Bronchitis - Symptoms, Causes, Risk factors, Treatment and Prevention
Bronchitis definition
Bronchitis is a lung condition characterized by inflammation of the bronchial tubes (bronchi- the passageways that carry air to the lungs), which swell, making it more difficult for air to move through and making it more challenging to breathe.
Bronchitis can be treated by a
pulmonologist who specialises in diagnosing and treating respiratory conditions, including the lungs, airways, and blood vessels.
Bronchitis meaning
Charles Bedham coined the term "bronchitis" which means "inflammation of the bronchial membrane" in 1808 from the word:
- Bronchia, which means "the bronchial tubes"
- Itis, which means "inflammation"
Bronchitis medical term breakdown: broncho + itis
Bronchitis prevalence
Bronchitis statistics in India and world: Here are some statistics on bronchitis in India and the world:
Bronchitis prevalence in India
In India, the prevalence of chronic bronchitis (CB) among adults over 35 is 3.49%. According to findings from a study on respiratory symptoms,
asthma, and chronic bronchitis this rate is lower for women at 2.7% and higher for men at 4.29%.
Bronchitis prevalence worldwide
Globally, acute bronchitis is one of the top five reasons people seek medical attention. Approximately 5% of adults are affected, while around 6% of children experience at least one episode each year. In the general population, the prevalence of chronic bronchitis ranges from 3.4% to 22.0%, but in individuals with COPD, it can exceed 74.1%.

Types of bronchitis
There are different types of bronchitis with different causes, symptoms and treatments which are mentioned below
- Acute bronchitis
- Chronic bronchitis
The primary distinction between acute and chronic bronchitis lies in the duration of the symptoms, including:
Acute bronchitis
Acute bronchitis is a respiratory condition characterised by inflammation and swelling of the bronchi (breathing tubes), leading to increased mucus production and other changes. It is a short-term condition that usually resolves on its own within a few days or weeks, and lung function returns to normal.
Chronic bronchitis
Chronic bronchitis is characterised by inflammation and swelling of the bronchi, a kind of
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) condition referred to as productive cough that lasts for at least 3 months or more, occurring within a span of 2 years which is more serious than acute.

Bronchitis symptoms
Signs and symptoms of bronchitis impact the quality of life. Bronchitis occurs when the bronchi are irritated and inflamed by an infection. This causes them to produce more mucus than normal, and the body produces coughing to eliminate the excess mucus. Based on the types, some of the common symptoms of bronchitis in adults are listed below:
Acute bronchitis symptoms
Acute bronchitis often comes after having a cold or flu-like illness. It can last from three to four days Up to three weeks to four weeks and is contagious in nature. Some of the acute bronchitis symptoms in adults are listed below:
- Chest discomfort
- Cough that produces mucus may be clear or yellow-green (acute bronchitis green phlegm)
- Low-grade fever
- Wheezing, fatigue
- Breathlessness or shortness of breath that gets worse during activity
Even after acute bronchitis has cleared, individuals may have a dry, nagging cough lasting 1 to 4 weeks.
Chronic bronchitis symptoms
As mentioned above, chronic bronchitis can last up to three months or even two years and typically worsens as the disease progresses; at first, they exhibit no symptoms or mild symptoms. Some of the chronic bronchitis symptoms in adults include:
- Regular cough or coughing produces a lot of mucus
- Wheezing
- Loud or whistling sounds produced during breathing
- Shortness of breath, particularly during exercise
- Chest tightness
Colds and flu are common respiratory diseases in individuals with chronic bronchitis, and severe bronchitis symptoms may include ankle, foot, or leg edema, lower muscle weakness, and weight loss.
Symptoms of bronchitis in children include a runny or stuffy nose, sore throat, malaise, or a general feeling of being unwell, a feeling of chest congestion or tightness, a cough that may be dry or produce mucus and may be accompanied by gagging or vomiting and a low-grade fever.

Bronchitis causes
Bronchitis disease causes inflammation of bronchial passages by a virus, bacterium and irritant particles. Although smoking is a significant risk factor, nonsmokers can also develop bronchitis. Some of the common causes of bronchitis in adults are listed below:
Acute bronchitis causes
Acute bronchitis in adults is often linked to viruses that cause infections in both the lower and upper respiratory tracts, as well as exposure to lung irritants and bacterial infections. The following are the viruses, bacterial infections, and lung irritants that cause acute bronchitis, including:
Viruses that cause lower respiratory tract infections include:
- Influenza A and B (most common cause of acute bronchitis)
- Parainfluenza
- Respiratory syncytial virus
- Human metapneumovirus
Viruses that cause infections of the upper respiratory tract include
- Rhinovirus
- Coronavirus
- Adenovirus
Bacterial infections cause a significantly lower percentage of acute bronchitis
- Chlamydia pneumoniae is mainly observed in young adults
- Bordetella pertussis
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Lung irritants such as
- Tobacco smoke
- Air pollution
- Vapours
- Dust and fumes
Chronic bronchitis causes
Chronic bronchitis in adults is often linked to prolonged exposure to irritants that damage the lungs and airways, however, other factors can also contribute, including:
- The primary leading cause is cigarette smoke, and inhaling tobacco smoke from other sources, such as pipes and cigars, can also cause chronic bronchitis.
- Exposure to other inhaled irritants, including air pollution, second-hand smoke, and chemical fumes or dust from the environment or workplace, can lead to chronic bronchitis.
- Rarely alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency is a genetic condition that can cause chronic bronchitis. In this condition, the body cannot produce sufficient protein to protect the lungs from damage.
Bronchitis risk factors
Understanding the bronchitis risk factors can help prevent and maintain respiratory health. Some of the risk factors are listed below:
Acute bronchitis risk factors
- Smoking: Cigarette smoking or inhaling second-hand smoke (inhaling smoke that is exhaled by smokers) can break down the body's defence against infection. People who smoke are at a higher risk of developing acute bronchitis and experiencing a longer duration that could lead to chronic bronchitis.
- Weakened immune system: Having a weakened immune system makes it more difficult for the body to fight infections, raising the risk of bronchitis. Even a common cold or illness can strain the immune system.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): GERD may increase the risk of acute bronchitis by causing the stomach acids to backflow into the bronchial tree or from windpipe to air sacs.
- Chronic respiratory conditions: Chronic conditions like asthma, COPD, and bronchiectasis increase the risk of acute bronchitis in many ways due to continuous inflammation and damage of airways, mucos production, and decreased lung function making them more susceptible to infections and inflammation, which can trigger bronchitis.
Chronic bronchitis risk factors
- Older age: A study shows that the majority of people with chronic bronchitis start experiencing symptoms when they are at least 40 years old. As age increases, lung function decrease, which means the lungs become less effective at taking in air, even if they do not smoke or are not exposed to any lung irritants.
- Family history of lung disease: A family history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) also increases the risk of developing chronic bronchitis. If someone in the family has lung problems, they might be at high risk, especially if they are smokers.
- Female smoker: Women are more prone to the lung-damaging effects of cigarettes than men; they are likely to experience COPD and decreased lung function at an earlier age and or with lower levels of exposure.
Bronchitis Complications
Complications of bronchitis can arise when the condition is left untreated. These complications can differ in severity depending on whether the bronchitis is acute or chronic, which are mentioned below:
Complications of acute bronchitis
- Pneumonia: Pneumonia is the most frequent complication of acute bronchitis occurring when the infection spreads further into the lungs, causing air sacs to fill with fluid.
- Spontaneous pneumothorax: Lung diseases such as acute bronchitis can increase the risk of developing spontaneous pneumothorax, also known as a collapsed lung. This condition occurs when air builds up in the pleural space which connects lungs and chest wall which is a very rare condition and a complication of bronchitis in elderly people.
- Chronic bronchitis: Repeated episodes of acute bronchitis led to chronic bronchitis especially in smokers and individuals with other lung conditions.
Complications of chronic bronchitis
- Respiratory failure: Respiratory failure in chronic bronchitis occurs because of prolonged airway obstruction or by impaired gas exchange. Chronic inflammation and mucus buildup reduces oxygen intake and CO2 elimination which causes strain on the lungs leads to respiratory failure
- Cor pulmonale: Chronic bronchitis can lead to cor pulmonale, a heart disease characterised by an enlarged right ventricle. This causes the right side of the heart to fail, hindering the heart's ability to pump blood to the lungs due to prolonged hypoxia because of chronic inflammation and increased pressure in the pulmonary arteries.
- COPD: Chronic bronchitis is a form of COPD, and its progression can cause worsening lung function.
Bronchitis diagnosis
Bronchitis diagnosis is based on clinical assessment, which includes medical history and physical examinations. The evaluation focuses on symptoms such as cough, its duration, and mucus production. The following are tests that can be advised by general physician or pulmonologist that can be done alone or in combination to diagnose bronchitis:
- Medical history
- Physical examination
- Acute bronchitis physical exam findings
- Chronic bronchitis physical exam findings
- Other diagnostic tests for bronchitis
- Chest X-ray
- Arterial blood gas
- Pulse oximetry
- Blood test for bronchitis or a CBC for bronchitis
- Cultures of sputum or bronchitis sputum test
- Nasal swab
- Pulmonary function test
- Bronchoscopy
- Fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) test
Bronchitis treatment
Bronchitis treatment may varies depending on the types, symptoms and causes. Treatment options for bronchitis are listed below:
Conservative treatment
- Acute bronchitis treatment
- Acute bronchitis treatment at home
- Over the counter medicine for acute bronchitis
- Analgesic and antipyretic
- Chronic bronchitis treatment
- Antibiotics
- Bronchodilators
- Corticosteroids
- Mucolytics
- Antitussives
- Oxygen therapy
- Pulmonary rehabilitation
- Vaccines
Surgical treatment
- Bronchial rheoplasty
- Lung transplantation
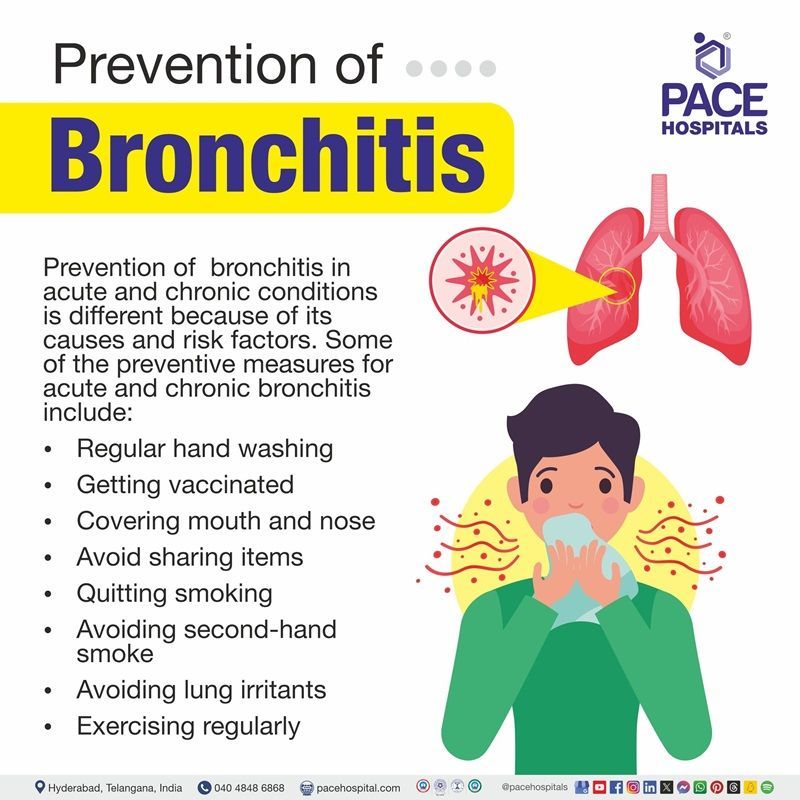
Bronchitis prevention
Bronchitis prevention in acute and chronic conditions is different because of its causes and risk factors. Some of the preventive measures for acute and chronic bronchitis include:
Acute bronchitis prevention
Prevention of acute bronchitis can be achieved by staying healthy and keeping others healthy by taking the following actions:
- Regular hand washing: Wash hands with soap or water, especially after coughing, sneezing, and being in public places.
- Getting vaccinated: Get flu vaccines every year and pneumonia vaccines based on age helps in prevention.
- Covering mouth and nose: Cover your mouth and nose during sneezing and coughing to avoid spreading.
- Avoid sharing items: Avoid sharing pillows, towels, and glasses can prevent transmission from infections.
Chronic bronchitis prevention
Prevention on chronic bronchitis mainly focuses on reducing the risk factors that lead to disease development and progression. Some preventive methods listed below:
- Quitting smoking: If you’re a smoker, quitting smoking is the most crucial step in chronic bronchitis prevention because smoking is the leading cause of it.
- Avoiding second-hand smoke: Experts recommend avoiding second-hand smoke as it is a leading risk factor for developing respiratory infections.
- Avoiding lung irritants: Avoid exposure to air pollution, chemical fumes and dust by wearing a mask can decrease the risk of chronic bronchitis.
- Exercising regularly: Exercise regularly to enhance breathing by improving lung function.
Difference between Bronchitis and Pneumonia
Bronchitis vs Pneumonia
Bronchitis and pneumonia, both are lung conditions that cause coughing and make it hard to breathe, but they affect different parts of the respiratory system and have different causes and severity which are mentioned below.
| Elements | Bronchitis | Pneumonia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which are the airways that supply air to the lungs. | Pneumonia is a lung disease that destroys the air sacs. |
| Cause | It is usually caused by a virus, but sometimes bacteria are also linked to smoking and air pollution. | It can be caused by various organisms, such as viruses, bacteria, or fungi. |
| Severity | Acute bronchitis is a self-limiting condition where, whereas chronic bronchitis is a long-term condition | It is a life-threatening condition, particularly in elders, infants and weakened immune system. |
Difference between chronic bronchitis and emphysema
Chronic bronchitis vs Emphysema
Chronic bronchitis and emphysema are lung conditions classified under the term chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Although the two disorders have similar symptoms, like wheezing and shortness of breath, they are distinct conditions. A few differences are listed below:
| ELEMENTS | Chronic bronchitis | Emphysema |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A lung disease known as chronic bronchitis is where microscopic hairs in the lung’s airways called cilia are destroyed. | A lung disease called emphysema is damage to the air sacs or alveoli. When these air sacs are injured, less oxygen can reach the circulation |
| Symptoms | The main symptoms of chronic bronchitis are chronic cough and thick mucus | In emphysema, shortness of breath, which often gets worse during activities are the main symptoms. |
| Causes | Long term exposure to irritants like smoking pollution | Emphysema is caused by smoking and genetics |
| Treatment focus | Reducing inflammation, prevent infections and clearing mucus production | Reducing lung damage, improving airflow and oxygenation |
Difference between asthma and bronchitis
Bronchitis vs Asthma
Bronchitis and asthma are respiratory conditions that share similar symptoms, and the airways get blocked in bronchitis and asthma. Although they have similar symptoms, they have different triggers and other difference listed below:
| Elements | Bronchitis | Asthma |
|---|---|---|
| Symptoms | The main symptoms of bronchitis include cough and mucus production during coughing. | In asthma, wheezing and shortness of breath are the main symptoms |
| Duration of symptoms | Acute bronchitis symptoms last for a week or month, whereas chronic bronchitis symptoms continue for months to years | Symptoms of asthma may come and go with exposure to certain triggers |
| Triggers | Environmental exposures may lead to symptoms of bronchitis. Acute bronchitis is triggered by infections. Irritants like pollutants and cigarette smoke which trigger chronic bronchitis. | Environmental factors such as dust, pollens, air pollution, smoke, and weather changes may trigger symptoms of asthma, these triggers are different from person to person. |
| Risk factors | Smoking or exposed to second hand smoker, recurrent respiratory infections, and occupational exposures like dust, fumes or chemicals. | Family history of asthma, exposure to allergens, respiratory infections, air pollution and smoking. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Bronchitis
Is bronchitis contagious?
Yes, bronchitis is contagious that develop when the bronchial tubes (airways) in the lungs become inflamed. Bronchitis can be acute or chronic. Acute bronchitis results from infections, particularly viral infections and it is often contagious. Chronic bronchitis results from long term effects and irritation and it is non-contagious.
How to treat bronchitis?
The treatment of bronchitis typically revolves around symptomatic treatment and supportive therapy. Both pharmacological and non-pharmacological approaches are considered in treating bronchitis. Remedies such as hot tea, honey, and ginger are included in the non-pharmacological strategy. Drug classes such as antitussive agents, beta agonists, analgesics and antipyretics are prescribed to provide symptomatic treatment.
How long does bronchitis last?
Acute bronchitis resulting from viral infection is a very common and usually lasts for a few days or weeks whereas chronic bronchitis lasts for about three months and recurs every two years.
Can bronchitis be cured?
Acute bronchitis which develops from a viral infection is a self-limiting condition that resolves on its own within a few days or weeks. Chronic bronchitis cannot be cured but it can be managed. Management of bronchitis includes oxygen therapy, pulmonary rehabilitation and a few lifestyle modifications.
Can bronchitis cause high blood pressure?
Blood pressure (diastolic, systolic, and mean arterial pressure) may rise during an acute bronchitis attack and decrease as the disease recovers without antihypertensive medications. Therefore, it is necessary to follow up blood pressure during and after the attack.
What is bronchitis?
A disorder known as bronchitis that occurs when the lungs' bronchial tubes, or airways, become inflamed and produce mucus during coughing. The two types of bronchitis are acute (short-term) and chronic (long-term). A very common condition is acute bronchitis. The majority of patients recover after a few days or weeks. Chronic bronchitis is a condition that lasts for three months or more and continues for at least two years in a row.
Can bronchitis cause chest pain?
Yes, bronchitis can cause chest pain, which is one of the primary symptom of bronchitis, and often develops due to inflammation of airways called bronchial tubes.
How common is plastic bronchitis and explain it?
Plastic bronchitis, or bronchitis plastica, is a rare disease that is more common in children than adults. This condition is characterised by recurrent formation of bronchial casts, a complication seen in diseases with increased volume or viscosity of bronchial secretions .
Can a blood test detect bronchitis?
Blood tests can assist in diagnosing bronchitis by detecting signs of infection. A healthcare professional typically requests blood tests along with other diagnostic procedures to confirm bronchitis; however, there is no specific blood test available for bronchitis.
Can antibiotics cure bronchitis?
If a bacterial infection causes acute bronchitis, antibiotics may help the patient's condition. However, antibiotics are ineffective in treating viral infectious bronchitis, because they lack antiviral action. They can also be harmful because they adversely affect the natural bacteria that colonize the intestine.
How to prevent a cold from turning into bronchitis?
Bronchitis is less likely to occur when people take precautions against common colds. Hygiene is essential, such as frequent hand washing and not touching the face with fingers, which reduce the risk of a common cold. Wearing a medical mask is another way to stop the viruses from spreading to yourself and other people.
Can bronchitis progress to pneumonia?
Yes, Pneumonia can develop from bronchitis, but it is uncommon. This occurs when the infection moves from the lungs' mucous membranes to the lung tissue.
What causes chronic bronchitis in non-smokers?
Chronic bronchitis can be caused by exposure to other inhaled irritants. These include air pollution, second-hand smoke (smoke from other people), and dust or fumes from chemicals in the environment or at work. In rare cases, alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, a hereditary disorder, may contribute to chronic bronchitis.
What is the difference between bronchitis and bronchiectasis?
Temporary inflammation of the bronchial tubes is known as bronchitis, while bronchiectasis is permanent damage and enlargement of the bronchial tubes.
Can bronchitis cause high white blood cell count?
Yes, White blood cells increase in bronchitis because this indicates that the body is fighting against infections and inflammation.
How long does it take for bronchitis symptoms to go away?
The duration of bronchitis symptoms depends on the type. Acute bronchitis symptoms reduce within 1 to 3 weeks, whereas chronic bronchitis is a long-term condition, hence symptoms persist longer from months to years
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868
Appointment request - health articles
Thank you for contacting us. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Oops, there was an error sending your message. Please try again later. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Our Locations – Find the Best Hospital Near You
Metro Pillar Number C1772, Beside Avasa Hotel, Hitech City Road, Near HITEC City Metro Station, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Mythri Nagar, Beside South India Shopping Mall, Hafeezpet, Madeenaguda, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
040 4848 6868
Payment in advance for treatment at PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, Telangana, India (Pay in INR ₹)
For Bank Transfer:-
- Bank Name: HDFC
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.50200028705218
IFSC Code: HDFC0000545 - Bank Name: STATE BANK OF INDIA
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.62206858997
IFSC Code: SBIN0020299
Scan QR Code by Any Payment App (GPay, Paytm, Phonepe, BHIM, Bank Apps, Amazon, Airtel, Truecaller, Idea, Whatsapp etc).

CONTACT US
Call: +914048486868
WhatsApp: +918977889778
Email: info@pacehospitals.in
FOLLOW US
SUBSCRIBE
Subscribe to our newsletter and stay updated with the latest health information.
Subscribe to PACE Hospitals' Public Newsletter
Thank you for subscribing to PACE Hospitals' Newsletter. Stay updated with the latest health information.
Oops, there was an error. Please try again submitting your details.
ABOUT US
QUICK LINKS
Disclaimer
General information on healthcare issues is made available by PACE Hospitals through this website (www.pacehospital.com), as well as its other websites and branded social media pages. The text, videos, illustrations, photographs, quoted information, and other materials found on these websites (here by collectively referred to as "Content") are offered for informational purposes only and is neither exhaustive nor complete. Prior to forming a decision in regard to your health, consult your doctor or any another healthcare professional. PACE Hospitals does not have an obligation to update or modify the "Content" or to explain or resolve any inconsistencies therein.
The "Content" from the website of PACE Hospitals or from its branded social media pages might include any adult explicit "Content" which is deemed exclusively medical or health-related and not otherwise. Publishing material or making references to specific sources, such as to any particular therapies, goods, drugs, practises, doctors, nurses, other healthcare professionals, diagnoses or procedures is done purely for informational purposes and does not reflect any endorsement by PACE Hospitals – your trusted hospital near me.