Cervical Disc Prolapse - Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Prevention
Cervical disc prolapse definition
Cervical disc prolapse, also known as cervical disc herniation, is a condition where the soft inner material of the disc bulges between the vertebrae through a tear in the outer layer, compressing nearby nerves and leading to pain, tingling, or numbness.
Cervical disc prolapse is also termed as cervical slipped disc, cervical spinal disc prolapse, cervical disc protrusion, cervical slip disc, cervical disc bulge, cervical prolapsed intervertebral disc, and cervical ruptured or bulging disc.
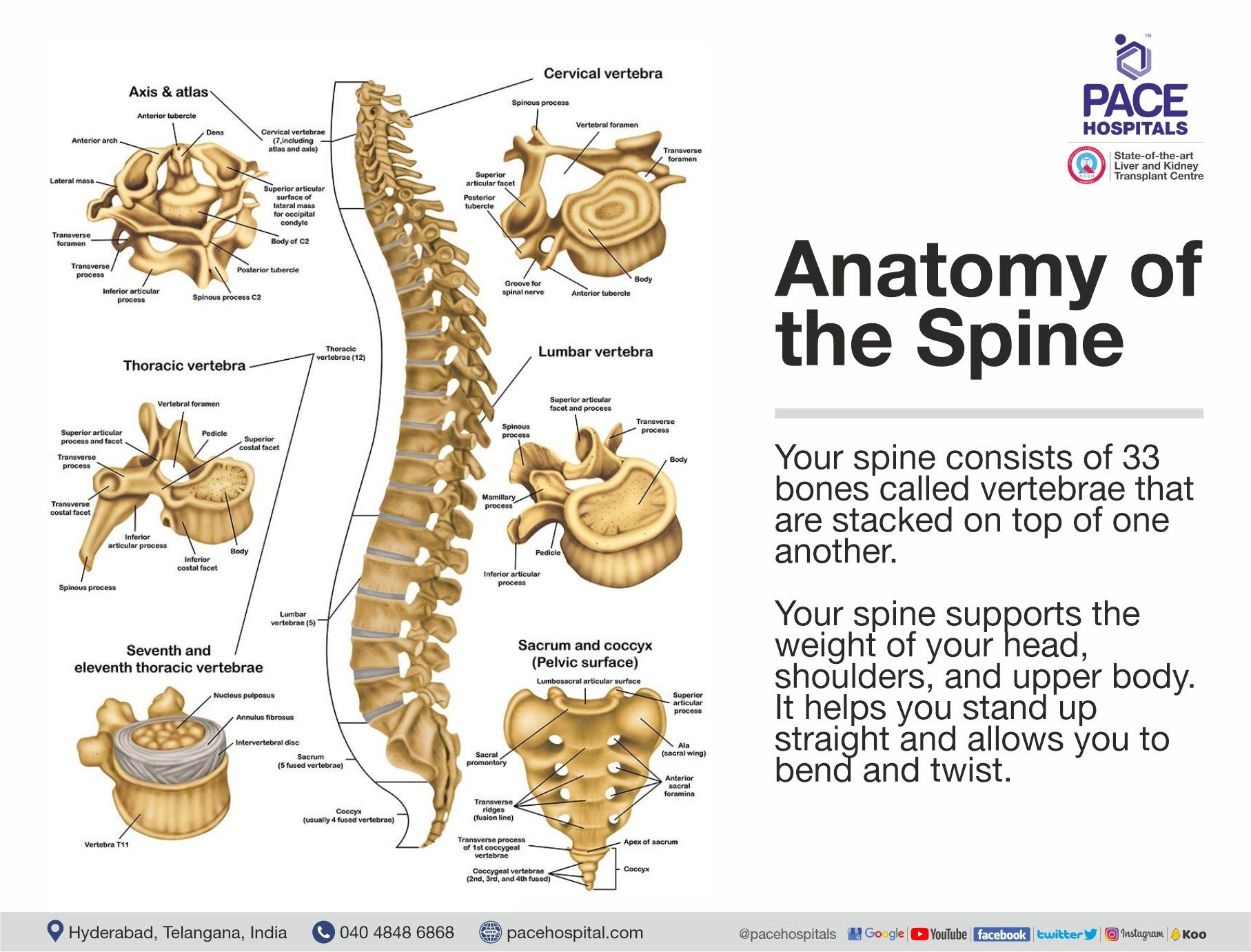
Cervical spine anatomy
The human spine has four regions: neck (cervical), upper back (thoracic), lower back (lumbar), pelvis (sacral), and is made of 33 bones (vertebrae) that are arranged one on top of the other to form the spinal column.
The cervical spine has seven vertebral bones, numbered C1 to C7, counting from the end of the skull to the thoracic spine. Cervical disc herniation typically occurs between C5-C6 and C6-C7 and may cause symptoms at C6 and C7, respectively.
Prevalence of cervical disc prolapse
Disc herniation prevalence is the most common, even in healthy people. Up to 20% of young adults and over 75% of older adults have spinal disc herniations, often without experiencing any issues. The incidence of cervical disc herniation rises with age for both men and women and is commonly seen in people in their 50s and mainly occurs in women (60%).
- A Romanian study published in 2015 demonstrated that the annual prevalence of cervical herniated disc cases could reach up to 5.5 patients per one lakh citizens. Seemingly, the study stated that the C5-C6 are the most effected vertebrae, followed by C4-C5 and C6-C7.
- As per Eastern India research, acute events like road traffic accidents, carrying heavy objects overhead, violence, assault, falls, repetitive strain in the neck, sports & recreation, and falling objects are some of the leading causes of cervical disc herniation and they published the following:
- Acute events leading to cervical disc herniation, including road traffic accidents, occur in 27.9% of cases within 48 hours.
- Lifting heavy objects accounted for 16.1% of the cases.
- Violence and assault accounted for 11.7% of the cases
- Road traffic accidents, violence, and assault may produce both radiculopathy with or without spinal cord injuries
- Fall accounted for 10.3% of the cases
- Repetitive strain accounted for 10.3% of cases
- Sports & recreation accounted for 7.3% of the cases
- Falling objects accounted for 4.4% of the cases
- No apparent cause (idiopathic) accounted for 11.7% of the cases

Cervical disc prolapse causes
The common cause of cervical disc prolapse is the degeneration and trauma to the cervical intervertebral disc. The cervical spine has smaller discs with high mobility; due to this, they are more prone to degeneration (wear and tear) from sudden forces and repetitive movement.
Other cervical disc herniation causes include the following:
- Age: When we are young, our spinal discs contain a significant amount of water. However, as we age, the amount of water in our spinal discs decreases, leading to a loss of flexibility in the discs. As a result, when we move, twist, or turn, there is a higher risk of developing disc herniation. This risk is particularly high in older individuals, as their discs can rupture with less force.
- Facet joints: Spinal changes arising from regular wear and tear, aggravated by age are seen usually among the discs and ligaments around the small joints at the back of the neck may induce a cervical herniated disc.
- Improper lifting: Instead of legs, using back muscles to lift heavy objects may cause a herniated disc, and twisting while lifting makes the muscles more vulnerable for herniation.
- Whiplash-type injury (Injury to the neck): Traumas or injuries such as accidents or sudden falls may force the cervical spine to cause a tear where the disc's inner gel bulges through the tougher outer layers leading to herniation.
- Movement (sudden twisting or bending of the neck): Sudden bending or twisting of the neck may strain the cervical spine discs. These motions may cause excessive pressure on discs, leading them to bulge resulting herniation.
- Repetitive activities that strain the spine: Constant neck bending in the forward motion, particularly in certain occupations or activities that require continuous pulling, lifting, twisting, or bending. Performing these actions repeatedly may strain the spine more.

Cervical disc prolapse symptoms
Cervical herniated disc symptoms may vary depending on which cervical disc has herniated and which nerve root has become inflamed or pinched. Signs and symptoms of cervical disc herniation include the following:
- Neck pain: Cervical herniated disc is a common cause of neck pain in adults due to spinal nerve swelling and inflammation caused by the pressure of the herniated disc, and severity ranges from mild to severe and even serious. This pain may radiate to the shoulder, arm, and hands, causing:
- Shoulder blades pain
- Arm pain
- Hand pain
- Radiculopathy: This condition may cause radiculopathy, a condition characterized by inflammation (swelling) and compression of the nerves near the cervical spine, resulting in other cervical disc protrusion symptoms, such as;
- Heaviness
- Weakness
- The tingling sensation of the affected arm/hand
Rarely, a large cervical disc herniation may cause a surgical emergency such as:
- Paraplegia: Paralysis of the legs and lower body
- Bladder incontinence: Loss of bladder control causing the leakage of urine
70% of patients may see some improvement within 4 to 6 weeks. Some people may experience mild and ongoing symptoms for several months.
Patients have been recommended to visit a healthcare professional if they experience any of the following emergency symptoms:
- Changes to eyesight (e.g., blurred or double vision)
- Severe headaches
- Vertigo (sensation of the environment around is moving or spinning)
- Numbness of face
- Difficulty in swallowing or speaking
- Significant loss of grip strength
- Metallic taste in the mouth
- Loss of hand dexterity (control in performing fine hand tasks)
- Unexplained trips or falls
- Changes to walking pattern

Cervical disc prolapse risk factors
Various lifestyle and behavioral factors may contribute to the development of a herniated cervical disc. Common risk factors for developing cervical disc herniation include the following:
- Age: Weakening of the disc happens with age, so middle-aged individuals are more prone to disc problems.
- Congenital abnormalities in the spinal canal: Congenital narrowing of the cervical spine may increase the risk of developing degenerative disease and traumatic injuries because of limited space in the canal.
- Occupational factors: Some occupational jobs need constant pulling, lifting, twisting, or bending. Performing these actions repeatedly may strain the spine, and jobs involving continuous repetitive motions may increase the risk of developing cervical disc herniation.
- Cervical spinal Injury or trauma: Accidents or sudden falls in the neck region may directly damage the discs, may tear, and increase the risk of developing cervical disc herniation.
- Lack of regular exercise: Lack of physical activity may weaken the muscles that support the spine, potentially raise the risk of cervical disc herniation.
- Tobacco use: Smoking may weaken the structure of the spinal discs and decrease the ability to heal, which may increase the herniated cervical disc risk.
- Poor posture: Improper lifting methods or continuous poor posture may strain the cervical spine, affecting discs by increasing stress.
- Inadequate nutrition: Insufficient nutrition may lead to weakened spinal structures, which reduces the ability to resist wear and tear, possibly increasing the likelihood of disc herniation.
- Poor lifestyle: Certain lifestyle habits, such as continuous sitting or lack of movement, may weaken the spine's supporting structures, potentially making it more vulnerable to herniation.
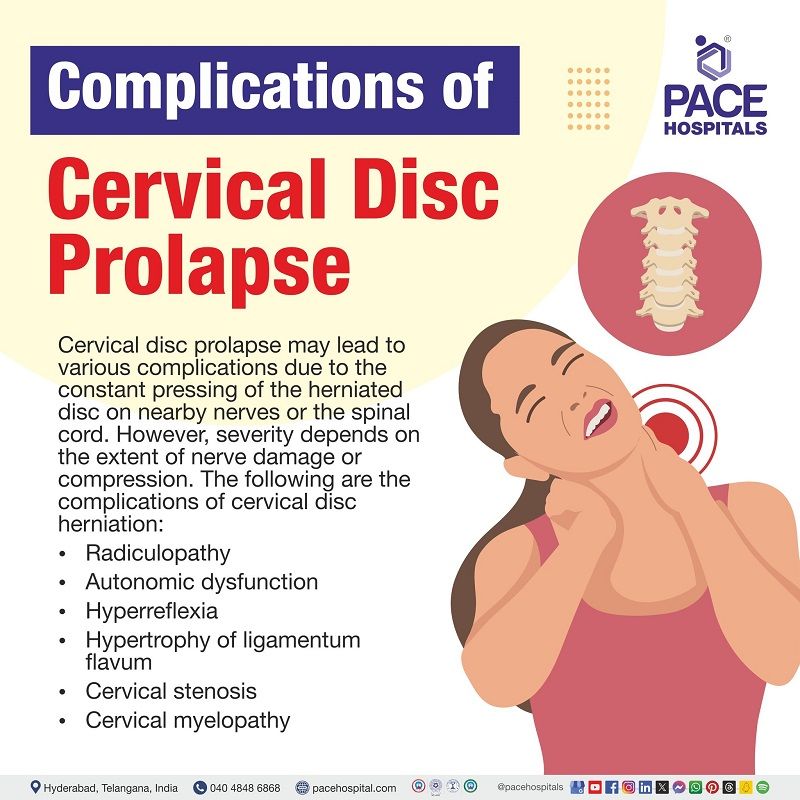
Cervical disc prolapse complications
Complications of cervical disc prolapse may occur if it is untreated. However, severity depends on the extent of nerve damage or compression. The following are the complications of cervical disc herniation:
- Radiculopathy: Nerve pain caused by pinching of nerves at the root
- Autonomic dysfunction: Abnormal or impaired functioning of the autonomic nervous system, it is the system of nerves that controls different body functions (e.g.: urinary urgency)
- Hyperreflexia: Overresponsive or overactive bodily reflexes to stimuli
Multilevel cervical degenerative disc disease (wear and tear on the discs and in the neck region) involves the breakdown of multiple neck discs, leading to the formation of bone spurs and osteophytes (bony growths) on the facet joints, causing the following complications:
- Hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum: Abnormal thickening of the ligamentum flavum, associated with spinal canal stenosis (Cervical stenosis: Narrowed spinal canal)
- Cervical myelopathy: The condition occurs due to compression of the spinal cord in the neck
Cervical disc herniation diagnosis
Diagnosis of cervical disc herniation mainly includes the following:
- History
- Physical examination
- Spurling test
- Hoffman test
- Lhermitte sign
- Lab tests
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive (CRP)
- Complete Blood Count (CBC)
- Imaging tests
- X-rays
- Computed Tomography (CT) imaging
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- CT myelography
- Other tests
- Discography
- Electrodiagnostic testing
- Electromyography
- Nerve conduction studies
History
When patients complain about neck pain and discomfort or other symptoms, healthcare professionals (including physicians specialized in neurology, orthopaedics, or spine care) may ask about how the pain started, when the symptoms began, what makes them worse or better, any numbness, shooting pain or tingling, past treatments, past medical history and medication history and family history to understand the problem better.
Evaluating some issues that indicate inflammatory conditions, infection, or malignancy along with neck pain may help in choosing the proper treatment; these include:
- Fever and chills
- Unexplained weight loss
- Night sweats
- History of inflammatory arthritis, malignancy, systemic infection, tuberculosis, drug use, HIV or immunosuppression
- Unrelenting pain
- Point tenderness over a vertebral body
Physical examination
Healthcare professionals (including physicians specialized in neurology, orthopaedics, or spine care) perform a physical exam to check the range of motion (how much a patient can move neck-neck movement) to understand the severity of pain and damage, reduced reflexes, and muscle weakness.
Solitary nerve lesions (nerve damage or injury) occur by compressed herniated discs in the cervical spine and often cause certain symptoms that include:
- C2 nerve: Eye or eye pain, headache
- C3, C4 nerve: Muscle spasms, vague neck and trapezial tenderness
- C5 nerve: Shoulder, neck and scapula pain
- C6 nerve: Neck, shoulder, and scapula pain.
- C7 nerve: Neck and shoulder pain
- C8 nerve: Neck and shoulder pain
- T1 nerve: Neck and shoulder pain
Provocative tests such as the Spurling, Hoffman, and Lhermitte sign tests might provoke certain symptoms indicating nerve problems.
- Spurling test: It involves rotating and bending the neck to one side while pushing down on the head to diagnose acute radiculopathy. If the person has cervical disc herniation, it may worsen neck pain by neuroforamen (narrowing the space for nerves).
- Hoffman test: It includes a flick on the person's fingertip, causing involuntary thumb movement, which indicates myelopathy (spinal cord compression).
- Lhermitte sign: During this test, a healthcare professional asks the patients to bend their neck forward, which may cause a sensation (electric shock) that travels down to the spine and limbs, signifying possible problems with the nerves or spinal cord.
Imaging tests
Most cases of herniation may resolve within the first four weeks without any treatment. Imaging tests are typically not recommended during this period since the treatment approach would not be affected.
Imaging is mainly advised if there's suspicion of neurological problems or potentially serious issues. Additionally, if conservative treatments on a patient might fail to aid after 4 to 6 weeks or if red flag symptoms persist, further examination, including additional imaging and lab tests, might be required to understand the underlying cause.
The following are the some of the common imaging tests that might be recommended based on patient condition:
- X-rays: It is the first test usually performed and is very accessible at many hospitals. Three various X-ray views (anteroposterior (AP), lateral, and oblique) aid in evaluating the overall alignment of the spine and diagnosing the degenerative or spondylotic changes. Lateral flexion (bending the spine sideways to the right or left) and extension (straightening the spine backward) X-ray views aid in detecting spinal instability. If imaging (X-ray) shows an acute (recent) fracture, this needs additional examination using a computed tomogram (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). For concerns about atlantoaxial instability (instability between the first two neck vertebrae), an odontoid (open mouth) view may be recommended to help diagnose.
- Computed Tomography (CT) imaging: It is a highly sensitive test for evaluating the bone structures of the spine, revealing details about degenerative changes or fractures. This test can also identify bone-related issues or calcified herniated discs that do not readily appear or are visible on other scans. In patients unable to undergo MRI testing, CT myelography acts as an alternative method to display herniated discs.
- MRI: It is the preferred imaging method and the sensitive test to visualize a herniated disc, as it provides detailed pictures of soft tissues and nerves, showing the disc and how it affects the nearby structures. They may produce higher-quality images of soft tissues commonly used to assess a herniated disc and show a disc bulge, protrusion, or herniation.
- CT myelography: It is a vital imaging method that combines the benefits of myelography and high resolution of CT. It utilizes a contrast dye and X-rays or computed tomography (CT) to check problems in the spinal canal, spinal cord, nerve roots, and other tissues. A healthcare professional may remove some amount of spinal fluid from the spinal canal and injects a small amount of contrast dye; the x-ray table might be tilted in different directions to pass the contrast dye to various areas of the spinal cord to get detailed images of the body.
Laboratory tests
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive (CRP): The ESR and CRP are both inflammatory markers that might be checked if a chronic inflammatory condition is suspected (such as polymyalgia rheumatica(condition that causes pain, stiffness and inflammation in the muscles around the shoulders, neck and hips), seronegative spondyloarthropathy (Seronegative spondyloarthropathies are a group of disorders characterized by inflammation of the spine, pelvis, or peripheral joints), rheumatoid arthritis). These tests might be beneficial if an infectious condition is suspected.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC):
A CBC test is useful when there's suspicion of cancer or infection and provides detailed information about different blood cell types such as neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils, helping in the diagnosis of similar symptoms.
Other tests
Discography: It is also called a discogram, and it is performed to detect painful spinal discs. It may show the source of pain in the patient's neck. It was first used in the lumbar region, but recently, it has been applied to the cervical region. The cervical disc will be punctured on its anterolateral surface (front or side of the cervical disc) to inject a small amount of fluid within the disc space in an attempt to bring out the patient's neck pain. This procedure gives detailed information about the pathologic origin of neck, shoulder, and arm pain (identifies the origin of pain from a specific disc).
Electrodiagnostic testing: It includes electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies, which may be performed in patients with unclear symptoms and imaging results to rule out peripheral nerve problems. However, their ability to find cervical radiculopathy differs with a sensitivity range of 50% to 71%.
Cervical disc prolapse treatment might be divided into three types, namely:
Conservative treatments
- Rest
- Medicines
- NSAID's
- Collar immobilization
- Physical therapy
- Cervical manipulation
- Cold and heat
- Traction
Interventional treatments
- Spinal steroid injections
- Neuromodulatory techniques
Surgical treatment
- Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF)
- Posterior cervical laminoforaminotomy
- Total disc replacement
- Cervical corpectomy and fusion
Conservative treatments (non-surgical treatment)
Most of the cases may resolve on their own within several weeks without treatment. However, conservative treatments may be initiated if the symptoms remain persistent. Acute cervical radiculopathies occurring by a herniated disc are often treated without a surgical approach; 75% - 90% of the patients will show improvement.
Non-surgical treatment (conservative treatment) for cervical herniated discs involves the following:
- Rest: Rest breaks taken throughout the day can help relieve pain. However, it is essential to avoid sitting for long periods.
- Medications: Medications such as analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs may relieve the pain. Muscle relaxants might be prescribed if the patient has arms, legs, or back spasms. There is insufficient evidence to support the use of NSAIDs in treating cervical radiculopathy. However, they may be beneficial for some patients. Using COX-1 and COX-2 inhibitors does not change the analgesic (pain-relieving) effect, but COX-2 inhibitors may be less harmful to the gastrointestinal tract. Healthcare professionals may prescribe short-term use of steroidal anti-inflammatories for severe acute pain in cervical radiculopathy.
- Opioid drugs may not usually be suggested for cervical radiculopathy because of no concrete evidence and higher risks of side effects. Anticonvulsants and antidepressants may have been used to treat neuropathic pain and provide a moderate analgesic effect.
- Physical therapy: It is commonly recommended after a short period of rest and immobilization. It often involves various methods, such as cervical disc prolapse exercises for strength and movement, range of motion, strengthening exercises, and therapies such as heat, ice, and electrical stimulation. These modalities may promote healing, strengthen (support) the patient's lower back and abdominal muscles, and reduce the symptoms in affected regions. Traction is also applied to the patient in the neck. The patient will be trained to sit, stand, and lift to avoid injuries in the cervical region.
- Cervical manipulation: It is a type of physical therapy where a trained healthcare professionals (includes nurse practitioners, primary care physicians, orthopaedic and neurosurgeons, pain specialists, chiropractors, physical therapists), applies controlled force to the neck joints to improve mobility, decrease pain, and enhance function in people with neck stiffness or specific neck conditions. However, there is limited evidence recommending that this procedure may provide short-term benefits for neck pain and cervicogenic headaches (headache that originates from the issues of the neck). Complications from this procedure are rare and may include worsening myelopathy, radiculopathy, spinal cord injury, and vertebral artery injury.
- Cold and heat: Applying cold compresses multiple times a day can help relieve pain. Once the spasms lower, gentle heat may be used to relieve symptoms.
- Traction: It is a treatment for neck pain that involves lightly pulling (stretching) at a specific neck angle (around 24 degrees bent forward) for 15-20 minutes to relieve pain and pressure by creating space around the nerves and bones in the neck for alleviating the symptoms of compressed nerves.
- Collar immobilization: It is also called a neck brace. It is a medical device designed to limit the neck movement and provide support. In patients with acute neck pain, this medical device might be recommended for a short time (around one week) to stabilize the cervical spine, allowing the affected area to heal by limiting motion and decreasing strain on the neck muscles and spine.
Interventional treatments
The following injections and neuromodulatory devices may offer minimally invasive, efficacious treatment approaches.
- Spinal steroid and perineural injections: These injections may target certain regions in the spine, confirmed by MRI, and might be given to reduce the local inflammation in the neck. These injections are often used instead of a surgical approach and conducted under radiologic guidance.
- Neuromodulatory techniques:
In recent years, neuromodulation techniques have been widely used to manage radicular pain associated with disc herniations. These techniques mainly consist of a spinal cord stimulation device (which sends electrical signals to the spinal cord to block pain signals) and an intrathecal pain pump (which delivers medication directly into the spinal fluid to decrease pain). These techniques are helpful for people who are not candidates for cervical herniated disc surgery.
Surgical treatment
Indications for surgery include severe or progressive neurological issues and continuous pain that is unresponsive to conservative treatments. Different surgical methods exist; however, the primary approach for cervical radiculopathy is anterior cervical discectomy with fusion.
- Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF): It is a procedure for a herniated disc in the neck to relieve pressure by removing the herniated disc. This procedure helps remove the problematic disc and avoids future nerve compression by fusing the injured spinal bones. For a fusion, a bone is inserted into the empty disc space; an artificial disc (made of plastic and metal) is placed into the disc space for a disc replacement.
- Posterior cervical laminoforaminotomy: It reduces nerve compression by removing parts of the bone and tissue in the cervical spine to obtain and decompress the affected nerve roots. During this procedure, neuro or ortho surgeon use small instruments to shave the thin plate of bone (lamina), which protects the spinal cord and removes the crowding tissues, bone, and disc pressing on nerves in the foramen (small opening). The incision will be closed, and the bandaged for healing.
- Total disc replacement (TDR): This process involves the replacement of natural cervical discs with an artificial disc, which the FDA recently approved. This surgery allows more movement and creates less stress on the remaining vertebrae. During the procedure, the neuro or ortho surgeon creates a small cut on the front or side of the neck. To access the spine, the surgeon moves the other structures to the side after the affected disc is removed from its place and replaced with an artificial disc between two vertebrae.
- Cervical corpectomy and fusion: It is a procedure performed to remove one or more bones (vertebrae) in the neck (cervical spine) and intervertebral disc material to relieve pain and pressure on the spinal cord. It involves the removal of degenerative vertebrae and their replacement and fusion with a bone graft or a metal cage filled with bone graft.

Cervical disc prolapse prevention
The following are some preventive measures that one may take to avoid cervical disc herniation:
- Maintaining a good posture: Maintaining a proper posture while playing sports or generally standing, sitting, and sleeping does help to avoid disc herniation.
- Practicing exercises: Practicing neck exercises such as shoulder stretch, chin tucks, etc., to improve flexibility and strengthen (support) the muscles around the neck.
- Managing weight: Controlling weight may help to reduce the strain on discs, which prevents spine problems or disc herniations.
- Avoiding prolonged sitting: Avoiding long-time sitting or standing to avoid increased pressure strain on the spinal discs. Doing simple neck stretches while sitting or standing in the same position for a long time strengthens the muscles.
- Preventing repetitive neck flexion: Repeating neck flexion may strain the spine more. Hence, it is recommended to avoid repetitive neck flexion.
- Having a proper diet: Eating green and leafy veggies, nuts, oily fish, and other foods may help fight inflammation if present.
Difference between cervical and lumbar disc herniation
Cervical vs Lumbar disc herniation
Although cervical and lumbar disc herniations are similar, they have slight differences. Below mentioned are some of the differences between cervical and lumbar disc herniation:
| Elements | Cervical disc herniation | Lumbar disc herniation |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Herniated cervical disc occurs in the neck (cervical) region of the spine. | Herniated lumbar disc occurs in the back spine (lumbar) region of the spine. |
| Affected nerves | Typically occurs between C5-C6 and C6-C7 | L4-S1 |
| Symptoms | Symptoms mainly include neck pain, which extends to shoulder, arm and fingers. Along with pain, some patients may experience numbness or weakness in the upper extremities. | Symptoms of lumbar disc herniation mainly includes lower back pain, that radiates to the leg and foot. Along with pain, some patients may experience weakness, numbness or tingling sensation in the lower extremities. |
| Causes | Usually, it occurs due to degeneration, trauma or injury in the neck region, repetitive neck movements, sudden twisting or bending of the neck | It mainly occurs due to lifting injuries, obesity, age related wear and tear. |
| Prevalence | Less common than lumbar disc herniation. | More common than cervical and thoracic disc herniation. |
| Complications | Complications of herniated cervical disc includes radiculopathy, autonomic dysfunction and hyperreflexia. | Complications of herniated lumbar disc includes chronic back pain, leg numbness or weakness and cauda equina syndrome. |
| Treatment | Treatment options include observation, pain medications, physical therapy, neck mobilization and surgery. | Treatment options include pain medications, collar immobilization, physical therapy and surgery. |
| Surgery | Surgical approaches of cervical disc herniation include anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF), posterior cervical laminoforaminotomy, total disc replacement, cervical corpectomy and fusion. | Surgical approaches of lumbar disc herniation mainly include discectomy (microdiscectomy and endoscopic discectomy). |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Cervical disc prolapse
Is cervical herniated disc dangerous?
Cervical herniated disc is not dangerous, it may cause significant pain or discomfort in the arms and neck. Most of the herniated discs are manageable. However, if left untreated, it may cause severe nerve compression, leading to weakness, numbness, or even bladder control problems. Although not inherently dangerous, it may impact daily activities and require medical attention for proper management.
Can I exercise with a cervical herniated disc?
Yes, one may exercise with a cervical herniated disc, but visiting a physical therapist or healthcare professional (including primary care physicians, emergency physicians, orthopaedic and neurosurgeons, pain specialists, chiropractors, physical therapists) for proper guidance is essential. Some healthcare professionals recommend avoiding high-impact exercises such as jumping, running, or powerlifting, which involve sudden or sharp movements and might significantly raise the strain on the neck, causing pain and slowing down healing. They may recommend exercises that help manage symptoms without progressing the condition, concentrating on gentle movements.
Is a cervical herniated disc permanent?
Cervical herniated disc is not permanent. The majority of cases of acute cervical disc herniation or acute spinal injury may resolve or heal within the first - four weeks without treatment. However, if the person is getting persistent neck pain radiating to nearby parts, it indicates some serious problem. If left untreated, a cervical herniated disc may cause permanent damage.
How long it will take for cervical herniated disc to heal?
For most patients, symptoms such as pain, restricted motion, and radiculopathy resulting from a cervical herniated disc, typically resolve on their own within six weeks. If they persist for more than six weeks, symptoms are less likely to improve without surgical intervention. In about one-third of patients, symptoms persist even after non-operative intervention.
when surgery is needed for cervical herniated disk?
Surgery is suggested in conditions when there are six months of persisting symptoms, severe or progressive neurological issues, and continuous pain that is unresponsive to conservative treatments (non-operative treatments). It is recommended to consult a healthcare professional if anyone is suffering from the above symptoms to improve faster.
What is prolapsed cervical disc?
A prolapsed cervical disc, also called a slipped disc or herniated disc, is a medical condition characterized by a displacement of disc material (nucleus pulposus-soft material) beyond the space of the intervertebral disc, thereby causing symptoms including pain, numbness, and neurological issues.
What does a cervical herniated disc feel like?
A cervical herniated disc may cause neck pain that feels like electricity or shock -radiating to the shoulder plates, down to the arms, and possibly into the hand. It may also lead to weakness, numbness, or tingling and is often associated with discomfort when performing certain activities or moving the neck. Sometimes, people may have uncontrollable muscle tightness (muscle spasms).
What are some strengthening exercises for cervical herniated disc?
Chin tucks, neck extensions (supported with a towel), one arm pec stretch – at a wall (do both sides), upper trapezius stretch, scapular retraction, isometric holds, neck rotations, and chest stretch are some of the strengthening exercises for a cervical herniated disc.
Can herniated cervical disc cause memory problems?
Herniated cervical discs may not cause memory problems directly. However, in rare cases, if the herniated disc compresses specific nerves moving to the brain, it may lead to persistent discomfort or pain, affecting sleep quality, which may show some impact on cognitive functions such as difficulty in concentrating or memory.
Can herniated cervical disc causes leg numbness?
If the herniated disc compresses nearby nerves in the cervical spine that extend down the arms and into the legs. In that case, it may cause symptoms such as leg numbness or weakness, problems with coordination or walking, and difficulty with bladder or bowel control. Having any of these signs requires prompt medical attention.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868