Ivermectin Tablet - Uses, Side Effects, Composition & Price
PACE Hospitals
Composition - Ivermectin is a mixture of two types of avermectins:
- 90% 5-O-demethyl-22,23-dihydroavermectin A1a (22,23-dihydroavermectin B1a) and
- 10% 5-O-demethyl-25-de(1-methylpropyl)-22,23-dihydro-25-(1-methylethyl) avermectin A1a (22,23-dihydroavermectin B1b).
Overview
In the mid-1970s, it was found that Streptomyces avermitilis (a type of bacteria) treated mice infested with Nematospiroides dubius (intestinal roundworm attacking rodents). Isolation of Streptomyces avermitilis led to the discovery of ivermectin. Since then, ivermectin for humans has been used to treat roundworms and other parasitic nematodes.
Ivermectin uses
Ivermectin is an antiparasitic medication with well-defined clinical applications. Health authorities including the USFDA, CDSCO, and EMA have approved its use for specific parasitic infections in humans, while emphasizing important restrictions about its misuse.
Human Medical Uses
- Strongyloidiasis - Treatment of intestinal roundworm (Strongyloides stercoralis) infection
- chocerciasis - Management of river blindness caused by Onchocerca volvulus
- Lymphatic Filariasis - Used in mass drug administration programs (in combination with other antiparasitic drugs)
- Scabies - Topical formulations approved for mite infestations
Veterinary Applications
- Heartworm prevention in dogs
- Parasite control in livestock
Critical Safety Information
- Not approved for viral infections (COVID-19, dengue) or bacterial diseases
- Veterinary formulations are unsafe for human consumption
- Should only be used as prescribed by a physician for approved parasitic conditions
Ivermectin tablet can be used for various parasitic infections such as thread worm infestation, river blindness disease, round worm infestation, whipworm infestation, filariasis (also called elephantiasis), tropical eosinophilia, and loiasis.
Apart from its antiparasitic activity, it has shown antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties.

Guidelines for taking Ivermectin tablet
- The patient is expected to follow all directions on the prescription label.
- Ivermectin is not to be taken in either larger or smaller amounts or for a longer duration than prescribed.
- Ivermectin may be taken on an empty stomach at least 1 hour earlier or 2 hours after a meal.
- Usually, a single dose of ivermectin is prescribed, which is to be taken with a full glass of water.
- Sometimes, the general medicine doctor may prescribe multiple frequencies of ivermectin therapy several months to a year after the first dose to effectively treat the infection, especially if the patient’s immune system is weak.
- Frequent stool samples may be provided to assess the performance of ivermectin.
- Store this medicine at room temperature, away from moisture and heat.
- In case of a missing dose on a therapeutic schedule, the missed dose must be taken as and when it was realised. If the patient remembers the missed dose almost to the next scheduled dose time, it should not be taken as it could account for an overdose. Extra medicine must never be taken to make up for the missed dose.
- In case of an overdose, the doctor must be consulted at once for medical attention.
- Alcoholism can potentiate specific side effects of ivermectin.
Ivermectin mechanism of action
Ivermectin tablets for humans are rapidly absorbed, reaching maximum plasma concentrations with a broad tissue distribution about 4 hours after a 12-mg dose. This drug immobilises affected organisms by inducing tonic paralysis of the musculature of the parasites by binding to the chloride ion channels of nerve or muscle cells.
Ivermectin tablet does not effectively kill adult worms, but blocks the release of microfilariae (minute larvae of a parasite causing filaria) for some months after therapy. After a single standard dose, microfilariae in the skin diminish rapidly within 2–3 days, remain low for months, and then gradually increase; microfilariae in the anterior chamber of the eye decrease slowly over months, eventually clear, and then gradually return. With repeated doses of ivermectin, the drug appears to have a low-level macrofilaricidalaction and to reduce microfilarial production permanently.
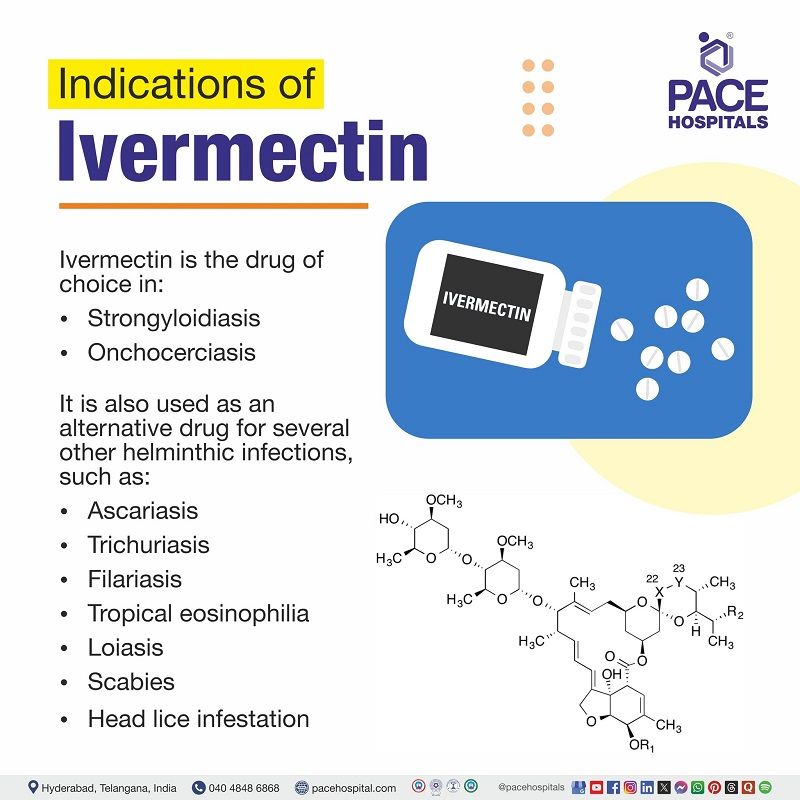
Ivermectin indications
Ivermectin is the drug of choice in:
- Strongyloidiasis (threadworm infestation caused by Strongyloides stercoralis through contaminated soil) and
- Onchocerciasis (also called river blindness, a tropical disease caused by Onchocerca volvulus (parasitic worm), transmitted by blackflies bites).
It is also used as an alternative drug for several other helminthic infections, such as:
- Ascariasis (parasitic infection of the small intestines by Ascaris lumbricoides – a roundworm through contaminated food).
- Trichuriasis (parasitic infection by Trichuris trichiura - whipworm).
- Filariasis (parasitic infection of Wuchereria bancrofti or Brugia malayi, transmitted by mosquitoes).
- Tropical eosinophilia (wheezing, fever and increased eosinophils linked with filariasis).
- Loiasis (parasitic infection by parasitic worm Loa loa - African eye worm transmitted by deerflies bites.
- Scabies (Skin infestation itch mite (Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis)).
- Head lice infestation (ectoparasitic infestations of pediculosis capitis).
Ivermectin dosage for humans
Ivermectin dosage for adults patients
Adult dosing:
- Strongyloidiasis - 0.2 mg/kg/dose given orally on an empty stomachper day.
- Onchocerciasis - 0.15 mg/kg/dose given orally on an empty stomach per day. The dosage may be repeated in 3-12months.
- Non-crusted scabies -0.2 mg/kg/dose given orally with food once every two weeks. It is provided as a 1st-line agent.
- Crusted scabies - 0.2 mg/kg/dose given orally with food once a day on the 1st day, 2nd day, 8th day, 9th day and 15th day. It may be provided on days 22 and 29 for severe cases, with 5% permethrin topical cream
- Head lice infestation (pediculosis capitis) -0.2 mg/kg/dose given orally with food twice every ten days
- Head lice infestation (pediculosis corporis)-12 mg given orally with food thrice a week.
- Head lice infestation (pediculosis pubis) - 0.25 mg/kg/dose given orally with food twice for 1-2 weeks.
Ivermectin dosage for children
Paediatric dosing
Strongyloidiasis
- 15-24 kg - 3 mg given once orally on an empty stomach per day
- 25-35 kg- 6 mg given once orally on an empty stomach per day
- 36-50 kg - 9 mg given once orally on an empty stomach per day
- 51-65 kg - 12 mg given once orally on an empty stomach per day
- 66-79 kg - 15 mg given once orally on an empty stomach per day
- >80 kg - 0.2 mg/kg/dose given once orally on an empty stomach per day
Onchocerciasis
- 15-25 kg - 3 mg given once orally on an empty stomach per day. The dosage may be repeated in 3-12 months.
- 26-44 kg - 6 mg given once orally on an empty stomach per day. The dosage may be repeated in 3-12 months.
- 45-64 kg - 9 mg given once orally on an empty stomach per day. The dosage may be repeated in 3-12 months.
- 65-84 kg - 12 mg given once orally on an empty stomach per day. The dosage may be repeated in 3-12 months.
- >85 kg - 0.15 mg/kg/dose given once orally on an empty stomach per day. The dosage may be repeated in 3-12 months.
Non-crusted scabies
- >15 kg - 0.2 mg/kg/dose given twice orally for two weeks with food. It is provided as a 1st-line agent.
Head lice infestation (pediculosis pubis)
- In adolescents- 0.25 mg/kg/dose is given orally with food twice for 1 to 2 weeks.
The dosage adjustments for adult and paediatric dosing in renal or hepatic impairment are not defined in the manufacturer's labelling.
Ivermectin for COVID
Emerging Evidence of Ivermectin’s Efficacy in the Prophylaxis and Treatment of COVID-19.
Since the early 2020s, researchers and institutions have delved into identifying any potentially effective treatment options for coronavirus disease (COVID-19) at the onset of the spreading pandemic. The efforts resulted in the identification of corticosteroids as the “proven life-saving treatment” for moderate to severe illness.
Further research on antiviral medicines such as remdesivir, lopinavir/ritonavir, antimalarials such as hydroxychloroquine, immunity boosters such as interferon, convalescent plasma, and monoclonal antibody therapy demonstrated a lack of impact on mortality in hospitalised patients suffering with COVID-19. The most concerning fact is that there haven’t been any proven effective agents to prevent disease in outpatients and hospitalisation.
Recently, the trials of ivermectin use for COVID-19 have shown a ray of hope in significant clinical and virologic outcomes, even mortality.
Ivermectin for COVID-19 prevented its transmission when given as prophylaxis to household members treating COVID-19 patients.
Prophylaxis is the process of taking medicine to prevent disease before its onset.
- Elgazzar et al. from Benha University in Egypt reported that 0.4 mg/kg of ivermectin given on day 1 and day 7 to household caregivers who wore personal COVID-19 protective equipment while dealing with COVID-19 patients are less likely to contract COVID-19 when compared with other household caregivers who only had the personal COVID-19 protective equipment.
- An observation by Carvallo et al. reported that when healthy volunteers were given 0.2 mg ivermectin + carrageenan daily for 28 days and compared them to other healthy volunteers who did not take the medicines, none of those volunteers receiving ivermectin were found positive for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-COV-2). On the contrary, 11.2% of the other group was positive.
- Behera et al. from India conducted a retrospective study in which they identified the healthcare workers who have taken some or other form of prophylaxis for COVID-19. It was found that the odds of contracting COVID-19 were markedly decreased in those workers who had taken two doses of ivermectin prophylaxis.
The All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) instituted a protocol for the prophylaxis of healthcare workers. Two doses of 0.3 mg/kg ivermectin must be taken 72 hours apart, and the dose must be repeated monthly.
Ivermectin efficacy in treating mildly ill COVID-19 outpatients
- Hashim et al. from Baghdad took outpatient and hospitalised patients and randomly divided them into two sets. In one group of patients, the standard treatment of COVID-19 was given; in the other set, a combination of doxycycline/ivermectin and standard of care was provided. While neither of the patients from either of the locations progressed or died, the time to recovery was significantly shorter in the group with ivermectin intervention.
- A hundred Bangladeshi COVID-19 patients demonstrated a faster symptomatic improvement (within 72 hours) without any necessity for hospitalisation when a combination of 0.2 mg/kg ivermectin and doxycycline was given. None of the patients died during the treatment.
- An Argentinian case series demonstrated that all the 135 mild illness patients survived when a combination protocol of ivermectin, aspirin, dexamethasone, and enoxaparin was used.
- Similarly, in Mexico, 28 patients in whom ivermectin was given, not only of them recovered, the full-time recovery was only 3.6 days on average.
Clinical studies depicting the efficacy of ivermectin in hospitalised patients
- Elgazzar et al. performed the largest random controlled trial among hospitalised patients. A total of 400 patients were randomised among four treatment groups of 100 patients each. Two of the groups (group 1 and 2) contain patients suffering from mild/moderate illness, and the rest two groups (group 3 and 4) only have severely ill patients. The treatment given to the groups are:
- Group 1: one dose of 0.4 mg/kg ivermectin + standard treatment
- Group2: apart from providing standard daily treatment, 400 mg of hydroxychloroquine was given twice on day 1, and then for five days, 200 mg was given twice daily for five days plus standard of care
- Group 3: one dose of 0.4 mg/kg ivermectin + standard treatment
- Group 4: hydroxychloroquine + standard treatment
- In all the groups, there are considerable differences in outcomes. Ivermectin intervention has reaped positive benefits when compared with the hydroxychloroquine intervention. In patients suffering from mild/moderate illness, the rate of COVID-19 progression is slow, without any deaths in group 1 (ivermectin group) but with four deaths in group 2 (hydroxychloroquine). While only 2% death was seen in group 3 (ivermectin group), the mortality rate was 20% in group 4 (hydroxychloroquine).
- Spoorthiet al. from Andhra, India, demonstrated that 50 hospitalised patients treated with ivermectin and doxycycline had a statistically significant shorter hospital stay (3.7 days) compared with 50 patients were given a placebo of vitamin B6 (4.7 days). The ivermectin group also demonstrated a shorter time in the complete resolution of symptoms (6.7 days) compared with the placebo group (7.9 days). No deaths were reported in this study.
Ivermectin in post-COVID-19 syndrome
- Long COVID is seen in 10-30% of cases in whom COVID-19 recovery was seen. It comprised persistent, vexing, and even disabling symptoms. Although there is no specific treatment, Aguirre-Chang et al. from Peru reported that with escalating doses of ivermectin (0.2 mg/kg and 0.4 mg/kg for mild and moderate symptoms, respectively) in 87.9% of the patients, all the symptoms resolved just after two doses of ivermectin. A 7% of the patients reported complete solution after a few additional doses.
The basis of evidence for ivermectin against COVID-19 from the aforementioned research can be listed as follows:
- Ivermectin suppresses SARS-CoV-2 replication and tissue binding.
- Ivermectin demonstrated potent anti-inflammatory properties.
- Ivermectin stops COVID-19 transmission and development in caretakers exposed to infected patients.
- Ivermectin speeds up the recovery in mild-moderate COVID-19 patients treated early after symptoms, thus preventing deterioration.
- Ivermectin administration hastens recovery without the necessity of ICU admission.
- Ivermectin administration helps in the avoidance of death in hospitalised patients.
- Ivermectin administration can reduce LONG COVID disease.
- Ivermectin's safety, availability, and affordability are unparalleled due to low medication interactions and moderate and uncommon adverse effects.
Despite its effectiveness, people shouldn’t indulge in self-medication of ivermectin tablets. It did not receive the approval of Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the indication of COVID-19. The treating physician retains the medical discretion of administering or discontinuing ivermectin tablet.
For their discovery of ivermectin, William C. Campbell and Satoshi Mura were awarded the 2015 Nobel Prize. Apart from its outstanding effectiveness against parasitic disorders and COVID-19, it continues to demonstrate therapeutic prowess against:
- the Semliki Forest virus, chikungunya alphaviruses, Sindbis virus, and yellow fever (flavivirus).
- the Zika virus (ZIKV) in in vitro screening assays
- the West Nile virus (a flavivirus).
Ivermectin side effects
Common side effects of Ivermectin tablets
- Mild pruritus (itchy skin)
- Feel giddiness
- Vomit sensation
- Pain in abdomen
- Difficulty in passing stools
- Lethargy (feeling low or lack of energy)
- Transient changes in electroencephalography (ECG)
Serious side effects Ivermectin tablets include:
- Hepatitis
- Neurotoxicity
- Loss of vision
- Decreased heart rate
- Increase asthma condition
- Seizures (uncontrolled electrical disturbance in the brain)
- Conjunctival haemorrhage (bleeding of eye membrane)
- Postural hypotension (low blood pressure when changing postures from lying down to sitting up to standing, etc.)
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome (rare, severe skin and mucous membranes disorder)
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis (life-threatening skin disorder due to drug reaction)
Side effects of ivermectin tablets on few specific organs and systems:
Cardiovascular:
- Ivermectin tablets can cause tachycardia (increased heart rate) while the patient is standing and supine (sleeping). It is also reported causing postural hypotension (a decrease in blood pressure when the patient goes from lying down to sitting up position or from sitting up to standing).
Respiratory:
- The patient can experiencebronchodilatation, which significantly reduces vital capacity after 24-30 hours. A few patients can also have dyspnoea (shortness of breath) and transient cough.
Nervous system:
- Ivermectin can cause vertigo and headache. Some patients had experienced a sudden change in behaviour, lethargy and anorexia.
- Ivermectin can cause Loa loa encephalopathy in Loa loa infections.
Hematologic:
- Patients treated with ivermectin for onchocerciasis had reported prolonged prothrombin time.
Skin:
- Ivermectin might cause pruritus, soreness, rashes or skin oedema.
- HIV patients who were prescribed ivermectin reported lymph node swelling and rashes
Musculoskeletal:
- Mild bone and joint pains
- Myalgia (muscle pain)
Reproductive system:
- Orchitis (inflammation of one or both testis) or epididymitis (inflammation ofthe epididymis) with scrotal tenderness
Ivermectin contraindications
The physicians do not prescribe ivermectin to patients who are hypersensitive to it.
Effect of Ivermectin on Pregnancy, Breastfeeding and Fertility
Pregnancy: There is little to nil data on the topical use of ivermectin in pregnant women. According to oral reproductive toxicity studies, ivermectin is teratogenic in rats and rabbits. Hence, ivermectin is contraindicated in pregnancy. However, in humans, teratogenicity is not expected based on limited clinical data.
Breastfeeding: Ivermectin is excreted in minimal amounts in human milk on oral administration. The excretion of topical administration in human milk has yet to be studied.
Post oral administration, ivermectin is excreted in human milk in low concentrations.
Evaluation of excretion in human milk after topical administration hasn't been done. Based on limited human data, there is no known risk of baby injury; no human data is available to assess the effects on milk production. The patient may use it while breastfeeding based on the risk/benefit analysis.
Fertility: There is no human data on the effect of ivermectin on fertility. In animal studies (rats), the ivermectin therapy did not affect mating or fertility.
Drug interactions
An interaction is said to occur when the effects of the drug are changed by the presence of another drug, food, drink or by some environmental chemical agent. The outcome can either be harmful (such as increasing the drug toxicity) or benedictory (such as a synergistic increase in outcome). The various interactions of ivermectin are:
- Acenocoumarol (anticoagulant) - increased INR (time for the blood to clot).
- A combination of albendazole (anthelmintic) and azithromycin (antibiotic) - causes moderate changes in the pharmacokinetics of all three drugs.
- Alcohol - ivermectin could be more potent.
- Levamisole (anthelmintic) - ivermectin could be more potent.
- Orange juice - ivermectin could be less potent.
Ivermectin tablet price in India
| Product | Company | Price in INR (₹) |
|---|---|---|
| New Ivermectol 12mg | Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd | ₹ 77 |
| Ivecop 12mg | A. Menarini India Pvt Ltd | ₹ 26 |
| Ivertreat 12mg | Zydus Cadila - Zydus Healthcare Limited | ₹ 77 |
| Iverlin 12mg | Linux Laboratories Private Limited | ₹ 104 |
| Lupimectin 12mg | Lupin Limited | ₹ 81 |
| Welmectin 12mg | Wellona Pharmaceutical Private Limited | ₹ 253 |
| Scabover 12mg | Brinton Pharmaceuticals Ltd | ₹ 61 |
| Iverwood 12mg | Woodrock Healthcare Pvt Ltd | ₹ 350 |
| I Cov 12mg | Abrik Remedies Private Limited | ₹ 350 |
| Iverhelmin 12mg | Curever Pharma Private Limited | ₹ 264 |
| Zeorizer 12mg | Sigma Softgel & Formulation | ₹ 274 |
| Ivermount 12mg | Hindayur Life Sciences Private Limited | ₹ 315 |
| Ivertac 12mg | Care Formulation Labs Pvt Ltd | ₹ 244 |
| Ividoc 12mg | Biorex Healthcare Pvt Ltd | ₹ 322 |
| Scabover 12mg | Brinton Pharmaceuticals Ltd | ₹ 354 |
Frequently asked questions (FAQs) on Ivermectin
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868