Cardiovascular Disease - Symptoms, Causes, Risk factors, Treatment and Prevention
PACE Hospitals
Cardiovascular disease definition
Cardiovascular Disease (CVD), also called heart or circulatory disease, is an umbrella term which refers to a group of conditions that affect the heart or blood vessels (veins and arteries).
It is frequently caused by the accumulation of fatty deposits (atherosclerosis) in the arteries, which can increase the risk of blood clots, and are often associated with damage to arteries in various organs, including the brain, heart, kidneys, and eyes.
Cardiologists diagnose and treat cardiovascular disease (CVD) that affects the heart and blood vessels. In some cases,
Primary care physicians may also play a role in the initial diagnosis and treatment.
Cardiovascular disease meaning
The meaning of cardiovascular disease comes from two parts
- Cardio: Derived from the Latinized form of the Greek “kardia” which refers to the “heart”
- Vascular: Derived from Modern Latin “vascularis” which refers to “blood vessels” that supply blood to the body.
Therefore, cardiovascular means anything related to the heart and blood vessels, and the term “cardiovascular system” has been used since 1981.
Prevalence of cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease prevalence worldwide
Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death globally. An estimated 1.79 crore people died in 2019, which represents 32% of total global mortality. Strokes and Heart attacks were responsible for 85% of these deaths.
Cardiovascular disease prevalence in India
The prevalence of cardiovascular disease in India is greater than the global average, with an age-standardized CVD death rate of 282 per 100,000 individuals, compared to the global average of 233 per 100,000. The annual number of CVD deaths in India is projected to increase from 22.6 lakh in 1990 to 47.7 lakh by 2020.

Cardiovascular disease types
There are different types of cardiovascular disease, mainly 4 types of cardiovascular diseases listed below:
- Coronary heart disease (CHD) or coronary artery disease (CAD)
- Angina pectoris
- Heart attack
- Heart failure
- Cerebrovascular disease (CVD)
- Stroke
- Transient ischemic attack (TIA)
- Peripheral artery disease (PAD)
- Aortic atherosclerosis
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) or Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Coronary heart disease develops when the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle becomes obstructed or decreased. This increases the strain on the heart, which leads to:
- Angina: It is a discomfort or pain in the chest that results when the heart muscle does not receive enough blood. It is usually not life-threatening.
- Heart attack: It is also called a myocardial infarction, a critical medical emergency characterised by a sudden blockage of blood flow to the heart, generally caused by a blood clot.
- Heart failure: Heart failure happens when the heart fails to efficiently pump blood throughout the body. It usually occurs when the heart has grown too weak or stiff.
Cerebrovascular disease (CVD)
Cerebrovascular disease is a set of disorders that impact blood flow and blood arteries in the brain. Types of cerebrovascular disease include:
- Stroke: A stroke arises when blood flow to the part of the brain is stopped. It can affect speech and movement and take a long time to recover. A stroke requires urgent medical care because it can be life-threatening.
- Transient ischemic attack (TIA): A transient ischaemic attack (TIA), also called a "mini-stroke", happens when blood flow to a part of the brain is temporarily blocked.
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD), also called peripheral vascular disease (PVD), occurs when fatty deposits build up in the arteries and limit blood flow to the muscles in the legs.
Aortic atherosclerosis
Aortic atherosclerosis is a condition where plaque builds up in the aorta, the largest artery in the body, which carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body and leads to narrowing, stiffening, or hardening of the artery.
Cardiovascular disease causes
The causes of coronary heart disease include:
- Plaque buildup: It is the main cause of coronary heart disease. The buildup of plaque in the arteries refers to atherosclerosis, which leads to hardening and narrowing of the arteries. This can decrease or block blood flow to the heart muscle, preventing the heart from receiving adequate oxygen-rich blood.
Cerebrovascular disease (CVD) causes
Cerebrovascular disease can occur for a variety of reasons, such as:
- Atherosclerosis: It is the primary cause of CVD, where the fatty deposits in the arteries can decrease blood flow to the brain when the arteries constrict.
- Thrombosis: It occurs when a blood clot blocks the blood vessel.
- Embolic arterial blood clot: It is a blood clot that forms in one part of the body that travels through bloodstream to block an artery. In CVD it blocks arteries in the brain.
- Cerebral venous thrombosis: Refers to blood clot in a vein of the brain
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) causes
The following are the common peripheral artery disease causes leading to stoppage of blood flow in the limbs:
- Atherosclerosis: It is typically caused by a buildup of fatty deposits, made up of cholesterol and other waste substances, in the walls of the leg arteries. This accumulation narrows and restricts blood flow to the legs.
Other causes could include:
- Inflammation of the blood vessels: This causes the arteries to tighten and harden, which reduces the blood supply to the limbs.
- Injury to the limbs: Injured blood vessels can damage the arteries, resulting in decreased blood flow. This can lead to constriction or blockage of an artery, stopping blood flow to the legs.
- Radiation exposure: This is a rare cause of PAD because a small number of people develop PAD by radiation, called radiation-induced peripheral artery disease (RIPAD). Radiation can damage blood vessels by blocking or narrowing, making it harder for blood to flow. This process is called arteriopathy, resulting in reduced blood flow to the limbs.
Aortic atherosclerosis causes
Below mentioned are the main causes of aortic arteriosclerosis leading to the build-up of the plaque in the aorta:
- Damage to the endothelium of the aorta: Damage to the endothelium, which is the inner lining, leads to the development of atherosclerosis. This damage causes plaques, fatty deposition causing aortic atherosclerosis.
- While certain risk factors enhance the likelihood of endothelium damage and atherosclerosis, they are not the primary causes of the disease.
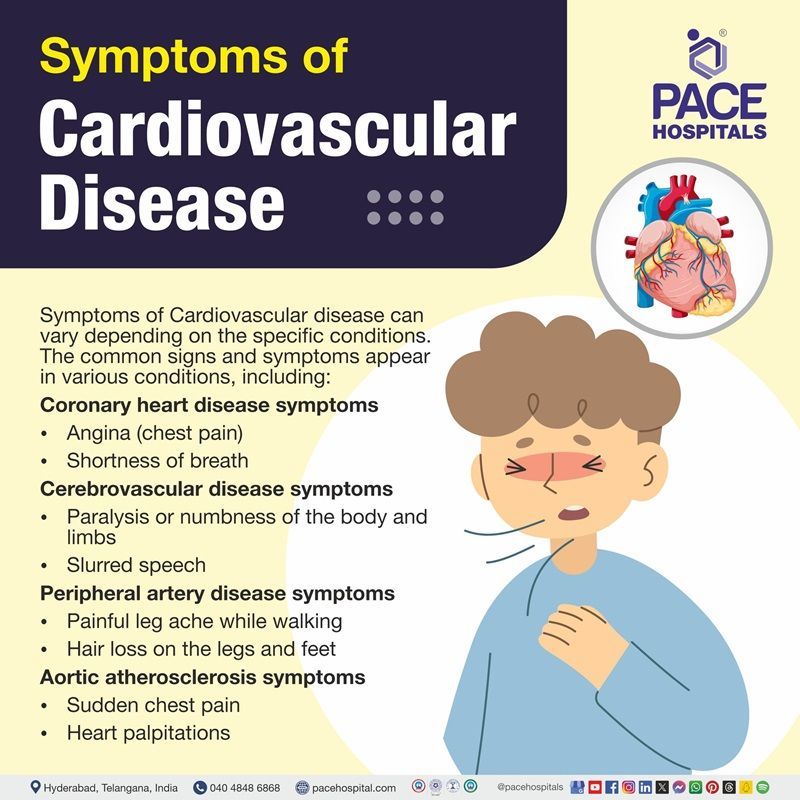
Symptoms of cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease can have no symptoms, and the first sign may be a heart attack or stroke. However, symptoms can differ based on the specific conditions. The common signs and symptoms of cardiovascular disease can appear in various conditions, including:
Coronary heart disease symptoms
Coronary heart disease is silent, which means some people may not have any symptoms before diagnosis, and not everyone has the same symptoms. Some of the main symptoms of CHD include:
- Angina (chest pain)
- Shortness of breath
- Pain in the neck, shoulders and jaw or arms
- Fainting
- Nausea.
Cerebrovascular disease symptoms
Symptoms of cerebrovascular disease (CVD) usually appear suddenly and vary based on which blood vessels of brain are impacted and the degree of reduced blood flow. Possible symptoms may include:
- Paralysis or numbness of the body and limbs
- Slurred speech
- Unexpected onset of severe headache
- Instability and falling
- Urinary Incontinence
- Blurred vision
- In severe circumstances, the patient may enter a coma or die.
Peripheral artery disease symptoms
The majority of people with PAD have no symptoms. However, some of them include:
- Some patients develop a painful leg ache when they walk, which usually disappears after a few minutes of rest, called "intermittent claudication".
- Both legs are frequently affected at the same time, but the pain may be more severe in one leg.
- Hair loss on the legs and feet.
- Numbness or weakness in the legs
- Erectile dysfunction in men
- Ulcers (open sores) on feet and legs, which do not heal
- Easily broken (brittle), slow-growing toenails
- Shrinking or wasting of leg muscles
- Changing the skin colour on the legs (paler or blue), shiny skin
Aortic atherosclerosis symptoms
The following are the common symptoms that are often associated with the atherosclerosis of the aorta:
- Sudden chest pain
- Heart palpitations
- Shortness of breath
- Numbness or tingling in the extremities due to inadequate circulation
- Dizziness, confusion, and loss of coordination
- Difficulty speaking or having slurred speech.
- Pain in arms, legs, neck, jaw, or back that last for several minutes

Cardiovascular disease risk factors
Cardiovascular disease includes modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors, which are mentioned below:
Modifiable or preventable risk factors for cardiovascular disease
- High blood pressure: High blood pressure causes cardiovascular disease because it thickens the wall of blood vessel and increases the burden on the heart.
- Smoking: Smoking is the major cause of many heart issues. Cardiovascular disease caused by smoking accelerates the buildup of plaque in arteries, leading to reduced blood flow and increased risk of many types of CVD, including stroke, coronary heart disease (CHD), atherosclerosis, peripheral arterial disease, and abdominal aortic aneurysm.
- High cholesterol: It can lead to the deposition of plaque or fatty substances in the arteries, narrowing them and blocking blood flow to the heart and other organs, which can increase the risk of CVD.
- Diabetes: The link between diabetes and cardiovascular disease is that diabetes is a lifelong disorder in which blood sugar levels grow too high and can damage blood vessels, leading to narrowing and resulting in increased CVD risk. People who have type 2 diabetes are obese, which raises their risk of heart disease.
- Kidney disease: When the kidneys do not function properly, the heart is put under strain. When someone has chronic kidney disease CKD, the heart has to work harder to provide blood to the kidneys, which may lead to heart disease.
- Inactivity: Physical inactivity can lead to the buildup of fat substances in the arteries, causing damage and blockage of blood vessels, as well as increased blood pressure, all of which increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Overweight or obese: Being overweight or obese develops the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD), as excess body fat can cause conditions such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes, all of these can harm the heart and blood vessels; additional excess weight puts extra strain on the heart, increasing the likelihood of heart problems even in the absence of other risk factors.
- Diet: Unhealthy diets may cause elevation in cholesterol levels and blood pressure, which damages blood vessels.
- Alcohol: Excessive drinking and high blood pressure cause blood vessels to constrict, resulting in strains on the heart muscle and the development of cardiovascular disease.
- Stress: The role of stress in the development of cardiovascular disease includes the hormone cortisol, which is released in response to stress. Studies have shown that elevated cortisol levels caused by long-term stress can raise blood cholesterol, blood sugar, triglycerides and blood pressure, which are common risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Non modifiable risk factors for cardiovascular disease
- Age: As people age, changes in the heart and blood vessels can raise a person's chance of developing heart disease and other health conditions. CVD is most common among people over 50, and the chance of getting it increases with age.
- Family history of CVD: A family history of cardiovascular disease increases the chance of developing CVD, particularly if a parent, brother, or sister has experienced angina or a heart attack before the age of 60.
- Gender: Men are more likely to acquire cardiovascular disease at an earlier age than women because of hormone levels, smoking and physical activity. After menopause, estrogen levels decrease, and women also experience a risk of CVD.
Coronary heart disease (CHD) risk factors
The modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors of CHD that develop atherosclerosis include:
- Smoking
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- High levels of lipoprotein
- High cholesterol levels
- Diabetes
- Lack of regular exercise
- Overweight or obese
- Family history of CHD
Cerebrovascular disease (CVD) risk factors
Many preventable and non-preventable risk factors for CVD have been identified. They include:
- Advancing age
- Hypertension
- Diabetes mellitus
- Hyperlipidemia
- Drinking alcohol
- Obesity
- Lack of physical activity
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) risk factors
The risk factors for PADs are similar to those for coronary heart disease, which is caused by atherosclerosis:
- Age
- Family history and genetics
- Smoking or regularly breathing in second-hand smoke
- Stress
- Chronic kidney disease
- Diabetes
- Obesity or overweight
- High cholesterol levels
- Blood clot disorders such as thrombocytosis (high platelet count) or antiphospholipid syndrome (autoimmune disorder causes blood clot)
- Fibromuscular dysplasia (occurs when cells in the artery walls grow too much, narrowing the artery)
- High BP
- Metabolic syndrome
Aortic atherosclerosis risk factors
Several risk factors lead to the development of aortic atherosclerosis. These include:
- Premature age
- Hereditary
- Autoimmune disease
- Endothelial inflammation
- Low density lipoprotein
- Untreated hypertension
- Sedentary lifestyle such as smoking
- High total cholesterol
Complications of cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease complications can have a major impact on a person's quality of life and may be fatal. The following are the issues connected with cardiovascular disease:
Complications of coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease may trigger severe complications, many of which are life-threatening. Key complications of CAD are listed below:
- Heart failure
- Arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat)
- Heart attacks
- Ventricular tachycardia (severe arrhythmia)
- Sudden cardiac death
Complications of Cerebrovascular disease
Cerebrovascular disease has a wide range of possible complications. The severity of complications depends on the type and location of the cerebrovascular event. Some of the consequences are listed below:
- Recurrent stroke
- Epileptic seizure
- Deep venous thrombosis (DVT)
- Pressure sores (ulcers)
- Pneumonia
- Pulmonary embolism
- Urinary tract infection (UTI)
- Depression
- Anxiety
Complications of Peripheral artery disease (PAD)
Untreated PAD restricts blood supply to the limbs, causing a variety of complications, such as:
- Amputation (loss of a limb)
- Critical Limb Ischemia (severe blockages in the limb arteries)
- Coronary heart disease (CHD)
- Angina
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- Poor wound healing
- Gangrene (death and decay of body tissues)
- Infected ulcers
Complications of Aortic atherosclerosis
Atherosclerotic changes impact the aorta, disrupting normal blood flow and causing a number of severe medical conditions, such as
- Stroke
- Aortic aneurysm (bulging or weakening of the aortic wall)
- Heart attack
- PVD
- Aortic dissection.
- Embolic complications: Restricted blood flow to critical organs such as the stomach, intestines, or kidneys results in tissue death, leading to mesenteric ischemia (intestinal embolism), renal infarction (kidney embolism)
Cardiovascular disease diagnosis
The diagnosis of cardiovascular disease in patients is based on symptoms presented and the conditions that the healthcare expert may suspect
Diagnosis of coronary heart disease
If healthcare expert suspects the risk of CHD, they may do a risk assessment, including
- Medical history
- Family history
- Physical examination, which includes checking blood pressure
Further tests: Several typical tests diagnose CHD problems, including:
- Blood tests
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Coronary calcium scan
- Stress test
- MRI scans
- CT scans
- Coronary angiography
- Echocardiogram
- Cardiac positron emission tomography (PET) scan
Diagnosis of Cerebrovascular Disease
The majority of cerebrovascular disorders are identified by using diagnostic imaging tests which are listed below.
Cerebral angiography
- Carotid duplex (also called carotid ultrasound)
- Computed tomography (CT or CAT scan)
- Doppler ultrasound
- Electroencephalogram (EEG)
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Magnetic Resonance Angiogram (MRA)
Diagnosis of Peripheral arterial disease (PAD)
Healthcare experts can confirm the diagnosis of PAD by performing the following steps:
- Asking about symptoms
- Physical examination
- Calculating ABPI test score
Additional tests include
- Ankle-brachial index (ABI) test
- Blood test
- Doppler Ultrasound
- 6-minute walking test
- Segmental Doppler pressure testing
- Computed tomography Angiography
Diagnosis of Aortic atherosclerosis
Healthcare experts use imaging tests to diagnose and assess the progression of aortic atherosclerosis. These tests include the following:
- Transthoracic Echocardiography
- Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE)
- CT scan
- MRI scan
- Epiaortic ultrasound imaging
- Cardiac catheterization
- Angiography
Cardiovascular disease treatment
Treatment options for cardiovascular disease vary based on the condition and may include the following:
- Lifestyle changes for cardiovascular disease
- Medication for cardiovascular disease
- Devices
- Medical procedures
Coronary heart disease or cardiovascular heart disease treatment
Coronary heart disease (CHD) treatment may help in managing symptoms and lower the risk of future complications.
Medicines for CHD
Different kinds of medications are used to treat CHD. They usually try to lower blood pressure, expand the arteries, or avoid blood clots, including:
- Blood-thinning medicines
- Statins
- Beta blockers
- Vasodilator
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
- Angiotensin-2 receptor blockers (ARBs)
- Calcium channel blockers
- Diuretics
Lifestyle changes
- Choosing heart-healthy foods
- Being physically active
- Quitting smoking
- Getting enough good-quality sleep
- Aiming for a healthy weight
- Controlling blood sugar
- Managing stress
Surgery and procedure for CHD
Here are some of the main procedures used to treat arteries that are blocked. They are:
- Coronary angioplasty
- Coronary artery bypass graft
- Heart transplant
Cerebrovascular disease treatment
Treatment is determined by the severity of the narrowing and the patient's condition. The following are the treatments that can be recommended to treat cerebrovascular disease, including:
- Antihypertensives
- Anticoagulants
- Statins
Surgery and procedure for cerebrovascular disease
- Minimally invasive brain microsurgery
- Endovascular surgery
- Radiosurgery
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) treatment
There is no cure for peripheral arterial disease (PAD), but making lifestyle changes and taking medications can help to manage the symptoms, which include:
Lifestyle changes
- Exercising regularly
- Quitting smoking
- Eating a balanced diet
- Managing weight
- Cutting down on alcohol
- Mental wellbeing
- Managing diabetes
Medicines for PVD
- Statins
- Antihypertensives
- Blood-thinning medicines
- Vasodilator or peripheral vasodilator
Surgery and procedure for PVD
There are two main types of revascularisation treatment for PAD, such as:
- Angioplasty
- Artery bypass graft
Aortic atherosclerosis treatment
Treatment for aortic atherosclerosis includes drugs and lifestyle adjustments that focus on minimizing the risk of complications and slowing disease progression, including:
Medication of aortic atherosclerosis
- Anticoagulants
- Antihypertensives
- Statins
- Antiplatelet Drugs
Lifestyle changes include
- Exercising Regularly
- Reducing salt intake
- Quitting smoking
- Eating healthy diet
Surgery and procedure for aortic atherosclerosis
- Aortic valve replacement

Cardiovascular disease prevention
Living a healthy life can minimize the risk of cardiovascular disease, and for individuals who already have CVD, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help prevent the condition from worsening. The following are some of the preventive measures that can help people to avoid CVD, including:
Quitting smoking: Smoking is the major cause of CVD; hence, stopping smoking can help to lower the risk of CVD.
Having a balanced diet: A healthy, balanced diet is advised to maintain a healthy heart. A balanced diet contains:
- Low quantities of saturated fat and sugar
- Low salt intake
- High fibre content
- Consumption of whole grains.
- Plenty of vegetables and fruit.
Exercising regularly: Adults are advised to engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate activity each week, such as cycling or fast walking. This can help with weight management and lower the risk of diabetes, another risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
Maintaining a healthy weight: Individuals who are overweight or obese are at high risk of developing CVD. Extra weight can increase stress on the heart and blood vessels. Exercising frequently and eating a well-balanced diet will help with weight loss.
Avoiding alcohol: Try to avoid alcohol, if individuals consume alcohol, the recommended limit for both men and women is 14 units per week, and drinking should be spread out over at least three days to prevent health problems.
Difference between Coronary heart disease and cardiovascular disease
Coronary heart disease vs cardiovascular disease
Coronary heart disease and cardiovascular disease are both conditions related to heart and blood vessels, but they are different kinds of health conditions as follows:
| Elements | Coronary heart disease | Cardiovascular disease difference |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Coronary heart disease is a form of cardiovascular disease that affects the coronary arteries. It develops when plaque (a combination of cholesterol, fat, calcium, and other compounds in the blood) accumulates in the arteries, resulting in clogged arteries or atherosclerosis. | Cardiovascular disease term refers to a condition that affects the heart or blood vessels (arteries). |
| Cause | CAD is caused by atherosclerosis (plaque deposition) in coronary artery. | CVD is caused by atherosclerosis and factors that affects heart and blood vessels such as high BP, smoking, high cholesterol, physical inactivity |
| Types | CAD leads to angina (chest pain), heart attack (MI) and heart failure in severe cases. | CVD involves conditions such as coronary heart disease, peripheral artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, and aortic atherosclerosis |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Cardiovascular disease
How to detect cardiovascular disease?
The healthcare experts can diagnose cardiovascular disease (CVD) using a combination of tests and diagnostic procedures along with patient's medical history, risk factors, and physical examinations. Some of the tests include blood tests, ECG, echocardiogram, chest X-ray, CT scan, MRI scan, cardiac catheterization, and coronary angiography.
What are the symptoms of cardiovascular disease?
The symptoms of cardiovascular disease vary according to the condition. Some common symptoms of CVD include chest pain, tightness, pressure, and discomfort; shortness of breath and easily tiring during exercise or activity; very fast or slow heartbeat; palpitations or fluttering in the chest; and pain in the left arm or left jaw.
Is cardiovascular disease genetic?
It is possible to inherit genes from parents or ancestors that increase the likelihood of developing heart disease. While no single gene causes cardiovascular disease, several genes can increase the risk by influencing factors such as high blood pressure and cholesterol.
What causes cardiovascular disease?
The main etiology of cardiovascular disease is atherosclerosis (plaque buildup in arteries), but it is also caused by a combination of risk factors, including lifestyle factors such as obesity and being overweight, smoking, underlying health conditions like hypertension, high cholesterol, diabetes and genetics.
How to prevent cardiovascular disease?
The prevention of cardiovascular disease includes maintaining a healthy diet and weight, regular exercise of at least 150 minutes per week, eliminating all tobacco use, managing blood pressure and stress, controlling cholesterol levels, and having regular health checkups.
How to avoid cardiovascular disease?
To avoid cardiovascular disease, eat a healthy diet, avoid smoking, exercise regularly, maintain a healthy weight, limit alcohol, manage stress, and get enough sleep.
Is hypertension a cardiovascular disease?
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is not a cardiovascular disease, but it is a major risk factor for CVD. High blood pressure can damage blood vessels increasing the risk of various heart conditions.
What are the 4 types of cardiovascular disease?
The four types of cardiovascular diseases are coronary heart disease (CHD) or coronary artery disease (CAD), cerebrovascular disease, peripheral artery disease (PAD), and aortic atherosclerosis.
How does Parkinson’s disease affect the cardiovascular system?
Parkinson's disease (PD) primarily affects the cardiovascular system by causing autonomic dysfunction, resulting in issues such as irregular blood pressure, particularly a drop in blood pressure when standing up (orthostatic hypotension), and abnormal heart rate variations, can potentially increase the risk of strokes, heart attacks, and heart failure due to this disruption in the body's ability to regulate blood pressure and heart rhythm. Additionally, Some drugs used to treat Parkinson's disease can contribute to cardiovascular adverse effects such as low blood pressure.
How to treat cardiovascular disease?
Cardiovascular disease treatments vary depending on the condition and severity. The treatment options include adopting lifestyle changes like eating a balanced diet, maintaining a healthy weight being physically active, quitting smoking and getting enough sleep. In addition to lifestyle changes, medications are available to treat risk factors such as blood pressure or dissolve blood clots. If medications aren't enough, a healthcare expert may perform a procedure or surgery, such as a stent, minimally invasive heart surgery, or open-heart surgery.
What is cardiovascular disease?
Cardiovascular Disease (CVD), also called heart or circulatory disease, refers to a group of conditions that affect the heart or blood vessels (veins and arteries). It is frequently caused by the accumulation of fat and cholesterol deposits (atherosclerosis) in the arteries, which can increase the risk of blood clots.
What is arteriosclerotic cardiovascular disease?
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is an umbrella term that describes any heart and blood vessel conditions caused by atherosclerosis. It is a vascular disease where the arteries are damaged by factors such as high cholesterol, high blood pressure, diabetes or certain genetic influences.
Is heart disease and cardiovascular disease the same?
Heart disease refers to many disorders that affect the heart's anatomy and function. Cardiovascular disease deals with the blood vessels or arteries. Remember, all heart diseases are cardiovascular problems. However, not all cardiovascular disorders are heart disease. Coronary heart disease is the most prevalent type of cardiovascular disease. The term "heart disease" commonly refers to coronary heart disease.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868