Best Urology Hospital in Hyderabad for all Urological Treatment
PACE Hospitals is one of the
Best Urology Hospital in Hyderabad, India, providing holistic and patient centric urological treatment. The team of experienced and skilled urologists, urology surgeon has vast expertise in managing all kind of critical urology disease and disorder, including:
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Urinary incontinence & retention
- Urinary bladder disease
- Kidney stone diseases
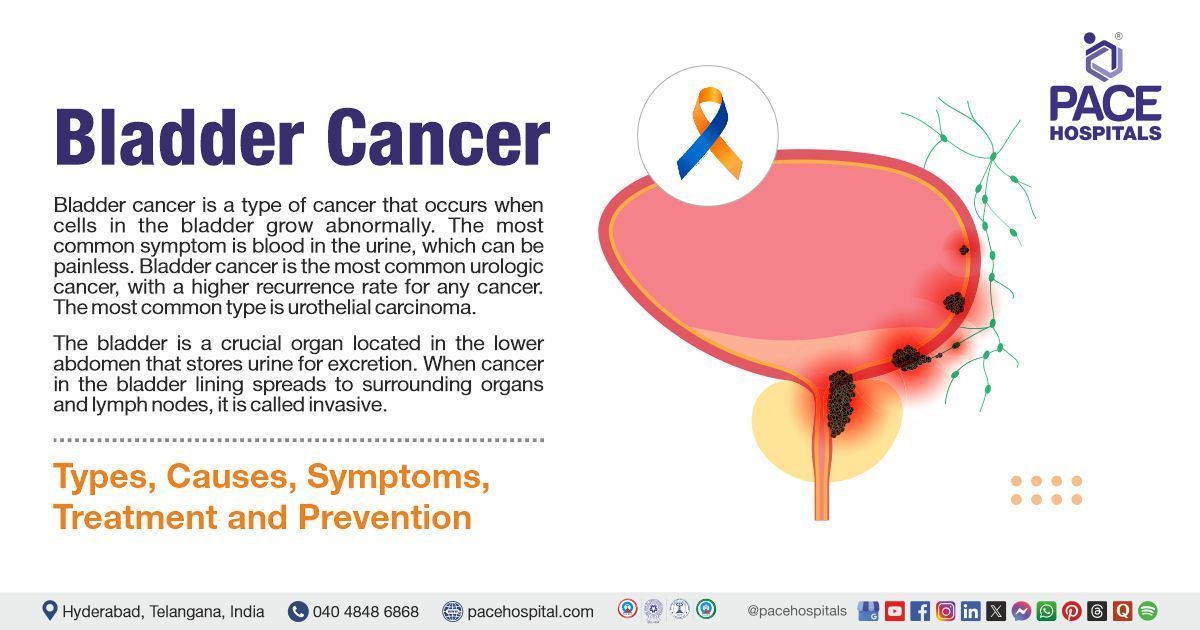
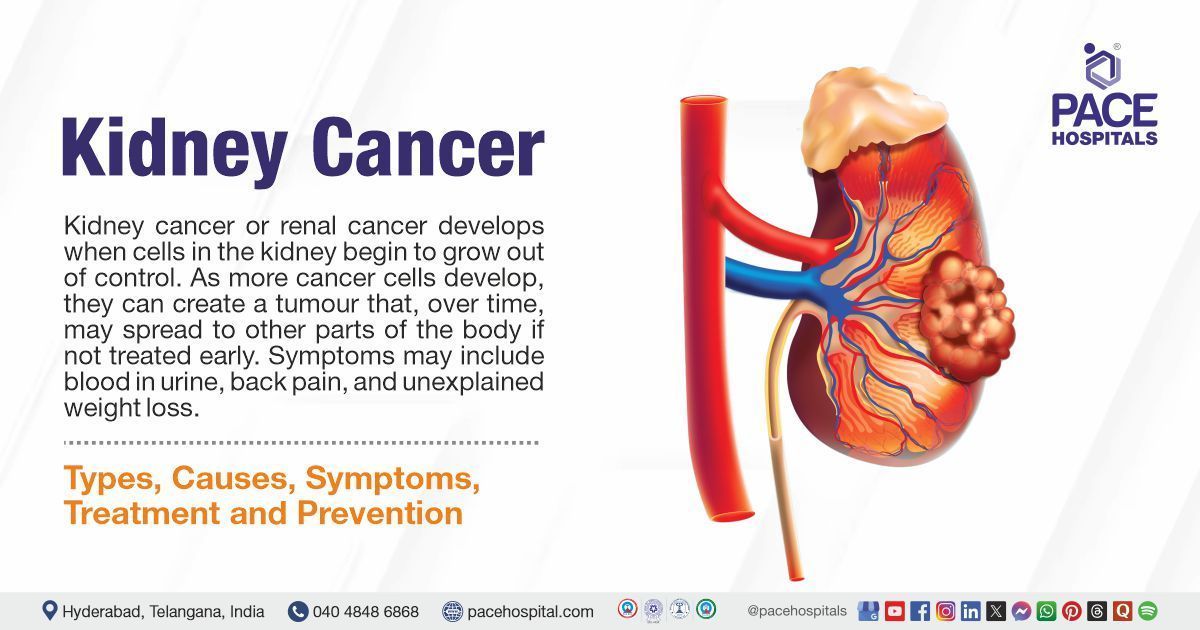
- Bladder, Kidney and Prostate cancer
- Hydronephrosis
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
- Ureteral stones
- Kidney transplantation
With state-of-the-art diagnostic and treatment facilities, we ensure advanced, minimally invasive, and personalized care for better patient outcomes.
Why Choose PACE Hospitals for Urology Treatments?
Comprehensive Urology Treatment
Providing treatment to a wide range of urology disorders including cancer of Prostate, Kidney and Bladder.
State-of-the-Art Diagnostic & Treatment Facilities
Equipped with advanced robotic and latest diagnostic equipment, treatment facilities for urology treatment.
Expert Team of Top Urologists in Hyderabad
Team of experienced urology specialist, urology surgeon with vast experience in lasers and laparoscopic surgeries.
Advanced Centre for Urology Treatment in Hyderabad, Telangana, India
The urology department at PACE Hospitals comprises a team of the renowned and top urologist in Hyderabad, Telangana, who are specialists in kidney transplantation (live and cadaver kidney transplant), dialysis, Uro-oncology, endourology, geriatric, pediatric urology and postoperative care with expertise in diagnosing, treating, and preventing various types of rare, serious urological related conditions and hospital-acquired infections.
The Department of Urology is equipped with state-of-the-art and cutting-edge facilities that offer a wide array of comprehensive care that includes advanced imaging systems, endoscopic equipment, minimally invasive surgeries (laser, laparoscopic and robotic), advanced prosthetic and implantable devices to manage a broad spectrum of urological conditions. The Urology doctor at PACE Hospitals, are well versed with latest treatment modalities, minimally invasive & advanced surgical procedures to cater efficient urological treatment with high success rate, quicker recovery, and minimum side effects.
3,12,338
98,538
684
2011
Best Urology Doctor in Hyderabad | Top Urology Specialist in India
Team of Best Urologist Doctor in Hyderabad, Telangana, India; having 40+ years of experience, offers a wide range of expertise and surgical treatment for urinary disorders of the male and female urinary tracts, as well as conditions of the male genital tract or reproductive system. The team is having long term experience in diagnosing and treating Kidney Stones, Prostate Enlargement, Prostate Cancer, Kidney Cancer, Bladder Cancer and Incontinence, Male infertility and Erectile Dysfunction – Impotence.
Dr. Vishwambhar Nath
MBBS, MS (General Surgery), DNB (Urology), M.Ch (Urology)
40+ years of Exp.
Senior Consultant Urologist & Renal Transplant Surgeon
Dr. Abhik Debnath
MBBS, MS (General Surgery - IMS, BHU), MCh (Urology - CMC Vellore), DNB (Urology)
10+ years of Exp.
Consultant Laparoscopic Urologist, Endourologist, Andrologist & Kidney Transplant Surgeon
Urology Diseases and Conditions Explained by Drs
Comprehensive Urologic Care Services

Struggling with common urinary issues or seeking treatment for kidney cancer, prostate cancer, bladder cancer, or critical urological disease and disorders like urinary tract infection, urinary incontinence, enlarged prostate, kidney stones, chronic cystitis, ureter stone or female pelvic health, we offer evidence-based solutions tailored to your needs. Our team of skilled and experienced urologists provides compassionate care for both men and women. Our treatment modalities include minimally invasive surgeries (laser, laparoscopic and robotic surgeries) for a wide range of urological disorders.
Advanced Urology Care & Comprehensive Urological Services
We specialize in treating various urological conditions affecting the urinary tract and female pelvic health. From kidney stones, bladder dysfunction and urinary tract infections to urological cancers, our team of urology specialist & urology surgeon offers patient centric comprehensive solutions for your urology health.
Patient Testimonials
Successful and safe Ureteric stone surgery in the presence of multiple comorbidities.
Patient was suffering with kidney tumor. Surgical removal done using Laparoscopic Nephrectomy.
20 mm Kidney Stone Removal through Retrograde Intrarenal Surgery (RIRS).
Urology Diagnostics, Preventive Care & Procedures
We provide comprehensive diagnostic tests; our advanced and latest screening approach examines kidney, bladder, and prostate health with precision. This results in early detection and precise evaluation, enabling our urologist to make an informed decision about proceeding with the appropriate treatment and surgical procedures.
Advanced Urological Diagnostic Tests
1. Urine Culture: It is a laboratory examination of urine that examines the presence of microorganisms such as bacteria and yeast. The term culture is defined as growing microorganisms in a laboratory by providing them with growth promoters in the urine sample. This procedure is used to check for Urinary Tract Infections (UTI). Diabetic patients, kidney disease, and regular intercourse (especially with new partners) need to have a regular urine culture test as a part of UTI screening, as these populations are at high risk of UTI.
2. Complete Urine Examination (CUE): A complete urine examination (CUE), also termed a urinalysis, is a diagnostic tool in urology that examines urine's physical, chemical, and microscopic properties. It starts with visual inspection for colour and clarity, followed by dipstick testing to find the presence of abnormalities in urine, such as glucose, protein, blood, or leukocytes. Microscopic analysis examines the sediment for cells, crystals, and casts. This thorough evaluation of urine helps diagnose urinary tract infections (UTIs), kidney diseases, and metabolic disorders. Abnormalities in urine composition can indicate underlying health issues, indicating further diagnostic steps.
3. Urodynamic Testing: Urodynamic study (UDS) is diagnostic procedure that assesses the functionality of the bladder, sphincters, and urethra that stores and releases urine. This test diagnoses patients with urinary incontinence and measures nerve function, muscle function, bladder pressure, and urine flow rates. The test is indicated if the patient is suffering from urine leakage, pain while urinating, difficulty passing urine, frequent washroom visits, urinary tract infections, or unable to empty the bladder completely.
4. Cystoscopy: It is a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure that visualizes the bladder or urethra using a camera known as a cystoscope, which will be inserted into the urethra and pass into the bladder. Flexible cystoscopy and rigid cystoscopy are the two types of cystoscopy. Flexible cystoscopy is used to view the bladder, whereas a rigid can be indicated for therapeutic applications, too. Cystoscopy is indicated to check for blood in urine, frequent urinary tract infections, chronic pelvic pain, difficulty in urinating, and collection of tissue (biopsy) samples to diagnose bladder cancer. Urinary tract infection and unable to pass urine after the procedure are the associated risks of cystoscopy.
5. Intravenous Pyelogram (IVP): It is an imaging test that is used to diagnose problems related to the kidneys or ureters. During this procedure, the radiologists inject an intravenous contrast dye that passes from the kidney into the bladder through the ureter. The X-ray images aid in locating any blockages in the kidneys and ureters as the dye passes through. This procedure is used to diagnose kidney diseases, prostate enlargement, bladder stones, urinary tract injury, and tumors.
6. Kidney Ultrasound: It is a non-invasive diagnostic exam that visualizes the blood flow, shape, size and location of the kidneys. The urologist will be placing an ultrasound transducer on the skin that emits high-frequency ultrasound waves that move through the kidney. These ultrasound waves produce images of the kidney that are presented to the computer. This test is used to diagnose the presence of cysts, obstructions, abscesses, stones and infections of the kidney. In addition, it is indicated after a kidney transplant to evaluate the transplanted kidney.
7. Prostate-specific Antigen Test: Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is a protein obtained from both normal and cancer cells of the prostate. The PSA test is used to measure the PSA protein levels in the blood sample. In the case of prostate cancer, there will be increased levels of PSA protein in the blood. In addition to prostate cancer, prostatitis and benign prostatic hyperplasia are the conditions where there will be an increase in PSA levels.
8. Renal scan: It is also known as renal scintigraphy, where the kidneys can be visualized with the help of nuclear radioactive material (radioisotope) that will be inserted into the vein (hand or arm). The images of the kidney can be created when the scanner detects the gamma rays released from the radioisotope. This test can be used to examine the size, shape and structure of the kidney. In addition, it is used to identify and evaluate the reduced flow of blood to the kidneys, high blood pressure in real arteries, kidney diseases, success or rejection of kidney transplant, renal abscesses, tumors, kidney inflammation due to infections, urine backflow from the bladder to the kidney and kidney failure.
9. Ureteroscopy: It is a procedure that is used to diagnose and treat ureter stones. This procedure is done by inserting a ureteroscope (a flexible tube). The ureteroscope consists of an eyepiece and a lens into the bladder through the urethra and up to the ureter to view, locate and remove the stone. Infections, injury and bleeding to the ureters are the risks associated with ureteroscopy.
10. Kidney Biopsy: A kidney biopsy is a diagnostic procedure that involves collecting a small piece of kidney tissue in order to view it under a microscope for indications of kidney damage or injury. In addition to this, kidney biopsy is indicated in the development of treatment plans based on the patient's condition to determine the kidney disease progression, extent of kidney damage, evaluation of prescribed treatment for kidney disease, and monitoring of transplanted kidney, which is failed to perform normal functions.
11. Prostate Biopsy: A prostate biopsy is a diagnostic procedure carried out to sample prostate tissue for analysis, typically to find out the presence of prostate cancer or other abnormalities. The method is often recommended when a patient has abnormal results on a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test, digital rectal examination (DRE), or imaging studies like MRI.
12. Bladder BIopsy: A bladder biopsy is a diagnostic procedure where a small tissue sample is taken from the bladder lining (mucosa) for examination. It is typically performed using a cystoscope. A bladder biopsy is needed when suspicious findings, such as abnormal growths, ulcers, or areas of inflammation, occur during a cystoscopy.
13. Antegrade Pyelogram: It is an imaging test that is used to locate the upper urinary tract blockages that include the kidney, bladder, and ureters. During this procedure, the radiologists inject contrast dye through a needle, which will be placed through the flank area of the back. The radiologists observe the contrast dye movement from the kidney into the ureter and bladder with the help of X-ray images. The X-ray images aid in locating any blockages in the kidneys and ureters as the dye passes through. This procedure is used to locate the urinary tract blockage caused by kidney stones, tumors, blood clots, and strictures (narrowing of the ureter).
Minimally Invasive Urology Procedures
1. Adrenalectomy: This is a surgical procedure where one or both adrenal glands will be removed, which are located at the top of each kidney. This procedure is initiated to treat tumors and the production of more hormones from the adrenal gland, which may lead to serious health problems. Blood clots, pneumonia, alteration in blood pressure, injury to adjacent organs, and lack of sufficient hormone production from the adrenal gland are risks associated with adrenalectomy. This procedure can be done by both minimally invasive procedures (laparoscopic, posterior retroperitoneoscopic and robotic surgery) and open surgery.
2. Cystectomy: It is also known as urinary bladder removal surgery, where the entire bladder might include prostrate in seminal vesicles in males and removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and part of the vagina in females. This procedure is indicated for cancer that spreads to the bladder, birth urinary tract irregularities, and inflammatory disorders that affect the urinary system. Infections, damage to adjacent organs or tissues, blood clots, internal bleeding, dislodging of blood clots towards the lungs or heart, and slow wound healing are the risks associated with the cystectomy procedure.
3. Nephrectomy: It is a surgical procedure that involves removal of a kidney. This procedure is indicated to treat kidney cancer, kidney diseases and traumas related to the kidneys. Nephrectomy is also used to remove a healthy kidney for transplantation from a donor who may be living or deceased. Partial and radical are two types of nephrectomies. This procedure can be done through laparoscopic or through open surgery approaches. Post-operative pneumonia, rare allergic reactions to anesthesia, bleeding that requires blood transfusion, and infection are the complications associated with this procedure.
4. Pyeloplasty: This is a surgical procedure that repairs the blockage at the ureteropelvic junction (junction where the ureter attaches to the kidney) and restores the normal urine flow in the ureter (a tube that connects the bladder and kidney). Infection, scarring, hernia, blood clots, and rarely injuries to the small intestine, large intestine, stomach, liver, spleen, ovary, fallopian tube, and major blood vessels are the risks associated with the pyeloplasty procedure.
5. Urethrotomy: It is a surgical procedure used to treat the narrowing of the urethra (a tube that carries urine and semen to the penis). This procedure is done with the help of a rigid telescope that will be inserted into the urethra to examine the narrowing. Through the urethrotomy (which consists of a small blade), the surgeon will make a cut in the scar tissue (that causes narrowing) and make the urethra wider. Chest infection, bleeding, allergic reactions to the equipment or medications used in the procedure, swollen penis, and difficulty passing urine are the complications associated with the procedure.
6. Bladder Augmentation: This procedure, also known as cystoplasty, is a surgical procedure that is used for bladder enlargement by using a section from a small or large intestine to hold more urine. This procedure is indicated if the patient is having urine leakage, Loss of tendency to hold urine in the bladder, bladder stiffness or increase in urine frequency, and inappropriate bladder muscle function. Slow healing, swelling, infection, bruising, anesthesia risks, hematoma formation or hernia, and unfavorable scarring are the risks associated with this procedure.
8. Ureteral Reimplantation: This procedure, also known as ureteroneocystostomy refers to reimplantation of the ureter into the bladder. This procedure is indicated in adult patients to treat trauma or disease conditions that involve the lower third portion of the ureter, resulting in obstruction or fistula. In children, this procedure is used to treat vesicoureteral reflux (backward flow of urine from the bladder into the ureters). Haematuria (blood in urine), infections, bladder spasms, urine extravasation and ureter obstruction are the acute complications associated with ureteral reimplantation. Urinary fistula, Contralateral reflux, Ureteral obstruction, and Persistent reflux are the long-term complications.
9. Cystolithalopaxy: Cystolithalopaxy is usually performed procedure that is indicated to treat bladder stones. The surgeon might insert an instrument known as a cystoscope (flexible tube with a camera) to visualise the exact location of the stone(s). A laser beam will be passed to the stone, resulting in crushing the large stone into small pieces. Transurethral cystolitholapaxy and percutaneous suprapubic cystolitholapaxy are the two types of cystolithalopaxy procedures. Urethra scar tissue, excess bleeding, blood clots in the legs, and reoccurrence of bladder stones are the complications of cystolitholapaxy.
10. Prostatectomy: Prostatectomy is the surgery indicated to remove a part of the prostate gland through the penis. The urology surgeon get access to the prostate by inserting a resectoscope that contains a camera and valves to control irrigating fluid to the end of the penis through the urethra. The resectoscope is also equipped with an electrical wire loop that cuts the tissue and seals the blood vessels. The urology surgeon uses the wire loop to remove the obstructed tissue in the urethra one piece at a time. The irrigating fluids transport the tissue fragments into the bladder , were they are later flushed out at the conclusion of the surgery.
11. Lithotripsy: Lithotripsy is a minimally invasive approach to disintegrating renal stones into small pieces so that they can easily move through the urinary tract and be expelled from the body. Different lithotripsy techniques include shock wave lithotripsy (SWL) and laser lithotripsy. In SWL, high-energy shock waves are applied to kidney stones from outside the body, aiming to break them into pieces to be discharged with the urine. In laser lithotripsy, a thin scope is inserted in the urinary tract to indicate and break the stones using laser energy. Lithotripsy is considered more effective than the traditional surgical approach because of its lesser recovery time.
12. Retrograde IntraRenal Surgery (RIRS): RIRS is a noninvasive procedure for kidney stones located within the kidney and upper urinary tract. This minimally invasive procedure is effective for medium to large complex kidney stones located anatomically in the critical position. In this procedure, an incision is not required; the surgeon inserts the flexible ureteroscope (a thin, lighted instrument with a camera) through the urethra and bladder into the ureter and kidney. With the help of navigational equipment, the urology surgeon navigates and visualizes the stone. Once the stone is identified, specialized tools like laser fibers and the basket are used to break the stone and collect it. The stone is extracted utilizing the retrieval basket or flushed out naturally through urine.
13. Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL): Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL) is a minimally invasive procedure used to remove large kidney stones that cannot be treated with other methods, like shock wave lithotripsy. This procedure is done under general anesthesia. To gain direct operating access to the kidney, a surgeon makes a small incision on the patient's back. A nephroscope is then inserted through the incision to locate and remove the stones. Laser or ultrasonic energy may be used to break it to extract large stones.
14. Urethral Sling Procedures: This minimally invasive procedure treats stress urinary incontinence in women and men. In a urethral sling procedure, a synthetic mesh sling is placed under the urethra to support and lift it to its normal position. This helps prevent urine leakage during activities that could increase abdominal pressure, such as coughing, sneezing, or lifting. This procedure effectively treats urinary incontinence and bladder control issues and has a high success rate.
15. Artificial Urinary Sphincter (AUS) Placement: Artificial urinary sphincter (AUS) placement is a surgical procedure to treat severe urinary incontinence caused by sphincter impairment that can happen in case of prostate surgery resection or other urinary system dysfunction. The AUS consists of a cuff, a pressure-regulating balloon (reservoir), and a control pump. The cuff is placed around the urethra, the balloon is positioned within the abdomen, and the control pump is placed in the scrotum. The surgeon carefully connects the cuff, ballon, and pump to ensure proper AUS function and effective control of urine flow. This whole procedure is performed under local anesthesia by making an incision on the lower abdomen around the bladder and urethra.
16. Urethroplasty: A urethroplasty is a surgical procedure used to treat the narrowing of the urethra, the tube that the body uses for eliminating urine. It improves easier flow of urine. Urethroplasty is often referred to as the best option for treating urethral stricture. Urethroplasty is used when optical urethrotomy and urethral dilatation are ineffective, or when the urethral stricture is too long. Over the stricture, the surgeon makes an incision, either on the penis or in the skin between the scrotum and the anus (the perineum). Postoperative complications, other than recurrent stricture, include scrotal swelling, urethral fistula, erectile dysfunction, and post-void dribbling.
17. Renal Artery Stenting: It is a surgical procedure which is used to clear blocked renal arteries (that carry oxygenated blood to the kidneys) and placing a tiny metal mesh tube that prevents further blockages. This procedure treats vascular atherosclerosis, a blockage greater than 60% in both or any one of the arteries, uncontrolled blood pressure that can't be managed with more than three medications, and rapid fluid build-up in the lungs. Bleeding at the insertion site, bruising at the insertion of the sheath and catheter, injury to the renal artery, and formation of clots are the risks associated with this procedure.
Health Blogs & Patient Education on Urology
Why choose PACE Hospitals?
- A Multi-Super Speciality Hospital.
- NABH, NABL, NBE & NABH - Nursing Excellence accreditation.
- State-of-the-art Liver and Kidney transplant centre.
- Empanelled with all TPA’s for smooth cashless benefits.
- Centralized HIMS (Hospital Information System).
- Computerized health records available via website.
- Minimum waiting time for Inpatient and Outpatient.
- Round-the-clock guidance from highly qualified urology physicians and surgeons.
- Standardization of ethical medical care.
- 24X7 Outpatient & Inpatient Pharmacy Services.
- State-of-the-art operation theaters.
- Intensive Care Units (Surgical and Medical) with ISO-9001 accreditation.