Best Breast Cancer Specialist Doctors in Hyderabad for Expert Care & Treatment
✅ Recommended by 8,925 Happy Patients. Get hassle-free appointments with breast cancer doctors.
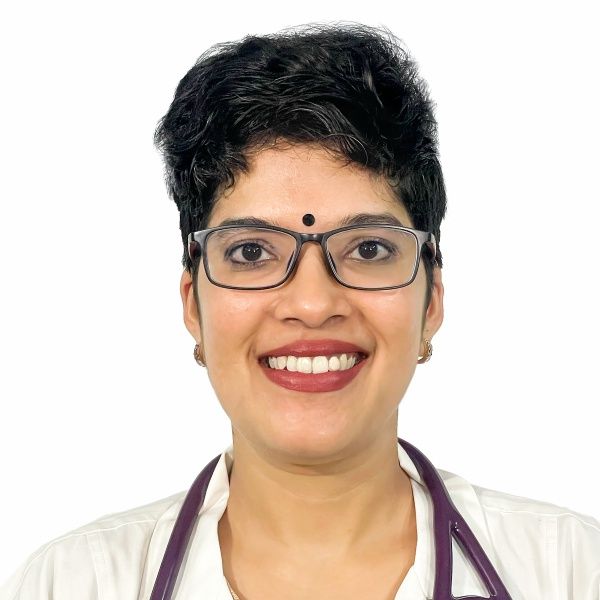
Dr. K Meena
MBBS, MD (General Medicine), DM (Medical Oncology), DrNB (Medical Oncology)
Experience : 14+ years
Medical Oncologist, Hemato Oncologist and Palliative Care Specialist, Europe Certified Medical Oncologist (E.C.M.O)
Specialist
Various cancers including Brain Tumors, Breast, Stomach / Gastric, Pancreatic, Oesophageal, Liver, Cervical, Colorectal, Lung, Ovarian and Other Gynaecological Cancers, Multiple Myeloma, Lymphomas, Leukaemia.
Expertise
Chemotherapy Administration, Immunotherapy and Monoclonal Antibodies, Cancer Screening and Genetic Counseling, Palliative Care, Targeted Therapy, Hormone Therapy.
Consultation Timing:
Mon to Sat - 9 am to 6 pm
Location:
PACE Hospitals, Hitech City
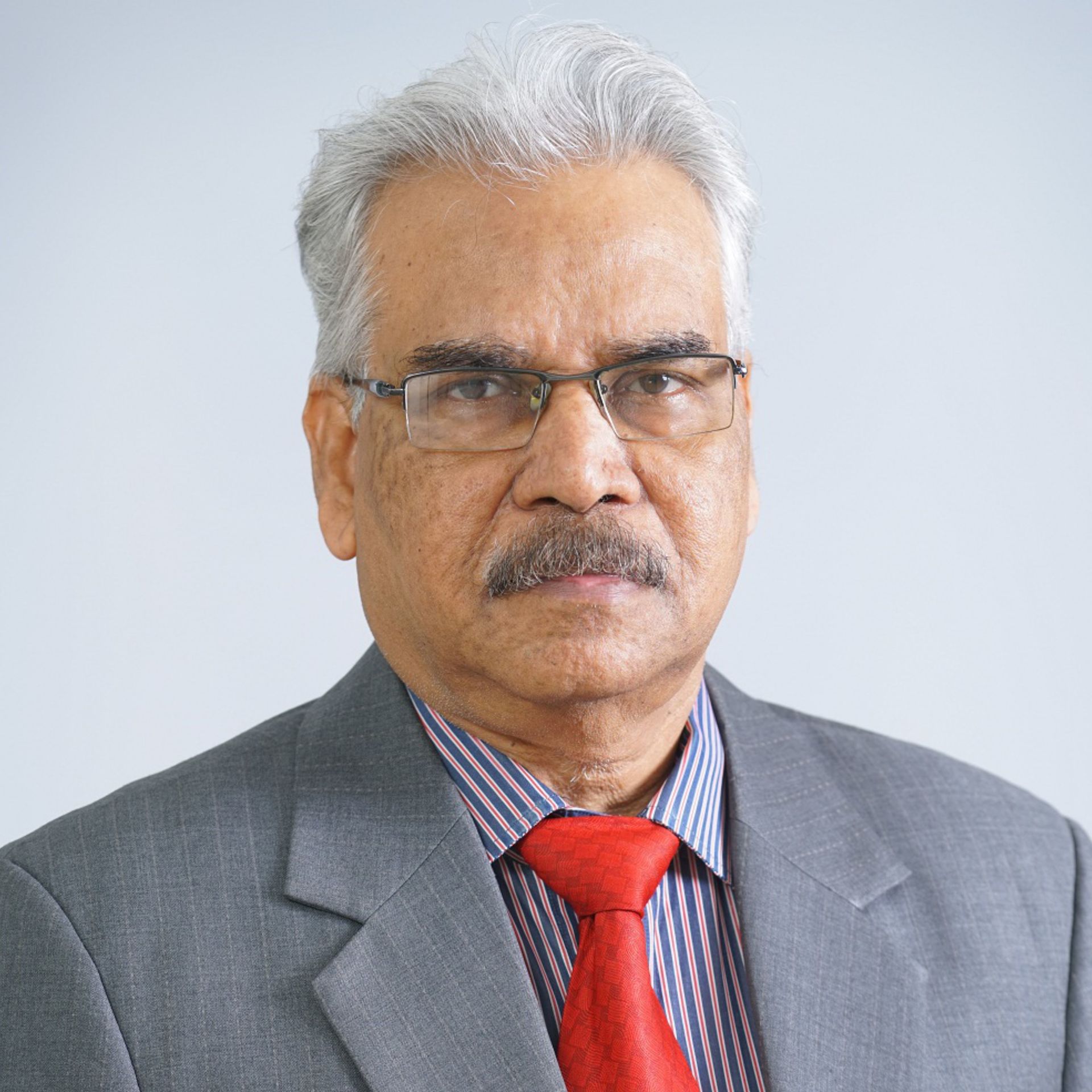
Dr. Ramesh Parimi
MS, FRCS, FAMS
Experience : 35+ years
Surgical Oncologist
Specialist
Specialist in Breast Cancer, Stomach Cancer / Gastric Cancer, Head & Neck Cancer, Oral Cavity Cancer, Oropharyngeal Cancer, Intra-Oral Cancer, Laryngeal Cancer, Endometrial Cancer, Cervical Cancer, Ovarian Cancer, Oesophageal Cancer, Uterus Cancer, Lung Cancer, Thyroid Cancer, Kidney Cancer, Colon Cancer.
Expertise
Surgery for Breast Cancer, Stomach Cancer / Gastric Cancer, Head & Neck Cancer, Oral Cavity Cancer, Oropharyngeal Cancer, Intra-Oral Cancer, Laryngeal Cancer, Endometrial Cancer, Cervical Cancer, Ovarian Cancer, Oesophageal Cancer, Uterus Cancer, Lung Cancer, Thyroid Cancer, Kidney Cancer, Colon Cancer.
Consultation Timing:
Mon to Sat - 9 am to 6 pm
Location:
PACE Hospitals, Hitech City
Breast Cancer Specialist in Hyderabad, India for Comprehensive Care & Treatment
PACE Hospitals in Hyderabad, India, are renowned for having one of the Best Breast Cancer Doctors in Hyderabad, India. The hospital's breast specialist doctors include surgical oncologists, medical oncologists, radiation oncologists, and radiologists who work together to provide comprehensive and personalized care to each patient for breast cancer diagnosis and treatment.
At PACE Hospitals, the focus is on early detection and accurate diagnosis of breast cancer, which is crucial for successful treatment and recovery. The hospital's advanced technology and state-of-the-art facilities enable breast cancer screening and diagnosis through mammography, ultrasound, and biopsy. The team of radiologists at PACE Hospitals are experts in breast imaging and provide accurate and timely diagnosis, ensuring that patients receive prompt and effective treatment.
The breast cancer surgeons at PACE Hospitals are highly skilled in various surgical procedures, including lumpectomy, mastectomy, and breast reconstruction. The medical oncologists provide chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and targeted therapy, while the radiation oncologists offer radiation therapy to destroy cancer cells and prevent recurrence. The team of breast cancer specialists at PACE Hospitals work together to develop a personalized treatment plan for each patient, taking into account their individual needs and preferences.
In addition to medical care, PACE Hospitals also provide emotional support and counseling to breast cancer patients and their families. The hospital's team of nurses, social workers, and counselors provide compassionate care and support throughout the cancer journey, from diagnosis to treatment and survivorship. PACE Hospitals are committed to providing the highest standards of care to breast cancer patients, ensuring the best possible outcomes and quality of life. If you are looking for the Best Breast Specialist Doctor in Hyderabad, India, PACE Hospitals are the right choice for you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Breast cancer
Is breast cancer hereditary?
Yes, some breast cancers are hereditary, and these cancers pass down through families. About 5% to 10% of breast cancers are linked to be hereditary, caused by abnormal genes passed from parent to child, especially mutated versions of BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes can lead to abnormal cell growth, causing cancer. However, most cases of breast cancer are not directly inherited.
Can breast cancer be cured?
Breast cancer can often be cured if detected early, however it can be challenging to treat in more advanced stages. As per the data, it was confirmed that 70-80% of patients with early-stage breast cancer were alive after being diagnosed within five years. However, outcomes vary based on factors like cancer stage and individual health. Regular screenings and early intervention are crucial to improving prognosis.
Can men get breast cancer?
Yes, men can get breast cancer, though it's infrequent in which cancer cells develop in the breast tissues and less common than in women. This cancer may occur in men at any age, but it usually happens between 60 and 70 years and accounts for less than 1% of all cases. Certain genetic factors, hormonal imbalances, or other risk factors can cause this cancer in males.
What are the most common signs of breast cancer?
A painless lump in the breast is typically the first sign of breast cancer. However, patients may not detect it themselves. Instead, many lumps are discovered through routine screening mammograms. Other common signs of breast cancer are skin changes, including swelling, redness, or other visible differences in one or both breasts, changes in one or both nipples, an increase in size or change in shape of the breasts, lumps or nodes felt on or inside of the breast and nipple discharge other than breast milk.
What are the treatment options available for different stages of breast cancer?
Treatment of breast cancer varies with stage. Early-stage cancer treatment can be a surgical operation, either lumpectomy or mastectomy, followed by radiation therapy and coupled with hormone therapy and chemotherapy. However, in cases where it advanced to the further stages, more aggressive interventions are required; for example, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or immunotherapy, according to the molecular characteristics of the cancer. Therefore, there is an individualization of the treatment plans, with consideration for the stage and molecular characteristics of the tumour.
Can breast cancer be detected through self-exams?
Breast self-examination can help detect changes or any abnormalities in shape or skin texture in the breasts early, however they has not revealed any improvement in patient outcomes, any patient-observed change or abnormality in the breast anatomy. However, self-exams should complement, not replace, routine mammograms and professional screenings for the most accurate detection.
What are the different types of breast cancer?
There are several types of breast cancer.
- The most common type is invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC), which forms in the milk ducts and can spread to nearby tissues.
- Other types include invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC), which begins in the lobules, as well as non-invasive forms such as ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS).
Each type can differ in growth rate and response to treatment.
How common is breast cancer in young women under 40?
Breast cancers rarely occur in young women, and the cases of the disease are fewer than 17 cases per 100,000, affecting only about 6% of all breast cancers in women of all ages. Nonetheless, accumulating evidence suggests that breast cancer in this age group is more aggressive and has a worse outcome than in the older age group. While some reports have identified very young age at diagnosis as a bad prognostic factor, this is likely a result of several factors such as late presentation, a late stage of the disease and possibly poor tumour characteristics.
What percentage of breast cancer cases are diagnosed at an early stage?
In India, approximately 30-35% of breast cancer cases are diagnosed at an early stage. Early detection rates are generally lower compared to developed countries due to various factors such as lack of awareness, limited access to screening programs, and socio-economic barriers. However, ongoing initiatives aimed at improving screening and public health education are gradually increasing early detection rates.
What are triple-negative breast cancer and its characteristics?
TNBC is a highly aggressive type of invasive breast cancer, comprising 10-15% of all forms of breast cancers and differs from other forms of invasive breast cancer in its higher growth and a faster rate of spread, with fewer treatment options, and tends to have a worse prognosis (outlook). These cancers occur more frequently in women under the age of 40, who are Black, or who have a BRCA1 mutation.
Can the type of breast cancer change over time?
Yes, breast cancer can change type over time. A patient may initially be diagnosed with one type and later develop another subtype. About 25% of breast cancer cases change their type as they grow and develop. Studies revealed that a subset of breast cancers can change their type during cancer progression.
These changes may influence how the health care provider foresees the progression of the disease and the treatment of it, or prognosis and management of the disease, as each type of distinct breast cancer subtype has distinct therapy options differently optimized for that given subtype.
What is the likelihood of a complete cure for early-stage breast cancer?
According to the American Cancer Society, the likelihood of a complete cure for early-stage breast cancer is relatively high; found and treated in the localized stage have five-year survival rates often exceeding 90%. However, factors such as the specific type of cancer, treatment options, and individual health can influence outcomes.
What is Stage 0 breast cancer, and how is it different from invasive cancer?
Stage 0 breast cancer is often classified as "ductal carcinoma in situ", a non-invasive condition in which abnormal cells are found within the lining of the breast ducts but have not been shown to spread beyond that area. For example, if cancer cells go beyond mere penetration of the ducts or lobules into the surrounding breast tissue, it is considered invasive breast cancer. The key difference lies in the ability to spread: stage 0 is contained in one place, whilst invasive cancer can spread to other tissues.
Can the stage of breast cancer change after diagnosis?
The stage of breast cancer indicates how advanced the disease is when it is diagnosed (severity of the disease). The stage remains the same even if the cancer shrinks or spreads to other areas during or after treatment. For example, if the patient is initially diagnosed with stage 1 breast cancer (early stage), but the tumour later grows and spreads, it will still be considered stage 1. However, to indicate if the cancer has responded to treatment, a new stage may be assigned with an "r" in front of it which stands as recurrent or restaging.
What are the most common risk factors associated with breast cancer?
Common risk factors for breast cancer include age, being a woman or a person assigned female at birth, genetic mutations (like BRCA1 and BRCA2), family history, hormonal factors (such as prolonged exposure to oestrogen), and lifestyle choices (like alcohol consumption and being overweight).
Are there specific genes that increase the likelihood of breast cancer?
Some genes make a person more prone to developing breast cancer. The most frequently implicated are BRCA1 and BRCA2. Mutations in these genes significantly raise a person's chances of developing breast cancer. About 5% to 10% of breast cancer cases are thought to be hereditary, where they result directly from gene changes (mutations) passed on from a parent.
Does obesity contribute to a higher risk of breast cancer?
Being overweight or obese after menopause raises breast cancer risk and also can increase the risk of breast cancer recurrence (coming back) in women who have had prior breast disease. This higher risk is due to the extra fat cells, which make more oestrogen in the body, which may make hormone-receptor-positive breast cancers develop and grow.
Are women with dense breast tissue at a higher risk for breast cancer?
Yes, breast density is a risk factor for breast cancer, with previous studies suggesting a 4‐ to 6‐fold increase in risk for women with highly dense breast tissue. Women with dense breasts have a higher risk than those with fatty breasts. This risk is separate from the impact on mammogram readings.
What changes in breast appearance should one be aware of?
Check with a healthcare physician if anyone notices unusual changes in their breasts, including any changes or abnormalities in the size or shape of the breast or nipples, a lump under the arm, firm or thick tissue in or near the breast or under the arm, or a feeling of breast lumps or nipple discharge other than breast milk. Breast lumps come in various shapes and sizes. However, most lumps are not breast cancer.
Is breast pain, swelling and discharge from nipple always a sign of breast cancer?
No, breast pain, swelling, and nipple discharge are not always signs of breast cancer. These symptoms can also be caused by benign conditions such as hormonal changes, infections, pregnancy, breastfeeding or cysts. That said, if anyone notices any such symptoms that cause distress, seek medical opinion to diagnose possible causes and rule out severe conditions.
What does a lump in the breast indicates?
A breast lump is a growth, mass or swelling within the breast tissue. Lumps in the breasts can have various causes. They're often caused by something harmless, such as a build-up of fluid (breast cyst) or non-cancerous tissue growth (fibroadenoma). Sometimes, a breast lump can indicate severe issue, including breast cancer. However, all breast lumps should be investigated by a healthcare professional.
What are the implications of breast cancer on reproductive health?
Some treatments, including chemotherapy or radiotherapy, lower fertility by making it challenging to become pregnant or to carry a pregnancy. Thus, breast cancer can have significant effects on reproductive health; a discussion of family planning, fertility, and fertility preservation should be an integral component of care for the affected individual when considering these hormonal treatments, which also affect menstrual cycles and reproductive function.
What are the initial steps in diagnosing breast cancer?
Diagnoses of the first steps for breast cancer usually include a clinical breast examination by a healthcare professional (oncologist) to look for anything abnormal, followed by imaging tests such as a mammogram or ultrasound. At any suspicious areas found, some tissue samples are obtained through a biopsy procedure in order to do laboratory analyses, thus helping to determine whether breast cancer exists and what type it is.
What imaging tests are commonly used for breast cancer diagnosis?
Common imaging tests for the diagnosis of breast cancer are mammography, which involves X-rays to focus on abnormalities, and ultrasound of the breast, which is used to evaluate lumps or changes that have been observed on a mammogram. MRI may also be used to help determine the extent of known cancer or in patients at higher risk. Whether a woman should be screened for breast cancer and which screening test to use will depend upon several factors.
What role does genetic testing play in breast cancer diagnosis?
Genetic testing can be important to establish one's predisposition to risk for breast cancer, especially for those with a family background or early onset of the disease. Testing on gene mutations such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 will identify hereditary cancer syndromes that may lead to an important surveillance and prevention agenda.
What is the role of clinical trials in breast cancer treatment?
Clinical trials help advance treatment for patients with breast cancer, showing evidence that new therapies, drug combinations, and different approaches to treatment may be safe and effective. For patients, involvement in clinical trials gives them access to newer treatments that have not necessarily been introduced as standard of care yet. It also helps in understanding how they may be improved. Involvement in clinical trials may also help identify potential side effects and tweak the existing treatment protocols.
How does the treatment approach differ for metastatic breast cancer?
The main strategies for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer are aimed at controlling it without curative intention because the distant parts of the body other than the breasts and lymph nodes have already been affected. The treatment plan often consists of systemic therapies, including
chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or hormone therapy, based on the type of cancer.
How does immunotherapy work for breast cancer, and who is it suitable for?
The
breast cancer treatment uses immunotherapy, which assists in provoking the immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells. It is most appropriately used for patients with certain types of breast cancer. For example, some varieties of breast cancer are identified as triple-negative and appear to be more sensitive to drugs that block immune checkpoints. This is appropriate when a patient has advanced or metastatic disease and is most commonly delivered in combination with other treatments for a better prognosis.
What types of surgeries are available for breast cancer?
There are several kinds of surgical treatments for breast cancer, mostly two kinds: namely, lumpectomy - removal of a structure which has only the tumour itself and a little surrounding tissue; and mastectomy - the removal of one or both breasts. A sentinel node biopsy is also carried out to confirm whether cancer has spread to the sentinel lymph nodes situated near the site of its origin. Surgical intervention is chosen based on the stage and site of cancer and, naturally, the patient's wishes.
What our patients have to say
Experts perspective
Why choose PACE Hospitals?
- A Multi-Super Speciality Hospital.
- NABH, NABL, NBE & NABH - Nursing Excellence accreditation.
- State-of-the-art Liver and Kidney transplant centre.
- Empanelled with all TPA’s for smooth cashless benefits.
- Centralized HIMS (Hospital Information System).
- Computerized health records available via website.
- Minimum waiting time for Inpatient and Outpatient.
- Round-the-clock guidance from highly qualified medical oncologists, surgical oncologists, radiation oncologists, and radiologists.
- Standardization of ethical medical care.
- 24X7 Outpatient & Inpatient Pharmacy Services.
- State-of-the-art operation theaters.
- Intensive Care Units (Surgical and Medical) with ISO-9001 accreditation.
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868
Appointment request - health articles
Thank you for contacting us. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Oops, there was an error sending your message. Please try again later. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Our Locations – Find the Best Hospital Near You
Metro Pillar Number C1772, Beside Avasa Hotel, Hitech City Road, Near HITEC City Metro Station, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Mythri Nagar, Beside South India Shopping Mall, Hafeezpet, Madeenaguda, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
040 4848 6868
Payment in advance for treatment at PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, Telangana, India (Pay in INR ₹)
For Bank Transfer:-
- Bank Name: HDFC
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.50200028705218
IFSC Code: HDFC0000545 - Bank Name: STATE BANK OF INDIA
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.62206858997
IFSC Code: SBIN0020299
Scan QR Code by Any Payment App (GPay, Paytm, Phonepe, BHIM, Bank Apps, Amazon, Airtel, Truecaller, Idea, Whatsapp etc).

CONTACT US
Call: +914048486868
WhatsApp: +918977889778
Email: info@pacehospitals.in
FOLLOW US
SUBSCRIBE
Subscribe to our newsletter and stay updated with the latest health information.
Subscribe to PACE Hospitals' Public Newsletter
Thank you for subscribing to PACE Hospitals' Newsletter. Stay updated with the latest health information.
Oops, there was an error. Please try again submitting your details.
ABOUT US
QUICK LINKS
Disclaimer
General information on healthcare issues is made available by PACE Hospitals through this website (www.pacehospital.com), as well as its other websites and branded social media pages. The text, videos, illustrations, photographs, quoted information, and other materials found on these websites (here by collectively referred to as "Content") are offered for informational purposes only and is neither exhaustive nor complete. Prior to forming a decision in regard to your health, consult your doctor or any another healthcare professional. PACE Hospitals does not have an obligation to update or modify the "Content" or to explain or resolve any inconsistencies therein.
The "Content" from the website of PACE Hospitals or from its branded social media pages might include any adult explicit "Content" which is deemed exclusively medical or health-related and not otherwise. Publishing material or making references to specific sources, such as to any particular therapies, goods, drugs, practises, doctors, nurses, other healthcare professionals, diagnoses or procedures is done purely for informational purposes and does not reflect any endorsement by PACE Hospitals – your trusted hospital near me.