Anal fissure - Fissure in ano: Symptoms, Causes, Types, Complications
Pace Hospitals
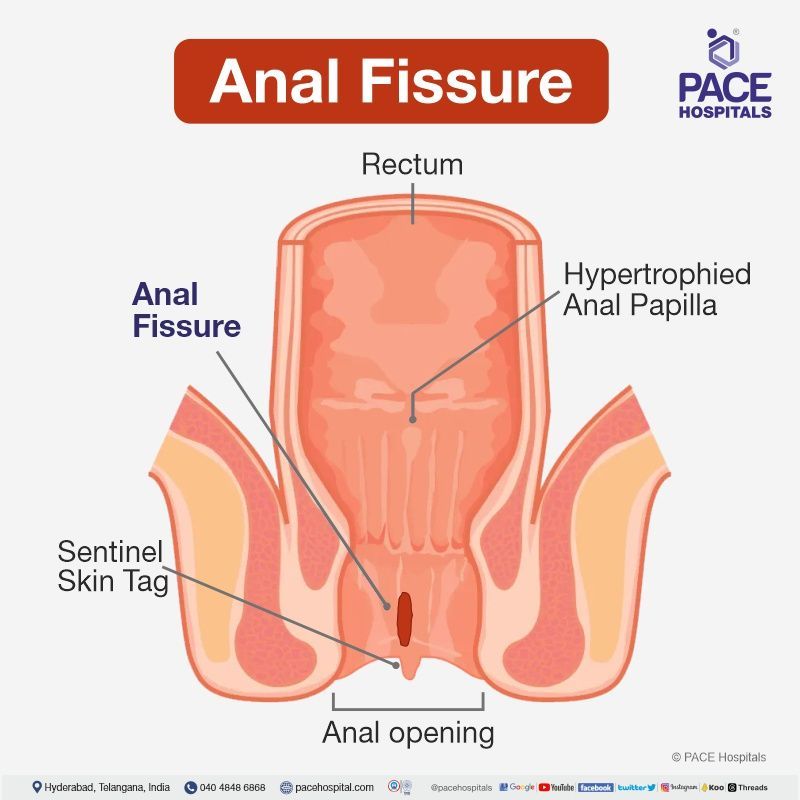
Anal fissure meaning
An anal fissure is also called fissure in ano, anorectal fissure, it is a laceration or tear (open sore) formed in the bottom section of the anal canal near the anus and rectal lining. These are usually common due to the inflammation of blood vessels. The skin tear in the anal region is superficial and distal to the dentate line and is classified into acute anal fissures and chronic anal fissures. Anal fissures and hemorrhoids are common, and both conditions tend to pass the stools much harder.
Incidence of anal fissures (fissure in ano)
Anal fissures (anorectal fissure) are commonly seen in infants and middle-aged individuals. For the past 30 years, there have been no evidence-based studies regarding the exact incidence or prevalence of anal fissures; this may be due to misattribution to haemorrhoid symptoms.
However, the incidence is more common in females than males; anal fissures are more prevalent in patients with comorbidities such as chronic constipation, inflammatory bowel disease, hypothyroidism, obesity, and solid tumours without metastasis.
Types of anal fissure (fissure in ano)
Anal fissures (anorectal fissure) are classified into two types based on the duration of time, they are:
- Acute anal fissures
- Chronic anal fissures
- Acute anal fissures: Anal fissures lasting less than six weeks are categorised into acute anal fissures. In terms of acute anal fissures, they heal quickly with simple management without the need for traditional procedure. They usually resolve within six weeks with mild to moderate symptoms.
- Chronic anal fissures: Anal fissures lasting more than six weeks are categorised into chronic anal fissures. The symptoms of chronic anal fissures worsen gradually. Only a few patients may heal the fissures without intervention, and most may not heal. Less than 10% of patients heal with traditional procedures; the rest need further management to resolve the problem. Anal spasms, severe pain, and bleeding on defecation are the typical symptoms usually seen in chronic anal fissures.
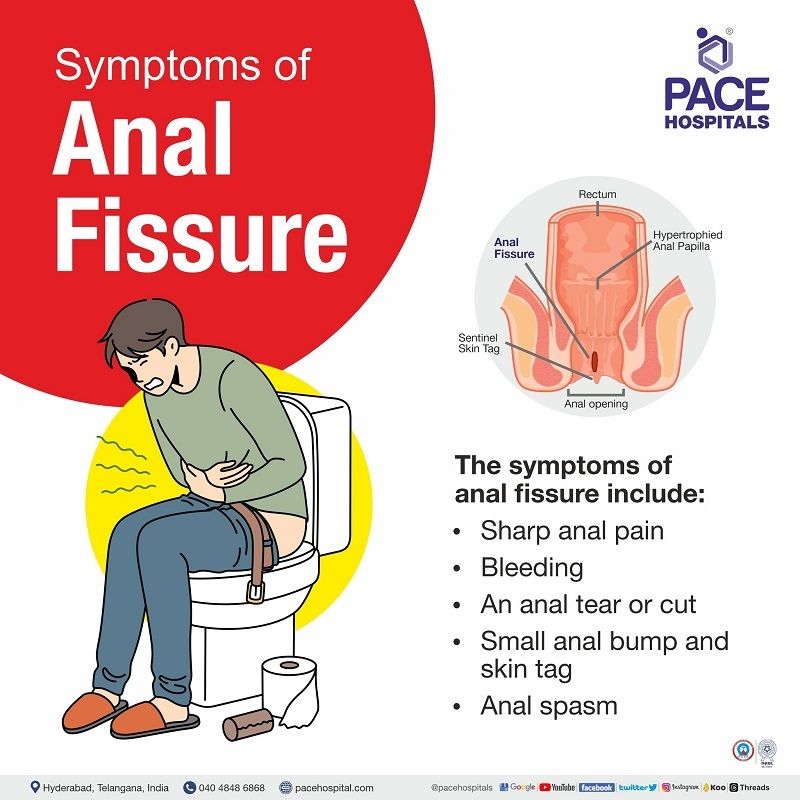
Anal fissure symptoms
The symptoms of anal fissure (fissure in ano) include:
- Sharp anal pain is seen during the stool passage, followed by burning pain for a few hours.
- Bleeding on defecation of stools.
- An anal tear or cut is especially seen in chronic fissures.
- Small anal bump or anal fissure and skin tag near the anus.
- Anal spasm.
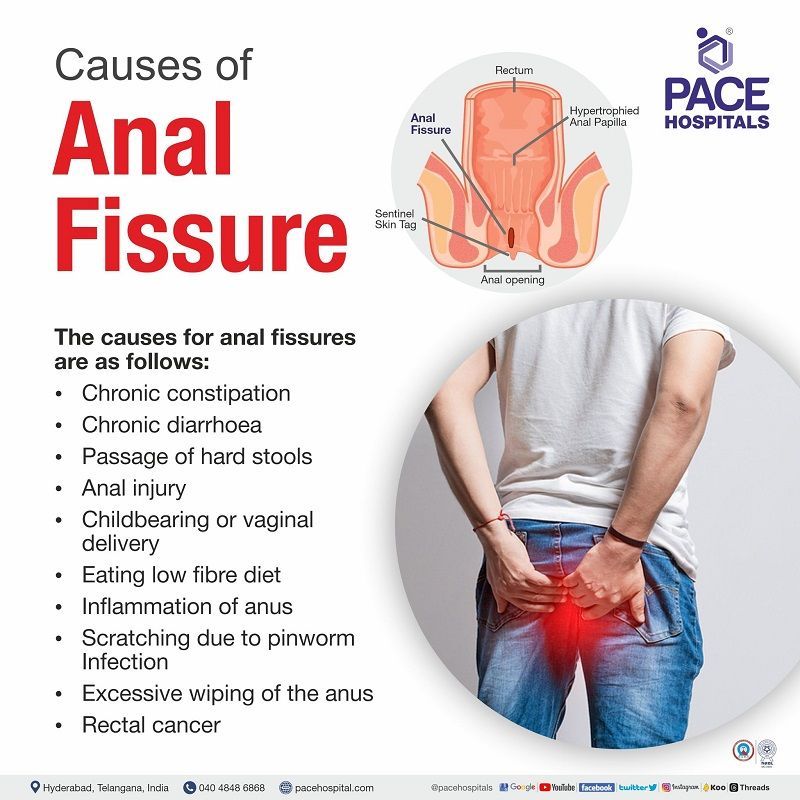
Anal fissure causes
The causes for anal fissures (fissure in ano) are as follows:
- Chronic constipation
- Chronic diarrhoea
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Passage of hard stools
- Anal injury
- Childbearing or vaginal delivery
- Eating low fibre diet
- Inflammation of anus
- Scratching due to pinworm Infection
- Excessive wiping of the anus after stool passage
- Rectal cancer
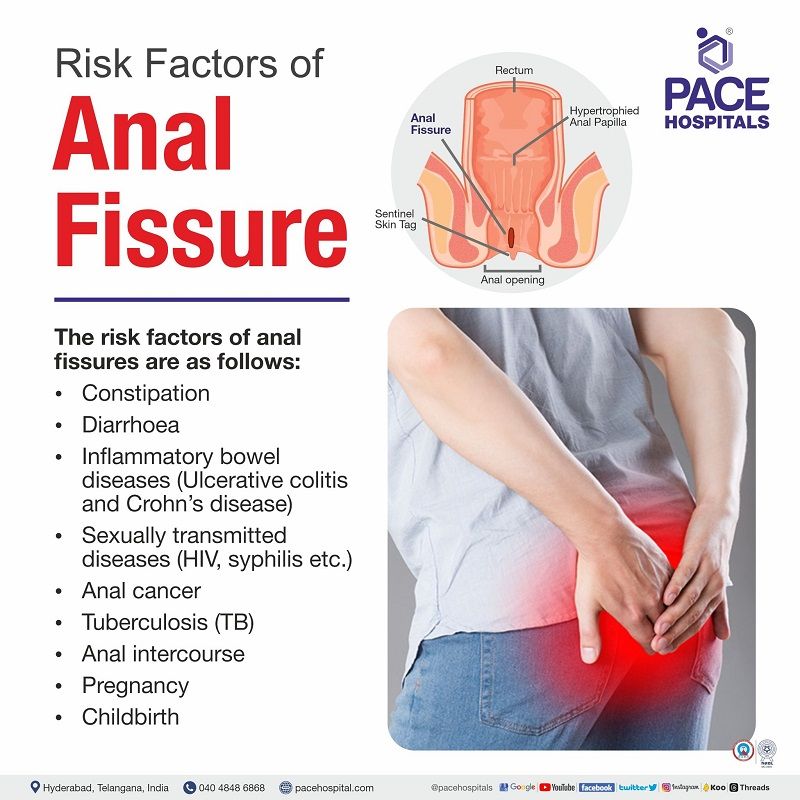
Anal fissure risk factors
Usually, the risk factors resemble the causes, but the risk factors differentiate with causes in terms of direct linkage. The risk factors are not the exact cause of the condition, but they are the factors that may lead to the condition.
The risk factors of anal fissures (anorectal fissure) are as follows:
- Constipation: It causes hard stools to pass, which may lead to an anal tear
- Diarrhoea: The anal skin is very sensitive, so diarrhoea can cause fissures by cracking/tearing the skin.
- Inflammatory bowel diseases (ulcerative colitis and crohn's disease): Peri anal diseases (piles, fissures) are the common complications of inflammatory diseases due to severe symptomatic conditions such as constipation and persistent diarrhoea.
- Sexually transmitted diseases (HIV, syphilis etc.): Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) cause ulcerations, lesions and bleeding in the anorectal regions, possibly leading to fissures.
- Anal cancer: Usually, the symptoms of anal cancer are the same as fissures causing lumps, pain, and bleeding, so people with colon or anal cancer may develop fissures, but people with fissures won't develop anal cancer.
- Tuberculosis (TB): TB is one of the inflammatory conditions in the anorectal region. It may cause symptoms such as itching, bleeding and discharge, which in turn causes anal fissure or fistula.
- Anal intercourse: Anal intercourse or inserting any objects into the anus may lead to an anal tear or crack due to the increased pressure near the anal sphincter.
- Pregnancy: Pregnant women may experience constipation due to hormonal changes and pressure by the foetus.
- Childbirth: Due to heavy contractions and pressure during labour, the women may experience anal fissures.
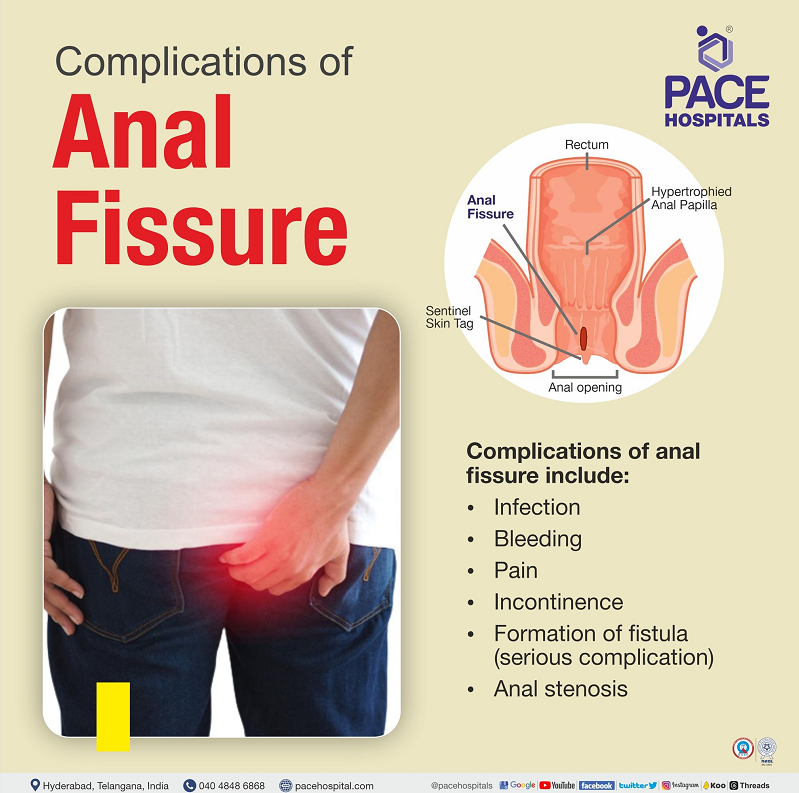
Complications of anal fissure (fissure in ano)
Complications of anal fissure (anorectal fissure) include:
- Infection: Chronic fissure may lead to the abscess formation
- Bleeding: Anal fissure hurts and may cause bleeding during stool passage
- Pain: The exposure of the external sphincter muscle under a tear leads to spasms and pain.
- Incontinence: In chronic anal fissure patients, the function of the internal sphincter is altered due to hypertonia and may cause a minor degree of incontinence.
- Formation of fistula (serious complication): In severe conditions, fistula may arise from chronic anal fissures.
- Anal stenosis: In anal fissure condition, it may develop hypertrophy in some conditions and lead to fibrous polyp’s formation. This could lead to anal stenosis and loss of compliance.
Anal fissure diagnosis
The diagnosis of anal fissure includes:
- Physical examination
- Digital rectal examination (DRE)
- Proctoscopy (medical procedure to examine rectum and anus)
- Anoscopy (medical procedure to examine the lining of the anus)
- Sigmoidoscopy (procedure to examine sigmoid colon) & Colonoscopy (medical procedure to examine the colon) for colon examination
- CT scan (computed tomography) and MRI scan (magnetic resonance imaging) will be done if the naked eye does not see the fissures.
Prognosis
Patients with acute anal fissures are lower in risk and resolved by conservative treatment. Still, in a few cases, they may develop into chronic anal fissures requiring surgical procedures and pharmacological management. The anal fissure cure will be seen within 3 to 4 weeks in patients who underwent surgical procedures.
Anal fissure treatment
The treatment for anal fissures includes:
- Lifestyle modifications (diet and habits)
- Analgesics for pain
- Laxatives
- Botulinum injection and anal fissure ointments containing nitrates
- Anaesthetics
- Surgeries:
- Open lateral internal sphincterotomy
- Closed lateral internal sphincterotomy
- Fissurectomy
- Laser surgery (laser sphincterotomy with fissurectomy)

Anal fissure prevention
Patients may prevent anal fissures by the following conditions:
Anal fissure diet:
- Taking fibre rich diet
- Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water
- Avoid too much alcohol and caffeine
- Taking fibre supplements such as ispaghula, methylcellulose, bran, or sterculia helps to prevent constipation
Medications:
- Using OTC (over-to-counter) anal fissure medications such as stool softeners and anal fissure pain relievers to reduce the disease progression
- Applying the lubricants or petroleum jelly to the anus
Habits:
- Doing exercises regularly
- Patients should only hold the stool for a short time, which may lead to the formation of hard stools.
- Taking sitz or tub baths for few times daily
- Avoiding straining in toilets
- Maintaining healthy weight
Anal fissure vs fistula | Difference between anal fissure and anal fistula
An anal fissure (fissure in ano) is a tear that occurs in the outer layer of the anal canal, whereas an anal fistula is an abnormal passage or tunnel that usually arises from the inside of the anal canal to the skin outside the anus.
| Characteristics | Anal fissure | Anal fistula |
|---|---|---|
| Symptoms | Pain on defecation and bleeding | Pain and discharge with a foul smell |
| Causes | Constipation, inflammatory bowel diseases, childbirth etc | Inflammatory bowel problems, problems with childbirth etc. |
| Risk factors | Constipation, diarrhoea, anal injuries, inflammatory bowel diseases etc | Having Crohn’s disease, childbirth, constipation etc. |
| Treatment | Usage of analgesics, antibiotics for anal fissure, laxatives, corticosteroids and treatment with surgical procedures. | Usage of antibiotics, anti-inflammatory agents, laxatives, vasodilators, and some surgical treatments. |
| Prevention | Taking fibre rich diet and making habitual changes such as having sitz bath, maintaining a healthy weight etc | Taking fibre rich diet and making some habitual changes, avoiding straining and maintaining dryness in the anal region etc |
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868