagnosed with well-differentiated adenocarcinoma of the sigmoid colon, exhibiting prominent villoglandular morphology. Tumor involvement was noted at the rectosigmoid junction and the bladder base. Additionally, the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) level was elevated at 7.81 ng/mL, which may suggest malignancy.
Treatment
Based on the diagnostic investigations, Surgical Gastroenterologist, Bariatric and Metabolic Surgeon, GI and HPB Oncologist, Liver Transplant Surgeon Dr. Phani Krishna Ravula and Dr. Suresh Kumar S have asserted that radical resection of sigmoid growth shall be done along with subtotal cystectomy and the patient was admitted for definitive surgical management. Pre-operative preparation included:
- Bowel preparation with PEG-LEC.
- Intravenous antibiotics and hydration.
- Detailed pre-anesthetic checkup (PAC).
Surgical findings
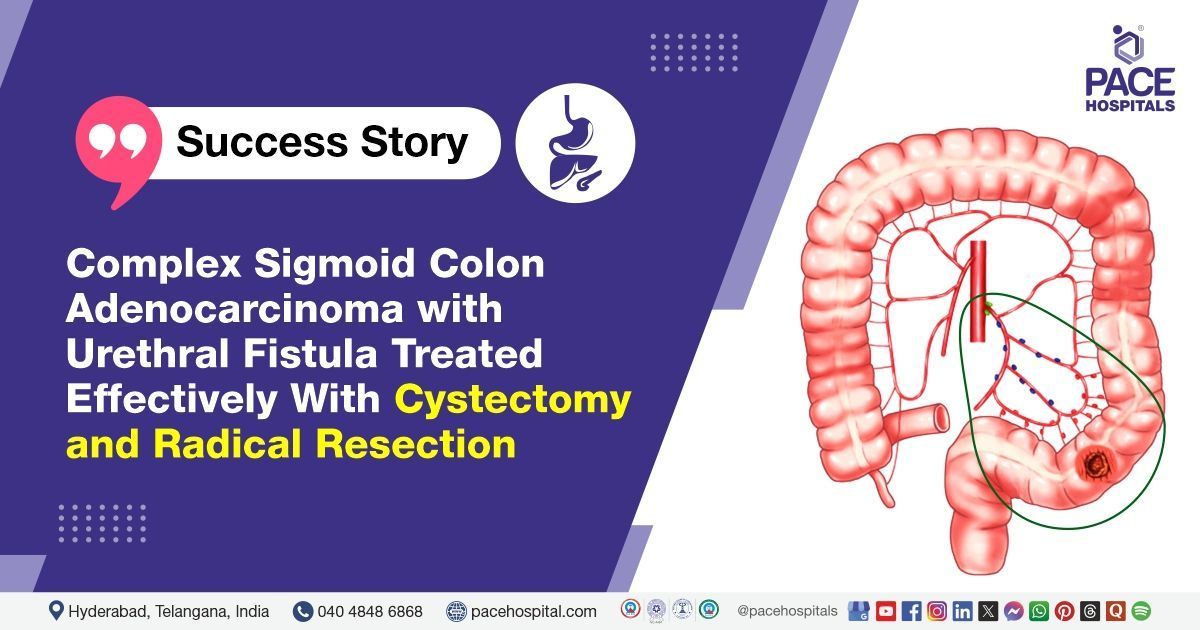
- 10x10 cm sigmoid colon growth: A significant tumor growth located in the sigmoid colon, indicating a malignancy that was resected during the procedure.
- Involvement of the posterior bladder wall, entire trigone, right external iliac vein distal to bifurcation, and vaginal wall: The findings suggest extensive involvement of multiple anatomical structures, indicating a locally advanced or invasive cancer, that had spread beyond the colon to affect surrounding organs.
Surgical procedures performed
- Cystoscopy: A procedure to examine the inside of the bladder using a cystoscope. It’s typically used to diagnose bladder issues, such as cancer, infection, or structural abnormalities.
- Staging laparoscopy: A minimally invasive procedure used to assess the extent (stage) of a disease, commonly performed in cancer staging colorectal (colorectal or bladder) cancer.
- Radical resection of sigmoid colon growth: Surgical removal of cancerous or abnormal growth from the sigmoid colon. This is often done for colorectal cancers or other growths in the sigmoid colon.
- Subtotal cystectomy: Partial removal of the bladder, typically done in cases of cancer, trauma, or other severe bladder conditions where a portion of the bladder is damaged.
- Patch reconstruction of the right external iliac vein: Surgical procedure used to repair a damaged or obstructed external iliac vein, possibly due to trauma, malignancy, or venous insufficiency, using a graft or patch.
- Augmentation ileocystoplasty: A bladder reconstruction surgery where a segment of the ileum (a part of the small intestine) is used to increase bladder capacity. It is typically done in cases of bladder dysfunction or reduced capacity.
- Bilateral ureteric reimplantation: A surgical procedure to reposition and secure the ureters into the bladder. This is often done for conditions such as vesicoureteral reflux, or injury to the ureters.
- Bladder neck repair: Surgical procedure to restore the function of the bladder neck, usually performed for conditions like urinary incontinence or bladder outlet obstruction.
- Colorectal anastomosis and ileostomy creation: Colorectal anastomosis is done where surgical connection of two ends of the colon or rectum after a resection. After anastomosis, Ileostomy creation was done where a part of the ileum is brought to the surface of the abdomen to divert waste into an external pouch, often done after significant bowel resection.
- SPC (Suprapubic catheter) placement: Placement of a catheter into the bladder through the abdominal wall above the pubic bone. This is usually done in patients with urinary retention or obstruction.
- Greater omental patching: A surgical technique where a portion of the greater omentum (a fatty tissue in the abdomen) is used to cover or repair a defect, often done in cases of gastrointestinal perforations or abdominal trauma.
Post-operative course
The post-operative course was uneventful, which suggests no immediate complications following the extensive surgical intervention. The recovery was satisfactory, and the patient appeared to be progressing well after surgery.
Post-operative management
- IV Antibiotics: Administered to prevent or treat infections, especially important after complex surgeries involving the bladder and gastrointestinal tract.
- Anticoagulation therapy: Used for thromboprophylaxis to prevent venous thromboembolism (VTE), which is common in patients undergoing major surgery.
- Painkillers: To manage post-operative pain, which is common after major surgeries.
- PPIs: Prescribed to prevent stress ulcers or gastric acid issues, especially important in ICU settings or after major abdominal surgery.
- Nutritional support: Vital for recovery, ensuring that the patient receives sufficient calories, vitamins, and nutrients to promote healing.
- Daily bladder washes with normal saline and sodium bicarbonate solution: This approach is often used to help reduce infection risk and maintain bladder hygiene, particularly following bladder surgery or involvement with malignancy.
- Blood transfusion as required: Given the extensive nature of the surgery and possible blood loss during the resection, blood transfusions may be necessary to maintain hemoglobin levels and ensure adequate oxygen delivery to tissues.
The combination of broad-spectrum antibiotics, anticoagulation therapy, pain management, and nutritional support suggests a comprehensive approach to managing this patient post-operatively, with a focus on preventing complications and promoting recovery.
Discharge notes
The patient was instructed to continue all previously prescribed medications. A high-protein, low-residue diet was suggested for the next week to promote healing and reduce strain on the digestive system. She was asked to focus on protein-rich foods like lean meats, eggs, and dairy food. Sodium bicarbonate bladder washes (1L daily) were instructed to be administered through the suprapubic catheter (SPC) and Foley catheter. This will help maintain a neutral pH in the bladder and prevent infection or assist in recovery. Ensure proper catheter care and technique to avoid complications.
Review Notes
The patient was advised to review with Dr. Phani Krishna Ravula in the surgical gastroenterology OPD after 1 week, ensuring a prior appointment is scheduled and the biopsy report is brought along for discussion. Additionally, a follow-up appointment in the urology OPD with
Dr. Abhik Debnath was scheduled in 1 week later to assess progress and provide further care as needed.
Post-surgical plan
The patient’s urine output should be monitored hourly during the daytime and every three hours at night to ensure proper kidney function and hydration. Drain management involves catheter removal after 2 weeks based on clinical assessment, while stent removal will be performed during the stoma closure procedure. Wound care requires maintaining strict hygiene, with any signs of infection to be reported immediately. Follow-up appointments for surgical and urology consultations should be attended as per the scheduled timelines to ensure optimal recovery and further management.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868