Tinnitus - Types, Causes, Symptoms, Risk factors, Treatment, Prevention
Tinnitus definition
Tinnitus is often described as a ringing sound in the ears or the perception of sound in the head or ears that comes from inside the body rather than an outside source. Tinnitus is not a disease in itself; it is a symptom of a problem in a person's hearing (auditory) system, which includes the ears and the brain. Currently, there is no cure for tinnitus. However, there are ways to reduce its symptoms.
Tinnitus meaning
The term “tinnitus” is derived from Latin; it comes from the word "tinnire", which means "ring, tinkle”, and stands for "ringing in the ears,". Typically, a person perceives sound in the absence of external sounds (outside sounds), and this perception is unrelated to any external source.
Prevalence of Tinnitus
Ear tinnitus is a common condition, affecting 10 to 25% of adults and even children. While it may improve or go away over time for some, it's important to note that in some cases, it may worsen. If it persists for three months or longer, it's considered chronic. Early intervention is key, as it's not usually a sign of anything serious and may improve on its own.
With 15% to 20% of the global population grappling with tinnitus, it's important to understand the significant impact it can have. For 25% of those affected, this condition disrupts their daily activities, making even the simplest tasks a challenge. In 1% to 3% of cases, the quality of life is severely affected, which highlights the need for better understanding and management of this condition.
Research on the Indian adult population uncovered that the prevalence of tinnitus is 6.7%; This study included 273 adults aged 18 - 60, using an online survey and random sampling. Some findings included:
- 76% of participants reported intermittent tinnitus.
- 15% reported sleep problems.
- None of them heard of tinnitus in their dreams.

Types of Tinnitus
There are 2 main types of tinnitus, which includes:
- Subjective tinnitus
- Objective tinnitus
Subjective tinnitus — These sounds are the most common type which patients only can hear.
Objective tinnitus — These sounds can hear by others such as doctor when they examine the patient and this condition be caused by noise coming from a blood vessel in the head or neck or from temporomandibular joint (the joint that connects the jaw to skull).
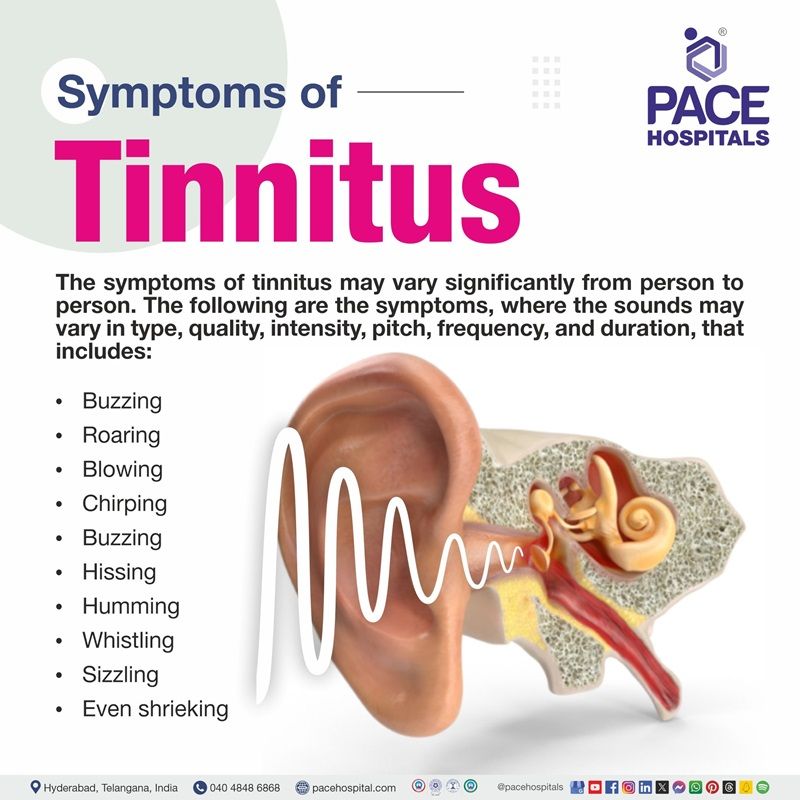
Tinnitus symptoms
The symptoms of tinnitus may vary significantly from person to person. The noises may seem to come from one ear (tinnitus in one ear) or both, inside the head, or from a distance. The following are the symptoms, where the sounds may vary in type, quality, intensity, pitch, frequency, and duration, that includes:
Phantom Sounds (Types and Qualities): Most people hear ringing sounds, and some may even think they're hearing air escaping, the inside of a seashell, water running or musical notes. Some people hear other types of sounds, such as:
- Buzzing
- Roaring
- Blowing
- Chirping
- Buzzing
- Hissing
- Humming
- Whistling
- Sizzling
- Even shrieking
Intensity and Pitch: The tinnitus sounds may have the following variations:
Soft vs. Loud
Low vs. High Pitched
Frequency and Duration: Sounds may have different patterns, that includes:
- Intermittent
- Persistent or constant
- Steady or pulsating
Somatosensory Tinnitus (Influence of Physical Movement): Sometimes, moving the head, eyes or neck or touching certain parts of the body may produce symptoms of tinnitus or temporarily (short time) change in the quality of the perceived sound:
- Effects of Head, Neck, or Eye Movement
- Effects of Touching Certain Body Parts
Some people with tinnitus also have symptoms of vertigo or hearing loss
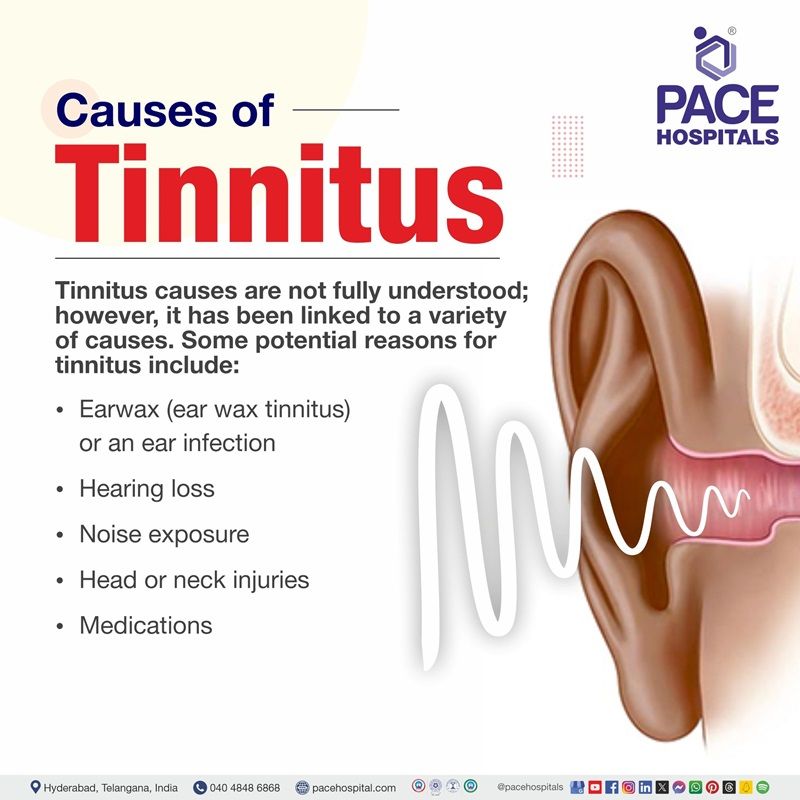
Tinnitus causes
Tinnitus causes are not fully understood; however, it has been linked to a variety of causes. Some potential reasons for tinnitus include:
- Earwax (ear wax tinnitus) or an ear infection
- Hearing loss
- Noise exposure
- Head or neck injuries
- Medications
Earwax (ear wax tinnitus) or an ear infection: Fluid from an ear infection or ear canal blockage by earwax can trigger tinnitus.
Hearing loss: It can be caused by factors such as ageing or exposure to loud noises. It is strongly associated with tinnitus, but some patients with hearing loss may never develop tinnitus.
Noise exposure: Many people experience tinnitus after exposure to a gunshot or loud noise at a sporting event, workplace setting or concert. This type of tinnitus can be annoying, though it usually resolves in a matter of hours. It is the most common service-related disability among veterans due to exposure to loud noises they may have experienced from machinery, gunfire, bomb blasts, or similar sources.
Head or neck injuries: A neck or head injury can damage the structures of the ear, areas of the brain that process sound, or the nerve that carries sound signals to the brain, causing tinnitus.
Medications: Certain medications may cause side effects, such as tinnitus, especially if taken at high doses. Medicines associated with tinnitus include certain antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, anti-cancer drugs, antidepressants, and anti-malaria medications.
Tinnitus risk factors
The below mentioned are some of the common tinnitus risk factors that have been linked to the development of tinnitus:
- Age-related hearing loss: Hearing loss due to ageing (presbycusis) often begins around the age of 60. The gradual loss of hearing due to the deterioration of the inner ear can lead to tinnitus. The worse the hearing loss, the more vulnerable the person is to developing tinnitus. Those with a hearing impairment have an increased risk of tinnitus, and the associated higher risk depends on the severity of the hearing impairment.
- Loud noise exposure: Regular exposure to loud noises, such as heavy equipment, chainsaws, or firearms, is a common risk for hearing loss and tinnitus. This is a major problem among active veterans and military members, who experience tinnitus more often than the general public. Noise-induced tinnitus and hearing loss can also be caused by listening to loud music, attending loud concerts frequently, or using headphones. It is likely to suffer from short-term tinnitus after visiting a concert; however, long-term exposure may cause permanent damage.
- Lifestyle habits: General health may get affected with the impact and severity of tinnitus. Researchers are not entirely certain why, but certain diet habits, physical activity, smoking cigarettes, sleep and stress levels (depression, anxiety), etc, play a role in increasing the risk of tinnitus.
Tinnitus can be a symptom of various ear problems, which are common risk factors for its development, which include:
- Ménière's disease: Tinnitus can be a symptom of an inner ear disorder called Ménière's disease. This disorder can cause balance problems and hearing loss, leading to a significant risk of tinnitus.
- Jaw joint problems: Close to the ear, a joint connects the lower jaw to the skull. Tooth grinding or jaw clenching can damage surrounding tissue, increasing tinnitus risk or worsening it.
- Tumour-related disorders: Some tumours, such as acoustic neuroma (vestibular schwannoma), are non-cancerous tumours on a nerve that leads from the inner ear to the brain. Acoustic neuromas and other tumours of the head, neck, and brain may increase the risk of tinnitus.
- Blood vessel problems: Issues with blood vessels, such as atherosclerosis, high blood pressure, or malformations in blood vessels, specifically if they are in or near the ear, may alter blood flow and increase the risk of tinnitus.
- Chronic conditions: Some chronic conditions such as migraines, diabetes, anaemia, thyroid disorders, and certain autoimmune disorders, including multiple sclerosis and lupus have been linked to the risk of development of tinnitus.
While tinnitus can have various causes, some people experience it without a known cause.
Tinnitus complications
Tinnitus complications can severely affect one's quality of life, causing substantial distress and impairing daily functioning. These challenges can diminish overall well-being and disrupt both personal and professional activities: The following are the possible complications of tinnitus:
- Sleep disturbances: Tinnitus can make it challenging to fall asleep, causing disturbances in sleep that result in sleep deprivation. Sleep deprivation can affect memory functions, worsening tinnitus symptoms and leading to memory impairment.
- Mood issues: In severe cases, tinnitus may lead to mental disturbances such as anxiety or depression, causing tension, irritability and frustration.
- Difficulty concentrating: Some people find that tinnitus affects their focus or concentration due to extreme sleep deprivation and mood issues.
- Other issues: Some people may also suffer from stress, fatigue, headaches, and problems with work and family life due to the impact of tinnitus.
Tinnitus diagnosis
Based on the above information, the ENT doctor refers the patient to an audiologist to measure hearing and evaluate tinnitus and advises the following diagnostic tests:
- Physical examination
- Audiogram
- Air-borne test
- Imaging tests
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Non contrast MRI of the brain
- Auditory brainstem response test
- Computed tomography (CT)
- CT angiography
- Ultrasonography
Tinnitus treatment
Treatment of tinnitus depends on the underlying physiological cause; the following are some of the treatments that an ENT doctor may suggest:
- Conservative treatments
- Medications (tinnitus medicine)
- Antidepressants
- Anti-anxiety medications
- Corticosteroids
- Sound Therapy
- Hearing aids
- Wearable sound generators
- Tabletop or smartphone (mobile) sound generators
- Behavioural therapy
- Education
- Cognitive behavioural therapy
- Tinnitus retraining therapy
- Combination devices
- Surgical and invasive treatments
- Cochlear Implants
- Stereotactic radiosurgery
- Cochlear and vestibulocochlear nerve ablation
- Deep brain and extradural stimulation
- Microvascular decompression

Tinnitus prevention
It is crucial to understand the prevention of tinnitus. Identifying the risk factors and understanding how to protect hearing can help mitigate its onset. Below mentioned are some of the measures to prevent the tinnitus:
- Reducing volume: Lower the volume on listening devices such as earbuds or headphones.
- Using protectors: If someone is often exposed to loud noises at home or work, it's essential to lower the risk of hearing loss (or further hearing loss) using specific protectors, including earplugs or earmuff-like or custom-fitted devices.
- Regular screening: Regular hearing examinations can help detect early signs of hearing loss and underlying conditions that might be associated with tinnitus.
- Monitoring and Managing health conditions: Monitoring and managing high blood pressure and diabetes is essential in avoiding ear problems.
- Lifestyle modifications: General lifestyle habits may affect the impact and severity of tinnitus. Because of this, it is recommended to assess diet, physical activity, sleep, and stress levels and take steps to improve them, which include:
- Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation and yoga for tinnitus
- Exercising regularly to improve the blood circulation
- Eating a balanced diet
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Tinnitus
Is tinnitus dangerous?
Tinnitus is not usually dangerous; it is often a symptom of other medical conditions, including ear infections, hearing loss or even high blood pressure. However, it isn't a sign of a serious condition. However, it can be a symptom of underlying issues such as ear infections, hearing loss, or even high blood pressure.
When tinnitus strikes suddenly, it is severe, and is associated with other symptoms such as dizziness, sleep disturbances or hearing loss, it's crucial to consult a medical professional. This step is not to cause alarm but to ensure the person's health and rule out more serious conditions.
How to cure tinnitus?
Although there is currently no cure for tinnitus, there are numerous ways to reduce its symptoms. Treatment options range from sound therapy and cognitive behavioural therapy to medications that address associated conditions or underlying causes. Managing stress and reducing exposure to loud noises can also help alleviate symptoms.
Does Tinnitus go away?
Yes, tinnitus can go away or improve over time, depending on the cause, especially if it's caused by a temporary problem like ear infection or earwax buildup. Tinnitus caused by certain medications usually resolves once the medication is stopped.
For others, it can be a chronic condition that persists despite treatment. Managing symptoms through specific treatment options, such as sound therapy, behaviour therapies (counselling), and lifestyle changes, can help improve quality of life.
What is the latest treatment for tinnitus?
As per the recent investigations by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and at other research centres across many countries that are working together to better understand the causes of tinnitus and to develop new treatment strategies, some examples of current advancements and research topics include neuromodulation techniques including deep brain stimulation, bimodal stimulation, electric stimulation, and repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS). Consulting a healthcare specialist is vital for utilizing the most appropriate and current treatments.
What if the patient doesn't seek treatment for tinnitus?
If the patient doesn't seek treatment for tinnitus, the symptoms can worsen. If left untreated, tinnitus may lead to additional health issues.
In severe cases, it can negatively impact the person's daily activities. Over the time, tinnitus can cause significant health problems, including impaired concentration, communication difficulties, poor sleep, chronic fatigue, anxiety, stress, or depression.
What does tinnitus sound like?
Tinnitus is often associated with a ringing sound in the ears, but each person's experience is unique. It can sound like ringing, buzzing, clicking, whistling, or static. For those with pulsatile tinnitus, it may sound like a low, rhythmic thumping similar to a heartbeat.
What is tinnitus retraining therapy?
This is a therapy which uses sound therapy and counselling to "retrain" the brain, both physiologically and emotionally, so that a person no longer notices the tinnitus. The counselling aspect of therapy targets to aid in reclassifying tinnitus sounds as neutral. Wearing a device that emits a continuous low-level sound in the ear can help the patient adapt to the presence of tinnitus.
Is tinnitus permanent?
Tinnitus can be temporary or permanent, depending on the cause: Tinnitus caused by exposure to a loud noise, like at a concert, is usually temporary and will subside on its own. Tinnitus caused by long-term exposure to loud noises or by other conditions, including age-related hearing loss, Ménière's disease, or some medications that can be chronic.
What is pulsatile tinnitus?
Pulsatile tinnitus is an uncommon condition that causes a sensation of hearing a rhythmic whooshing, swooshing, thumping, or throbbing, heartbeat sound in one or both ears, often in time with no external source, which can be quite disturbing.
It's a symptom of other conditions, such as heart disease or diseases that affect a person's arteries and veins. Pulsatile tinnitus causes include Blood vessel disorders, high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, Paget disease (primary bone disorder), and anaemia. Identifying potential conditions associated with pulsatile tinnitus is crucial as it can impact patient mortality and morbidity.
How to check for tinnitus?
An ENT doctor may also ask the patient to describe the tinnitus, including its intensity, duration, tonal quality and rhythm. They may also ask if it affects one or both ears. Checking the tinnitus starts with a physical exam of the ears, neck, and head to check for earwax buildup or ear infections. Medical history, audiological exam, and imaging tests such as computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or ultrasound can help reveal whether an underlying medical condition or structural problem is causing tinnitus.
Is there a surgery for tinnitus?
There isn't a specific surgery for tinnitus that works for every patient, as it depends on the underlying cause. Many wonder if cutting or severing the auditory nerve will eliminate their tinnitus. However, this procedure may cause permanent deafness and is not a reliable way to relieve tinnitus. Tinnitus may come back.
In cases where tinnitus is linked to issues such as tumours or middle ear problems, surgical interventions may help. However, many people find relief through non-surgical treatments such as sound therapy or hearing aids.
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868
Appointment request - health articles
Thank you for contacting us. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Oops, there was an error sending your message. Please try again later. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Our Locations – Find the Best Hospital Near You
Metro Pillar Number C1772, Beside Avasa Hotel, Hitech City Road, Near HITEC City Metro Station, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Mythri Nagar, Beside South India Shopping Mall, Hafeezpet, Madeenaguda, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
040 4848 6868
Payment in advance for treatment at PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, Telangana, India (Pay in INR ₹)
For Bank Transfer:-
- Bank Name: HDFC
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.50200028705218
IFSC Code: HDFC0000545 - Bank Name: STATE BANK OF INDIA
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.62206858997
IFSC Code: SBIN0020299
Scan QR Code by Any Payment App (GPay, Paytm, Phonepe, BHIM, Bank Apps, Amazon, Airtel, Truecaller, Idea, Whatsapp etc).

CONTACT US
Call: +914048486868
WhatsApp: +918977889778
Email: info@pacehospitals.in
FOLLOW US
SUBSCRIBE
Subscribe to our newsletter and stay updated with the latest health information.
Subscribe to PACE Hospitals' Public Newsletter
Thank you for subscribing to PACE Hospitals' Newsletter. Stay updated with the latest health information.
Oops, there was an error. Please try again submitting your details.
ABOUT US
QUICK LINKS
Disclaimer
General information on healthcare issues is made available by PACE Hospitals through this website (www.pacehospital.com), as well as its other websites and branded social media pages. The text, videos, illustrations, photographs, quoted information, and other materials found on these websites (here by collectively referred to as "Content") are offered for informational purposes only and is neither exhaustive nor complete. Prior to forming a decision in regard to your health, consult your doctor or any another healthcare professional. PACE Hospitals does not have an obligation to update or modify the "Content" or to explain or resolve any inconsistencies therein.
The "Content" from the website of PACE Hospitals or from its branded social media pages might include any adult explicit "Content" which is deemed exclusively medical or health-related and not otherwise. Publishing material or making references to specific sources, such as to any particular therapies, goods, drugs, practises, doctors, nurses, other healthcare professionals, diagnoses or procedures is done purely for informational purposes and does not reflect any endorsement by PACE Hospitals – your trusted hospital near me.