Best Hip Replacement Surgery Hospital
in Hyderabad, India
PACE Hospitals is recognized as the best hospital for hip joint replacement surgery in Hyderabad, Telangana, India. With a team of the best hip replacement surgeons, orthopedic doctors, we provide advanced orthopedic care through a patient-focused approach. Our experts specialize in minimally invasive techniques, ensuring faster recovery and improved mobility.
Hip replacement surgery is a highly effective procedure to relieve pain and restore joint function in patients with severe hip conditions. At PACE Hospitals, we offer state-of-the-art treatment options, utilizing the latest medical advancements to deliver safe and successful outcomes. With transparent hip replacement surgery costs and world-class facilities, we remain a trusted choice for Total Hip Replacement Surgery in Hyderabad.
Quick Navigation
Book an appointment for Hip Replacement Surgery
Hip Replacement Surgery appointment
Why Choose PACE Hospitals for Hip Replacement Surgery?

Best Hip Replacement Surgeons for Total Hip Replacement and Partial Hip Replacement
Hip Replacement Surgery with 99.9% Success Rate & Faster Recovery
Affordable & Cost-effective Hip Joint Replacement Surgery with Insurance and Cashless Coverage
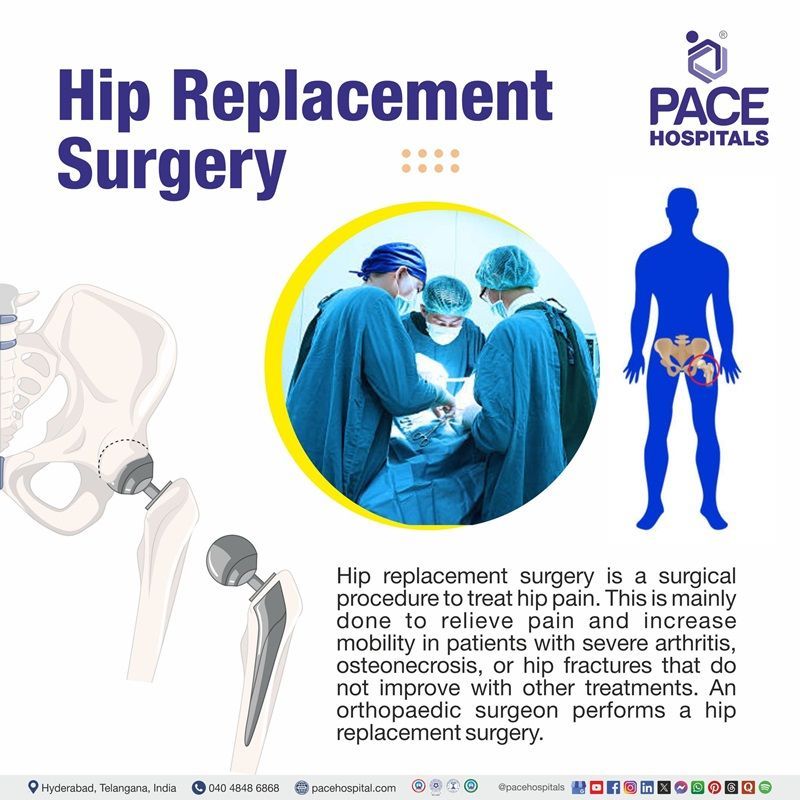
What is Hip Replacement Surgery?
Hip replacement surgery, also called hip arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure to treat hip pain. This surgery is mainly done to relieve pain and increase mobility in patients with severe arthritis, osteonecrosis, or hip fractures that do not improve with other treatments.
An orthopaedic surgeon replaces the damaged hip joint parts with new, artificial ones during a hip replacement surgery. These prosthetic components replicate (or mimic) the way a normal hip joint works.
Types of Hip Replacement Surgery
Hip replacement surgery can be divided into various types according to the technique and extent of the procedure. Below are the different types of hip replacement surgeries:
Total hip replacement (THR)
In this procedure, the entire hip joint—including the ball and socket components—is removed and replaced with a prosthetic implant. It is one of the most widespread orthopaedic procedures used to help patients with severe hip damage from injuries or arthritis by reducing pain and restoring function.
Hip ball replacement or Partial hip replacement
This procedure replaces only the ball of the hip joint; the socket is left unchanged. Since it is less invasive and requires less recovery time than total replacement, it is frequently performed on elderly patients, particularly following a hip fracture.
Partial hip replacement surgery is mainly of two types:
- Unipolar hip replacement: This procedure involves replacing the femoral head with a prosthetic implant that articulates directly with the natural acetabulum, or hip joint socket.
- Bipolar hip replacement: This involves inserting a prosthetic ball into a larger ball to replace the femoral head. The natural acetabulum then articulates with the larger ball. Because it lessens the strain on the natural socket, this design may have some benefits.
Hip resurfacing
In this kind of surgery, the femoral head is not entirely removed, but rather is capped with a smooth metal surface. Younger, more active patients with good bone quality are typically advised to have it. Although less common in recent years, hip resurfacing preserves more bone than a total hip replacement.
Hip revision surgery
When a hip implant fails because of wear, infection, or loosening, this procedure is performed. In revision surgery, any issues that may have developed from the original procedure are addressed by removing the old implant and replacing it with a new one.
Hip Replacement Prosthesis
- Metal-on-Polyethylene: This type is traditional and popular; the socket is lined with polyethylene, and the ball is made of metal. It provides a track record of success, but over time, it may result in wear and tear.
- Ceramic-on-Polyethylene: This particular type uses a ceramic ball with a polyethylene-lined socket, providing better wear resistance than metal-on-polyethylene.
- Ceramic-on-Ceramic: This type is known for its durability, as it uses ceramic for both the ball and socket, considerably decreasing wear and tear.
- Ceramic-on-Metal: It combines a ceramic ball and a metal socket, providing an ideal balance between durability and compatibility.
- Metal-on-Metal: Despite its durability, this type has gone out of favour due to concerns regarding metal ion release and related health dangers.
Surgical approaches
Hip replacement surgery can also employ a variety of surgical techniques:
- Posterior approach: This is the most common approach, in which the surgeon reaches the hip joint from behind the femur. This method reduces muscle damage, enabling faster recovery time.
- Anterior approach: This method involves making an incision at the front of the hip. Since there is less muscle disruption, it is regarded as a minimally invasive option that may lead to less postoperative pain and a quicker recovery.
- Minimally invasive techniques: Compared to traditional methods, these techniques require smaller incisions and less muscle dissection. Although they may necessitate specific training for surgeons, they are intended to shorten recovery time and postoperative pain.
Symptoms Indicating Hip Joint Replacement Surgery
Several conditions which cause severe pain and functional impairment can benefit from hip replacement surgery. The following are the main indications for hip replacement surgery:
- Osteoarthritis (OA): The most common factor leading to hip replacement is end-stage symptomatic osteoarthritis. Patients usually suffer from severe pain and decreased mobility, particularly after conservative measures have failed.
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA): Over time, hip joint damage from inflammatory arthritis, especially rheumatoid arthritis, can result in pain and functional limitations. A total hip replacement may be needed when conservative treatments are no longer effective.
- Avascular necrosis (AVN): When the femoral head's blood supply is disrupted, osteonecrosis, also known as AVN, develops, which can result in bone death and possible joint collapse. In its later stages, this condition frequently necessitates hip replacement.
- Congenital hip disorders: Hip dysplasia is one condition that can cause premature joint degeneration, necessitating surgery to improve quality of the life.
- Ankylosing spondylitis (AS): Surgery may be necessary when conservative measures fail to reduce the severe stiffness and pain in the hip joints caused by this chronic inflammatory disease.
- Trauma: Hip replacement surgery may be required for hip fractures or severe trauma, especially in older adults whose function cannot be restored by conservative measures.
- Failed previous hip surgery: Individuals who have had failed hip surgeries in the past or who have experienced complications like infection or implant failure may benefit from revision surgery.
- Significant functional impairment: Patients who have significant functional limitations (such as trouble walking or carrying out daily tasks) and persistent pain at rest or during activity may be candidates for hip replacement surgery if other treatments are unsuccessful.
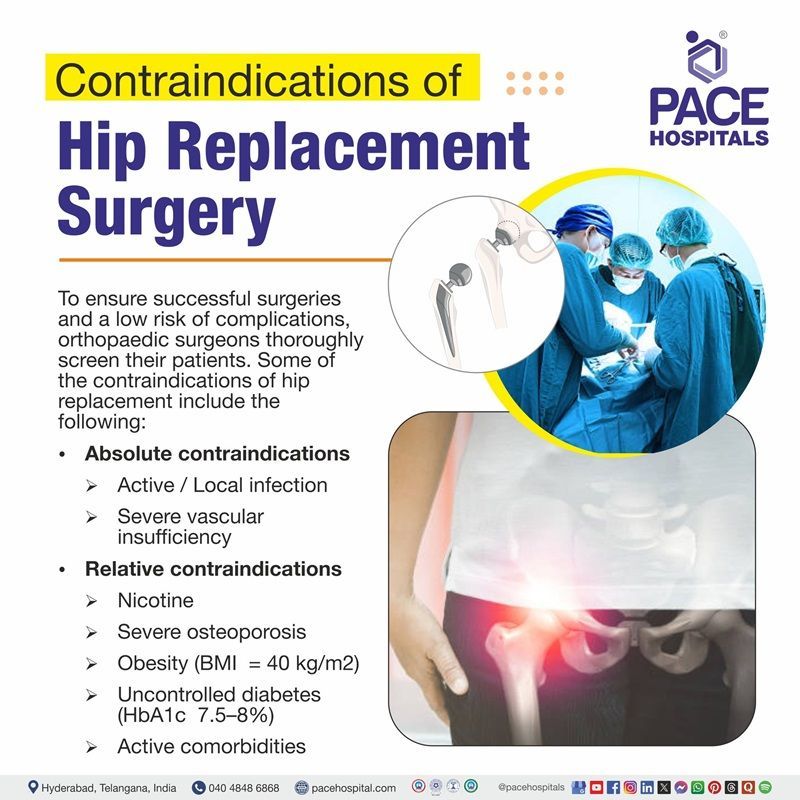
Contraindications of Hip Replacement Surgery
To ensure successful surgeries and a low risk of complications, orthopaedic surgeons thoroughly screen their patients. Individuals may be informed that they are not currently eligible for hip replacement surgery if they have a higher-than-average risk of complications following surgery. Some of the contraindications of hip replacement include the following:
Absolute contraindications
- Active/local infection: Patients who are prone to infection may not be eligible for this surgery, and an active infection is an absolute contraindication. Severe post-operative infection cases may necessitate extended intravenous antibiotic courses, readmissions to the hospital, and, in certain situations, the removal of the artificial hip.
- Severe vascular insufficiency: Healing and implant stability are compromised by peripheral vascular disease or insufficient limb blood flow.
Relative contraindications
- Nicotine use: Medical complications are more common in smokers and other tobacco users, and they are also more likely to require revision hip replacement surgery or follow-up surgery. Smokers were roughly ten times more likely than nonsmokers to have undergone a second (revision) joint replacement procedure, according to one study. Candidates for total hip replacement are advised to reduce or stop smoking to reduce the risks associated with the procedure.
- Severe osteoporosis: A new joint prosthesis cannot be supported or adhered to by brittle bones. While mild to moderate osteoporosis is usually acceptable, it may influence a surgeon's surgical planning. Additionally, before hip replacement surgery, a patient may be asked to take actions to increase bone density. Following surgery, this treatment might be continued to prolong the life of the hip replacement.
- Obesity (BMI ≥= 40 kg/m2): Patients are advised to reduce their weight below a BMI of 30 kg/m2 before hip replacement surgery.
- Uncontrolled diabetes (HbA1c ≥7.5–8%): High HbA1c increases the risk of infection and surgery. So, before surgery, glycaemic control to an HbA1c value below 8% is recommended for patients with diabetes mellitus.
- Active comorbidities: Perioperative risks are increased by untreated heart, lung, or kidney conditions.

Benefits After Hip Replacement Surgery
For patients with severe hip conditions, hip replacement surgery offers many benefits that greatly improve their quality of life. Below are the main advantages of hip replacement surgery:
- Pain relief: Significant pain relief is one of the main advantages of hip replacement surgery. After the procedure, most patients report complete or nearly full relief from the pain related to arthritis or other hip conditions.
- Improved mobility and function: Following surgery, patients usually regain the ability to carry out everyday tasks like walking, climbing stairs, and getting in and out of chairs more easily. Restoring independence is significantly aided by this increase in mobility.
- Enhanced quality of life: An enhanced quality of life is a result of both pain relief and increased mobility. Because they are able to participate in activities, they enjoy without experiencing discomfort, patients frequently report feeling more independent and mentally well.
- High success rate: With more than 95% of patients expressing satisfaction with their results, hip replacement surgery has a high success rate. With 90–95% of implants still functioning well after 10 years and 80–85% after 20 years, long-term success rates remain high.
- Long-lasting results: Revision surgery is less likely with modern artificial hip joints because they are made to last for many years. According to studies, a significant portion of hip replacements continue to function for at least 20 years.
- Restoration of normal activities: Many patients notice that their hip pain no longer prevents them from engaging in certain pastimes and activities after they recover, improving their overall quality of life.
- Psychological benefits: Being able to move around freely and engaging in social activities can improve mental health outcomes by lowering depressive or lonely feelings related to chronic pain conditions.
Hip Replacement Procedure
Hip replacement surgery steps include the following:
Before hip replacement surgery
- In addition to a thorough medical history, the orthopedic surgeon usually performs a complete physical examination to ensure patients' good health before undergoing through the surgical procedure, which may include blood tests or additional diagnostic tests.
- Patients need to inform the doctor if they are sensitive to or allergic to any medications, tape, latex, or anesthetic agents (local and general).
- Patients must inform their doctor if they have a history of bleeding disorders or are using any anticoagulant (blood-thinning) medications, aspirin, or other blood-clotting inhibitors. Certain medications may be required to be discontinued prior to the surgery.
- Patients need to inform the doctor about all medication (prescription and over the counter) and herbal supplements they are taking.
- Patients who are pregnant or suspect they might be pregnant need to inform their doctor.
- The doctor will explain the procedure clearly to the patient and allow them to ask any questions they may have.
- Patients are required to do a signature on a consent form authorizing the doctors to perform the surgery. Patients should carefully read the form; if there are any questions, they can ask the doctors.
- Patients should refrain from drinking or eating anything from the night before their procedure.
- Patients need to look for and arrange for someone to assist them around the house for a week or two once they are discharged from the hospital.
- Patients need to discuss requirements with their surgeon and other healthcare team members. They need to refer to one of the websites listed in the relevant resources section to learn more about the process or to request written information.
- Before surgery, patients need to ask their surgeon what exercises they can do to strengthen their legs, upper body, and core.
- Patients who smoke need to decide to stop or reduce their smoking habit.
- Patients should try to lose weight if they are overweight. Overweight patients are more likely to experience problems during or following surgery.
- Transportation must be arranged by the patient for both the procedure and any follow-up appointments with the surgeon.
During hip replacement surgery
- Hip replacement surgery is usually performed while patients are asleep under general anaesthesia. The anaesthesiologist will discuss this with the patients beforehand.
- Patients are asked to take off their garments and will be provided a gown to wear.
- An intravenous (IV) line is inserted in the patient's arm or hand.
- Patients are positioned on the operating table, and a urinary catheter is inserted.
- In case of excessive hair at the surgical site, it may be trimmed.
- The anaesthesiologist will monitor the blood pressure, heart rate, and other vital signs during the procedure.
- The skin around the surgery site will be cleaned with an antiseptic solution.
- Over the hip, the surgeon will make an incision. Many factors, such as the patient’s size, the type of joint issue, and the surgeon's preferences, will determine the incision's size.
- The surgeon will remove the diseased bone tissue and cartilage from the hip joint.
- The surgeon will replace the acetabulum’s surface and the femur’s head with new artificial components.
After hip replacement surgery
- Following surgery, patients will be brought to the recovery room for observation. Patients will be moved to their hospital room once their blood pressure, pulse, and respiration have stabilized, and they are alert. A few days' stay in the hospital is normally required.
- A physical therapist will visit patients shortly after surgery to plan an exercise program.
- Pain will be managed with medicines so patients can participate in the physical activity. Patients will be provided with an exercise schedule to follow while in the hospital and after discharge.
- Patients will be discharged and sent home or to a rehabilitation facility. In any instance, the doctor will arrange for continued physical therapy until patients regain muscular strength and range of motion.

Hip Replacement Complications
A hip replacement is a common and safe surgery, but there are risks associated with any type of surgery. Below are the complications that may occur following hip replacement surgery:
- Wound infection: After surgery, there is a slight chance that the hip wound may develop an infection. Antibiotics are typically used to treat this. Patients may require additional surgery if the infection spreads deep into the hip joint.
- Blood clots or DVT (deep vein thrombosis): Following a hip replacement, the way blood flow changes, increases the risk of blood clots or DVT (deep vein thrombosis). Doctors may prescribe anticoagulant medications to patients who have a blood clot that is causing them pain or swelling. Sometimes, a blood clot that starts in the leg can move to the lungs (pulmonary embolism), which can lead to serious complications. Patients will most likely be prescribed compression stockings to wear to lower their risk of blood clots.
- Damage to nerves or tissues: Damage to a blood vessel, nerve, or ligament surrounding the hip joint may occur during surgery. This is uncommon and may either heal on its own or be repaired during surgery.
- Hip dislocation and wear: The hip replacement may dislocate occasionally. Although rare, this may cause pain and swelling. Additionally, some people may hear popping or clicking sounds coming from the joint. It might occur shortly after surgery before the joint has had time to heal completely. Additionally, it may occur years after surgery.
- Difference in leg length: The leg where the hip has been replaced may occasionally end up being a little longer than the other leg after hip replacement surgery. The surgeon will make every effort to prevent this. The difference is frequently so slight that most people are unaware of it. Patients may occasionally need to wear a raised heel on their other leg or something similar.
- Fracture of femur or pelvis: Breakage or fracture of the pelvis or femur may occur during surgery and occasionally go unnoticed. Additional surgery may be needed during the procedure, and in rare cases, a follow-up procedure may be required a few days later. Although it is extremely uncommon, patients may need to remain in bed or in traction for a few weeks following surgery if the bones break or crack.
- Heterotopic ossification: This occurs when bone develops in the soft tissues that surround the hip. This may need to be occasionally removed because it can be uncomfortable and stiff. This is extremely uncommon in the hip.
Hip Replacement Recovery
After hip replacement surgery, particularly Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA), patients can expect to recover gradually and return to several light daily activities within three to six weeks. With supervised physical therapy, patients begin their initial recovery in the hospital and are generally discharged in a few days. Ninety-one per cent of patients report better outcomes at 6 weeks, with many reporting improved functioning and decreased pain compared to preoperative levels. It can take up to a year to completely recover, and physical therapy is necessary to regain strength and mobility.
Hip Replacement Exercises
Here are some effective hip replacement exercises to improve mobility, strength, and flexibility after surgery:
Early Recovery Exercises (First Few Weeks)
- Ankle Pumps – Move your foot up and down to improve circulation.
- Quadriceps Sets – Make tight your thigh muscles & hold for a moment.
- Glute Squeezes – Squeeze your buttocks for a few seconds, then release.
- Heel Slides – Slowly slide your heel towards your buttocks while lying down.
- Leg Raises – Lift your leg straight while lying down to strengthen your hip.
Intermediate Exercises (After a Few Weeks)
- Standing Hip Abduction – Stand and lift your leg sideways to improve balance.
- Seated Knee Extensions – Extend your leg while sitting to strengthen your thigh.
- Hip Bridges – Lie on your back and lift your hips to strengthen the glutes.
- Step-Ups – Step onto a low platform to build leg strength.
- Mini Squats – Perform gentle squats while holding onto a stable surface.
Advanced Exercises (After Full Recovery)
- Clamshells – Lie on your side and open your knees while keeping feet together.
- Resistance Band Hip Abductions – Use a band to strengthen the hip muscles.
- Stationary Cycling – Low-impact cardio to improve joint mobility.
- Swimming – Helps build strength without putting pressure on the hip joint.
- Walking on Even Surfaces – Encourages natural movement and improves endurance.
Questions that the patients can ask the healthcare team about hip replacement surgery?
- When can I go home?
- When do I need to see my doctor again?
- What is the expected recovery time?
- What problems can occur after hip replacement surgery?
- Are there any specific exercises I should avoid while recovering?
- What precautions should I take?
- What kind of pain can I expect?
- When can I go back to my regular activities?
- Will I require physical therapy after surgery, and for how long?
- How do I expect my hip to look over time?
- How long will my recovery take, and what kind of assistance will I require throughout that time?
- Do I need any further treatment?
Difference Between Hemiarthroplasty and Total Hip Replacement Surgery
Hemiarthroplasty vs Total hip replacement
Hemiarthroplasty and total hip replacement are two surgical techniques used to treat hip joint conditions, mainly in cases of femoral neck fractures. Below are the main parameters that help in differentiating hemiarthroplasty and total hip replacement:
| Parameters | Hemiarthroplasty | Total Hip replacement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Surgery in which only the hip joint's femoral head, or ball, is replaced. | Surgery that replaces the hip joint's acetabulum (socket) and femoral head. |
| Indications | It is employed most often in older, less active patients with displaced femoral neck fractures. | It is employed most often in younger or more active patients with displaced femoral neck fractures, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, or avascular necrosis. |
| Surgical scope | Acetabulum remains intact; partial replacement. | Replacement of the entire hip joint, including the ball and socket. |
| Surgical complexity | Less complicated, requiring less time for surgery and leading to less blood loss. | More complicated, involving more blood loss and a longer operating time. |
| Recovery time | Shorter initial recovery time, but it could result in long-term issues like acetabular wear. | Greater long-term results in terms of pain relief and mobility but a longer recovery time. |
We are recognized as the best hospital for hip replacement surgery in India, offering comprehensive treatment for all types of hip replacements. We specialize in total hip replacement, partial hip replacement, hip resurfacing, and revision hip replacement to address various hip joint conditions. With advanced technology, expert orthopedic surgeons, and a patient-centric approach, we ensure optimal outcomes and faster recovery for improved mobility and quality of life.
Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty vs Total Hip Replacement Surgery
These are two separate surgical procedures for treating hip joint problems. BHA comprises replacing only the femoral head with a two-piece prosthesis while retaining the native acetabulum. It is frequently recommended for older patients with limited mobility due to its shorter operating time, reduced blood loss, and lower cost.
In contrast, THR replaces both the femoral head and the acetabulum, giving a more comprehensive therapy for severe hip joint disorders, yielding better functional outcomes and lesser revision rates, however, it may have a higher dislocation risk.
Cemented vs Uncemented Hip Replacement Surgery
The primary difference between cemented and uncemented hip replacements is how the prosthetic implant is attached to the bone. Cemented hip replacements attach the implant with polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) bone cement, giving rapid fixation and allowing for weight-bearing shortly after surgery. This approach is frequently favoured for elderly people with weaker bones or those with illnesses such as osteoporosis.
Uncemented hip replacements, on the other hand, rely on bone ingrowth into a porous surface, which allows for a more natural healing process and potentially longer implant longevity, particularly in younger patients with high bone density. Uncemented implants are less prone to produce complications like cement loosening, but they need a longer recovery time for bone integration.
Hip Replacement Surgery Cost in Hyderabad, India
Hip replacement surgery cost in Hyderabad, India ranges varies from ₹1,35,000 to ₹5,45,000 (US$1,582 to US$6,390). However, the actual hip replacement cost may vary depending on several factors such as:
- Type of Surgery: Partial vs. Total Hip Replacement
- Unilateral vs. Bilateral Surgery: Single hip vs. both hips
- Implant Quality: Standard vs. premium imported prosthetics
- Hospital Stay & Room Category: General, semi-private, or private rooms
- Surgeon's Expertise: Fees vary based on experience and reputation
- Insurance & Cashless Facilities: Coverage through health insurance or corporate tie-ups
Breakdown of Hip Joint Replacement Cost in Hyderabad, India
Unilateral (Single Hip) Replacement:
- Total Hip Replacement (THR): ₹1,55,000 – ₹2,80,000 (US$1,817 – US$3,284)
- Partial Hip Replacement (PHR): ₹1,35,000 – ₹2,38,000 (US$1,582 – US$2,790)
Bilateral (Both Hips) Replacement:
- Total Hip Replacement (TKR): ₹3,15,000 – ₹6,20,000 (US$3,693 – US$7,270)
- Partial Hip Replacement (PKR): ₹2,40,000 – ₹5,45,000 (US$2,814 – US$6,390)
At PACE Hospitals, we provide advanced hip joint replacement surgery in Hyderabad, Telangana, India, with cutting-edge technology, expert orthopedic surgeons, and affordable pricing. We also offer insurance and cashless payment options for a hassle-free experience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Hip Replacement Surgery
Does hip replacement cure avascular necrosis?
Avascular necrosis (AVN) cannot be cured by hip replacement, but it can be effectively managed by replacing the damaged joint, particularly when the condition is advanced. Research using the Harris Hip Score has demonstrated that hip replacement significantly improves joint function and quality of life. Nevertheless, regenerative treatments like core decompression or stem cell therapy may delay or avoid the need for hip replacement at an earlier stage.
What is the difference between partial and total hip replacement?
Only the femoral head (ball) of the hip joint is replaced in a partial hip replacement (hemiarthroplasty), whereas the acetabulum (socket) and femoral head are replaced in a total hip replacement. While total replacements are preferred for more extensive joint damage, such as in cases of arthritis, partial replacements are usually performed for isolated femoral head problems or fractures.
What are the risks associated with hip replacement surgery?
Risks associated with hip replacement surgery are hip dislocation, wound infections, thromboembolic events, nerve injury, and implant loosening. Other problems include heterotopic ossification, periprosthetic fractures, and bleeding, with risk factors including hip deformity and considerable blood loss during surgery.
What is the expected lifespan of an artificial hip joint?
The expected lifespan of an artificial hip joint lasts 10 to 20 years, though many patients live for more than 25 years. This lifespan is affected by the patient's age, degree of activity, and the implant's materials; modern advances have significantly improved durability.
Is hip replacement surgery safe?
Most people agree that hip replacement surgery is a safe and effective way to reduce pain and improve joint function. Studies have shown that the rates of adverse events for various surgical techniques are low, and complications like dislocation are uncommon. Its safety profile is further improved by using appropriate surgical techniques and patient selection.
What is Bipolar hip replacement surgery?
Bipolar hip replacement involves inserting a prosthetic ball into a larger ball to replace the femoral head. The natural acetabulum then articulates with the larger ball, As it lessens the strain on the natural socket, this design may have some benefits.
Is hip replacement a major surgery?
Yes, hip replacement surgery is considered a major surgery. It requires removing and replacing damaged hip joint components with prosthetic ones, necessitating extensive intervention, anaesthesia, and a recovery period for rehabilitation to regain mobility and decrease pain.
What exercises should be avoided after hip replacement surgery?
High-impact exercises like running, jumping, and skating need to be avoided after hip replacement surgery to avoid putting excessive stress on the newly replaced joint. Because of the risk of hip dislocation and strain, exercises that require the hip to bend more than 90 degrees, twist, or cross the legs, as well as the use of exercise machines like leg presses or inner thigh adductors, are not recommended.
When can I bend after hip replacement surgery?
For the first 6 to 12 weeks following hip replacement surgery, patients need to avoid bending the hip over 90 degrees to lower the risk of dislocation and promote healing. Depending on the recovery and progress, a physical therapist or surgeon will advise patients when it is safe to resume bending past this point.
How long is hip replacement surgery?
Depending on the procedure's complexity and whether it's a partial or total replacement, hip replacement surgery usually takes 1.5 to 2 hours. The entire operating room stay takes roughly two to three hours, including additional time needed for anaesthesia and setup.
What are the symptoms of hip replacement dislocation?
Severe hip or groin pain, difficulty walking, noticeable variation in leg length, and weakness or immobility in the affected leg are some symptoms of hip replacement dislocation. In addition, there may be visible deformity, popping or clicking sounds, decreased range of motion, and joint swelling.
Why is titanium used in hip replacements?
Because of its superior biocompatibility, high resistance to corrosion, and capacity for osseointegration—the integration of titanium with bone—titanium is commonly used in hip replacements. Its strength and lightweight make it perfect for making long-lasting implants that lessen the strain on the surrounding bone while lowering the possibility of rejection or unfavourable reactions.
How long to use a walker after hip replacement surgery?
Depending on their overall recovery and physical therapy progress, most patients use a walker for two to three weeks following hip replacement surgery. When strength and stability increase, a gradual transition to using a cane or walking independently usually takes place.
How to reduce leg swelling after hip replacement surgery?
Patients need to elevate the leg above heart level, apply ice packs for 20-minute intervals, and wear compression stockings to improve circulation in order to reduce leg swelling after hip replacement. Anti-inflammatory medications and mild exercise, like walking, can also be useful in effectively managing swelling. For optimal outcomes, patients need to always take the advice of the surgeon.
Do you gain weight after hip replacement surgery?
Each patient experiences a different weight change following hip replacement surgery. While some people lose weight as their mobility improves, others gain weight as a result of decreased physical activity or fluid retention during recovery. Research shows that while non-obese patients frequently maintain or lose weight, obese patients are more likely to gain weight, which can affect long-term results.
How to put on compression stockings after hip replacement surgery?
Compression stockings should be put on as soon as possible after hip replacement, when leg swelling is at a minimum. First, roll the stocking down to the heel, then put the foot inside and slowly pull it up the leg. To avoid discomfort and decreased effectiveness, patients should make sure there are no wrinkles or bunching. It may be simpler to use equipment like rubber gloves or a stocking donner.
How successful is hip replacement surgery in the long term?
The long-term success rate for hip replacement surgery is high, with implant survival rates ranging between 70%-77% at 20-24 years and roughly 60% at 25-30 years. Patients also experience considerable improvement in pain relief and functional results, as indicated by Harris Hip Score increases from 43.6/100 to 91.0/100.
Can both hips be replaced at the same time?
Yes, both hips can be replaced at the same time using an approach known as simultaneous bilateral total hip replacement. This technique requires only one operation, hospitalisation, and a recovery period, making it suitable for individuals with severe hip problems that involve both hips. However, it is often suggested for younger, healthier patients because of higher risks, such as blood loss and problems associated with extended anaesthesia.
Why PACE Hospitals is considered as the Best Hip Replacement Hospital in Hyderabad?
PACE Hospitals, recognized as the Best Hospital for Total Hip Replacement in Hyderabad, Telangana, India, is home to some of the finest hip replacement surgeons. We specialize in advanced treatments for hip joint disorders, including total hip replacement, partial hip replacement, hip resurfacing, and revision hip replacement. Our expert orthopedic specialists utilize state-of-the-art technology and minimally invasive techniques to ensure faster recovery, reduced pain, and improved mobility. With a commitment to personalized care and excellence, PACE Hospitals is a trusted destination for hip replacement surgery in Hyderabad.