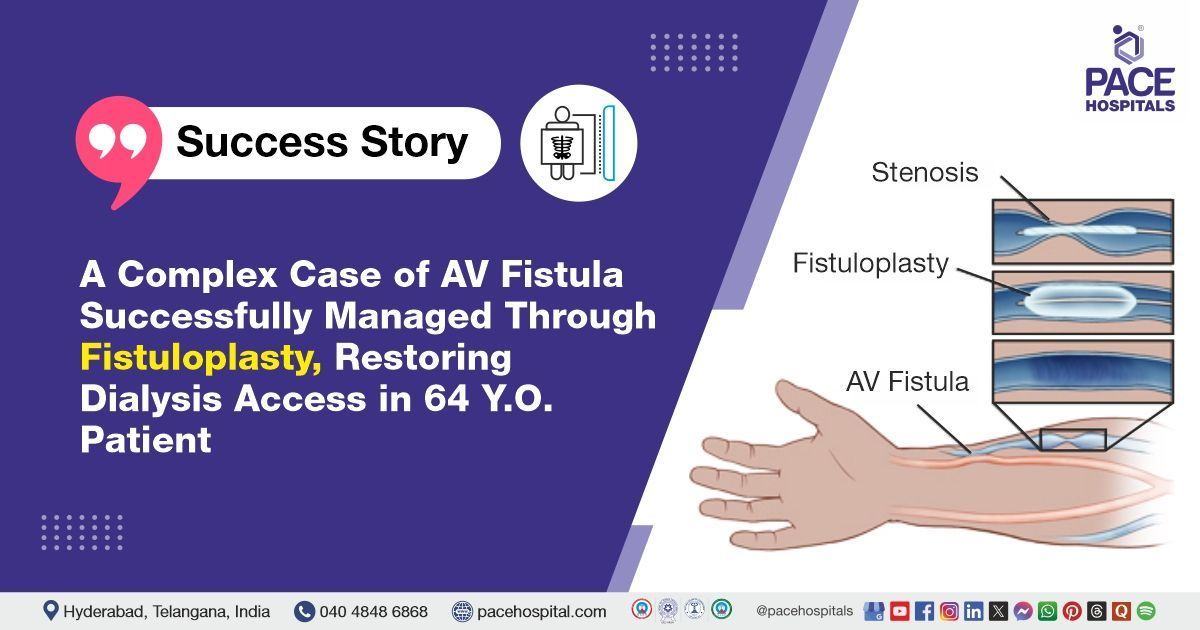
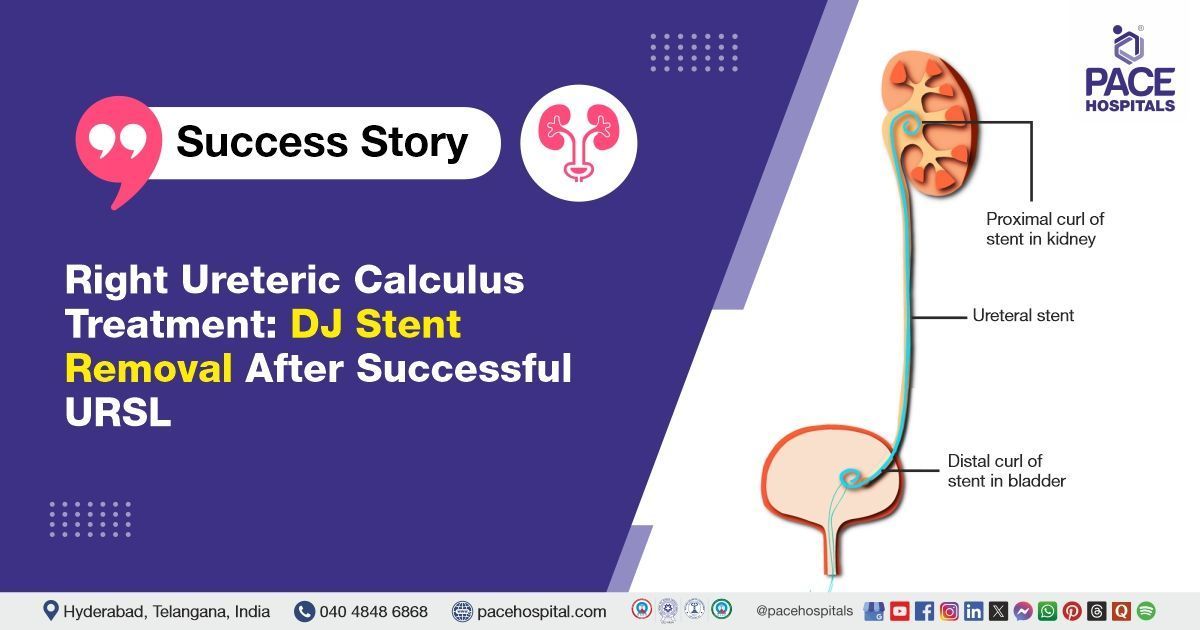
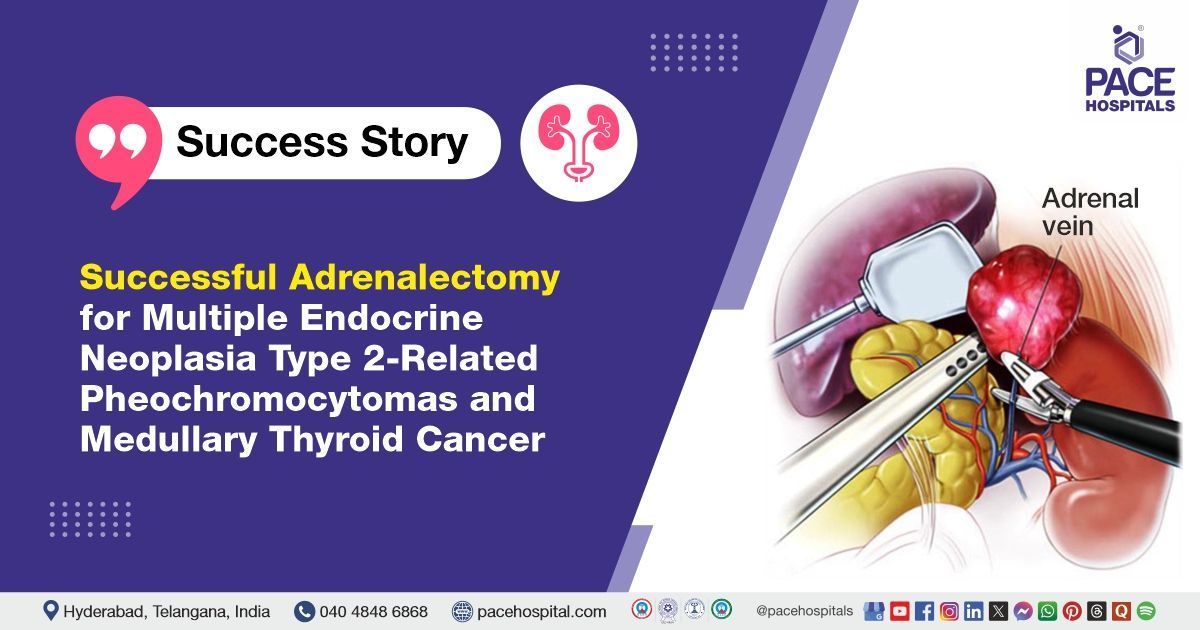
Diabetic Foot: Types, Causes, Symptoms, Complications, Treatment & Prevention
Diabetic Foot Definition
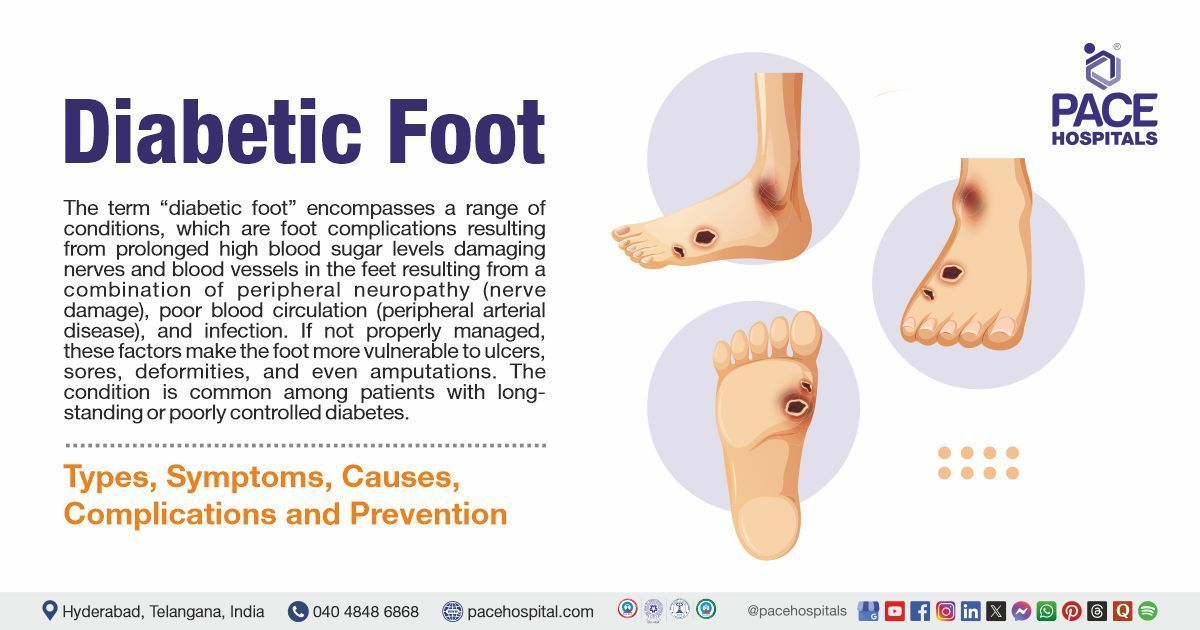
The term “diabetic foot” encompasses a range of conditions, which are foot complications resulting from prolonged high blood sugar levels damaging nerves and blood vessels in the feet resulting from a combination of peripheral neuropathy (nerve damage), poor blood circulation (peripheral arterial disease), and infection. If not properly managed, these factors make the foot more vulnerable to ulcers, sores, deformities, and even amputations. The condition is common among patients with long-standing or poorly controlled diabetes.
Diabetic foot problems may not seem severe, but they are the most common and serious complication of diabetes, as they often take a long time to heal. Unfortunately, more patients with diabetes are hospitalized due to foot wounds or infections than due to nephropathy (any disease or damage to the kidney), retinopathy (any damage to the retina of the eyes), heart attack, and stroke.
Early detection and management by an endocrinologist or diabetologist can significantly reduce the risk of severe complications.
Diabetic Foot Meaning
Diabetic foot is a complex joint and bone disorder affecting the ankle and foot in patients with persistent diabetes, primarily caused by peripheral neuropathy.
Prevalence of Diabetic Foot
Diabetic Foot (DF) is among the most serious complications of diabetes mellitus that results in hospital admissions and burdens the healthcare system. Foot disease affects nearly 6% of individuals with diabetes and includes infections, ulcerations, or tissue destruction in the foot.
Prevalence of Diabetic Foot Worldwide
- The global prevalence of diabetic foot ulcers is estimated at 6.3% among individuals with diabetes.
- Around 15%–25% of people with diabetes are at risk of developing a foot ulcer during their lifetime.
- Diabetic foot complications are responsible for more hospitalizations than any other complication of diabetes.
- The estimated prevalence of diabetic foot infections (DFIs) ranges from 6% to 11%. Neuropathy is recognized as the most significant factor contributing to infections in diabetic foot wounds.
Prevalence of Diabetic Foot in India
- India holds a significant position in the global landscape of diabetes prevalence as it has become the diabetes capital of the world, with a projected 10.9 crore patients with diabetes by 2035. India ranks second (after China) with more than 6.68 crore diabetics in the age group of 20-70 years.
- The prevalence of diabetes in India is 8.6%, and as of 2013, more than 10 lakh Indians die each year due to diabetes-related causes.
- Approximately 15% of diabetics in India are affected by foot ulcers, and 1 lakh amputations are performed annually due to diabetes-related foot infections.
- Diabetic foot ulcers are linked to high levels of morbidity, mortality, and significant financial costs.

Types of Diabetic Foot Problems
Diabetic foot conditions are broadly classified based on the underlying cause such as neuropathy, ischemia, or infection, each affecting the foot's structure and healing ability in different ways. The diabetic foot classification is as follows:
Diabetic Neuropathy (Neuropathic Foot: diabetic foot neuropathy)
- Loss of sensation in the feet
- Symptoms include tingling, numbness & burning pain
Ischemic Foot
- Symptoms include cold feet, shiny skin, and absent pulses
- Caused by peripheral arterial disease (PAD)
Neuroischemic Foot
- Open wounds or sores that occur on the feet of people with diabetes
- Caused by a combination of peripheral neuropathy (nerve damage) and ischemia (reduced blood flow)
Charcot Foot
- A serious complication resulting in bone and joint damage
- Causes foot deformities such as a “rocker bottom” appearance
Infected Diabetic Foot
- Bacterial infections in ulcers or deep tissues.
- May progress to cellulitis, abscesses, or osteomyelitis (bone infection).

Diabetic Foot Causes
Diabetic foot problems are primarily caused by high blood sugar damaging nerves which damages blood vessels, leading to nerve damage (neuropathy) and poor circulation, making the feet more vulnerable to injury, poor healing, and infection. The following are the diabetic foot causes:
- Peripheral Neuropathy: This is nerve damage caused by high blood sugar, leading to loss of feeling in the feet. Without pain sensation, small cuts or pressure points go unnoticed and can turn into serious wounds.
- Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD): PAD reduces blood flow to the legs and feet, making it hard for wounds to heal. Poor circulation increases the risk of infections and ulcers.
- Uncontrolled diabetes: It leads to neuropathy and peripheral arterial disease through complex metabolic pathways.
- High Blood Sugar Levels: Consistently high blood sugar weakens the immune system, damages nerves and blood vessels, and slows down healing—setting the stage for diabetic foot complications.
- Occlusive Footwear (shoes or boots that enclose the feet tightly): Wearing improper footwear that encloses the feet tightly, limiting airflow and potentially trapping moisture, can lead to excessive sweating and increase the risk of fungal infections. It also increases the risk of pressure ulcers and trauma.
- Poor Foot Hygiene: Allows microbial entry and infection.
- Trauma or Minor Injuries: Can escalate quickly due to reduced sensation.
- Smoking: Narrows blood vessels, reducing blood supply.

Diabetic Foot Symptoms
Diabetic foot signs and symptoms usually develop gradually over months or years due to prolonged high blood sugar levels. Early signs often go unnoticed until complications begin to surface.
- Pain (diabetic foot pain): Tingling, burning, or pain in the feet
- Numbness: Loss of feeling in the feet or toes
- Swelling: Swelling in the feet or ankles
- Skin changes: Dry, cracked skin, changes in skin colour, or loss of hair on the feet
- Nail changes: Thickened, yellow toenails, or ingrown toenails
- Foot sores: Blisters, ulcers, infected corns, or sores that don't heal
- Foul smell: Foul-smelling discharge from a wound
- Foot deformities: Bunions, hammertoes, or Charcot's foot
- Foot odor: Foul odor from the feet
- Leg pain: Pain or cramping in the buttocks, thighs, or calves during physical activity
- Diabetic foot gangrene: Blackened toes or gangrene (late-stage)
Risk Factors of Diabetic Foot
Individuals are at a higher risk of developing diabetic foot complications if they have the following risk factors:
- Age: Older individuals are at a higher risk.
- Sex: Males are more prone to develop diabetic foot disease.
- Family history: A family history of diabetes can increase the risk.
- Poor blood sugar control: Uncontrolled blood sugar levels can damage nerves and blood vessels, increasing the risk of foot problems.
- Kidney disease (Diabetic nephropathy): Kidney disease can be associated with an increased risk of diabetic foot disease.
- Infections: Diabetic patients have a higher susceptibility to infections, which can worsen foot ulcers.
Other risk factors:
- History of previous foot ulcers or amputations
- Visual impairment
- Foot deformities
- Limited mobility
- Inappropriate footwear
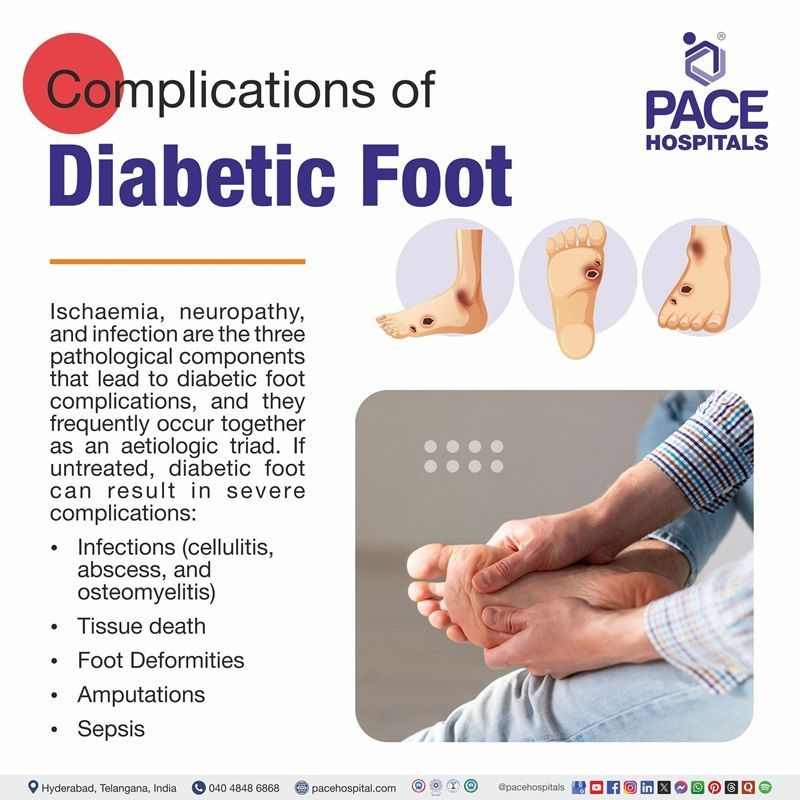
Diabetic Foot Complications
Ischaemia, neuropathy, and infection are the three pathological components that lead to diabetic foot complications, and they frequently occur together as an aetiologic triad. If untreated, diabetic foot can result in severe complications:
- Infections (Diabetic foot infection): Including cellulitis, abscess, and osteomyelitis
- Gangrene: Tissue death due to infection or lack of blood supply
- Foot Deformities: From Charcot's foot or improper healing
- Amputations: Partial or full removal of the foot or leg
- Sepsis: A life-threatening systemic infection
Diabetic Foot Diagnosis
Diagnosis involves clinical examination and specialized tests to assess the extent of nerve damage, blood flow, and infection, including:
Clinical Evaluation
- Inspection of skin, nails, ulcers
- Neurological examination (monofilament test, tuning fork)
- Palpation of foot pulses
- Gait and footwear assessment
Laboratory Tests
- HbA1c (glycaemic control)
- Complete blood count (to detect infection)
- ESR/CRP (to detect inflammation)
- Wound swab culture
Imaging
Diabetic Foot Treatment
Diabetic foot management involves controlling the underlying diabetes, healing existing wounds, and protecting the foot from further injury. Early and proper care can significantly enhance outcomes and improve the quality of life for patients, including:
Wound Care (diabetic foot care)
- Regular cleaning and dressing of ulcers
- Debridement to remove dead tissue
- Negative pressure wound therapy (VAC)
Medications
- Antibiotics (oral or IV for infected ulcers)
- Pain management (neuropathic pain)
- Blood sugar control (insulin or oral antidiabetics)
Offloading
- Use of special shoes, insoles, or total contact casts to relieve pressure from ulcers
Surgical Intervention
- Drainage of abscesses
- Removal of necrotic tissue
- Revascularization procedures (angioplasty or bypass for PAD)
- Amputation in severe or gangrenous cases

Prevention of Diabetic Foot
Proactive foot care is essential to prevent diabetic foot complications:
- Daily foot inspection: Look for cuts, blisters, redness, or swelling.
- Proper footwear: Use well-fitted shoes; avoid walking barefoot.
- Good hygiene: Wash feet daily and keep them dry.
- Blood sugar control: Maintain target HbA1c levels.
- Routine podiatry check-ups: Especially if previous ulcers or neuropathy are present.
- Smoking cessation: Improves circulation.
- Nail care: Cut nails straight across; avoid injury.
- Education: Patients should be educated about foot care and risk signs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Diabetic Foot
How does diabetes cause foot problems?
Diabetes can damage nerves (neuropathy) and blood vessels, reducing sensation and blood flow to the feet. This makes it harder to feel injuries or heal properly, increasing the risk of infections and ulcers.
How long does a diabetic foot ulcer take to heal?
Healing time varies depending on blood sugar control, severity of the ulcer, and presence of infection. On average, it may take weeks to several months, with some ulcers requiring more extensive treatment.
Can a diabetic foot ulcer lead to amputation?
Yes, if an ulcer becomes infected and the infection spreads to deeper tissues or bone, amputation may become necessary to prevent life-threatening complications. Early treatment is key to preventing this.
How does smoking affect diabetic foot health?
Smoking narrows blood vessels and worsens circulation, especially in the legs and feet. This significantly raises the risk of ulcers, delayed healing, and amputations in people with diabetes.
What is a diabetic foot ulcer?
A diabetic foot ulcer is an open sore or wound that typically occurs on the bottom of the foot in people with diabetes. It develops due to poor circulation and nerve damage, which reduce the body’s ability to heal and sense injuries.
Can diabetic neuropathy affect only one foot?
Yes, although diabetic neuropathy often affects both feet, it can sometimes start in one foot or be more severe on one side. This may happen if there's uneven pressure, injury, or asymmetrical nerve damage.
How to check your foot for diabetes?
Check your feet daily for cuts, blisters, redness, swelling, or any changes in skin colour or sensation. Use a mirror or ask for help if needed and see a doctor regularly for foot exams and early detection of problems.
Why are diabetic foot ulcers often painless, even when severe?
Due to peripheral neuropathy, many people with diabetes lose the ability to feel pain, heat, or injury in their feet. As a result, ulcers can become large or infected before being noticed, making them more dangerous.
What is Diabetic Foot Debridement?
Debridement is the medical removal of dead or infected tissue from a wound or ulcer. It promotes healing and helps prevent the spread of infection.
Can tight shoes cause diabetic foot?
Yes, tight or ill-fitting shoes can create pressure points, leading to blisters or skin breakdown. In someone with diabetes, even a small blister can turn into a serious ulcer if unnoticed and untreated.
What role does poor circulation play in diabetic foot ulcers?
Poor blood flow (peripheral arterial disease) limits the supply of oxygen and nutrients to foot tissues, slowing healing and increasing infection risk. This makes ulcers harder to treat and more prone to complications.
Is it safe for a diabetic to walk barefoot at home?
No, walking barefoot increases the risk of stepping on sharp objects or injuring the feet without noticing. People with diabetes should always wear protective footwear, even indoors.
What is Charcot foot, and how is it related to diabetes?
Charcot foot is a rare but serious condition in which bones in the foot weaken and fracture, often without pain due to neuropathy. It can cause foot deformity and increase the risk of ulcers and disability.
What is the difference between diabetic Foot and diabetic foot ulcer symptoms?
Diabetic foot refers to general foot complications in individuals with diabetes, such as numbness, poor circulation, or deformities. A diabetic foot ulcer is a specific type of open wound, often characterized by redness, drainage, and a risk of infection.
What is the Footwear for Diabetic Foot?
Patients with diabetes should wear footwear that fits well and protects their feet. Proper shoes should have enough length, depth, and width. Studies show that therapeutic footwear is more effective than conventional shoes at reducing pressure in the forefoot area for diabetic patients.
What is Diabetic Foot Amputation?
Amputation involves removing part of the foot or leg due to severe infection, gangrene, or non-healing ulcers. It is usually a last resort when other treatments fail.
What is the Wagner Classification of Diabetic Foot?
The Wagner Classification is a system used to assess the severity of diabetic foot ulcers, ranging from a superficial ulcer (Grade 1) to full-foot gangrene (Grade 5), with Grade 0 representing a pre-ulcerative lesion or healed ulcer. It helps healthcare professionals to assess severity and guide treatment.
- Grade 0: Skin is intact, no open lesion or pre-ulcerative lesion.
- Grade 1: Superficial ulcer, partial or full-thickness ulcer.
- Grade 2: Deep ulcer extending to ligament, tendon, joint capsule, or deep fascia, without abscess or osteomyelitis.
- Grade 3: Deep ulcer with abscess, osteomyelitis, or joint sepsis.
- Grade 4: Gangrene localized to the portion of the forefoot or heel.
- Grade 5: Gangrene of the entire foot.
What are the Home Remedies for Diabetic Foot Pain?
Gently massage the feet to improve circulation, and moisturize daily to prevent cracks. Wear proper footwear, and elevate feet to reduce swelling always avoid hot soaks if wounds are present. Research suggests that olive oil enhances blood flow and reduces inflammation, aiding in healing ulcers. Additionally, honey has antibacterial properties, assists in managing wound infections, and promotes epithelial cell growth. A mixture of heated honey and olive oil in daily dressings can effectively treat diabetic foot ulcers.
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868
Appointment request - health articles
Thank you for contacting us. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Oops, there was an error sending your message. Please try again later. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Our Locations – Find the Best Hospital Near You
Metro Pillar Number C1772, Beside Avasa Hotel, Hitech City Road, Near HITEC City Metro Station, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Mythri Nagar, Beside South India Shopping Mall, Hafeezpet, Madeenaguda, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
040 4848 6868
Payment in advance for treatment at PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, Telangana, India (Pay in INR ₹)
For Bank Transfer:-
- Bank Name: HDFC
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.50200028705218
IFSC Code: HDFC0000545 - Bank Name: STATE BANK OF INDIA
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.62206858997
IFSC Code: SBIN0020299
Scan QR Code by Any Payment App (GPay, Paytm, Phonepe, BHIM, Bank Apps, Amazon, Airtel, Truecaller, Idea, Whatsapp etc).

CONTACT US
Call: +914048486868
WhatsApp: +918977889778
Email: info@pacehospitals.in
FOLLOW US
SUBSCRIBE
Subscribe to our newsletter and stay updated with the latest health information.
Subscribe to PACE Hospitals' Public Newsletter
Thank you for subscribing to PACE Hospitals' Newsletter. Stay updated with the latest health information.
Oops, there was an error. Please try again submitting your details.
ABOUT US
QUICK LINKS
Disclaimer
General information on healthcare issues is made available by PACE Hospitals through this website (www.pacehospital.com), as well as its other websites and branded social media pages. The text, videos, illustrations, photographs, quoted information, and other materials found on these websites (here by collectively referred to as "Content") are offered for informational purposes only and is neither exhaustive nor complete. Prior to forming a decision in regard to your health, consult your doctor or any another healthcare professional. PACE Hospitals does not have an obligation to update or modify the "Content" or to explain or resolve any inconsistencies therein.
The "Content" from the website of PACE Hospitals or from its branded social media pages might include any adult explicit "Content" which is deemed exclusively medical or health-related and not otherwise. Publishing material or making references to specific sources, such as to any particular therapies, goods, drugs, practises, doctors, nurses, other healthcare professionals, diagnoses or procedures is done purely for informational purposes and does not reflect any endorsement by PACE Hospitals – your trusted hospital near me.