Acute Pancreatitis (AP): Symptoms, Causes, Risk Factors, Complications, Treatment & Prevention
Acute pancreatitis definition
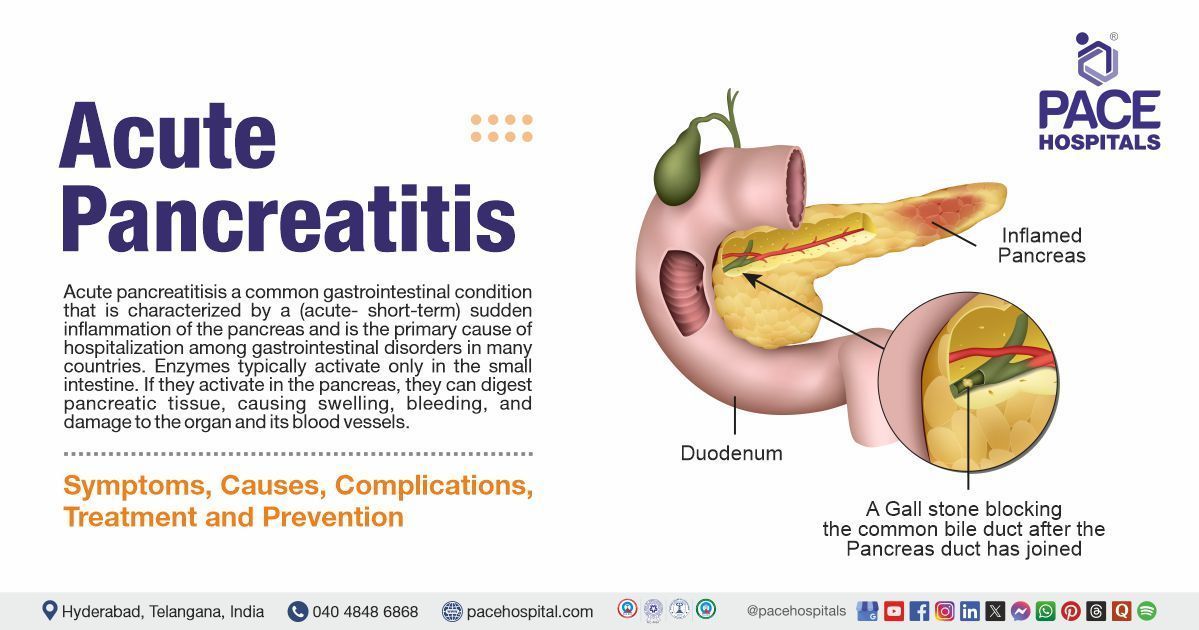
It is a common gastrointestinal condition that is characterised by a (acute- short-term) sudden inflammation of the pancreas and is the primary cause of hospitalisation among gastrointestinal disorders in many countries. Enzymes typically activate only in the small intestine. If they activate in the pancreas, they can digest pancreatic tissue, causing swelling, bleeding, and damage to the organ and its blood vessels.
Acute pancreatitis, in contrast to chronic pancreatitis, usually results from a triggering event and goes away quickly with the proper medical care. Inflammation of the pancreas causes digestive problems, pain in the abdomen, and, in rare instances, serious systemic complications. Most individuals with this condition may recover within a week and have no further problems; however, severe cases can lead to serious complications and may even be fatal.
Acute Pancreatitis Meaning
- Acute: Short term condition
- Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas
Acute Pancreatitis Prevalence
The highest rate of acute pancreatitis occurs in individuals during their fifth (ages 40-49) and sixth (ages 50-59) decades of life; however, mortality rates increase with age.
The mortality rate of acute pancreatitis ranges from 3% in individuals with mild pancreatitis to as high as 20% in those with pancreatic necrosis.
In 2019, it was estimated that there were 2,814,972 cases of acute pancreatitis globally, with 115,053 deaths (4.1%).
In 2024, the incidence of acute pancreatitis in India is estimated to range from 12 to 20 cases per 100,000 individuals per year, with common causes including idiopathic factors, gallstones, and biliary ascariasis.
Acute Pancreatitis Classification
This condition is classified on the basis of the presence of necrosis and the severity of the condition, with the two main types being interstitial oedematous Pancreatitis (mild) and necrotising Pancreatitis (severe).
Here's a breakdown of the types of acute pancreatitis:
Interstitial Oedematous Pancreatitis (Mild) or Acute Oedematous Pancreatitis
- This condition doesn't have significant tissue death (necrosis). However, it is characterised by swelling and inflammation of the pancreas and surrounding tissues.
- It may be associated with peripancreatic fluid collections.
- Often resolves without complications.
Necrotizing Pancreatitis (Severe) or Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis
- Characterised by tissue death (necrosis) within the pancreas and/or surrounding tissues.
- It can lead to more severe complications such as prolonged illness and organ failure
- It may be further classified as sterile or infected necrosis.
- It can be associated with acute necrotic collections and walled-off necrosis.
Severity Classification (Based on the Revised Atlanta Classification)
- Mild Acute Pancreatitis: No pancreatic or peripancreatic necrosis, organ failure, local or systemic complications.
- Moderate Acute Pancreatitis: Sterile pancreatic or peripancreatic necrosis, transient organ failure (<48 hours), or both.
- Severe Acute Pancreatitis: Infected pancreatic or peripancreatic necrosis or persistent organ failure (>48 hours).
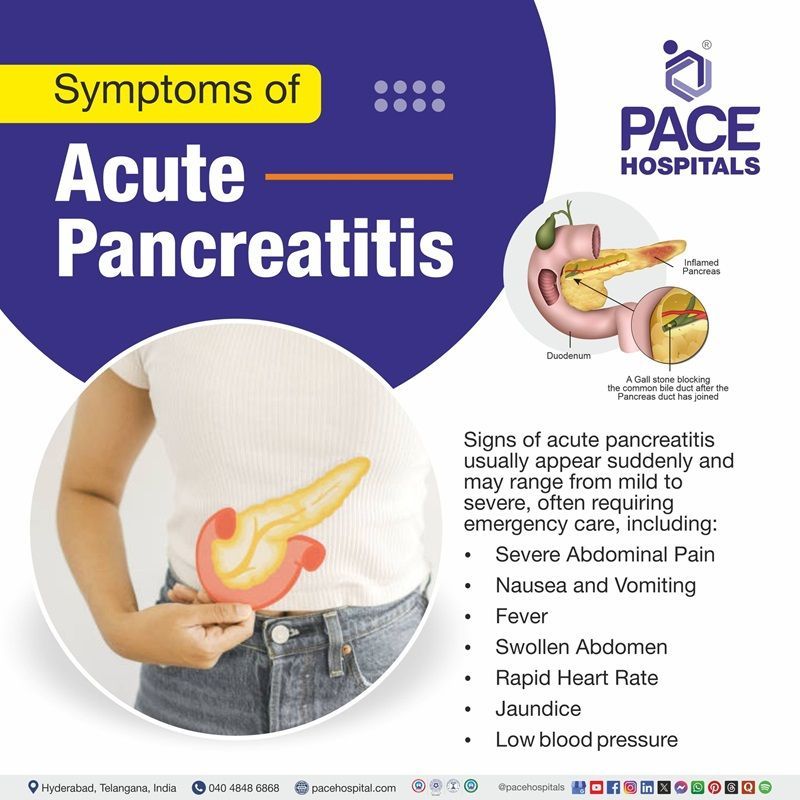
Acute Pancreatitis Symptoms
Acute pancreatitis presents as an emergency, requiring urgent admission to the hospital. Typically, signs of acute pancreatitis develop suddenly and may range from mild to severe. Below-mentioned are common acute pancreatitis signs and symptoms, including:
- Severe tummy pain: Patients almost always mention severe, constant abdominal pain (similar to peritonitis), usually of sudden onset and, in 80% of cases, associated with vomiting.
- The pain may radiate to the back, usually to the lower thoracic area.
- Fever: In some cases, fever accompanies acute pancreatitis due to inflammation.
- Rapid Heart Rate (Tachycardia): An increased heart rate is common due to systemic inflammation and fluid loss.
- Abdominal Swelling: Abdominal examination shows epigastric tenderness, with muscle guarding that may occur due to fluid accumulation and inflammation.
- Jaundice: Yellowish discolouration of the skin and eyes can be seen in patients with acute pancreatitis, which occurs when the bile ducts are obstructed.
- Low Blood Pressure: A drop in blood pressure can be seen in severe cases, causing organ failure and shock.

Acute Pancreatitis Causes
It is an unpredictable and potentially lethal disease that has a variety of causes, with the most common causes being gallstones (50%) and alcohol (25%), as per European and North American studies:
- Gallstones: Gallstones are the most common cause. Migrating gallstones cause transient obstruction of the pancreatic duct, a mechanism shared by other causes such as endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), as well as potential causes (i.e., pancreas divisum and sphincter of Oddi dysfunction).
- Alcohol: It is the second most common cause of acute pancreatitis. It usually occurs in individuals who consume four to alcoholic five drinks daily for over five years. Heavy drinkers have a lifetime risk of 2% to 5% for developing pancreatitis. The risk is higher for men than for women, possibly due to differences in alcohol intake or genetic background.
Other causes (5%) and acute pancreatitis risk factors include:
- Medications: Certain drugs account for less than 5% of all cases of acute pancreatitis, although hundreds of drugs have been implicated. Some medications, such as corticosteroids, certain antibiotics, and chemotherapy drugs, can increase the risk of acute pancreatitis.
- Elevated fat levels: Elevated triglyceride levels in the blood can increase the risk of developing acute pancreatitis.
- Trauma or Injury: Physical trauma to the abdomen, such as a car accident, can injure the pancreas and lead to acute pancreatitis.
- Infections: Certain viral or bacterial infections, including mumps, can result in acute pancreatitis.
- Morbid obesity: It is one of the risk factors for both acute pancreatitis and severe acute pancreatitis.
- Genetic mutations: Specific mutations and polymorphisms in several genes are linked with acute (and chronic) pancreatitis.
- Type 2 diabetes: As per some studies, it was found that this condition also increases the risk of acute pancreatitis by a factor of 2 or 3. However, both
obesity and
diabetes are also risk factors for chronic pancreatitis and
pancreatic cancer.
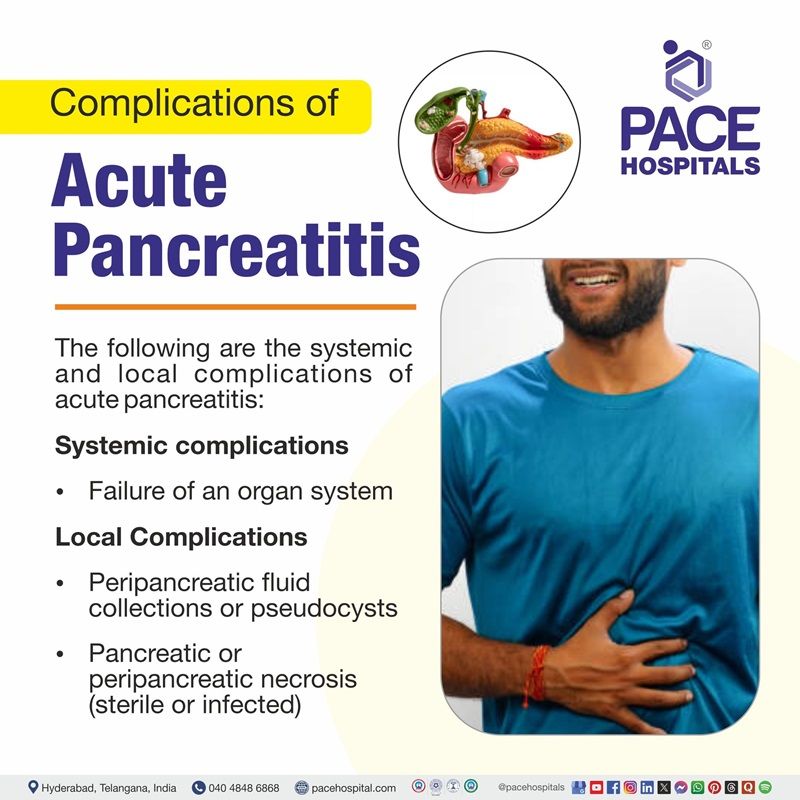
Complications of Acute Pancreatitis
After acute pancreatitis, pancreatic exocrine and endocrine dysfunction develops in approximately 20 to 30% of patients, and clear-cut chronic pancreatitis develops in one-third to one-half of those patients. The following are the other systemic and local complications:
- Systemic complications
- Organ Failure
- Local Complications
- Peripancreatic fluid collections or pseudocysts
- Pancreatic or peripancreatic necrosis (either sterile or infected)
Acute Pancreatitis Diagnosis
Involves several tests to confirm the condition and determine its severity:
Acute Pancreatitis Treatment
Treatment for acute pancreatitis focuses on managing symptoms, supporting the pancreas, and preventing complications:
- Hospitalisation
- Fluid Replacement
- Pain Management
- Antibiotics
- Nutritional support
- Surgical Intervention
- Endoscopic Procedures

Prevention of Acute Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis and recurrent episodes can be prevented by taking the following precautions:
- Reducing alcohol consumption
- Maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding obesity
- Quitting smoking
- Early Gallstone Treatment
- Dietary Adjustments (A diet low in fat)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Acute Pancreatitis
How is Acute Pancreatitis diagnosed?
Acute pancreatitis is diagnosed using blood tests that show elevated pancreatic enzymes and imaging tests (such as CT scans or ultrasound) to assess pancreatic inflammation and any complications like gallstones or pseudocysts.
What is the treatment for Acute Pancreatitis?
Treatment typically includes hospitalisation, management of pain, intravenous fluids, fasting, and addressing the underlying cause of the pancreatitis. In some cases, surgery or endoscopic interventions are necessary to remove gallstones or treat complications like pseudocysts.
Is acute pancreatitis curable?
Acute pancreatitis can be cured in many cases with proper treatment, especially if it is mild and the underlying cause (such as gallstones or alcohol use) is addressed. Most patients recover fully with supportive care, though severe cases may lead to complications that require long-term management.
Can Acute pancreatitis be prevented?
Acute pancreatitis can be prevented by limiting alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy weight, consuming a balanced diet, quitting smoking, and managing conditions like high cholesterol and gallstones.
Can Acute Pancreatitis lead to cancer?
While it does not directly cause cancer, however, repeated episodes of pancreatitis, mainly if they are severe or unresolved, can increase the risk of developing pancreatic cancer over time.
Is Acute Pancreatitis a serious condition?
Yes, acute pancreatitis can be a life-threatening condition if not treated promptly. However, with proper medical care, many people recover fully. Severe cases may lead to complications like organ failure, infection, and pseudocysts.
What is severe acute pancreatitis?
Severe acute pancreatitis is a serious form of acute pancreatitis characterised by extensive pancreatic necrosis, organ failure, and potential complications like infection or haemorrhage. It often requires intensive care and can lead to long-term complications or even death if not managed appropriately.
Can acute pancreatitis cause diabetes?
Yes, acute pancreatitis can cause diabetes if it leads to damage to the pancreas, particularly its insulin-producing cells. Severe or recurrent pancreatitis may impair the pancreas' ability to regulate blood sugar, leading to diabetes in some cases.
Can acute pancreatitis reoccur?
Yes, acute pancreatitis can recur, especially if the underlying cause (like gallstones, alcohol consumption, or high triglyceride levels) is not resolved. Chronic pancreatitis can develop in some individuals who experience repeated episodes of acute pancreatitis.
What to eat after acute pancreatitis?
After recovering from acute pancreatitis, it is important to follow a low-fat, well-balanced diet to allow the pancreas to heal. Gradually reintroduce solid foods, starting with easily digestible items like bland foods, fruits, and vegetables while avoiding alcohol and high-fat foods.
Can you treat acute pancreatitis at home?
Mild cases of acute pancreatitis can sometimes be managed at home with rest, hydration, and over-the-counter pain medications under a doctor's guidance. However, more severe cases require hospitalisation for IV fluids, pain management, and monitoring for complications. Always seek medical attention if symptoms worsen.
What is a pancreatic attack?
Acute pancreatitis is defined as an acute inflammatory attack of the pancreas with a sudden onset of symptoms. The commonest causes for acute pancreatitis are gallstones (40–65%) and alcohol (25–40%), and the remainder (10–30%) are due to a variety of causes including autoimmune and genetic risk factors.
What is acute interstitial pancreatitis?
Acute interstitial pancreatitis is a subtype of acute pancreatitis characterised by inflammation and oedema of the pancreatic tissue without severe tissue damage or necrosis. It is typically a milder form of acute pancreatitis (mild acute pancreatitis) than other types, such as acute necrotising pancreatitis.
What is acute or chronic pancreatitis?
It occurs when a person with chronic pancreatitis experiences a sudden flare-up of symptoms. This involves an acute episode of inflammation superimposed on existing pancreatic damage, leading to increased pain and potential complications.
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868
Appointment request - health articles
Thank you for contacting us. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Oops, there was an error sending your message. Please try again later. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Our Locations – Find the Best Hospital Near You
Metro Pillar Number C1772, Beside Avasa Hotel, Hitech City Road, Near HITEC City Metro Station, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Mythri Nagar, Beside South India Shopping Mall, Hafeezpet, Madeenaguda, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
040 4848 6868
Payment in advance for treatment at PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, Telangana, India (Pay in INR ₹)
For Bank Transfer:-
- Bank Name: HDFC
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.50200028705218
IFSC Code: HDFC0000545 - Bank Name: STATE BANK OF INDIA
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.62206858997
IFSC Code: SBIN0020299
Scan QR Code by Any Payment App (GPay, Paytm, Phonepe, BHIM, Bank Apps, Amazon, Airtel, Truecaller, Idea, Whatsapp etc).

CONTACT US
Call: +914048486868
WhatsApp: +918977889778
Email: info@pacehospitals.in
FOLLOW US
SUBSCRIBE
Subscribe to our newsletter and stay updated with the latest health information.
Subscribe to PACE Hospitals' Public Newsletter
Thank you for subscribing to PACE Hospitals' Newsletter. Stay updated with the latest health information.
Oops, there was an error. Please try again submitting your details.
ABOUT US
QUICK LINKS
Disclaimer
General information on healthcare issues is made available by PACE Hospitals through this website (www.pacehospital.com), as well as its other websites and branded social media pages. The text, videos, illustrations, photographs, quoted information, and other materials found on these websites (here by collectively referred to as "Content") are offered for informational purposes only and is neither exhaustive nor complete. Prior to forming a decision in regard to your health, consult your doctor or any another healthcare professional. PACE Hospitals does not have an obligation to update or modify the "Content" or to explain or resolve any inconsistencies therein.
The "Content" from the website of PACE Hospitals or from its branded social media pages might include any adult explicit "Content" which is deemed exclusively medical or health-related and not otherwise. Publishing material or making references to specific sources, such as to any particular therapies, goods, drugs, practises, doctors, nurses, other healthcare professionals, diagnoses or procedures is done purely for informational purposes and does not reflect any endorsement by PACE Hospitals – your trusted hospital near me.