Asthma - Symptoms, Causes, Types, Diagnosis and Treatment
Asthma definition
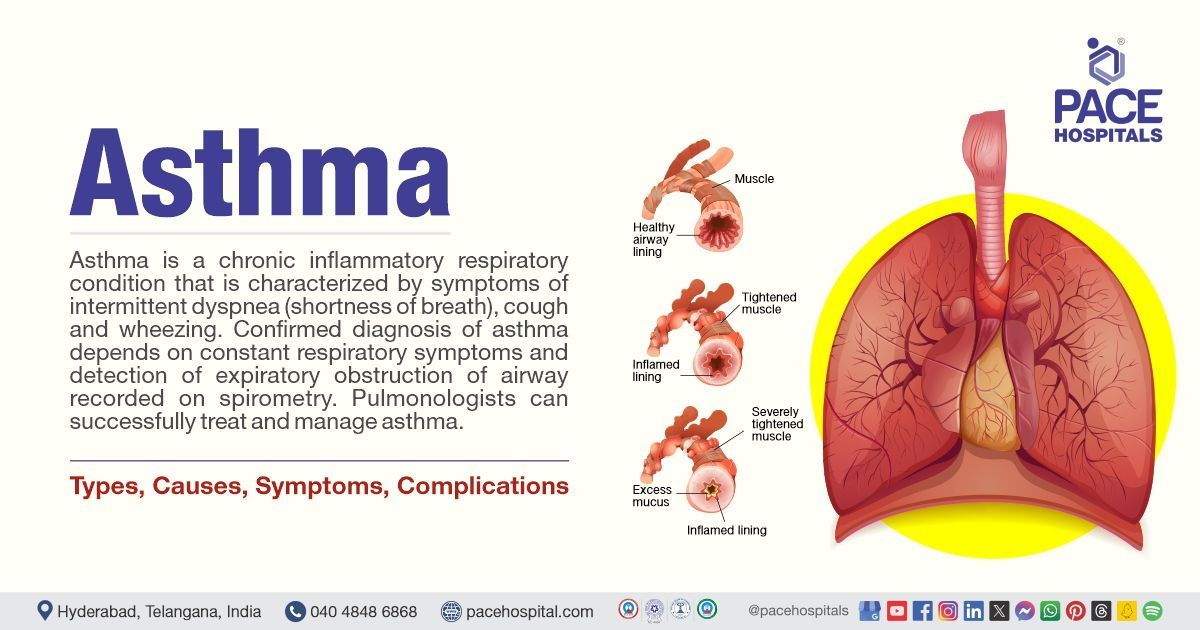
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory respiratory condition that is characterized by symptoms of intermittent dyspnea (shortness of breath), cough, and wheezing. Distinguishing asthma from other respiratory illnesses can be challenging because of the non-specific nature of these symptoms. Asthma that develops in childhood involves a complex interaction between genetic and environmental factors. A confirmed diagnosis of asthma depends on constant respiratory symptoms and detection of expiratory obstruction of the airway recorded on spirometry. Physicians prioritize symptomatic control and preventing future progression through tailored treatment by considering the severity and potential risk in a systematic and step wise approach.
Pulmonologists can successfully treat and manage asthma.
Asthma meaning
The actual term asthma is derived from the Greek word “aazein” which means to exhale with an open mouth, to pant. The word asthma appeared for the first time in the Iliad with the meaning of short drawn breath, but the Corpus Hippocraticum was the earliest term from where the medical term was found.
Prevalence of asthma
Asthma prevalence worldwide
With increasing prevalence rates in many countries, asthma is a substantial global health problem. As per World Health Organization (WHO) reports, 30 crore people have asthma, and two lakh fifty-five thousand (255000) people died due to asthma in the year 2005.
Prevalence of asthma in India
Asthma prevalence in India is estimated to be 3% (3 crores) with a prevalence of 2.4 percent in adults aged more than 15 years and between 4 and 20 percent in children. About 57,000 deaths attributed to asthma were reported in the year 2004. It has become one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in rural India and is predicted to increase in the coming year.

Types of asthma
Asthma is no longer thought of as a single disease, and it is categorized into different types based on the factors causing it. Following are some of the types of bronchial asthma:
- Allergic asthma - Also called atopic asthma, it is the onset or development of asthma symptoms due to allergic reactions caused by inhaled allergens. Allergens include pollen, dust, animal dander, and mold. These allergens are harmless substances that are mistaken for harmful and attacked by the body’s immune system. The immune response leads to symptoms of asthma.
- Non allergic asthma - Also called non-atopic asthma. This type of asthma is not triggered by allergens such as pollen or dust, it often develops later in life and is triggered by factors that are not allergens such as household chemicals, certain medications, infections such as cold and flu, outdoor air pollution, and tobacco smoking.
- Seasonal asthma - This type of asthma develops only at certain times of year such as during hay fever season or when the weather is cold.
- Occupational asthma or work-related asthma - Symptoms of asthma that occur due to exposure to certain chemicals or irritants at the workplace are known as occupational asthma.
- Childhood onset asthma - Symptoms of asthma that develop during childhood are known as childhood asthma. This is the most common type of asthma.
- Adult-onset asthma - Symptoms of asthma that develop or present for the first time during adulthood, with the age varying from 12 to 65 years are termed adult-onset asthma.
- Eosinophilic asthma - High levels of eosinophils in the airway cause eosinophilic asthma, it is a severe type of asthma.
- Exercise induced asthma - This type of asthma occurs when the airways tighten, and airflow gets obstructed during or after exercise.
Asthma Phenotypes and Endotypes
Asthma is a heterogeneous disease and since early childhood, depending on the phenotypes and endotypes many classifications have been proposed. A deep understanding of the endotype and phenotype of the patient gives an idea regarding a tailored therapeutic approach.
- Phenotypes include clinical features of asthma-like age of onset, triggers, comorbidities, and response to treatment over a period of time.
- Endotypes are difficult to define, these include immunopathological mechanisms of the disease.
Asthma phenotypes classification
Five major phenotypes in adult patients include
- Mild to early onset allergic disease
- Moderate early onset allergic disease
- Late onset eosinophilic non allergic disease
- Severe early onset eosinophilic allergic disease
- Late onset non allergic neutrophilic severe asthma with fixed airflow obstruction.
Asthma endotypes classification
Four major endotypes of asthma include:
- Early onset mild allergic asthma
- Moderate to severe allergic remodeling asthma
- Late onset allergic non eosinophilic asthma and
- Late onset allergic eosinophilic asthma.

Asthma symptoms
Symptoms of asthma occur intermittently and last for about a few hours to days. These symptoms resolve when the triggers are removed or with the administration of medications.
Common asthma signs and symptoms include
- Shortness of breath (SOB)
- Cough
- Tightness of chest
- Decrease in peak flow meter
- Waking up at night due to a worsening of cough
Severe asthma symptoms
Symptoms of severe asthma are often persistent, and these symptoms are observed at least once a day. Below are some of the asthma attack symptoms observed in patients:
- Breathlessness which is persistent and continuous
- Heavy feeling in the chest
- Wheezing
- Severe cough
- Difficulty in speaking
- Allergic responses to pollen and dust
- Extreme sensitivity to scents and smell
- Blue lips or fingers
- Rapid heart rate
- Drowsiness
- Confusion
- Dizziness

Asthma causes
The exact cause of asthma is not known, and the causes may vary from person to person, however, asthma can develop when the body’s defense system reacts strongly to a new substance in the lungs. Asthma usually develops during childhood (called childhood asthma); however, some people don’t show signs of asthma until adulthood (adulthood asthma). Many factors like allergens in the environment, viral infections, and family history work together to develop asthma.
Several factors have been linked to the development of asthma although it is difficult to identify the actual cause. Below are some of the causes of bronchial asthma:
- Family history: Asthma is more likely to develop when there is a family history of asthma, that is if one of the family members, like a father or a sibling, has asthma.
- Allergy conditions: Patients with allergic conditions such as eczema and rhinitis are more prone to develop asthma.
- Lifestyle factors: A sedentary lifestyle in urban areas increases the prevalence of asthma.
- Development of the lungs can be affected by certain events in childhood such as low birth weight, prematurity, exposure to smoke, and air pollution. When the lungs are not developed fully, they do not function effectively and increase the prevalence of asthma.
- Being overweight or obese in children or adults also causes asthma.
- Exposure to environmental allergens and irritants including outdoor and indoor, air pollution, dust, mites, molds, and exposure to chemicals in occupational areas also increases the risk for the development of asthma.
Asthma risk factors
Asthma is believed to result from the interaction between genetic and environmental factors. Several risk factors contribute to asthma, and these factors of bronchial asthma are described below:
- Atopy: It is a genetic tendency to develop allergic diseases like allergic rhinitis, and asthma.
- Tobacco: Smoking is a known risk factor for asthma. It is more difficult to control asthma in asthmatic smokers than non-smokers with asthma.
- Pollution: Exposure to outdoor and indoor air pollution remains a significant risk factor.
- Obesity: Many studies indicated that asthma is more likely to develop in obese patients
- Occupational risk factors: Exposure to chemicals or pollutants at workplaces is a potential risk factor for asthmatic patients.
- Microbes: Asthmatic patients are susceptible to viral and bacterial infections.
- Stress: Recent studies suggested that there are some potential mechanisms that underly the association between chronic psychosocial stress and asthma genetics.

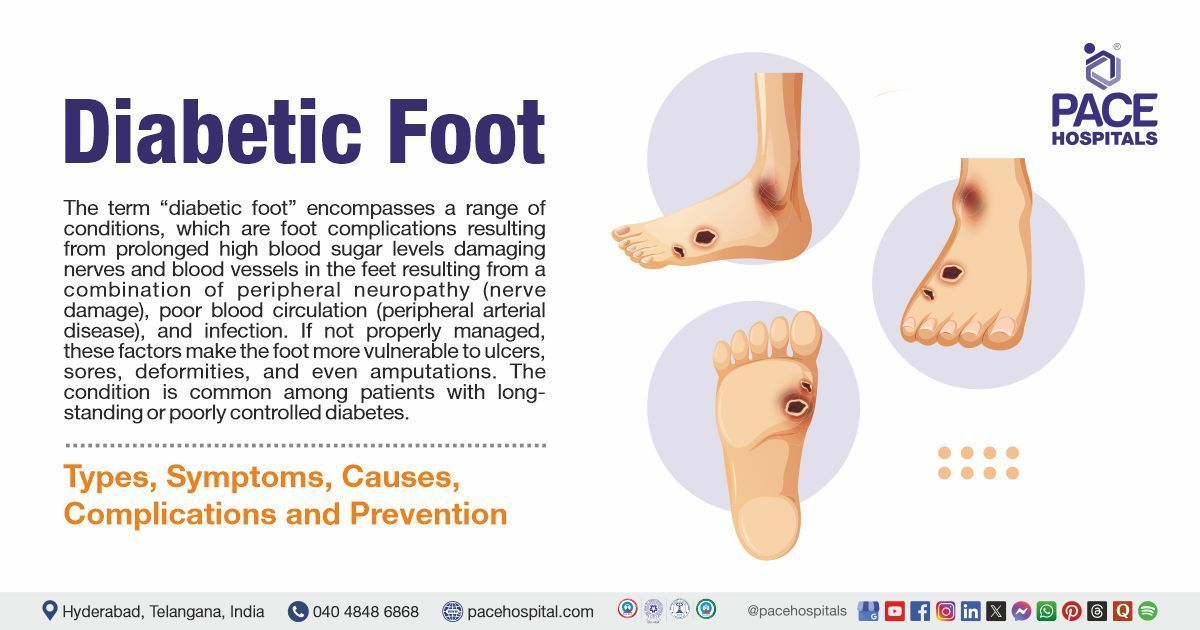
Complications of asthma
The complications of bronchial asthma include complications that are disease related and adverse effects of glucocorticoids and endotracheal intubation. Some of the common complications associated with asthma are as follows:
- Decline in lung function: Airway remodeling (structural airway changes and inflammation) in asthma results in declined lung function.
- Osteoporosis: Patients with asthma may develop Osteoporosis, a condition where bone becomes weak and brittle.
- Infections: Asthma increases the risk of infection due to damaged airways.
- Hypertension (high blood pressure): Chronic inflammation in asthma can contribute to high blood pressure over a prolonged period.
- Diabetes: Asthma can increase the risk of type 1 and type 2 diabetes due to systemic inflammation
- Sleep disorder: Respiratory disturbances during sleep are common. Severe coughing and wheezing in asthma cause frequent arousals from sleep at nighttime.
- Obstructive sleep apnea: Asthmatic patients are more prone to develop obstructive sleep apnea.
- Mood disorder: Asthma increases the risk of mood disorders like anxiety and depression.
- Cardiac arrest: Inflammation in asthma over time may build up plaque which leads to cardiac arrest, heart attack, etc.
- Glaucoma: Inhaling steroids increases the risk of glaucoma which is a condition where the optic nerve that connects the eye to the brain gets damaged.
- Respiratory failure: Asthma over time causes respiratory failure.
- Pneumothorax: In patients with asthma, bronchospasm increases pleural pressure and causes pneumothorax which is a life-threatening condition. Pneumothorax is the collection of air outside the lungs within the pleural cavity).
Asthma diagnosis
Early diagnosis and treatment of asthma is necessary to prevent the progression of asthma. General physicians and pulmonologists develop a definitive diagnosis. Following are some of the tests to diagnose asthma:
- Medical history
- Physical examination
- Laboratory testing
- Complete blood cell (CBC) count
- Serum alpha 1 antitrypsin level
- Seum IgE
- Imaging tests
- Chest radiographs
- Computed tomography (CT)
- Pulmonary function test
- Spirometry
- Bronchoprovocation testing
- Peak flow meter
- Exhaled nitic oxide
Asthma treatment
Treatment of asthma depends on the age, severity of the disease, and how the body responds to the specific drug.
Nonpharmacological treatment of asthma
Drug therapy is important in the treatment of asthma and in keeping the disease under control. But some non-pharmacological interventions are also suggested in the treatment of asthma. Nonpharmacological management of asthma includes:
- Regular exercise
- Maintaining healthy body weight
- Proper diet
- Stopping smoking
- Relaxation and breathing techniques
Pharmacological treatment of asthma
Treatment mainly focuses on providing education, regular assessment of symptoms, providing access to fast acting bronchodilators and controller medications. The following are the treatment options available:
- Quick relief asthma medication
- Inhaled short acting beta 2 agonist
- Oral corticosteroids
- Short acting anticholinergics
- Long term asthma control medications
- Corticosteroids
- Biologic medications
- Leukotriene modifiers
- Inhaled mast cell stabilizers
- Inhaled long-acting bronchodilators
- Allergy shots.
Treatment of asthma in pregnancy
Below are some of the measures that can be followed for asthma treatment during pregnancy:
- Continued use of preventer inhalers that are prescribed during pregnancy
- Avoiding smoke
- Regular exercise and a healthy diet
- Avoiding allergens that trigger asthma such as pet fur and pollen
Types of asthma inhalers
Inhalers are devices that deliver or incorporate medications in a fine mist right into the lungs. These are considered as the first line treatments for asthma and can be used to treat other respiratory conditions.
Following are some of the common types of inhalers:
- Metered dose inhaler – It is the most common type of inhaler, and this is held in front or put into the mouth when the medicine is released in puffs. A chemical is used to push forward the medicine into the lungs.
- Nebulizer – In this type of inhaler medicine is released as fine liquid mist, and the mouthpiece delivers the medicine. A nebulizer is often recommended to patients who cannot use metered dose inhalers.
- Dry powder inhaler – This inhaler are used by children and adults. Medicines such as dry powder is released when patients breathe in at the mouthpiece.
Asthma prevention
The exact cause of asthma is unknown; therefore, it may not be possible to prevent asthma, but the severity and further progression of the disease can be prevented.
Further progression of the disease severity can be prevented by adopting a stepwise approach to disease management and strategies to prevent risk factors. Essential parts of asthma management include patient education, monitoring the symptoms to prevent the progression of the disease, controlling factors that trigger asthma, managing co-morbid conditions, and following a stepwise treatment approach.
The severity of asthma varies and differs among individuals and different age groups therefore it is essential to monitor the effectiveness of asthma control to suggest the required adjustments or modifications in a treatment plan.
Below are some of the measures to prevent asthma from further progression and severity:
- Encouraging patients to build a healthy lifestyle by educating them about the potential triggers of asthma.
- Recognizing early warning signs of an asthma attack and seeking medical attention when necessary.
- Emphasizing the importance of medication adherence to prevent further progression of disease severity.
- Individuals with active asthma are recommended for routine follow up visits every six months. During these follow-ups physicians assess lung function, exacerbations, the efficacy of medications, quality of life, and patient satisfaction.
Difference between Asthma and COPD
Asthma vs COPD
Both asthma and
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are respiratory diseases that affect breathing, but they have some key differences. The following are the parameters that differentiate asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD):
| Parameters | Asthma | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | It is a chronic inflammatory respiratory condition characterized by dyspnea, cough, and wheezing | It is a common respiratory condition that is characterized by progressive airflow limitation and tissue destruction. |
| Symptom | Shortness of breath, coughing, wheezing, and chest tightness. | Dyspnea, chronic cough with sputum production, wheezing, chest tightness. |
| Causes | Causes are unknown but there are some factors that trigger asthma such as allergens, dust, pollen, air pollution, and mold. | Causes include prolonged exposure to harmful gases and smoking. Environmental and occupational exposure, and deficiency of alpha 1 anti-trypsin are the other causes that cause chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. |
| Treatment | Treatment mainly focuses on providing education, regular assessment of symptoms, providing access to fast acting bronchodilators and controller medications. | Treatment includes drug classes such as bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, and systemic glucocorticoids. |
Difference between asthma and bronchitis
Asthma vs bronchitis
Asthma and bronchitis both are respiratory conditions that present cough as their symptom, but they have some key differences. Below are some of the factors that differentiate between asthma and bronchitis.
| Parameters | Asthma | Bronchitis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | It is a chronic inflammatory respiratory condition characterized by dyspnea, cough, and wheezing | It is a condition which is characterized by inflammation of bronchial tubes that cause coughing. Cough is often associated with the production of sputum. |
| Symptom | Shortness of breath, coughing, wheezing, and chest tightness. | Cough with mucus, chest pain, tiredness, shortness of breath, wheezing. |
| Causes | Causes are unknown but there are some factors that trigger asthma such as allergens, dust, pollen, air pollution, and mold. | Acute bronchitis is caused by viral infections such as cold, flu, it is also caused by viral infections. Chronic bronchitis is caused by several factors like smoking, exposure to fumes, family history of asthma or other respiratory conditions. |
| Treatment | Treatment mainly focuses on providing education, regular assessment of symptoms, providing access to fast acting bronchodilators and controller medications. | Treatment includes oxygen therapy, pulmonary rehabilitation, and a few lifestyle modifications like smoking cessation. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Asthma
Is asthma curable?
There is no cure for asthma, but treatment helps in decreasing symptoms, preventing complications and helps in slowdown of disease. Treatment involves the use of inhalers that provide relief from symptoms. Tablets are prescribed in severe cases and when inhalers alone cannot control symptoms.
Are there any surgical options for asthma treatment?
Surgical treatment of asthma includes the following classifications:
- Tissue therapy includes glomectomy (removal of the glomus cell or glomus body), pulmonary roots denervation, ganglionectomy (removal of a ganglion or ganglion cyst), and vagotomy (removal or excision of vagus) as first generation.
- Intervention in the vegetative nervous system like implantation of neurostimulators of Sino carotid, vagus, and diaphragmal nerves, sympathetic trunks as second generation
- Implants of programmed microchips as third generation therapy.
What is the role of immunotherapy in asthma treatment?
The role of immunotherapy in the treatment of asthma:
To treat asthma, immunotherapy uses house dust mite, this allergen improves symptoms of asthma and airway hyperresponsiveness and decreases drug needs. With subcutaneous immunotherapy long term use of medications that treat asthma is reduced. It improves quality of life and immunotherapy reduces the use of quick relief providing drug class (bronchodilators). The effect of immunotherapy lasts for about a year and the progression of disease can be prevented.
What are the treatment options available for asthma?
The treatment goal of asthma is to achieve and maintain control of the disease to prevent the worsening of symptoms and decrease the rate of morbidity and mortality. Drug treatment can be divided as
- Controllers (these agents control the disease by anti-inflammatory action). Examples include leukotriene receptor antagonist (LRA), inhaled corticosteroids (ICS), and long-acting muscarinic receptor antagonist (LAMA).
- Reliever medications including rapid acting inhaled beta 2 agonist and inhaled anticholinergics
- Allergen specific immunotherapy is also suggested for patients with allergic asthma.
What are controller and reliever medications in asthma?
Controller and reliever are the two types of medications used in the treatment of asthma.
- Controller medications: Inflammation in the lungs is reduced by this medication, these medications include steroids and can be used every day.
- Reliever medications: These medications relieve acute symptoms by clearing airways, this treatment is enough to control the disease. During exercise, these medications can be used to prevent asthma attacks.
What is bronchial thermoplasty and is it suitable for all asthma conditions?
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the year 2010 approved bronchial thermoplasty, which is a device based nonpharmacological treatment for severe asthma. In this procedure, radiofrequency energy is released during bronchoscopy to selectively separate or remove airway smooth muscle. The right middle lobe part of the lung is not treated using bronchial thermoplasty.
What is spirometry, how does it help diagnose asthma?
Spirometry is a pulmonary function test that measures the amount of air inhaled or exhaled. It measures forced expiratory volume in 1 sec (FEV) and forced vital capacity (FVC) by measuring maximum inhalation which is followed by rapid and forced exhalation into a spirometer. On the spirometer, asthma presents an obstructive pattern indicated by a reduced forced expiratory volume (FEV) to forced vital capacity (FVC) ratio.
Is allergy testing necessary for asthma diagnosis?
Yes, allergy testing is important for the diagnosis of asthma. About 2 to 3 crores of people are affected by asthma which commonly has an allergic component. Allergy testing has many indications of which persistent asthma is one of them. This test does not directly diagnose asthma, but it identifies allergens that trigger asthma.
Will asthma show upon a chest x ray?
Chest X-rays are usually normal in asthma patients, however during exacerbations abnormal findings like hyperinflation and bronchial thickening may be observed. Chest X-ray is suggested for patients aged 40 years or older with new onset or moderate or severe asthma. It also rules out conditions that imitate asthma mediastinal mass with tracheal compression.
How to treat cough variant asthma?
Treatment of cough variant asthma is similar to the treatment of asthma. Inhaled corticosteroid is the first line of treatment in cough variant asthma. When monotherapy with inhaled corticosteroid is insufficient other agents such as long-acting beta 2 agonist and leukotriene receptor antagonist are prescribed.
What are the goals of asthma management?
The goals of asthma management include preventing symptoms, maintaining pulmonary function and activity levels normal, preventing exacerbations of asthma and monitoring adverse effects of medications.
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868
Appointment request - health articles
Thank you for contacting us. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Oops, there was an error sending your message. Please try again later. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Our Locations – Find the Best Hospital Near You
Metro Pillar Number C1772, Beside Avasa Hotel, Hitech City Road, Near HITEC City Metro Station, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Mythri Nagar, Beside South India Shopping Mall, Hafeezpet, Madeenaguda, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
040 4848 6868
Payment in advance for treatment at PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, Telangana, India (Pay in INR ₹)
For Bank Transfer:-
- Bank Name: HDFC
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.50200028705218
IFSC Code: HDFC0000545 - Bank Name: STATE BANK OF INDIA
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.62206858997
IFSC Code: SBIN0020299
Scan QR Code by Any Payment App (GPay, Paytm, Phonepe, BHIM, Bank Apps, Amazon, Airtel, Truecaller, Idea, Whatsapp etc).

CONTACT US
Call: +914048486868
WhatsApp: +918977889778
Email: info@pacehospitals.in
FOLLOW US
SUBSCRIBE
Subscribe to our newsletter and stay updated with the latest health information.
Subscribe to PACE Hospitals' Public Newsletter
Thank you for subscribing to PACE Hospitals' Newsletter. Stay updated with the latest health information.
Oops, there was an error. Please try again submitting your details.
ABOUT US
QUICK LINKS
Disclaimer
General information on healthcare issues is made available by PACE Hospitals through this website (www.pacehospital.com), as well as its other websites and branded social media pages. The text, videos, illustrations, photographs, quoted information, and other materials found on these websites (here by collectively referred to as "Content") are offered for informational purposes only and is neither exhaustive nor complete. Prior to forming a decision in regard to your health, consult your doctor or any another healthcare professional. PACE Hospitals does not have an obligation to update or modify the "Content" or to explain or resolve any inconsistencies therein.
The "Content" from the website of PACE Hospitals or from its branded social media pages might include any adult explicit "Content" which is deemed exclusively medical or health-related and not otherwise. Publishing material or making references to specific sources, such as to any particular therapies, goods, drugs, practises, doctors, nurses, other healthcare professionals, diagnoses or procedures is done purely for informational purposes and does not reflect any endorsement by PACE Hospitals – your trusted hospital near me.