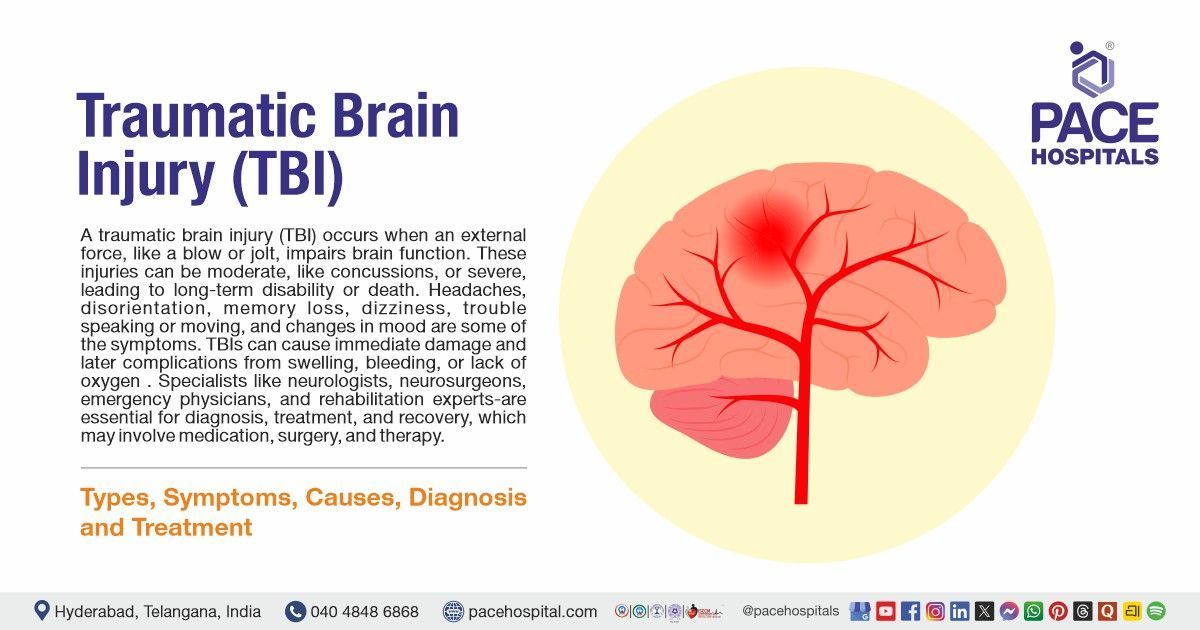
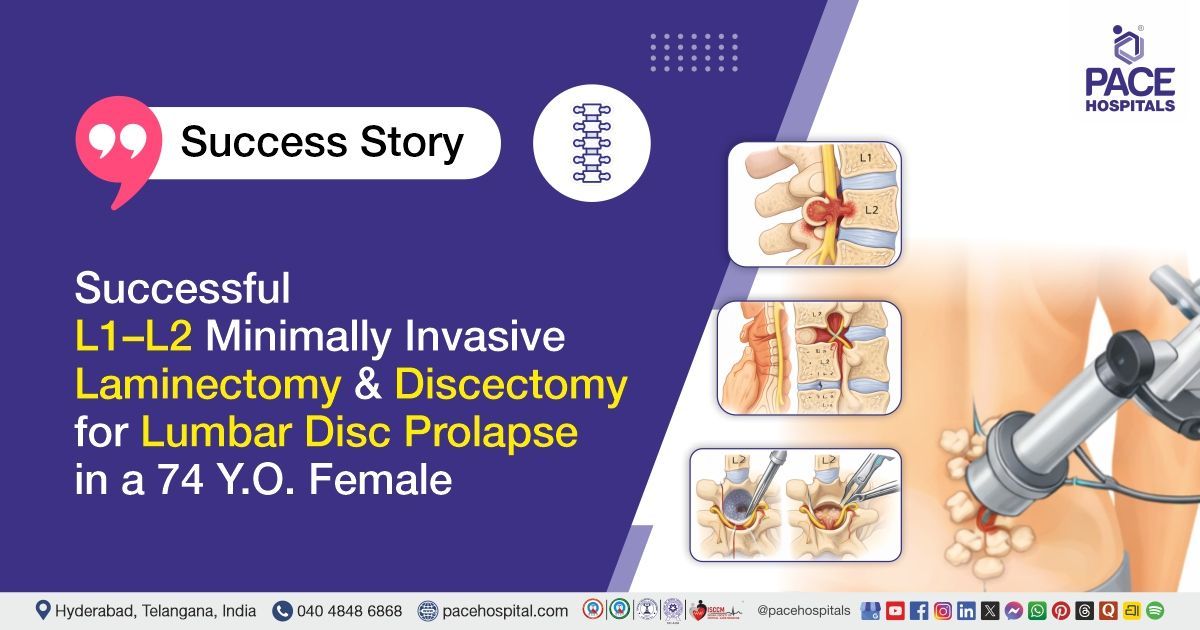
Brain cancer - Symptoms, Types, Causes, Complications, Treatment
PACE Hospitals
Brain cancer definition
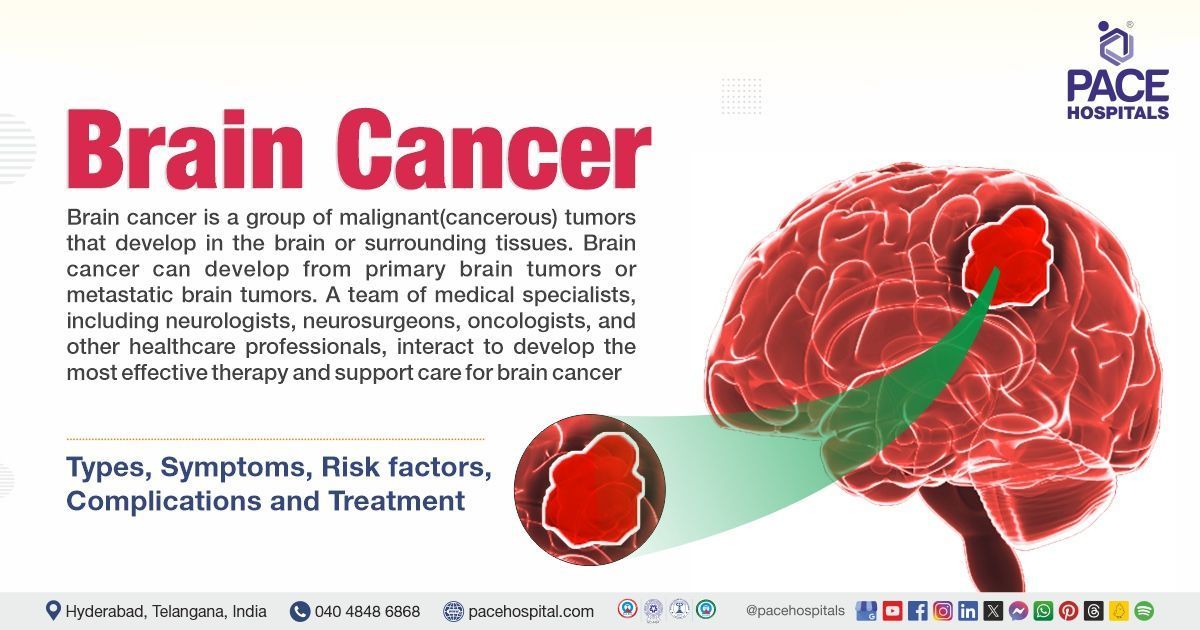
Brain cancer, also referred to as intracranial neoplasms, is a group of malignant(cancerous) tumors that develop in the brain or surrounding tissues. Cancer is a group of diseases identified by uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells in the body. These cells can become tumors and interrupt the functioning of organs and tissue. Brain cancer can develop from brain tissue itself known as a primary brain tumor or because of cancer spreading from another part of the body known as a metastatic brain tumor.
A team of medical specialists, including neurologists, neurosurgeons, oncologists, and other healthcare professionals interact to develop the most effective therapy and support care for brain cancer.
Brain cancer meaning
Brain cancer is the combination of two words in which
- The word “brain” is a derivation from Old English “braegen," which originated from the Proto-Germanic source “bragnan” (source also of Middle Low German bregen, Old Frisian and Dutch brein). All the derivations describe it as a “soft, greyish mass which fills the cranium of any vertebrate."
- The term "cancer" is taken from the Greek word “karkinos”, which means "crab" and "tumor". Hippocrates, a Greek physician (460-370 BC), is credited with using the word approximately 400 BC to describe tumors.
Brain Cancer Statistics
Brain cancer statistics worldwide
Brain cancer is a major health concern worldwide, but its prevalence and incidence vary by place and population (as of September 2021). Brain cancer accounts for nearly two percent of all cancer cases worldwide. In 2019, 347,992 newly identified cases of brain cancer were reported globally, with 187,491 (54%) males and 160,501 (46%) females being diagnosed.
Brain cancer statistics in India
In India, the incidence of central nervous system (CNS) tumors ranges between 5 and 10 per 100,000 people, with an increasing trend, and constitutes 2% of all malignancies (cancers). Male incidence rates for brain cancer range from 2.53 (Chennai registry) to 4.14 (Delhi registry), while female incidence rates vary from 1.46 (Bhopal registry) to 2.66 (Delhi registry). Brain cancer incidence rates have increased in both sexes across all registries except in Delhi. The incidence increased for the Bhopal registry and decreased for the Delhi registry, but was not statistically significant. In Mumbai, Chennai, and Bangalore registries, there was a substantial increase of over 3% in age-adjusted incidence rates of brain cancers in both sexes.
Brain Cancer Types
Brain cancer, often known as a brain tumor, is the abnormal growth of cells in the brain. These tumors can be either benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Brain Cancers (Typically malignant) include the following types:
- Chordoma
- Chondrosarcoma
- Medulloblastoma
- Olfactory neuroblastoma
- Lymphoma
- Gliosarcoma
- Rhabdomyosarcoma
- Paranasal Sinus Cancer
- Atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor (AT/RT)
Chordomas: A rare type of bone cancer (<1%) seen in the skull base or the lower back. It can pressure the nearby nerve tissue with its invasion. Despite displaying benign tendencies with its slow growth, its refractory nature is as lethal as a malignant as it keeps returning to spread to other areas.
Chondrosarcoma: A malignant bone cancer that develops between 50-70 years of age, affecting the cartilage. This aggressive cancer could grow in the thighbone, arm, pelvis, etc, spreading to the head and spine. It could also develop directly in the face bones or skull base.
Medulloblastoma: One of the most frequent malignant brain tumors in pediatric patients (5-9 years), medulloblastoma arises in the cerebellum. It is of various types with varying aggressivity.
Olfactory neuroblastoma: A rare malignancy associated with nose bleeds and difficulty breathing from the nose, olfactory neuroblastoma develops in the nose in the olfactory nerve (nerve transmitting olfactory impulses (smell) to the brain). Gradually, patients lose their sense of smell.
Lymphoma: A type of tumor that forms in the lymphatic system (part of the body's immune system). Lymphomas can either spread from other body parts to the brain or directly form in the brain (primary central nervous system lymphomas). Usually, primary CNS lymphomas are treated with chemotherapy and radiation.
Gliosarcoma: Rare type of glioma combined with other supportive tissues. These can be aggressive and spread to other areas apart from being resistant to therapy.
Rhabdomyosarcoma: A rare soft tissue cancer occurring not only in the head but also in many parts of the body (in muscles). Children have more of an affinity to develop rhabdomyosarcomas, which starts with complaints of the eyes or face.
Paranasal Sinus Cancer: Formed in the cells lining the hollow spaces of the bones around the nose (maxillary sinuses (in the cheekbones under the eyes) and the ethmoid sinuses (beside the upper nose)).
Atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor (AT/RT): An embryonal tumor that typically affects children lesser than seven years of age. It is an aggressive cancer with low survival rates despite providing therapy.

Brain Cancer Symptoms
The symptoms of brain cancer may change depending on the location and the size of the tumor within the brain. Below are some of the main symptoms of brain cancer:
- Cognitive changes: These include memory issues, trouble concentrating, confusion, changes in personality, and changes in judgment.
- Headaches: They can be persistent and severe, potentially worsening over time. Headaches may be more severe in the morning or after waking up.
- Vision problems: These may include blurry vision, double vision, and loss of peripheral vision.
- Seizures: An uncontrolled electrical activity in the brain can cause seizures. Seizures vary in severity from mild to severe and may cause loss of consciousness or convulsions.
- Nausea and vomiting: It occurs mainly when accompanied by additional symptoms such as headaches or vision abnormalities.
- Balance and coordination difficulties: These include trouble walking, losing balance, or controlling movements.
- Speech difficulties: These include difficulty finding words, slurred speech, and difficulty understanding speech.
- Behavioural changes: These may include mood swings, irritability, depression, or other unexplained behavioral changes.
- Sensory alterations: These include tingling, numbness, or decreased sensation in the legs and arms.
- Weakness or paralysis: It refers to gradual or sudden weakening in the legs or arms, typically on one side of the body.

Brain Cancer Causes and Risk Factors
While the specific reasons for brain cancer are unknown, research indicates that some risk factors may raise the likelihood of developing brain cancer, which are as follows:
Non-modifiable factors
- Age
- Gender
- Immune system
- Hormonal factors
- Family history
Modifiable factors
- Exposure to rays
- Nutrition
- Smoking
- Alcohol
- Mobile phones
- Aspartame
Non-modifiable factors
Some risk factors of brain cancer cannot be altered (changed), known as non-modifiable risk factors. It includes:
- Age: While brain cancer can develop at any age, it is most commonly identified in young children and the elderly.
- Gender: In general, men have a greater risk of developing brain cancer than women.
- Immune system: The exact level of immunological decrease that leads to cancer cell development in patients remains uncertain. Cancer cells release immunosuppressive cytokines, reducing immunity and promoting tumor growth in the body. Immunocompromised people, either due to a congenital or acquired cause, such as acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) or human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), are more likely to develop certain types of brain cancer.
- Hormonal factors: According to Cowppli-Bony et al., the incidence of brain tumors rises during menarche and menopause and falls after hormone therapy.
- Family history: A family history of cancer may indicate a genetic predisposition due to similar environmental factors among family members.
Modifiable factors
Some risk factors of brain cancer can be changed, known as modifiable risk factors. It includes:
- Exposure to rays: Exposure to high and moderate levels of ionizing radiation increases the risk of developing nervous system tumors.
- Nutrition: Consuming fruits and vegetables has an inverse association with brain tumors. Vitamins C, E, and phenylol found in fruits and vegetables, as well as carotenoids and folate, play a role in the development of brain tumors. On the other hand, antioxidants and certain phytoestrogens slow tumor growth. Processed meat and other food groups have been linked to higher infection rates.
- Smoking: It is one of the leading causes of cancer in humans. Smoking increases the adsorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and nitrous chemicals.
- Alcohol: Alcohol intake is associated with 3.6% of global cancers. Alcohol intake has been associated with lower cancer survival rates and tumor growth.
- Mobile phones: Increased use of mobile phones raises the incidence of brain tumors in individuals over 20 years old.
- Aspartame: More than 20 crore individuals worldwide eat aspartame, an artificial sweetener. A daily intake of 20 mg of aspartame raises the risk of nervous system tumors. Long-term consumption can lead to myelin degeneration and an increased chance of developing a tumor.
Brain Cancer Complications
Brain cancers can cause both neurological and medical complications. Early diagnosis and treatment of brain cancers help in reducing complications of brain cancers. Below are some of the complications seen in brain cancer patients:
- Brain herniation: The shifting of the brain tissue from one space in the skull to the another space by several openings and folds. It occurs because of the increased pressure in the skull.
- Seizures: This disorder depicts a neurological condition that may cause brief episodical unconsciousness and convulsions, during which the body shakes uncontrollably due to abnormal electrical activity in the brain.
- Mass effect: It describes the impact of growing mass on neighboring structures or tissues. It can be caused by several intracranial processes, such as hemorrhages, tumors, trauma, and ischemia.
- Hydrocephalus: It is a neurological condition caused by an abnormal collection of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the ventricles (cavities) deep inside the brain. This excess fluid widens the ventricles, putting more pressure on the brain's tissues. It may be present at or shortly after birth or may occur over time because of injury or damage.
- Neurological deficit: Abnormal neurological function of the body that occurs because of the injury to the brain, spinal cord, muscles, and nerves is referred to as neurological deficit.
Brain Cancer Diagnosis
Healthcare professionals such as neurologists, neurosurgeons, oncologists, and radiologists conduct several tests and evaluations to diagnose brain cancer. Here's an overview of the steps involved in diagnosing brain cancer:
- Medical history
- Family history
- Physical examination
- Imaging tests
- Computed tomography (CT) scan
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS)
- Positron emission tomography (PET) scan
- Single photon emission computerized tomography (SPECT)
- Biopsy
- Lumbar puncture (Spinal Tap)
- Molecular testing
- Neurological tests
After confirming a diagnosis of brain cancer, the medical team will identify the type of tumor, its grade (a measure of aggressiveness), and its stage (the extent of spread within or outside the brain).
Brain
Brain Cancer Treatment
Brain cancer treatment depends on parameters such as tumor type, size, location, grade (aggressiveness), and overall health of the patient. The treatment approach involves multidisciplinary healthcare professionals, such as neurologists, neurosurgeons, radiation oncologists, medical oncologists, and supportive care specialists. The brain cancer treatment options include the following:
- Surgery
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Carmustine implants (glial wafers)
- Targeted therapy
- Immunotherapy
- Stereotactic radiosurgery
- Supportive care
Why Choose PACE Hospitals?
Expert Super Specialist Doctors
Advanced Diagnostics & Treatment
Affordable & Transparent Care
24x7 Emergency & ICU Support
Brain Cancer Prevention
In a rare circumstances where a family history or personal history of numerous head X-rays indicates an elevated risk of brain cancer, regular screening by a neurologist may allow growing malignancies to be diagnosed early. Besides, there are no recognized methods of preventing brain cancers.
Difference between Brain Tumor and Brain Cancer
Brain tumor vs Brain cancer
Not all brain tumors are malignant (cancerous), but all brain cancers are considered tumors. Below are some of the parameters that differentiate brain tumors and brain cancer:
| Parameters | Brain tumor | Brain cancer |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Brain tumor, also known as intracranial tumor, is generally described as the growth of abnormal cells in the areas of the brain. Cells in the brain may multiply abnormally and uncontrollably, forming an abnormal mass of tissue, thus causing the brain tumor. | Brain cancer, also referred to as intracranial neoplasms, is a group of malignant(cancerous) tumors that develop in the brain or surrounding tissues . |
| Origin | These include tumors that originate from the brain's tissues or its immediate surroundings. | Brain cancer can develop from primary brain tumors (from brain tissue) or from metastatic brain tumors (because of cancer spreading from another part of the body) |
| Types | Meningioma, vestibular schwannoma, pituitary adenoma | Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), astrocytomas, medulloblastomas, oligodendrogliomas |
| Growth | Benign brain tumors typically grow slowly, have different borders, and rarely spread. | Typically, they grow rapidly and invade surrounding healthy brain structures. |
| Treatment | Medicines, surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted drug therapy, tumor-treating fields, and rehabilitation | Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, carmustine implants (glial wafers), targeted therapy, immunotherapy, stereotactic radiosurgery and supportive care |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Brain cancer
Is brain cancer curable?
The prognosis for a malignant brain tumor (brain cancer) is determined by factors such as location, size, and grade. It can occasionally be cured if detected early on, but a brain tumor frequently recurs and is sometimes impossible to remove.
Is a brain tumor a cancer?
While all brain cancers are tumors, but not all brain tumors are malignant (cancerous). Benign brain tumors are those that are not cancerous. They usually grow slowly, have clear borders, and rarely spread. Malignant brain tumors are cancerous. They often spread quickly and invade nearby healthy brain areas.
Can brain cancer be mistaken for MS?
Yes, multiple sclerosis (MS) and other demyelinating illnesses of the central nervous system (CNS) can occasionally cause a misdiagnosis of brain or spinal cord tumors. Some forms of MS may resemble brain cancers or abscesses, and nonneoplastic demyelinating processes may be difficult to diagnose using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Can radiotherapy cure brain cancer?
Strong beams of energy are usually used to kill cancer cells in the radiotherapy. Radiation therapy is helpful in controlling the growth of certain types of brain tumors. It is generally used in combination with chemotherapy or surgery to treat brain tumors.
Can bone cancer spread to the brain?
Yes, bone cancer can spread to the brain. The primary cancerous bone tumors such as chondrosarcoma, osteosarcoma (osteogenic sarcoma), chordoma, Ewing's sarcoma, and fibroblastic/fibrohistiocytic tumors are reported to metastasize (spread) to the brain.
What is brain cancer?
Brain cancer is the uncontrolled proliferation(growth) of cells in the brain. Brain cancer includes a wide range of tumors that affect various types of brain cells. Brain cancers can grow quickly or slowly over many years, depending on the location and type of cell involved. Brain cancers are generally hard to treat, and a complete cure is sometimes impossible.
How does brain cancer kill you?
Malignant brain tumors are cancer in nature. They often grow quickly and invade neighboring healthy brain areas. Brain cancer can be fatal (causing death) because of the changes it causes to the brain's vital structures.
Can prostate cancer spread to the brain?
Prostate cancer usually spreads to the pelvic lymph nodes, axial skeleton, and lungs. Brain metastases from prostate cancer is rare and usually found after death. It is quite rare for metastatic prostate cancer to occur primarily in the brain.
What tests are done to diagnose brain cancer?
Brain cancer can be diagnosed using computed tomography (CT) scan, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), positron emission tomography (PET) scan, single photon emission computerized tomography (SPECT), biopsy and lumbar puncture.
What is stage four brain cancer?
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is a stage four brain cancer that arises from the glial cells (brain cells). It is the most severe type and aggressive tumor. The tumor develops new blood vessels as it grows because of the abnormal tumor cells. The tumor may develop necrosis (death of cells).
Can stem cells cure brain cancer?
California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (CIRM)- funded researchers are trying ways to genetically engineer stem cells to produce cancer-killing molecules. When transplanted into the brain, the stem cells look for cancer cells and deliver the treatment directly.
Why do brain cancer patients sleep so much?
Brain cancer patients sleep so much because the tumor is close to the orexin-producing cells present in the hypothalamus, which are essential in maintaining wakefulness. The tumor may destroy or affect these cells during partial or whole-brain radiation or surgery.
Has anyone survived brain metastases?
Ten and a half years ago, people suffering from brain metastases survived for nearly less than six months. Nowadays, treatment options for brain metastases have improved, and individuals suffering from brain metastases live longer than before.
Is brain cancer painful?
Headaches associated with brain cancer are persistent and severe, potentially worsening over time. Headaches may be more severe in the morning or after waking up. They are usually referred to as dull, pressure-type headaches. These patients may also suffer from stabbing (sharp) pain.
When to consult a doctor for brain cancer?
Consult a doctor for brain cancer if you notice persistent or unusual symptoms that affect your head, vision, or coordination, such as:
- Persistent or worsening headaches
- Nausea or vomiting
- Blurred or double vision
- Seizures or loss of balance
- Sudden changes in memory, speech, or behaviour
If these symptoms persist or worsen, it's crucial to consult a brain cancer specialist, such as a neurologist or neuro-oncologist, for further evaluation. Early diagnosis can aid in managing the condition and improving outcomes.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868