Laser Prostatectomy – Best Treatment Option for Enlarged Prostate
Pace Hospitals
Introduction
The men's prostate gland is a tiny, walnut-shaped organ that is located just beneath the bladder. It surrounds the urethra, the tube that transports urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. Although small, the prostate plays a vital role in male reproductive and urinary health, producing seminal fluid, which supplies nutrients and carries sperm.
However, as men age, the prostate gland tends to enlarge. This condition, called Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) or benign enlargement of the prostate, is non-cancerous but can cause significant urinary symptoms. It can majorly impact the quality of life if left untreated and even lead to urinary retention, bladder damage, or kidney problems.
In recent years, laser prostatectomy has emerged as one of the most effective, minimally invasive treatments for BPH, offering faster recovery, minimal bleeding, and excellent symptom relief.
Understanding Prostate Enlargement (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia- BPH)
BPH is a natural part of aging in men, particularly after 50 years of age. The prostate tissue grows in size and compresses the urethra, obstructing urine flow.
Key Facts about BPH:
- It is benign (non-cancerous) and does not increase the risk of prostate cancer.
- Around 50% of men above 50 years and up to 90% of men above 80 years experience some degree of prostate enlargement.
- If treatment is delayed, symptoms will progressively worsen, but they can be effectively controlled with medication, surgery, or lifestyle changes.
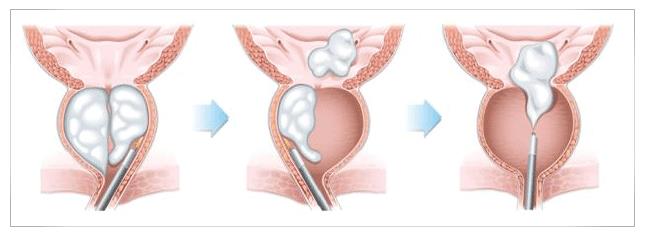
Symptoms of Prostate Enlargement
Symptoms of BPH are classified into irritative (storage) and obstructive (voiding) symptoms.
Irritative Symptoms:
- Frequency: Need to urinate more often than usual.
- Nocturia: Increased urge to urinate at night.
- Urgency: Sudden, uncontrollable urge to urinate.
- Burning sensation while passing urine.
Obstructive Symptoms:
- Hesitancy: Delay in starting urination.
- Poor urinary stream or thin flow.
- Interrupted flow (stopping and starting).
- Straining during urination.
- Feeling of incomplete bladder emptying.
When ignored, these symptoms may worsen and lead to serious complications.
Complications of Untreated Prostate Enlargement
If BPH is not managed properly, it may cause:
- Acute Urinary Retention: An emergency catheterisation is necessary due to a sudden inability to pass urine.
- Bladder Stones: Caused by urine stagnation.
- Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Because of insufficient bladder emptying, recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs) occur.
- Renal Failure: Chronic backflow of urine (hydronephrosis) that impairs kidney function.
- Bladder Weakness: Loss of muscle tone due to excessive work.
Treatment Options for Prostate Enlargement
The prostate size, symptoms severity, and the overall health of the patient all can affect the treatment. The main objectives are to improve urine flow, reduce blockage, and avoid complications.
Lifestyle Changes
Mild symptoms may be managed with behavioral and dietary changes:
- Limit evening fluid intake, especially within 2 hours of bedtime.
- Avoid diuretics such as caffeine, alcohol, and carbonated drinks.
- Reduce foods that increase urine output, like coffee, tea, citrus fruits, chocolate, and grapes.
- Maintain a healthy weight and exercise regularly.
- Empty the bladder completely every time you urinate.
These measures can help in the starting stages but may not be enough for moderate or severe cases.
Medical Treatment
If lifestyle changes don't provide relief, then medications are the next step.
Commonly prescribed drugs:
- Alpha Blockers: These medications relax the muscles of the prostate and the bladder neck to improve urinary flow.
- Side effects: Low blood pressure, dizziness, and reduced ejaculation.
- 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors: These medications gradually shrink the prostate by blocking hormonal changes.
- Side effects: Erectile dysfunction, Reduced libido.
While these medications can help, they often need to be taken long-term and may not work in all men.
Surgical Treatment
When symptoms become severe or unresponsive to medication, surgery becomes the best solution.
The two most common surgical options include:
- Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP): This traditional method removes obstructing prostate tissue using an electric loop inserted through the urethra. While effective, it involves a higher risk of bleeding and a longer recovery time.
- Laser Prostatectomy (Advanced Minimally Invasive Technique): This advanced technique clears the urinary pathway by vaporising or enucleating the enlarged prostate tissue using high-precision laser energy.
- Worldwide, this has become a great innovation in prostate surgery.
Laser Prostatectomy – The Modern Solution
High-intensity laser energy is applied during a laser prostatectomy via a thin fibre that is inserted through the urethra. The laser minimises damage to nearby structures while precisely locating and excising enlarged prostate tissue.
Types of Laser Procedures:
- Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate (HoLEP)
- GreenLight Laser Vaporization
- Thulium Laser Prostatectomy
Prostate size, bleeding risk, and patient comorbidities are taken into consideration when choosing these advanced laser systems.
How Laser Prostatectomy Works
Step-by-Step Detailed Overview:
- Anesthesia: The patient receives spinal or general anesthesia.
- Laser Fiber Insertion: A thin instrument with a laser fiber is inserted through urethra.
- Vaporization or Enucleation: The laser beam vaporizes or removes the excess prostate tissue compressing the urethra.
- Tissue Removal: Removed tissue fragments are flushed out through irrigation.
- Catheter Placement: A urinary catheter is placed temporarily (usually removed within 24 hours).
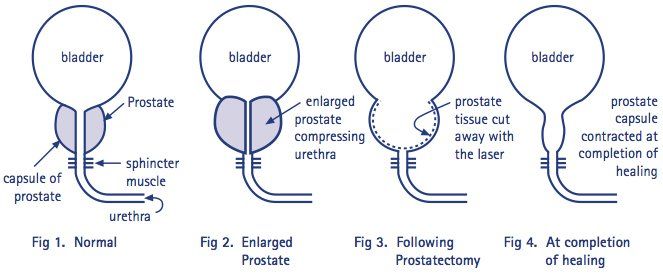
Advantages of Laser Prostatectomy Over Traditional TURP
Laser prostatectomy is increasingly replacing TURP due to its precision and superior safety profile.
| Feature | Laser Prostatectomy | Conventional TURP |
|---|---|---|
| Bleeding | Minimal | Moderate to high |
| Hospital Stay | 1–2 days | 4–5 days |
| Catheter Duration | < 24 hours | 2–3 days |
| Recovery Time | 3–5 days | 2–3 weeks |
| Usable for Large Prostates | Yes | Limited |
| Suitable for Heart/Anticoagulant Patients | Yes | Risky |
| Postoperative Complications | Low | Moderate |
| Durability of Results | Excellent | Moderate |
Laser surgery offers quicker recovery, less pain and long-term symptom relief.
Ideal Candidates for Laser Prostatectomy
Laser prostatectomy is recommended for:
- Men with moderate to severe urinary obstruction.
- Patients who have failed medication therapy.
- Those with large prostates (>60–80 grams).
- Patients on blood thinners (anticoagulants) where bleeding must be minimized.
- Elderly or cardiac-risk patients needing a safer surgical option.
Recovery and Postoperative Care
Most patients experience dramatic improvement in urine flow within 24 hours after surgery.
Typical Recovery:
- Catheter removal within 24 hours.
- Hospital stay of 1–2 days.
- Return to routine activities in 5–7 days.
- Temporary mild burning or urgency may occur for a few days post-surgery.
Long-term results are excellent, with most of the patients reporting major improvement in urinary symptoms and overall quality of life.
Potential Side Effects (Usually Temporary)
- Mild burning during urination for a few days.
- Increased frequency or urgency temporarily.
- Rarely, retrograde ejaculation (semen enters bladder instead of exiting).
- Extremely rare complications include infection or narrowing of the urethra.
The Bottom Line
Laser prostatectomy is a true boon to prostate patients. It provides an effective, long-term solution for men suffering from bothersome urinary symptoms due to an enlarged prostate.
When compared to more traditional techniques like TURP, laser surgery provides:
- Very little blood loss
- Quicker recovery
- Reduced length of hospital stay
- Safe results for patients at high risk
If you or a loved one is struggling with urinary issues such as poor flow, frequent urination, or incomplete bladder emptying, consult a urologist. Modern laser treatments can restore comfort, improve the quality of life, and help you regain normal urinary function.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Laser Prostatectomy
What is laser prostatectomy?
A laser prostatectomy is a minimally invasive procedure used to remove extra prostate tissue that is obstructing the flow of urine in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
How is it different from traditional prostate surgery (TURP)?
Laser prostatectomy causes far less bleeding, shorter hospital stay, and quicker recovery compared to traditional TURP, making it ideal for elderly or high-risk patients.
Is laser prostatectomy safe for patients with heart problems or on blood thinners?
Yes. It is the preferred option for such patients because the laser seals blood vessels instantly, reducing the risk of bleeding.
How long does the surgery take?
Typically, it takes about 45–90 minutes, depending on the prostate size and complexity.
Will I need a catheter after laser prostatectomy?
Yes, but only for 12–24 hours in most cases — significantly shorter than traditional surgeries.
How long does it take to recover from a laser prostatectomy?
Within a week, the majority of patients resume their regular activities, with improved comfort and flow of urine.
Can laser prostatectomy affect sexual function?
Erectile function is generally preserved. Some men may experience retrograde ejaculation, which is harmless but changes the direction of semen flow.
How effective is laser prostatectomy in the long term?
It provides lasting relief from symptoms with low risk of reoperation — success rates exceed 90–95%.
Is laser prostatectomy painful?
No, it is performed under anesthesia, and postoperative discomfort is minimal compared to conventional procedures.
Who should consider laser prostatectomy?
Men with moderate to severe urinary symptoms, enlarged prostate, or those unfit for traditional surgery due to heart or bleeding risks.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868
Appointment request - health articles
Recent Articles











