Blood Clots Can Be Deadly – Understanding Thrombosis
PACE Hospitals
Written by: Editorial Team
Medically reviewed by: Dr. Lakshmi Kumar Chalamarla - Consultant Senior Interventional Radiologist & Abdominal Imaging Specialist
Overview: Why Blood Clots Are a Silent Killer
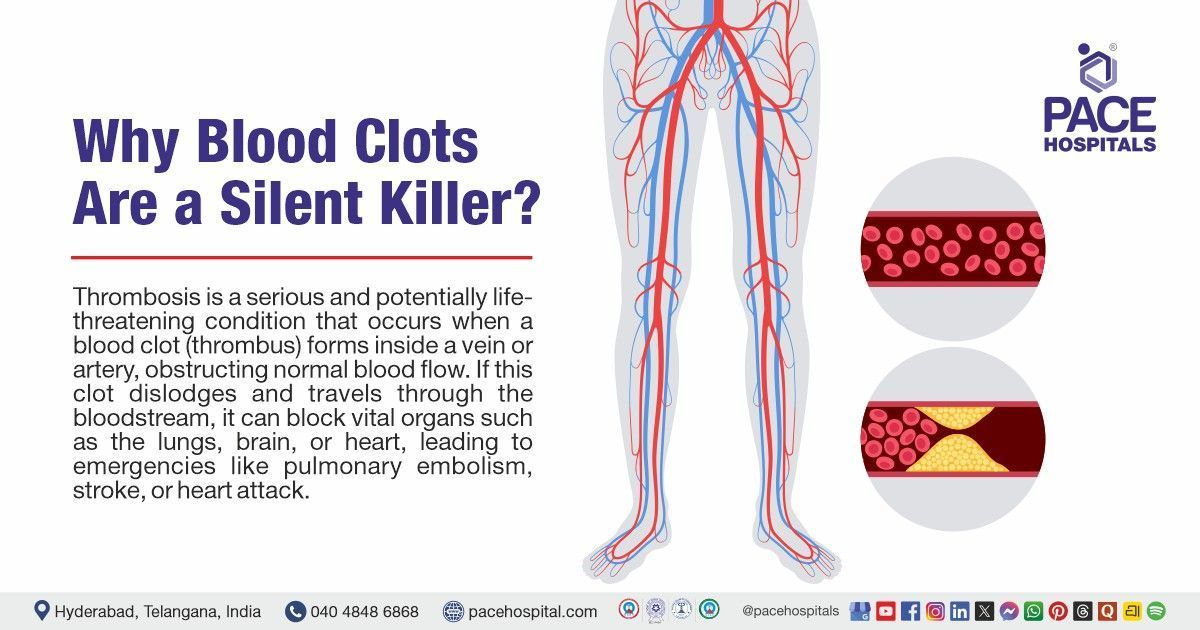
Thrombosis is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) forms inside a vein or artery, obstructing normal blood flow. If this clot dislodges and travels through the bloodstream, it can block vital organs such as the lungs, brain, or heart, leading to emergencies like pulmonary embolism, stroke, or heart attack.
At PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, our vascular specialists, cardiologists, and critical care teams work together to diagnose and manage thrombosis with the latest imaging, clot-dissolving medications, and minimally invasive procedures. Early recognition and timely treatment can save lives and prevent irreversible complications.
What Is Thrombosis?
Thrombosis develops when a blood clot forms in a vein (venous thrombosis) or artery (arterial thrombosis), obstructing blood flow. Gradually, this can give rise to tissue damage, swelling, or even organ failure.
Common medical terms related to thrombosis include:
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): The development of a blood clot within the deep veins, most commonly found in the legs or pelvic region.
- Pulmonary Embolism (PE): A serious and potentially fatal condition that occurs when a blood clot breaks loose and travels to the lungs, blocking blood flow.
- Post-Thrombotic Syndrome: A long-term complication of DVT that leads to persistent leg swelling, heaviness, and pain due to vein damage.
- Thromboembolism: Is a vascular disorder where a blood clot, called thrombus, forms and then a piece breaks off to travel through the bloodstream, lodging in a vessel and causing a blockage (embolism).
Risk Factors for Thrombosis
Certain lifestyle habits, even medical conditions, or surgical situations can enhance the risk of developing blood clots.
Common Risk Factors Include:
- Injury or Trauma: Any injury that damages veins or arteries can trigger clot formation as the body attempts to heal.
- Obesity: Excess body mass can increases pressure on veins of the legs and pelvis, this can slow down blood flow and give rise to clots.
- Family History: A family history of blood clots increases your personal risk.
- Smoking: Nicotine and carbon monoxide damage blood vessel linings, making platelets stickier and increasing clot formation.
- Prolonged Immobility: Sitting for long hours, especially on long flights or during illness, slows blood flow in the legs, allowing clots to form.
- Hormonal Factors
- Oral contraceptives and hormone replacement therapy increase clotting risk, especially in smokers.
- Pregnancy naturally raises clotting tendency due to hormonal changes and reduced blood flow from the growing uterus.
- Surgery and Hospital Stay : Major surgeries such as joint replacements or abdominal surgery, can lead to vein injury or long bed rest, which promotes clot formation.
- Chronic Diseases
- Cancer and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) cause hypercoagulability (increased clotting tendency).
- Heart failure reduces circulation efficiency.
- Diabetes and high cholesterol levels can damage blood vessels.
If you have multiple risk factors, discuss a preventive plan with your doctor at PACE Hospitals.
Thrombosis and Pregnancy
Pregnancy naturally increases clotting tendency as a protective mechanism to prevent bleeding during childbirth. However, this can become harmful when:
- The growing uterus compresses pelvic veins, slowing blood flow.
- Hormonal changes increase clotting factors.
- C-section deliveries or prolonged bed rest further may raise risk.
The danger remains up to six weeks postpartum. Early recognition and mobility after delivery help reduce risk. At PACE Hospitals, obstetric and vascular teams monitor high-risk pregnancies for early signs of thrombosis.
Symptoms of Thrombosis
Symptoms can vary based on the clot's location and severity. In some cases, no symptoms occur until a pulmonary embolism develops, which can be fatal.
Common Warning Signs of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT):
- Swelling in one leg (foot, ankle, or calf) or Bulged veins in the legs
- Persistent cramping or throbbing pain in the calf or thigh region
- Warmth or tenderness feeling in the affected area
- Red/purple or bluish/greenish skin discoloration
- Unexplained and triggering pain in foot or ankle
Signs of Pulmonary Embolism (PE):
- Sudden shortness of breath
- Rapid heartbeat
- Chest pain (worse on deep breathing)
- Coughing up blood
- Dizziness or fainting
If any of these symptoms arises, seek emergency care immediately. A pulmonary embolism can be life-threatening within minutes.
How Thrombosis Is Diagnosed at PACE Hospitals
Accurate diagnosis is critical because thrombosis can mimic other conditions like muscle strain or infection.
At PACE Hospitals Hyderabad, our specialists apply advanced diagnostic techniques:
- Doppler Ultrasound:
- Non-invasive imaging technique used to detect clots in veins or arteries.
- D-Dimer Blood Test:
- It is one of the common lab test method that measures clot breakdown fragments and indication of it high levels suggest active clotting.
- Venography or CT Venogram:
- Provides a complete and detailed X-ray or CT visualization of veins.
- CT Pulmonary Angiography:
- It is Gold-standard test for diagnosing pulmonary embolism.
- MRI Venography:
- Useful to detect for clots in pelvic or abdominal veins.
These technologies and methods help confirm the diagnosis and identify clot location, size, and risk of embolization.
Treatment Options for Thrombosis
The main goals to treat blood clot is to stop the clot from growing, reduce the chance of a pulmonary embolism, and stop additional clots formation.
- Anticoagulant Medications
- These medicines usage prevents and checks clot growth and helps the body dissolving it naturally.
- Regular monitoring ensures safe dosage and prevents bleeding complications.
- Compression Stockings
- Specially designed comfortable medical grade stockings improve blood flow and prevent leg swelling.
- They also lower the risk of developing post-thrombotic syndrome (chronic leg pain and discoloration).
- IVC Filter (Inferior Vena Cava Filter)
- A small metal filter inserted into the large abdominal vein.
- It traps clots before they reach the lungs, typically used when anticoagulants are contraindicated.
- Thrombolytic Therapy (Clot-Dissolving Drug Usage)
- It is used in emergency situations to break apart big clots.
- Administered intravenously or by a catheter into the clot.
- Surgical or Catheter-Based Thrombectomy
- In severe or critical cases, a minimally invasive catheter-directed procedure removes the clot.
At PACE Hospitals, team of interventional radiologists and vascular surgeons use state-of-the-art techniques for safe, targeted clot removal with minimal recovery time.
Complications of Untreated Thrombosis
If left untreated, thrombosis can lead to serious and sometimes fatal complications. Major Complications are:
- Pulmonary Embolism (PE): A life-threatening medical condition that arises when a blood clot travels to the lungs and blocks an artery, leading to sudden chest pain, breathlessness, or collapse of lungs.
- Post-Thrombotic Syndrome (PTS): A long-term issue which happens after deep vein thrombosis (DVT) that causes leg swelling, pain, and skin discolouration due to vein valve damage.
- Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI): A long-term medical condition that occurs when the blood circulation in the leg veins is reduced, often resulting in venous leg ulcers, skin darkening, or varicose veins.
- Recurrent Thrombosis: The return of blood clots in the same or different veins, especially when risk factors remain untreated such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE).
Thrombosis Management at PACE Hospitals Hyderabad
PACE Hospitals provides top and best comprehensive thrombosis care through a multidisciplinary team of healthcare experts involving:
- Vascular medicine specialists and Endovascular surgeons
- Interventional radiologists
- Cardiologists, Cardiac Surgeons and hematologists
- Critical care experts
Our Services Include:
- 24/7 Emergency Pulmonary Embolism Management
- Advanced Imaging Tests such as Doppler Ultrasound, CT scan, and MRI venography
- Endovascular clot removal procedures
- Personalised anticoagulant therapy plans
- Long-term rehabilitation and follow-up programs
- We target not only to treat thrombosis but also to prevent recurrence through lifestyle counseling, patient-focused early mobility programs, and vascular health education.
Cost of Thrombosis Diagnosis and Treatment in Hyderabad
- The Doppler Ultrasound and D-Dimer test generally cost between ₹3,000 and ₹6,000, depending on the diagnostic center and location.
- A CT Venogram or Pulmonary Angiogram diagnosis test is generally priced between ₹10,000 and ₹20,000, based on the hospital setup and imaging technology used.
- Anticoagulant medications, which are essential for ongoing treatment and prevention of blood clots, may cost around ₹1,500 to ₹4,000 per month.
- For patients requiring IVC filter placement to prevent clot migration, the procedure cost ranges from ₹1,00,000 to ₹1,50,000 (USD $1,200–$1,800).
- Advanced procedures like catheter-directed thrombectomy or thrombolysis usually range between ₹1,50,000 and ₹2,50,000 (USD $1,800–$3,000), depending on the case complexity and hospital facilities.
PACE Hospitals offers insurance support, EMI options, and personalized thrombosis care packages at its both location - Hitech City and Madinaguda branches.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Frozen Shoulder
What is thrombosis?
Thrombosis occurs when a blood clot develop inside a vein or artery, blocking blood flow. It can progress to serious complications like pulmonary embolism or stroke.
What are the early signs of thrombosis?
Common symptoms include leg swelling, cramping pain, skin warmth, vein changes and discoloration. Seek medical help if you experience sudden breathlessness or chest pain.
What causes blood clots to form?
Injury, immobility, obesity, pregnancy, smoking, and certain medical conditions (like cancer or heart failure) increase clot formation risk.
How is thrombosis diagnosed?
Through Doppler ultrasound, D-Dimer tests, CT scans, or MRI venography. PACE Hospitals provides full diagnostic facilities for accurate detection.
What are the dangers of untreated thrombosis?
It can cause pulmonary embolism, chronic venous insufficiency, or post-thrombotic syndrome, leading to long-term complications or death.
How is thrombosis treated?
Treatment includes blood thinners, compression stockings, IVC filters, or minimally invasive clot removal at specialized vascular centres.
Can surgery cause thrombosis?
Yes. Major surgeries such as joint replacements or abdominal procedures, increase risk due to immobility and vessel injury.
Is thrombosis preventable?
Yes. Regular movement, hydration, quitting smoking, weight control, and preventive medications can significantly reduce your risk.
What is the cost of thrombosis treatment in Hyderabad?
Treatment at PACE Hospitals ranges from ₹3,000 for diagnostics to ₹2.5 lakh for advanced endovascular procedures, depending on severity.
Why choose PACE Hospitals for thrombosis care?
PACE Hospitals offers 24×7 emergency thrombosis management, advanced vascular imaging, minimally invasive treatment, and long-term prevention programs.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868