Chronic Calcific Pancreatitis (CCP): Symptoms, Causes, Complications, Treatment & Prevention
Chronic calcific pancreatitis definition
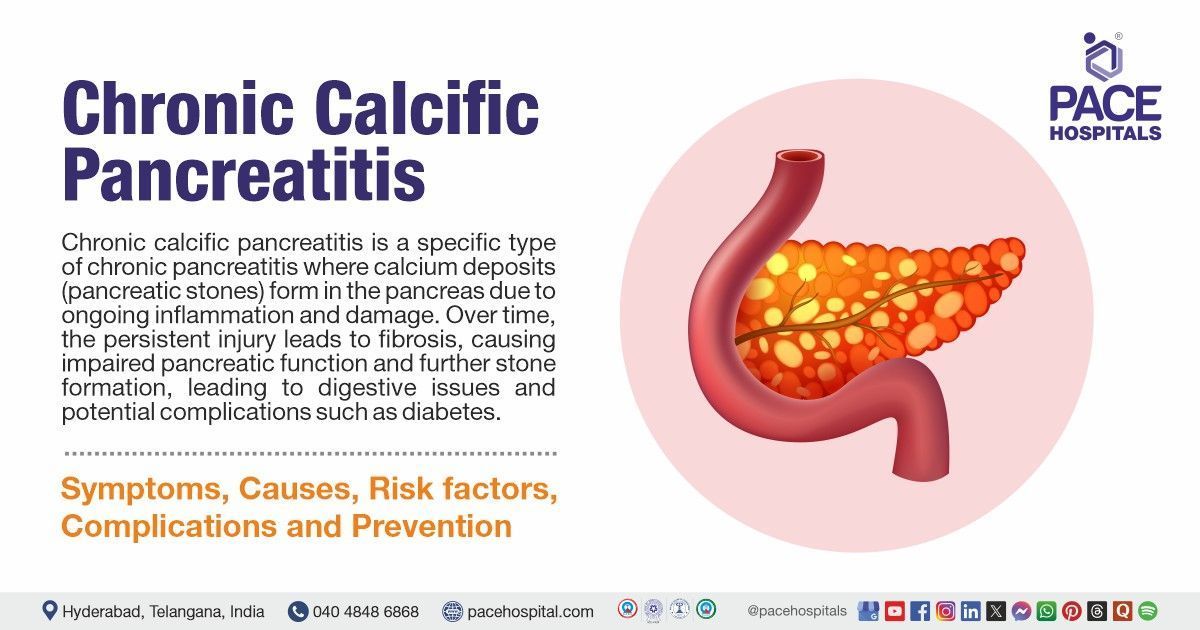
Chronic calcific pancreatitis is a specific type of chronic pancreatitis where calcium deposits (pancreatic stones) form in the pancreas due to ongoing inflammation and damage. Over time, the persistent injury leads to fibrosis, causing impaired pancreatic function and further stone formation, leading to digestive issues and potential complications such as diabetes.
Chronic pancreatitis is a long-term pancreas inflammation, while chronic calcific pancreatitis involves the formation of calcium deposits in the pancreas due to prolonged inflammation, often leading to further damage. Both conditions are similar in cause but differ in the presence of calcification.
Chronic calcific pancreatitis meaning
- Chronic: A long-lasting or persistent condition that develops and progresses over time rather than being acute or short-term.
- Calcific: Accumulation of calcium deposits, which result from ongoing inflammation, leads to hardening or scarring of the pancreatic tissue.
- Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas
- Chronic Calcific Pancreatitis: This condition refers to long-term inflammation of the pancreas that results in calcium deposits (calcifications), which can impair pancreatic function, leading to digestive issues and potential complications such as
diabetes.

Chronic calcific pancreatitis symptoms
The symptoms can develop gradually and persist over time, often becoming more severe with disease progression.
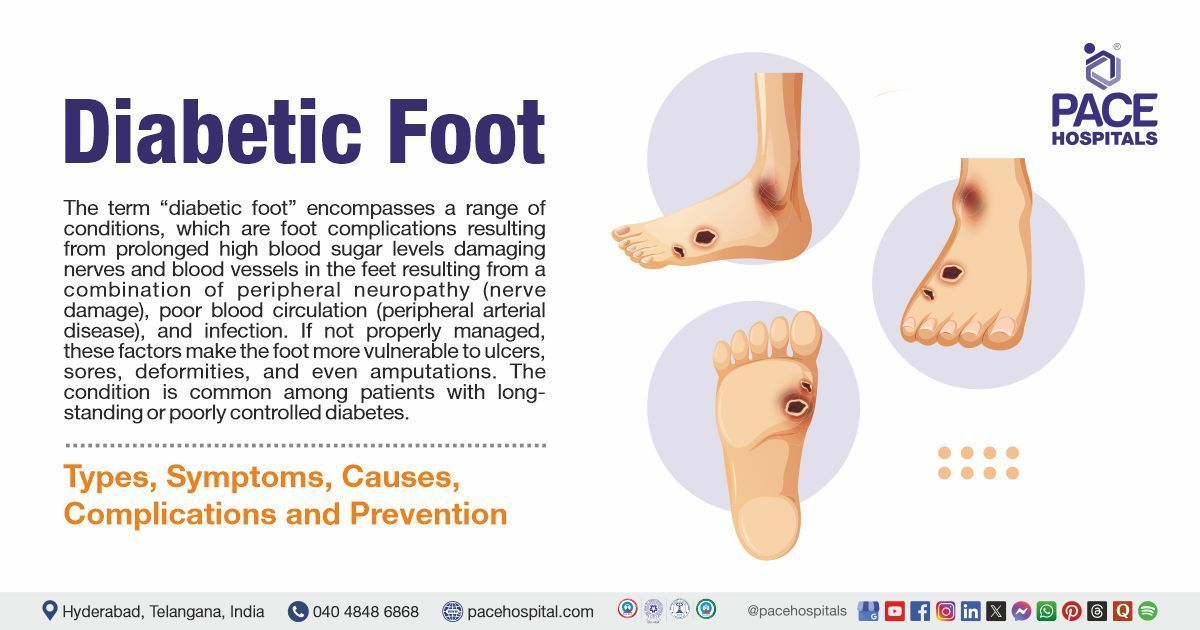
- Abdominal Pain: Pain, usually in the upper abdomen, is a hallmark of CCP, often aggravated by eating and can become chronic or episodic.
- Steatorrhea (Fatty Stools): Due to impaired pancreatic enzyme production, undigested fat leads to oily, foul-smelling stools, signalling poor fat absorption.
- Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss occurs as a result of malabsorption, where the body is unable to absorb nutrients from food properly.
- Jaundice: If pancreatic damage obstructs bile ducts, jaundice occurs (characterized by yellowing of the eyes and skin), hindering bile flow.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Chronic nausea and occasional vomiting are common, often linked to digestive difficulties caused by the pancreas's reduced function.
- Diabetes: As the pancreas becomes more damaged, insulin production declines, leading to the development of diabetes in many individuals with CCP.
- Malnutrition: Due to poor nutrient absorption and digestive disturbances, malnutrition is a frequent and serious concern in individuals with chronic calcific pancreatitis.

Chronic calcific pancreatitis causes
The following factors play a role in the gradual deterioration of the pancreas, resulting in its fibrosis and calcification as time progresses, includes:
- Genetic factors: Alterations in genes such as CFTR (Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator) or SPINK1 can predispose individuals to develop the condition.
- Alcohol Consumption: Excessive and prolonged consumption of alcohol is the primary cause of chronic calcific pancreatitis, leading to pancreatic inflammation and the formation of fibrous tissue.
- Obstructive causes: Narrowing of pancreatic ducts due to strictures, stones, or tumors can lead to chronic inflammation and calcification in the pancreas.
- Autoimmune conditions: Diseases such as autoimmune pancreatitis (where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the pancreas) can result in ongoing inflammation and the formation of calcium deposits.
- Hypercalcemia: Elevated calcium levels in the blood, whether due to metabolic disorders or parathyroid dysfunction, may increase the risk of calcifications in the pancreas.
- Idiopathic causes: In certain instances, the underlying cause of chronic calcific pancreatitis is unknown and referred to as idiopathic.
Chronic calcific pancreatitis risk factors
Risk factors for Chronic Calcific Pancreatitis (CCP) develop over time due to various lifestyles, genetic, and environmental factors. These risk factors may persist or intensify, contributing to the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Alcohol Consumption: Chronic (long-term), heavy drinking is a primary risk factor, often leading to repeated inflammation and eventual pancreatic calcification.
- Genetic Mutations: Inherited genetic conditions, such as mutations in the CFTR gene (associated with cystic fibrosis), can increase the risk of developing CCP, often from a young age.
- Smoking: Cigarette smoking contributes to pancreatic damage and significantly raises the risk of developing chronic pancreatitis and its complications.
- High-Fat Diet: A diet rich in fats can promote obesity and pancreatic inflammation, both of which are associated with the development of CCP.
- Hyperlipidaemia: Elevated cholesterol or triglyceride levels in the blood can contribute to pancreatitis by increasing the risk of pancreatic inflammation and damage.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like autoimmune pancreatitis, where the body attacks its own pancreatic cells, can raise the risk of chronic pancreatitis, including calcification.
- Pancreatic Duct Obstruction: Blockages in the pancreatic ducts due to conditions like gallstones or tumors can result in chronic inflammation and calcification in the pancreas.
- Previous Episodes of Acute Pancreatitis: Repeated acute pancreatitis episodes can lead to scarring and calcification in the pancreas, raising the risk of chronic pancreatitis.
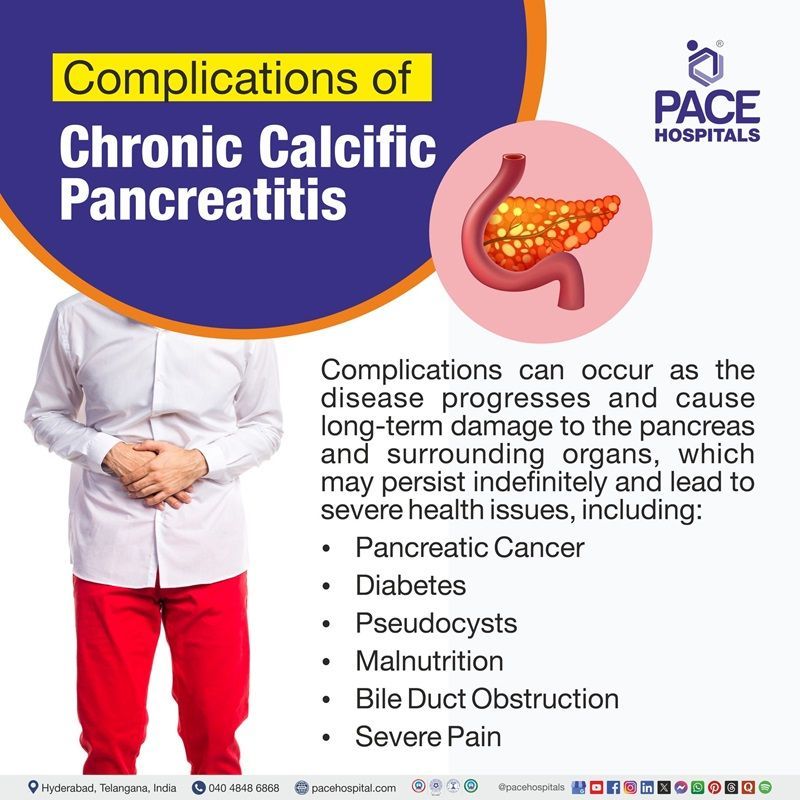
Chronic calcific pancreatitis complications
Complications can occur as the disease progresses and cause long-term damage to the pancreas and surrounding organs, which may persist indefinitely and lead to severe health issues, including:
- Pancreatic Cancer: Chronic inflammation and scarring can increase the risk of pancreatic cancer, which is often diagnosed late and has poor outcomes.
- Diabetes: As the pancreas becomes increasingly damaged, its ability to produce insulin declines, leading to the development of diabetes in many patients with CCP.
- Pseudocysts: Fluid-filled sacs, known as pseudocysts, can form in the pancreas, leading to infection, rupture, or bleeding, which may require surgical intervention.
- Malnutrition: Impaired digestion due to decreased enzyme production can lead to malabsorption of certain nutrients, resulting in malnutrition and vitamin deficiencies.
- Bile Duct Obstruction: Calcification and scarring in the pancreas can obstruct bile ducts, leading to jaundice and associated liver problems.
- Severe Pain: Chronic abdominal pain due to the ongoing inflammation and damage to pancreatic tissue is one of the most debilitating symptoms, requiring long-term management.
Chronic calcific pancreatitis diagnosis
Certain tests will be recommended to diagnose chronic calcific pancreatitis when patients exhibit persistent abdominal pain, digestive issues, or other symptoms that suggest pancreatic dysfunction, including:
- Clinical Examination
- Physical exam
- Medical history
- Imaging Tests
- CT scans
- MRI
- Ultrasound imaging
- Blood Tests
- Liver function tests
- Pancreatic enzyme levels
- Other tests
- Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
- Biopsy
Chronic calcific pancreatitis treatment
Treatment for chronic calcific pancreatitis aims to alleviate symptoms, prevent complications, and enhance the patient's quality of life. Options include medical management, lifestyle changes, and, in some cases, surgery, such as:
- Pain Management
- Medications
- Analgesics
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Nerve blocks (severe pain)
- Lifestyle Modifications
- Insulin Therapy
- Pancreatic Enzyme Replacement Therapy (PERT)
- Endoscopic Interventions
- Surgery

Chronic calcific pancreatitis prevention
Preventive measures are essential to reduce the risk of developing chronic calcific pancreatitis and protect the pancreas from further damage. Adopting these measures can help maintain overall digestive health.
- Limiting Alcohol Consumption: Overconsumption of alcohol is a major risk factor for CCP, so reducing or eliminating alcohol intake can significantly lower the chances of developing the condition.
- Eating a balanced diet: A diet rich in vegetables, lean proteins, fruits and whole grains supports healthy pancreas function and reduces the risk of pancreatitis.
- Quitting Smoking: Smoking is another risk factor for CCP, and quitting can help prevent further pancreatic damage and improve overall health.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Obesity and high-fat diets are linked to pancreatitis, so maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the risk of developing CCP.
- Controlling Blood Lipid Levels: Controlling cholesterol and triglyceride levels through medication and diet can help prevent complications related to CCP.
- Addressing underlying Conditions: Addressing conditions such as gallstones or high blood pressure that affect the pancreas or bile ducts can reduce the risk of CCP.
Frequently Asked Questions on Chronic Calcific Pancreatitis (CCP)
How is Chronic Calcific Pancreatitis diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves specific medical examinations, including imaging tests such as CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds to detect pancreatic calcifications. Blood tests can measure pancreatic enzyme levels, and in some cases, an endoscopic procedure like ERCP is used to assess the ducts.
Can Chronic Calcific Pancreatitis lead to cancer?
Chronic inflammation in the pancreas from CCP increases the risk of pancreatic cancer. Patients with CCP need to be monitored regularly for signs of cancer, as the condition can create a more favourable environment for tumor growth.
How is Chronic Calcific Pancreatitis treated?
Treatment emphasizes managing symptoms and preventing any additional damage. This may include pain management, enzyme replacement therapy to aid digestion, lifestyle changes (like dietary adjustments), and insulin therapy for those with diabetes. In some cases, surgery or endoscopic interventions may be required.
What lifestyle changes are recommended for Chronic Calcific Pancreatitis?
Patients with CCP are advised to avoid alcohol, quit smoking, eat a low-fat, balanced diet, and maintain a healthy weight. These changes help reduce inflammation and improve overall pancreatic function, slowing the progression of the disease.
Is Chronic Calcific Pancreatitis hereditary?
Specific genetic factors can play a major role in the development of CCP. Inherited genetic mutations, such as those found in the Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator CFTR gene, can predispose individuals to chronic pancreatitis, even in the absence of lifestyle risk factors like alcohol consumption.
Can Chronic Calcific Pancreatitis be reversed?
CCP is a progressive, irreversible condition, meaning it cannot be fully cured. However, with proper management and lifestyle changes, symptoms can be controlled, and further damage to the pancreas can be slowed down.
What is chronic pancreatitis calcification?
Chronic pancreatitis calcification is the formation of calcium deposits in the pancreas due to long-term inflammation and damage. This process arises from chronic pancreatitis, leading to scarring and impaired pancreatic function.
Can Chronic Calcific Pancreatitis cause diabetes?
Yes, as the pancreas becomes damaged and its ability to produce insulin decreases, many individuals with CCP develop diabetes. This occurs because the pancreas's endocrine function, which is responsible for insulin production, is impaired due to inflammation and scarring.
How to remove the calcification of the pancreas?
Pancreatic calcifications can be removed with endoscopic therapy or surgery. The treatment depends on the size of the calcifications, the location of the disease, and the patient's tolerance for surgery.
Unfortunately, calcifications occur late during chronic pancreatitis, being associated with severe disease as they indicate chronic damage and inflammation in the pancreas, typically from conditions like Chronic Calcific Pancreatitis. Over time, this can impair the pancreas's ability to produce digestive enzymes and insulin, leading to digestive problems, malnutrition, and diabetes. Additionally, it increases the risk of developing more severe complications like pancreatic cancer.
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868
Appointment request - health articles
Thank you for contacting us. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Oops, there was an error sending your message. Please try again later. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Our Locations – Find the Best Hospital Near You
Metro Pillar Number C1772, Beside Avasa Hotel, Hitech City Road, Near HITEC City Metro Station, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Mythri Nagar, Beside South India Shopping Mall, Hafeezpet, Madeenaguda, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
040 4848 6868
Payment in advance for treatment at PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, Telangana, India (Pay in INR ₹)
For Bank Transfer:-
- Bank Name: HDFC
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.50200028705218
IFSC Code: HDFC0000545 - Bank Name: STATE BANK OF INDIA
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.62206858997
IFSC Code: SBIN0020299
Scan QR Code by Any Payment App (GPay, Paytm, Phonepe, BHIM, Bank Apps, Amazon, Airtel, Truecaller, Idea, Whatsapp etc).

CONTACT US
Call: +914048486868
WhatsApp: +918977889778
Email: info@pacehospitals.in
FOLLOW US
SUBSCRIBE
Subscribe to our newsletter and stay updated with the latest health information.
Subscribe to PACE Hospitals' Public Newsletter
Thank you for subscribing to PACE Hospitals' Newsletter. Stay updated with the latest health information.
Oops, there was an error. Please try again submitting your details.
ABOUT US
QUICK LINKS
Disclaimer
General information on healthcare issues is made available by PACE Hospitals through this website (www.pacehospital.com), as well as its other websites and branded social media pages. The text, videos, illustrations, photographs, quoted information, and other materials found on these websites (here by collectively referred to as "Content") are offered for informational purposes only and is neither exhaustive nor complete. Prior to forming a decision in regard to your health, consult your doctor or any another healthcare professional. PACE Hospitals does not have an obligation to update or modify the "Content" or to explain or resolve any inconsistencies therein.
The "Content" from the website of PACE Hospitals or from its branded social media pages might include any adult explicit "Content" which is deemed exclusively medical or health-related and not otherwise. Publishing material or making references to specific sources, such as to any particular therapies, goods, drugs, practises, doctors, nurses, other healthcare professionals, diagnoses or procedures is done purely for informational purposes and does not reflect any endorsement by PACE Hospitals – your trusted hospital near me.