Pancreatic Pseudocyst: Types, Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Prevention
Pancreatic pseudocyst definition
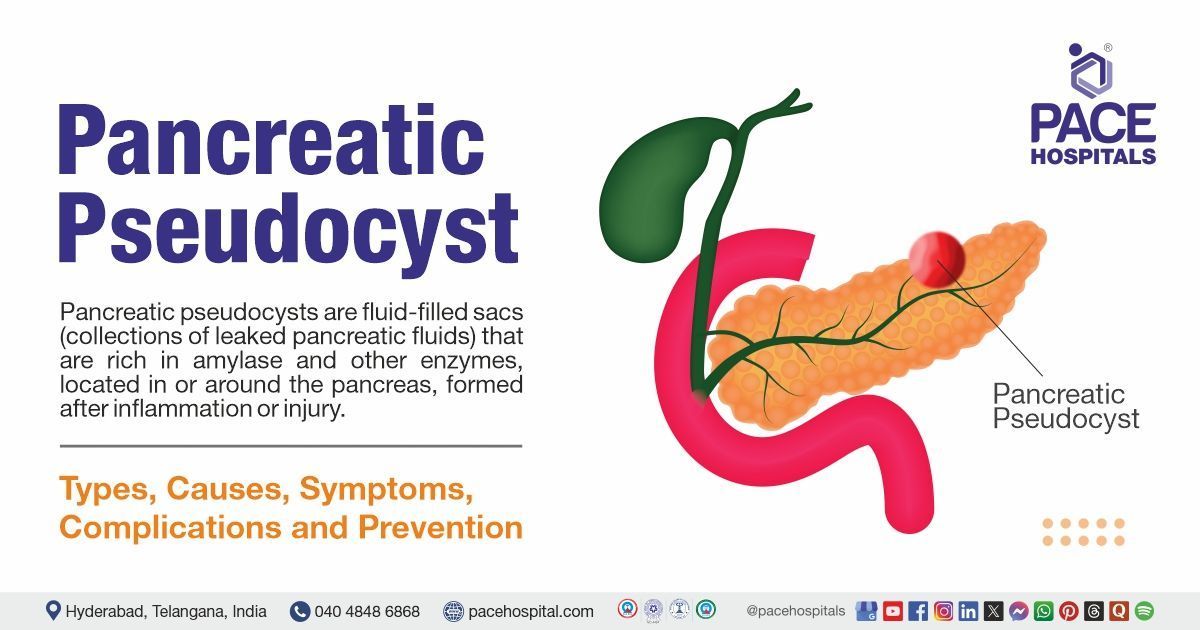
Pancreatic pseudocysts are fluid-filled sacs (collections of leaked pancreatic fluids) that are rich in amylase and other enzymes, located in or around the pancreas, formed after inflammation or injury, and surrounded by a fibrous wall. These are a known complication of acute and
chronic
pancreatitis. It is important to find any complications that may arise to reduce the associated morbidity and mortality.
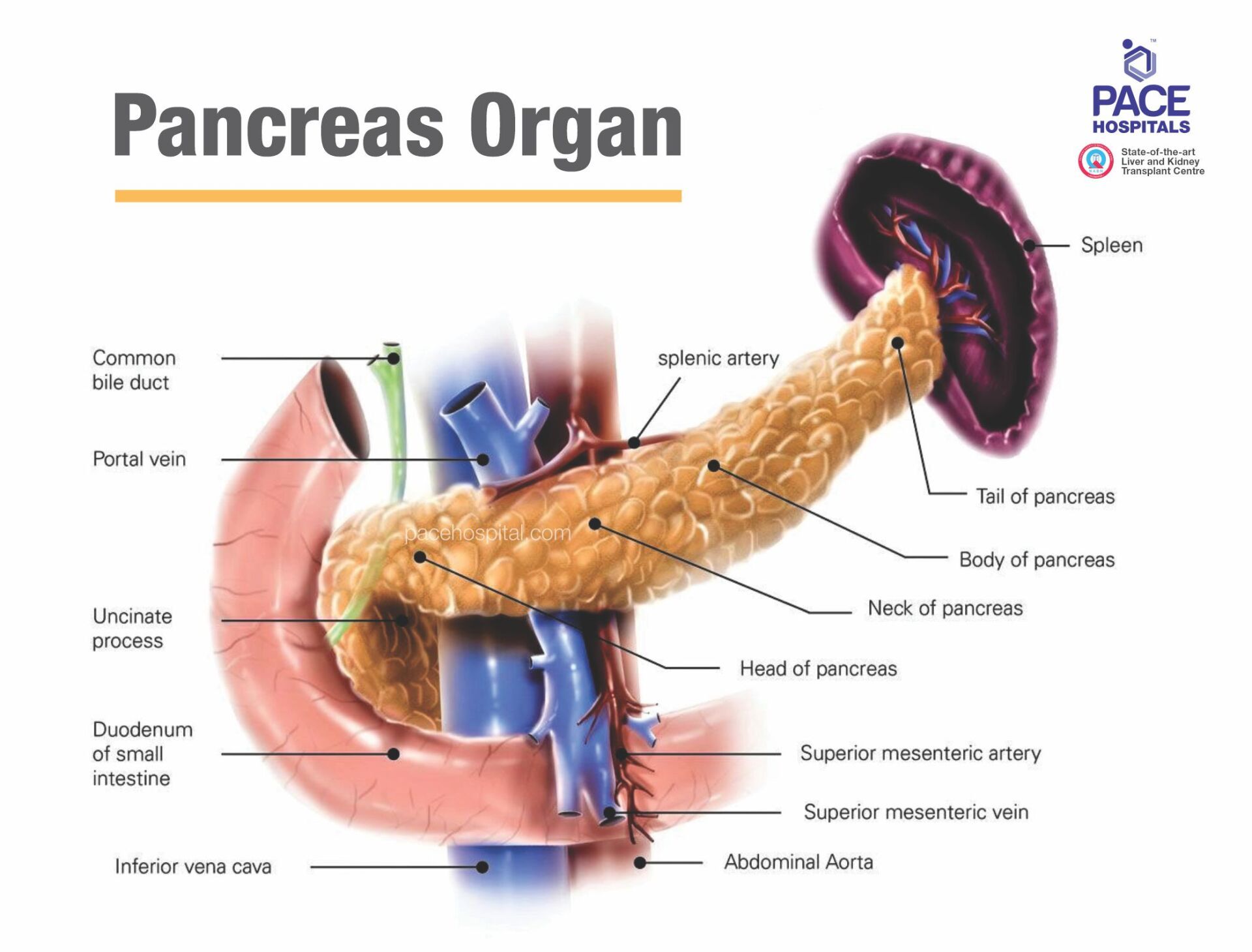
What is pancreas?
The pancreas is a large organ located behind the stomach and makes fluids that flow through a duct into the small intestine to digest food.
As mentioned, pancreatic pseudocysts are a known complication of acute and chronic pancreatitis.
Pancreatitis is characterised by the inflammation of the pancreas, causing the digestive enzymes to leak, which leads to collections of fluid forming, resulting in damage to the pancreas.
Patients with pancreatitis may develop pseudocysts, which rarely become cancerous and differ from true pancreatic cysts and pancreatic abscesses.
Prevalence and incidence of pancreatic pseudocysts
Pseudocysts are a common clinical problem that can occur after pancreatitis in any age group. They develop much more often in patients with underlying chronic pancreatitis than in patients with acute pancreatitis. Pseudocysts are more prevalent in males due to the higher incidence of pancreatitis.
The prevalence of pancreatic pseudocysts in acute pancreatitis has been found to range from 6% to 18.5%, and for chronic pancreatitis, it is 20% to 40%.
Pseudocysts complicate acute pancreatitis in approximately 10-23% of cases and 30% to 40% of patients during chronic pancreatitis.
According to various studies, regardless of the cause (aetiology) of the pseudocyst, the incidence is low, ranging from 1.6% to 4.5%, or approximately 0.5 to 1 case per 100,000 adults per year.
In acute pancreatitis, the incidence of pseudocysts ranges from 5% to 16%.
Pseudocysts are more common in chronic pancreatitis, with incidence rates between 20% to 40%.
Pancreatic pseudocyst classification
In 1991, D’Egidio and Schein classified Pancreatic pseudocysts into three distinct types of pancreatic pseudocysts depending on the underlying cause of pancreatitis (acute or chronic), the anatomy of the pancreatic duct, and the presence of communication between the cyst and pancreatic duct.
- Type I, or acute post-necrotic pseudocysts
- Type II, or post-necrotic pseudocysts
- Type III, or retention pseudocysts
Type I, or acute “post-necrotic” pseudocysts: These arise after an episode of acute pancreatitis and are linked with normal duct anatomy and rarely communicate with the pancreatic duct.
Type II, also post-necrotic pseudocysts: Type 2 pseudocysts occur after an episode of acute-on-chronic pancreatitis, where the pancreatic duct is diseased but not obstructed (diseased). There is often communication between the duct and the pseudocyst.
Type III, or retention pseudocysts: These occur in chronic pancreatitis and are consistently linked to duct strictures and pseudocyst communication.
Nealon and Walser proposed another classification based entirely on pancreatic duct anatomy.
- Type I: Normal duct/no communication with the cyst.
- Type II: Normal duct with duct-cyst communication.
- Type III: Normal duct with stricture and no duct-cyst communication.
- Type IV: Normal duct with stricture and duct-cyst communication.
- Type V: Normal duct with a complete cut-off.
- Type VI: Chronic pancreatitis, no duct-cyst communication.
- Type VII: Chronic pancreatitis with duct-cyst communication

Pancreatic pseudocyst causes
The occurrence of pseudocysts is closely related to pancreatitis, as the causes of pseudocysts are similar to those of pancreatitis. The following are the common causes of pancreatitis resulting in pancreatic pseudocysts.
- Inflammation: Pseudocysts result when the pancreatic cells become inflamed or injured and pancreatic enzymes begin to leak.
- Acute pancreatitis: Although pseudocyst formation is less common after acute than chronic pancreatitis. Pancreatic pseudocysts can start after an episode of sudden (acute) pancreatitis.
- Chronic pancreatitis: People with chronic pancreatitis can also get pseudocysts.
- Gallstone disease: Gallstone disease causes pancreatitis by blocking the bile or pancreatic ducts, leading to increased pressure and enzyme leakage. This can result in pancreatic inflammation and the formation of pseudocysts.
- Pancreatic Ductal Disruption and Increased Ductal Pressure: Pancreatic ductal disruption happens when increased pressure from stenosis, stones, or protein plugs obstructs the main duct. It can also follow pancreatic necrosis due to acute pancreatitis.
- Trauma: Physical injury to the pancreas can lead to pancreatitis, which may result in the formation of pancreatic pseudocysts.
- Alcohol: Alcohol abuse, gallstone disease, and trauma are the leading causes of the underlying pancreatitis. Alcohol-related pancreatitis is the primary cause in studies from countries with high alcohol consumption, accounting for 59%-78% of all pseudocysts.

Pancreatic pseudocyst symptoms
The pancreatic pseudocyst symptoms tend to be non-specific and present only with vague symptoms. There are no specific symptoms that are exclusively characteristic of pseudocysts. Some of the signs and symptoms that are suggestive of pseudocyst are:
- Persistent abdominal pain: A constant ache or pain in the abdomen or upper left abdomen that may radiate to the back
- Abdominal swelling: Bloating of the abdomen
- Anorexia (Eating disorder: an abnormal loss of appetite for food): It is a result of the body's response to severe pancreatitis
- Nausea and vomiting: These symptoms may occur along with difficulty eating and digesting food.
- Abdominal mass: New abdominal mass after an episode of pancreatitis.
- Jaundice or shock (Rarely)
Findings that have limited sensitivity:
- Abdominal tenderness
- Palpable abdominal mass
- Signs of peritonitis (in case of a ruptured cyst)
- Fever
- Scleral icterus (yellowing of the eyes)
- Pleural effusion (unusual amount of fluid around the lung)
Pancreatic pseudocyst risk factors
Pancreatitis is a leading cause of pancreatic pseudocysts, as inflammation of the pancreas can result in fluid collection. The following lifestyle factors and conditions can contribute to developing pancreatitis and pseudocysts.
- Pancreatitis: The most common cause of pancreatic pseudocysts is pancreatitis, which can be caused by gallstones, heavy alcohol use, or abdominal trauma
- Gender: Pancreatic pseudocysts are more common in men than women.
- High cholesterol levels: Increased levels of cholesterol in the blood can increase the risk of pancreatitis.
- Alcohol use: Heavy consumption of alcohol increases the risk of pancreatitis
- Smoking: One complicating factor in some studies is cigarette smoking, which is often linked to alcohol abuse. Smokers are 3 times more prone to develop chronic pancreatitis than non-smokers.
- Pancreatic damage: Pancreatic damage from medicines can also be a risk factor.
- Obesity:
Obesity raises the risk of severe acute pancreatitis in individuals with a BMI of 25 or higher and may worsen the condition by releasing unsaturated fatty acids (UFAs) that inhibit complexes I and V.

Pancreatic pseudocyst complications
Generally, larger cysts are more prone to become symptomatic or cause complications causing severe issues, even death, if they are left untreated. Fortunately, most problems are relatively rare. Possible pancreatic pseudocyst complications include:
- Infection: Cyst infection is the common complication resulting in sepsis and shock.
- Cyst haemorrhage: It happens when blood vessels within the cyst rupture resulting in inflammation, trauma, or erosion into nearby structures.
- Pancreatic pseudoaneurysm: A pancreatic pseudoaneurysm is when a blood vessel in or around the pancreas weakens and bulges, potentially leading to bleeding.
- Biliary complications or portal hypertension: Compression of the surrounding structures causes portal hypertension and biliary complications.
- Cyst rupture: Rupture into the gastrointestinal tract causing signs and symptoms of bleeding.
- Free rupture into the peritoneal cavity: The pseudocyst bursts into the space around the organs in the abdomen (peritoneum), causing severe abdominal pain, infection (peritonitis), and potentially fatal complications if untreated. Bleeding into the spleen or a blood clot in a spleen vein
- Blockage of the bile duct: A pancreatic pseudocyst can press on the bile duct, causing a blockage that leads to jaundice, dark urine, and pale stools.
- Gastric outlet obstruction: The cyst can compress the stomach or duodenum, resulting in difficulty in stomach emptying, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal discomfort.
Large pseudocysts have been reported to cause increased intra-abdominal pressure, which may present with orthopnoea (difficulty breathing while lying down), dyspnoea (shortness of breath), abdominal pain, distention (swelling), and new organ failure.
Pancreatic pseudocyst diagnosis
A gastroenterologist can advise a variety of diagnostic tests to confirm a pancreatic pseudocyst, including:
Physical examination
Imaging tests
- Abdominal ultrasonography or Transabdominal ultrasonography
- Endoscopic ultrasonography or Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)
- Abdominal CT scanning
- MRI
Laboratory evaluations
- Serum amylase and lipase levels (limited utility)
- Serum bilirubin and liver function tests (limited utility)
- Cyst fluid analysis or cyst aspiration
Minimally invasive diagnostic techniques
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
- Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
Pancreatic pseudocyst treatment
The treatment of pancreatic pseudocysts can be broadly classified into conservative and non-conservative approaches based on the severity and location of the cyst. Conservative treatments focus on managing smaller or asymptomatic cysts, while non-conservative treatments involve more invasive procedures to drain or remove the cyst.
Conservative treatments
- Observation
- Supportive medical care
- Intravenous fluids
- Analgesics
- Antiemetics
Non-Conservative Treatments
- Surgical Internal Drainage
- Pseudocystogastrostomy
- Pseudocystoduodenostomy
- Pseudocystojejunostomy
- Cystogastrostomy
- Cystoduodenostomy
- Surgical Resection
- Distal pancreatectomy
- Distal splenectomy
- Endoscopic Drainage
- Endoscopic transpapillary drainage
- Endoscopic transmural drainage
- External drainage
- Percutaneous catheter drainage

Pancreatic pseudocyst prevention
To effectively prevent pancreatic pseudocysts, it is crucial to avoid pancreatitis, which is the primary contributing factor to the development of these cysts. Here are some ways to prevent pancreatitis:
- Eating a healthy diet: A balanced diet, high in fiber and low in fat, can help prevent conditions like pancreatitis, which may lead to pseudocyst formation.
- Stopping drinking alcohol: Excessive consumption of alcohol is a major risk factor for pancreatitis, which can lead to pseudocyst formation. Limiting the amount of alcohol or quitting alcohol can help reduce this risk.
- Managing gallstones: If gallstones are causing pancreatitis, the patient can seek medical help to treat them first to avoid pancreatic pseudocysts.
- Managing high blood triglycerides: High levels of triglycerides in the blood can also raise the risk of pancreatitis. Getting the treatment of high blood triglycerides can help to prevent pancreatitis.
- Early management of pancreatitis: Properly managing acute or chronic pancreatitis through medical treatment can prevent complications like pseudocyst development.
Difference between Pancreatic phlegmon and pseudocyst
Pancreatic phlegmon vs pseudocyst
Pancreatic phlegmon and pseudocyst are complications arising from pancreatic inflammation, typically due to acute pancreatitis. While a phlegmon is an inflammatory mass, a pseudocyst is a fluid-filled collection that forms following pancreatic injury or inflammation. Here are the common differences:
| Elements | Pancreatic phlegmon | Pancreatic pseudocyst |
|---|---|---|
| What it is | An inflammatory mass in the pancreas due to infected pancreatic tissue or surrounding fat. | A fluid-filled collection that forms after pancreatic injury or inflammation. |
| Composition | Contains necrotic tissue, inflammatory cells, and sometimes pus. | Contains fluid (usually pancreatic enzymes) and sometimes debris. |
| Cause | Due to acute pancreatitis or pancreatic infection. | Commonly follows acute pancreatitis, trauma, or pancreatic duct disruption. |
| Symptoms | May cause fever, pain, and signs of systemic infection (sepsis). | May be asymptomatic, or cause abdominal pain, swelling, loss of appetite nausea, or vomiting if large or infected. |
| Complications | Can progress to abscess or lead to sepsis. | Can lead to infection, rupture, or compression of adjacent organs. |
| Treatment | May resolve with appropriate treatment, but can cause fibrosis. Treatment options include antibiotics, drainage, and sometimes surgical debridement. | May resolve spontaneously if small and uncomplicated. Otherwise, intervention is needed. Treatment options include supportive care (Intravenous fluids, analgesics, antiemetics), drainage (percutaneous, endoscopic, or surgical) if symptomatic or complicated. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Pancreatic pseudocyst
How common are pancreatic pseudocysts?
Pseudocysts are more common in patients with chronic pancreatitis affecting approximately 35% and 10% of patients with acute pancreatitis. They're the most common type of pancreatic mass, accounting for about 75%. But they're uncommon overall. They affect approximately 3% of adults each year and rarely children.
How long do pancreatic pseudocysts last?
Cystic pancreatic lesions that occur after an episode of acute pancreatitis may resolve without treatment within 4 to 6 weeks. In contrast, spontaneous resolution of pseudocysts is rare in chronic pancreatitis due to the maturation of the cyst wall being already complete.
Can pancreatic pseudocysts become cancerous?
No, pancreatic pseudocysts are rarely cancerous and are considered non-cancerous (benign) but often require treatment to prevent severe complications. A true cyst has more potential to be cancerous than a pseudocyst.
How serious is a pancreatic pseudocyst?
A pancreatic pseudocyst can range from mild to serious, depending on its size, location, and potential complications. While many pseudocysts resolve on their own without treatment, they can become serious if they grow large, cause pain, become infected, or rupture, leading to life-threatening conditions. Timely medical attention and treatment are essential to avoid complications.
Do pancreatic pseudocyst go away on its own?
Pancreatic pseudocysts commonly develop following an episode of acute pancreatitis. They may resolve on their own within 4 to 6 weeks. Healthcare professionals typically intervene if pseudocysts last over six weeks. Approximately one-third resolve on their own in that time, but the chances decrease with multiple cysts or long-term complications from chronic pancreatitis.
What is the rule of 6 for pancreatic pseudocysts?
The "Rule of 6" for pancreatic pseudocysts identifies key factors in their formation after acute pancreatitis, including location, size, duration, symptoms, and complications. Surgeons typically follow this rule, which suggests that treatment may be necessary if a cyst is larger than 6 cm or has been present for more than 6 weeks. This approach allows time for the cyst to resolve on its own as well as its wall to strengthen, making surgical intervention safer.
What is the most common complication of a pancreatic pseudocyst?
Common complications of pancreatic pseudocyst include cyst infection, haemorrhage or rupture, blockage of the bile duct, portal hypertension, gastric outlet obstruction and bleeding into the spleen or a blood clot in a spleen vein.
Why is a pancreatic pseudocyst called a false cyst?
A pancreatic pseudocyst is called a "false cyst" because it differs from a true cyst. While both are fluid collections, a true cyst is a closed structure with a cell lining that separates it from surrounding tissue. A pseudocyst, on the other hand, is open and lacks this lining, so it doesn't have a distinct boundary from nearby tissues.
What size is a pancreatic pseudocyst?
Pancreatic pseudocysts can vary in size, typically ranging from a few centimeters to more than 10 cm in diameter. The term "giant pancreatic pseudocyst" is typically used to describe pseudocysts that are larger than 10 cm in size. However, cases of pseudocysts exceeding 20 cm have been reported, although they are rare. The size of the pseudocyst is an important factor in deciding whether treatment is needed.
How do healthcare professionals diagnose pancreatic pseudocysts?
Healthcare professionals can usually recognise pancreatic pseudocysts on a high-quality imaging test, including a contrast CT scan or MRI. However, sometimes, a sample of cystic fluid is required to distinguish a pseudocyst from another type of mass, which may be obtained with endoscopic ultrasound and fine needle aspiration.
Treatment for a complicated or high-risk pancreatic pseudocyst may involve drainage or surgical intervention. If the cyst is large, infected, or causing symptoms, interventional gastroenterologists may recommend procedures such as endoscopic drainage, percutaneous drainage, or surgery to remove it. In some cases, a drainage procedure is done to prevent further complications such as infection or rupture. The approach depends on the cyst's size, location, and severity of symptoms.
Can pseudocysts get resolved without surgery?
Many pseudocysts resolve with supportive care. Healthcare professionals may observe the pseudocyst to determine if it is improving and check for complications. A patient may also require another imaging test to see if the pseudocyst has disappeared.
What are the differences between pancreatic abscesses and pseudocysts?
A pancreatic abscess is a collection of pus that forms due to infection, often as a complication of pancreatitis, whereas a pancreatic pseudocyst is a non-infected, fluid-filled sac formed by pancreatic enzymes and tissue breakdown. Pseudocysts are typically sterile, while abscesses are infected and can cause more severe symptoms like fever and pain. Abscesses require antibiotic treatment and drainage, while pseudocysts may resolve on their own or need drainage if they cause complications.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868