Hepatectomy Surgery - Types, Procedure Indications, Benefits & Cost
At PACE Hospitals, state-of-the-art advanced operation theatre is equipped with World’s 1st AI robotic surgery system and 3D HD laparoscopic instruments to perform minimally invasive major and supra-major liver surgery.
We have team of the liver specialist doctors, HPB & liver transplant surgeons in India, they are having over 35 years of immense experience in performing liver resection surgery for the treatment of liver cancer and performing liver transplantation with the high success rate.
Request an appointment for Hepatectomy Surgery
Hepatectomy Surgery Appointment Query
Thank you for contacting us. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 7842171717
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Thank you for contacting us. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 7842171717
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
What is hepatectomy and its purpose?
Hepatectomy meaning
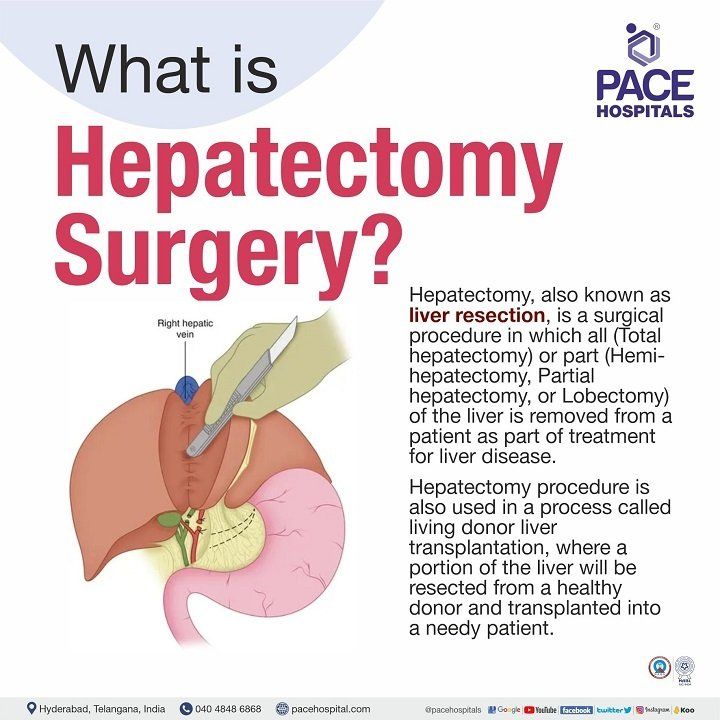
Hepatectomy, also known as liver resection, is a surgical procedure in which all (total hepatectomy) or part (hemi-hepatectomy, partial hepatectomy, or lobectomy) of the liver is removed from a patient as part of treatment for liver disease. Hepatectomy surgery is also used in a process called liver transplantation, where a portion of the liver will be resected from a healthy donor and placed into a patient with liver disease whose liver is no longer working properly.
The decision of the surgeon to perform a liver resection (either total or partial) is based on the functionality and healthiness of the liver. Patients with two-thirds of liver damage can be taken for liver surgery (to remove the damaged area) only when the remaining part of the liver is deemed healthy. Similarly, in
liver transplantation, at least one-third of the liver must be healthy to donate so that the liver can regrow to its standard size in the donor.
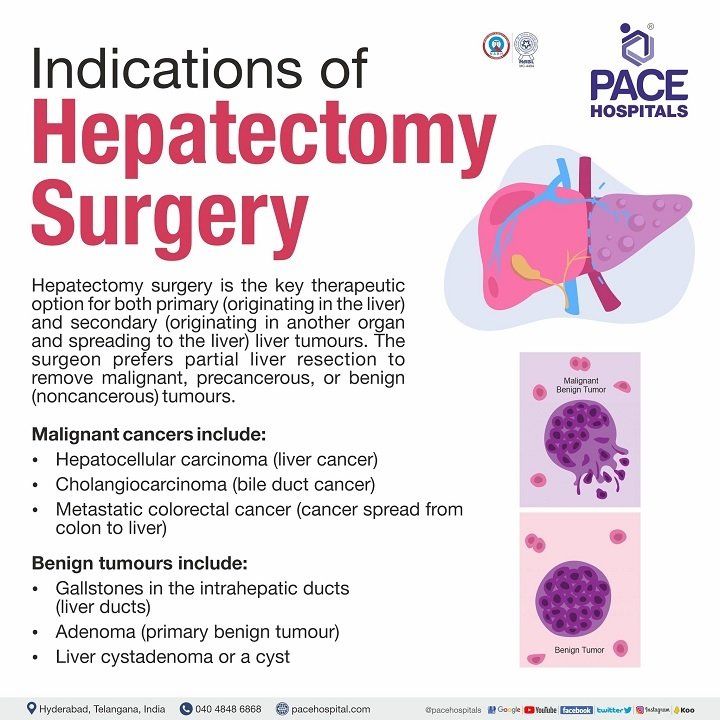
Hepatectomy surgery is the key therapeutic option for both primary (originating in the liver) and secondary (originating in another organ and spreading to the liver) liver tumours. The surgeon prefers partial liver resection to remove malignant, precancerous, or benign (noncancerous) tumours.
- Malignant cancers include - Hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer), Cholangiocarcinoma (bile duct cancer), Metastatic colorectal cancer
- Benign tumours include - Gallstones in the intrahepatic ducts, Adenoma (primary benign tumour), Liver cystadenoma or a cyst
In addition, hepatectomy surgery is also used for the following:
- Inherited diseases - Wilson's disease, Hemochromatosis (Iron overload)
- Viral infections - Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C
- Immune system diseases - Autoimmune hepatitis, Primary biliary cholangitis
- Consumption of toxins - Alcohol-related fatty liver disease, Non-alcohol-related fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
Types of hepatectomy surgery
The liver mainly consists of three lobes (caudate, left, and right) with eight segments in total. The types of hepatectomy surgery are generally based on the removal of liver segments, such as:
- Right hepatectomy
- Left hepatectomy
- Extended left hepatectomy (left trisegmentectomy or left lobectomy)
- Extended right hepatectomy (right trisegmentectomy or right lobectomy).
- Hepatic segmentectomy
- Non-anatomical wedge resection
- Left lateral sectionectomy
- Right posterior sectionectomy
- Right hepatectomy: A right hepatectomy or lobectomy is the surgical resection of segments 5th, 6th, 7th, and 8th.
- Left hepatectomy: A left hepatectomy or lobectomy involves the resection of segments 2nd, 3rd, and 4th.
- Extended left hepatectomy (left trisegmentectomy or left lobectomy): It involves the further resection of segments 5th and 8th along with 2nd, 3rd, and 4th.
- Extended right hepatectomy (right trisegmentectomy, or right lobectomy): Combining a resection of segment 4 with a right hepatectomy (5th, 6th, 7th, and 8th) is classified as an extended right hepatectomy.
- Segmental hepatectomy: A surgical resection of one or more functional anatomic liver segments is known as a segmental hepatectomy. A "segmentectomy" is the removal of a named part, and a "bi-segmentectomy" is the removal of two contiguous segments.
- Non-anatomical wedge resection: Resections crossing anatomical planes, regardless of size, are classified as non-anatomical resections.
- Left lateral sectionectomy: Removing the 2nd and 3rd segments of the left lateral section is termed a left lateral sectionectomy.
- Right posterior sectionectomy: The removal of the 7th and 6th segments of the right posterior section is termed a right posterior sectionectomy.
The hepatectomy surgery can also be classified into major and minor liver resections based on the removal of segments. Resections that include the removal of fewer than three segments are considered minor, whereas major resections remove more than three.
Methods of hepatectomy surgery
The methods of hepatectomy are mainly based on the technique and apparatus used:
- Open hepatectomy surgery
- Laparoscopic hepatectomy surgery
- Robotic hepatectomy surgery
Open hepatectomy surgery:
The patient will be positioned supine 15 degrees (Trendelenburg) with their right arm at a 90-degree angle. The surgeon will create an incision across the superior abdomen following the curvature of the ribs. For bigger resections, it can be bilateral subcostal and solely to the left for minor resections. The surgeon will place a retractor to keep the coastal railings apart, allowing for greater surgical field visibility for long periods. The use of intraoperative ultrasonography is critical for determining the position of the nodules during surgery as well as their relationship to the liver's blood veins. The surgeon removes the abnormal tissue or a healthy tissue for transplant with the help of ultrasonic energy devices, and closes the operated area with the sutures. It is also possible to detect new nodules that are not visible on CT or MRI. Open surgical resection of the liver was the standard treatment for many years, but it was limited due to high morbidity rates, death, and disease recurrence.
Laparoscopic hepatectomy surgery:
Laparoscopic surgery is considered minimally invasive because of the small incisions made and the limited exposure of internal organs. It takes highly specialised tools and trained surgeons in laparoscopic and liver surgery to perform a laparoscopic hepatectomy. The patient will be positioned supine on the operating room table, and surgeons often make between four and six incisions, with a minimum of two 12 mm incisions, to insert instruments like a 30-degree flexi-tip camera (laparoscope), a working port for the insertion of the laparoscopic ultrasonography probe, a stapler, and an ultrasonic aspirator. The location of the incisions depends on the segment of the liver to be removed. The use of ultrasonic energy in conjunction with aspiration device separates the liver parenchyma, skeletonizing tiny parenchymal arteries and biliary structures larger than 2mm.
Robotic hepatectomy surgery:
The patient will be positioned supine on the operating room table, and general endotracheal anaesthesia is administered. The bedside surgeon stands to the patient’s right, and the scrub nurse stands to the patient's left side. Before port placement, the operating room table is positioned in a slight reverse Trendelenburg position (up to thirteen degrees) and a left or right tilt for a lesion in the right or left liver lobe, respectively. The patient is injected into the umbilicus for local anaesthesia before making an incision. An 8-mm vertical incision is made in the umbilicus without an injury to the umbilical ring. The robotic camera is inserted, and diagnostic laparoscopy is undertaken. A robotic trocar (5 mm) is inserted, and a pneumoperitoneum (air or gas is pumped in the abdomen to achieve sufficient operative space) is established with carbon dioxide at 15 mmHg. The remaining robotic trocars (8-mm) are inserted when diagnostic laparoscopy confirms no barriers to tumour resect ability. The surgeon then removes the abnormal or healthy part of the liver with the help of ultrasonic energy devices.
Preparation for hepatectomy surgery
The surgeon will check for the best option to treat the patient’s condition based on the following:
- Is the patient healthy enough to tolerate surgery?
- Is the patient’s liver technically operable?
- Is the patient's cancer had metastasis to other organs near the liver?
The healthcare provider will decide whether the patient should have a partial hepatectomy surgery or a liver transplant from a donor based on the tumour's extent, functionality of the liver post-resection, the patient's liver health status, and the patient's condition for a transplant.
The surgical oncologist might prescribe radiation therapy, interventional radiology, or chemotherapy to reduce the cancer's size and ease the surgery process and be safer.
The primary care doctor might request imaging tests such as a CT scan or an MRI, blood tests such as liver biopsy and liver function tests. The patient needs to inform the surgeon regarding the following:
- Any history of allergies to substances such as latex, tape, and medicines (including local and general anaesthesia).
- Current or planned pregnancy status of the patient.
- Medication intake (current medication), includes prescribed, non-prescribed (over-the-counter), and supplemental pills. The physician would make specific recommendations to the patient regarding any recent medication changes that the patent might be using.
The entire procedure and risk (if any) of the hepatectomy surgery will be clearly explained to the patient. The patient will be provided with a consent form to sign, permitting them to do the procedure. The patient needs to read the consent document carefully and ask any questions they may have before signing.
Hepatectomy procedure steps
The steps of the hepatectomy procedure differ depending on the surgical technique used by the surgeon. It may take two to six hours, depending on the extent of the resection. In general, a hepatectomy procedure follows these steps:
- The patient will be provided with a surgical gown to change the dress.
- An intravenous line will be inserted into the patient’s arm or hand, through which medications will be administered.
- The patient will be positioned supine and put to sleep with general anaesthesia. The surgeon might place a gastric tube, which would be used to decompress the stomach.
- During surgery, the patient’s vital signs (heart rate, blood pressure, breathing rate, and blood oxygen level) will be monitored.
- Depending on the technique, the surgeon will make incisions on the patient's body to gain liver access.
- The techniques involved are open surgery, laparoscopic surgery, and robotic surgery.
- If the surgeon chooses open surgery, the patient might have a transversus abdominis plane nerve block, which helps in post-surgery pain management. The surgeon also makes one long incision across the patient’s abdomen to open the abdominal cavity to gain liver access.
- In laparoscopic or robotic surgery, the surgeon will make four to six small incisions, through which a camera and other surgical tools (robotic arms) will be inserted to do the procedure.
- The surgeon may use intraoperative ultrasound to map the patient's liver. The surgeon may also remove the gallbladder if the liver part that needs to be removed is near the gallbladder.
- Once the surgeon has access to the patient’s liver, the surgeon will remove a section while isolating the surrounding blood vessels and bile ducts, thus securing them in place with metal clips or staplers. The surgeon uses an ultrasonic energy instrument to dissect the liver, stop the bleeding with the help of a medical gauze, and close the incisions with the help of sutures once the procedure is complete.
- If the patient is having laparoscopic or robotic surgery, the surgeon will create a second 2- to 5-inch incision to remove the dissected part of the liver. The incision's size is determined by the extent of liver removal and the size of the tumour.
- The surgeon may insert a suction drain (a small tube) to collect blood and other fluids that accumulate at the surgery site, and it will be removed after 2 to 3 days of surgery.
Post hepatectomy surgery
After having a hepatectomy surgery, depending on the type of technique, the patient needs to stay in the hospital for a few more days.
- After the hepatectomy surgery, patients will be taken into a recovery room or post-anaesthesia unit once their vital signs (heart rate, respiration rate, and blood pressure) are stabilised.
- In a few complex cases, the patient might be in intensive care for one or two days, during which the patient’s fluid / electrolyte balance, blood glucose levels, and blood loss are closely monitored.
- The patient will be transferred to the inpatient room from the post-anaesthesia unit. The diet will be gradually improved, and the patient will begin to move around. Drains will be removed depending on the amount of seroma formed. The surgeon might prescribe pain medication.
The doctor / surgeon will provide specific instructions related to incision, drain care, signs of infection, and dressing at the time of discharge, such as:
- Whom to contact if there is an infection at the site of the procedure
- How to replace a wet dressing with a clean one after taking a bath.
- When to resume the old medication, which was stopped earlier because of surgery.
- Usage of medications for pain management and infection control.
- A follow-up visits after two weeks.
Recovery from hepatectomy surgery
Hepatectomy recovery depends on the technique used by the surgeon. If the patient underwent an open hepatectomy, it might take between four and eight weeks to heal, and it takes up to 12 weeks to be normal. The patient should refrain from lifting any heavy things or doing vigorous exercise during this time.
The recovery is generally quicker if the patient undergoes laparoscopic or robotic surgery. The patient will recover within two to four weeks (14 days to 28 days), and it might take six to eight weeks to feel complete back to normal. Five to six days will be the average hospital stay after a major hepatectomy depending on the patient’s condition.
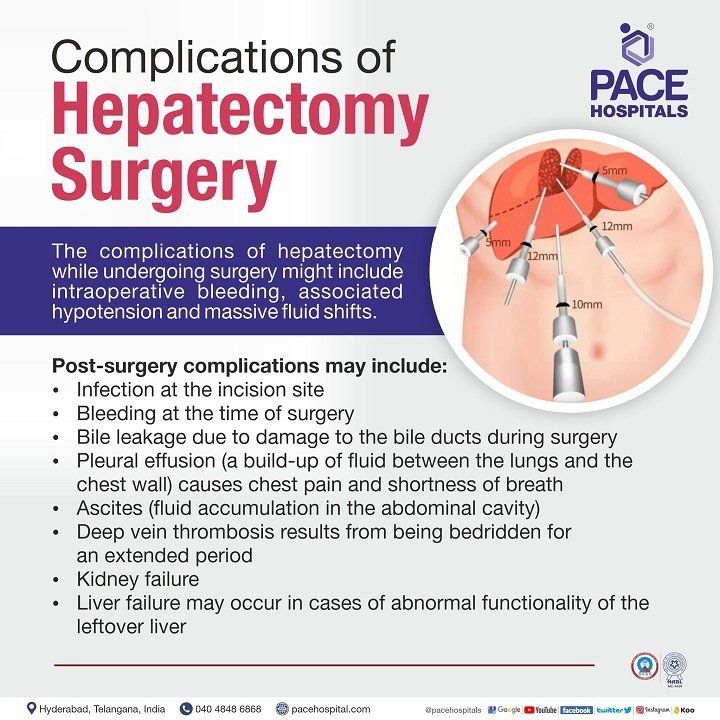
Complications of hepatectomy surgery
The complications of hepatectomy while undergoing surgery might include, intraoperative bleeding, associated hypotension and massive fluid shifts. The morbidity rate after liver resection ranges from 12% to 46%, and mortality can reach up to 3%. Post-surgery complications may include:
- Infection at the incision site.
- Bleeding at the time of surgery.
- Bile leakage due to damage to the bile ducts during surgery.
- Pleural effusion (a build-up of fluid in the chest cavity) causes chest pain and shortness of breath.
- Ascites (build-up of fluid in the abdominal cavity).
- Deep vein thrombosis as a result of being bedridden for an extended period.
- Kidney failure.
- Liver failure occurs in cases of abnormal functionality of the leftover liver.
What questions to ask post hepatectomy surgery?
Post hepatectomy surgery, the patient might have the following questions before getting discharged:
- What was the size of the lobe removed?
- Were all the damaged cells removed during hepatectomy surgery?
- What are the possibilities of the disease returning? What are the specific signs or symptoms I should watch for?
- Do I need to take any more medication following hepatectomy surgery, even if the damaged cells were completely removed? If so, what is the reason for this, and how long should I take it?
- Can you explain my pathology report (lab results)?
- Do I need additional surgery after hepatectomy surgery?
- When will I return to work and/or my daily routine? Is there anything I should avoid doing?
- What long-term side effects are possible based on the current treatment I received, and who should I contact if I experience any of those?
- When to visit for follow-up tests, and how often will those tests be needed?
Difference between Open Hepatectomy and Laparoscopic / Robotic Hepatectomy
Both procedures are used to remove diseased or abnormal liver tissues. Depending on the patient's condition, the surgeon chooses either of the following methods.
| Elements | Laparoscopic / Robotic Hepatectomy | Open Hepatectomy |
|---|---|---|
| Technique | Advanced and minimal invasive. | Old traditional |
| Liver access | By placing a small keyhole incision (4 to 6), the surgeon inserts a laparoscope and long instruments to complete the liver resection. Robotic arms will be used to complete liver resection in the case of robotic surgery. | Through laparotomy (a surgical incision into the abdominal cavity, in preparation for major surgery). |
| Severity | As the movement is minimal, surgeons traditionally use it for less complex liver resections. However, major surgeries can also be done with the advancement of surgical techniques. | It’s best suited for more complex procedures as the liver is directly exposed. |
| Hospitalisation | Less hospitalisation stays. | More extended hospital stays in comparison to laparoscopic or robotic hepatectomy. |
| Recovery | It takes less time to recover (6-8 weeks). | It takes more time (12 weeks). |
-
What is a partial & complete hepatectomy procedure?
A surgical procedure where the surgeon removes the complete liver based on the patient's disease condition as a part of a treatment called a "complete hepatectomy" further replaces it with a healthy liver from a cadaver donor.
If the patient’s liver is partially damaged, the damaged part will be removed, called a “partial hepatectomy”. Hepatectomy procedures can be performed either through an open incision or with minimally invasive techniques such as laparoscopic or robotic.
-
Is hepatectomy surgery painful?
The patient may experience pain after a hepatectomy surgery and it varies from person to person. A liver specialist doctor may prescribe medicines based on individual patient conditions.
-
Which doctor is qualified to perform hepatectomy surgery?
A highly skilled surgical gastroenterologist with experience of 10-15 years in conducting liver surgery and liver transplants and having expertise in providing pre and post-surgery care will be the best choice. To have a successful liver hepatectomy surgery or liver transplant, a group of health care professionals contributes as a team that consists of a surgical gastroenterologist, interventional radiologist, oncologic-oriented hepatologist, radiation oncologists, gastroenterologist, HPB oncologist, and other medical staff.
-
Why blood sugar level falls rapidly after hepatectomy?
Blood sugar levels drop significantly after hepatectomy surgery because liver tissue is being removed during this procedure. The glycogen stored in the liver is a form of glucose, the body's primary energy source. The removal of liver tissue will cause a progressive drop in glycogen levels, leading to a decrease in blood glucose levels.
Frequently asked questions:
How long can you live with your liver removed?
The liver is a vital organ in the human body, as it manages waste products in the blood, removes toxins, and stores excess energy as glycogen. There is no way to exist without a liver. However, if patients have up to two-thirds of the liver removed, it can regenerate to its original size.
Liver dialysis can help a failing liver by eliminating toxins from blood circulation. Patients with liver failure, which occurs when the liver entirely shuts down, usually only have a few days to survive if they are not treated with liver transplantation.
Is tumour in liver curable?
A liver tumour that is benign or malignant is often treatable. Malignant tumours (cancer) can be treated using surgical and therapeutic approaches.
Surgical approaches:
- Hepatectomy (remove part or all of the liver)
The therapeutic approach includes:
- Chemotherapy (anti-cancer drug treatment used to kill fast-growing cells).
- Radiotherapy (high doses of radiation to kill cancer cells and shrink tumours).
- Thermal ablation (removing tissue or a body part using heat).
- Targeted medicines (agents which block signals that make cancer cells grow or can signal the cancer cells to destroy themselves).
The treatment will depend on the following factors:
- The size and type of liver cancer
- Location of the cancerous tumours
- The overall health of the patient
What causes liver tumours to grow?
Mutations in the DNA of liver cells cause liver tumours. The DNA in a cell specifies how to carry out every chemical reaction in the body. Mutations bring about changes to these instructions in the DNA. In some cases, cells may grow out of control, leading to a tumour, a mass of malignant cells.
Is chemo needed after liver resection?
Yes, postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy is recommended for all patients following liver resection unless the patient's physical status is inadequate or unwilling to accept chemotherapy.
What is post hepatectomy liver failure?
Post hepatectomy liver failure is defined as a rise in the international normalised ratio (INR) and hyperbilirubinemia on or after postoperative day 5, indicating a decline in the liver's ability to maintain its synthetic, excretory, and detoxifying activity.
Based on the impact on clinical management, post-hepatectomy liver failure is classified into three grades as follows:
- Grade A post-hepatectomy: The liver failure requires no change in the patient’s clinical management.
- Grade B post-hepatectomy: Patients with grade B post-hepatectomy liver failure, which deviates from the regular course but does not require invasive therapy.
- Grade C post-hepatectomy: There is a need for invasive treatment.
What is donor hepatectomy?
Donor hepatectomy is a surgical procedure performed on healthy donors who donate a portion of their liver to a patient suffering from end-stage liver disease. The donated part of the liver in the donor will regenerate to nearly full size in the first month of post-surgery.
How much does hepatectomy cost in India?
Hepatectomy cost in India ranges vary from Rs. 4,75,000 to Rs. 8,62,000 (four lakh seventy-five thousand to eight lakh sixty-two thousand). However, cost of hepatectomy surgery in India depends upon multiple factors and differs from case to case. However, cost may vary depending upon the different hospitals in different cities.
What is the cost of hepatectomy in Hyderabad?
Hepatectomy cost in Hyderabad ranges vary from Rs. 5,65,000 to Rs. 8,37,000 (five lakh sixty-five thousand to eight lakh thirty-seven thousand). However, the cost of hepatectomy surgery in Hyderabad depends upon the multiple factors such as patient condition, age, room selection in hospital and, CGHS, EHS, ESI, TPA-insurance or corporate approvals for cashless facility.
Our Locations – Find the Best Hospital Near You
Metro Pillar Number C1772, Beside Avasa Hotel, Hitech City Road, Near HITEC City Metro Station, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Mythri Nagar, Beside South India Shopping Mall, Hafeezpet, Madeenaguda, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
040 4848 6868
Payment in advance for treatment at PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, Telangana, India (Pay in INR ₹)
For Bank Transfer:-
- Bank Name: HDFC
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.50200028705218
IFSC Code: HDFC0000545 - Bank Name: STATE BANK OF INDIA
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.62206858997
IFSC Code: SBIN0020299
Scan QR Code by Any Payment App (GPay, Paytm, Phonepe, BHIM, Bank Apps, Amazon, Airtel, Truecaller, Idea, Whatsapp etc).

CONTACT US
Call: +914048486868
WhatsApp: +918977889778
Email: info@pacehospitals.in
FOLLOW US
SUBSCRIBE
Subscribe to our newsletter and stay updated with the latest health information.
Subscribe to PACE Hospitals' Public Newsletter
Thank you for subscribing to PACE Hospitals' Newsletter. Stay updated with the latest health information.
Oops, there was an error. Please try again submitting your details.
ABOUT US
QUICK LINKS
Disclaimer
General information on healthcare issues is made available by PACE Hospitals through this website (www.pacehospital.com), as well as its other websites and branded social media pages. The text, videos, illustrations, photographs, quoted information, and other materials found on these websites (here by collectively referred to as "Content") are offered for informational purposes only and is neither exhaustive nor complete. Prior to forming a decision in regard to your health, consult your doctor or any another healthcare professional. PACE Hospitals does not have an obligation to update or modify the "Content" or to explain or resolve any inconsistencies therein.
The "Content" from the website of PACE Hospitals or from its branded social media pages might include any adult explicit "Content" which is deemed exclusively medical or health-related and not otherwise. Publishing material or making references to specific sources, such as to any particular therapies, goods, drugs, practises, doctors, nurses, other healthcare professionals, diagnoses or procedures is done purely for informational purposes and does not reflect any endorsement by PACE Hospitals – your trusted hospital near me.