Pancreatitis - Acute and Chronic: Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
Pancreatitis definition
Pancreatitis is the inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas is an organ found in the abdomen. Abdominal pain is the most common symptom seen in this condition. With early diagnosis and prompt treatment it can be managed. It could lead to various complications, such as increasing the risk of progression to pancreatic cancer in case of ill treatment or delayed treatment. Pancreatitis can be successfully treated by an experienced gastroenterologist.
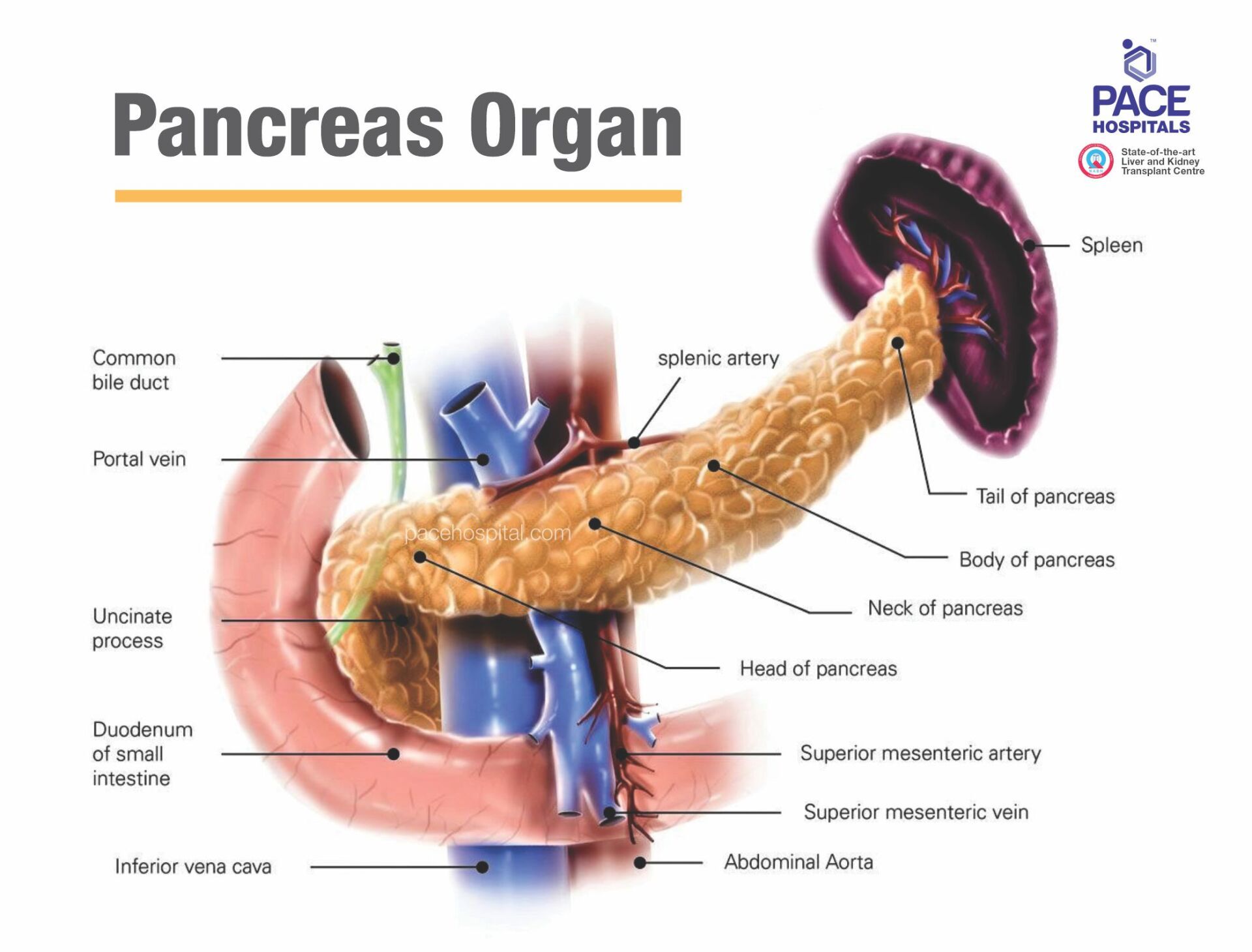
Pancreas is an organ which is found in the abdominal cavity located behind the stomach. Every day it secretes about 236 ml of pancreatic juice (containing pancreatic enzymes). The function of pancreatic juice helps in digestion of fats, carbohydrates, and proteins.
Although the inflammation of pancreatitis is called pancreatitis, there are broadly two types of pancreatitis. They are:
- Acute pancreatitis: If the pancreatitis is temporary, it is called acute pancreatitis.
- Chronic pancreatitis: If the pancreatitis is life-long, it is called chronic pancreatitis.
While 80% of the acute pancreatitis cases resolve on their own without arising of any serious complications, with only 5% mortality, the chronic pancreatitis on the other hand reported a 9-16-fold risk of pancreatic cancer.
Pancreatitis meaning
Acute pancreatitis meaning: The etymology of “acute” is derived from Latin word “acutus” which meant sharp and pointed, implying the sudden attribution of disease severity. Pancreatitis is an amalgamation of the organ “pancreas” + “itits” (which meant inflammation).
Chronic pancreatitis meaning: Chronic roots are from the Greek word “Khronos” which meant time, implying the longevity and persistence of a disease to accumulate its severity. Pancreatitis is an amalgamation of the organ "pancreas" + "itits" (which meant inflammation).
Pancreas function
The Pancreas secret pancreatic juice (a transparent fluid consists of electrolytes, water, and enzymes) that is rich in proteins and consists of bicarbonate fluid, digesting enzyme such as amylase, trypsin, nucleases, elastase, chymotrypsinogen, carboxypeptidase and lipase, these enzymes are essential for the digestion of fat, protein, fat, and carbohydrate in the food.
The pancreas performs two most important functions i.e. exocrine and endocrine function for human body -
- Exocrine function: It releases digestive enzymes to break down and digest fats, foods, carbohydrates, and proteins in our small intestine. The enzymes normally are produced and carried in an inactive form to the small intestine, where the enzymes are activated as needed. It also makes and releases bicarbonate that neutralizes stomach acids and allows for the activation of pancreatic enzymes.
- Endocrine function: it produces five hormones, beta cells secrete insulin, alpha cells secrete glucagon, delta cells secrete somatostatin, epsilon cells secrete ghrelin and PP (gamma) cells secrete pancreatic polypeptide; and releases them into the blood. These hormones regulate sugar (glucose) transport into the body's cells, where it is used for energy and to help maintain normal blood sugar levels.
Prevalence of pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis prevalence worldwide: While there were about 28,14,972.3 cases of acute pancreatitis in 2019, 4.1% (115,053.2) of them met their demise. According to a study published in 2021, India is one of the top three countries that contained the greatest number of incident cases of acute pancreatitis: the others being China and America.
Prevalence of acute pancreatitis in India
The overall prevalence of acute pancreatitis in India seemed to increase which could be either due to an increase in diseases which cause pancreatitis (such as gallstones) or due to the overall improved diagnostics. Nevertheless, it must be understood that the prevalence of acute pancreatitis in India might not be consistent across the country owing to the varied lifestyles and eating habits.
While a Government Hospital in New Delhi reported 62 patients per year, the hospital situated in Shimla reported 123 acute pancreatitis patients per year. The overall mortality of acute pancreatitis was approximately 5%, while the necrotizing and interstitial pancreatitis were 17% and 3%, respectively.
Types of pancreatitis
There are a different type of conditions related to the pancreas including-
- Acute pancreatitis is a short term condition and occurs suddenly; causing inflammation of the pancreas. Acute pancreatitis may be mild and can develop further complications if not treated and monitored properly, such as necrotizing pancreatitis, pancreas infection, pancreatic pseudocyst, or organ failure.
Severe abdominal pain, tender and swollen belly, diarrhea, nausea, bloating, vomiting and fever are the common symptoms of acute pancreatitis. - Chronic pancreatitis is a long-term condition, causing inflammation of the pancreas. It is a progressive disorder associated with the damaging of the tissues of the pancreas that can't be reversed. It is more common in male aged between 32 and 45 years. Not only that, but it is long-term progressive disease; causing permanent damage to the pancreas. Initially symptoms of the chronic and acute pancreatitis are similar such as severe abdominal pain, tender and swollen belly, diarrhea, nausea, bloating, vomiting and fever.
In chronic pancreatitis patient can develop unwanted weight loss,
malnutrition, and
malabsorption.
- Hereditary pancreatitis is a rare genetic condition to occur due to recurrent pancreatic attacks, which can lead to chronic pancreatitis. Symptoms include severe abdominal pain, tender and swollen belly, diarrhea, nausea, bloating, vomiting and fever. It also increases lifetime risk of pancreatic cancer. Hereditary pancreatitis can't be cured completely, can be managed by medical management, pancreatic enzyme supplements to cope-up with indigestion, insulin for diabetes, medications to control pain and lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of pancreatic cancer.
- Pancreatic cancer occur when uncontrolled cell growth begins in the tissues of the pancreas. Cancerous and noncancerous tumors growths can occur in the pancreas. Pancreatic cancer can be cured if detected early but in most of the cases due to no symptoms is early stages it’s difficult to find it. Pancreatic cancer can also slow down the production of digestive enzymes by the pancreas, resulting in difficulty to break down food and absorbing nutrients. This malabsorption causes bloating, watery, greasy, foul-smelling stool, further can lead to weight loss and vitamin deficiencies.
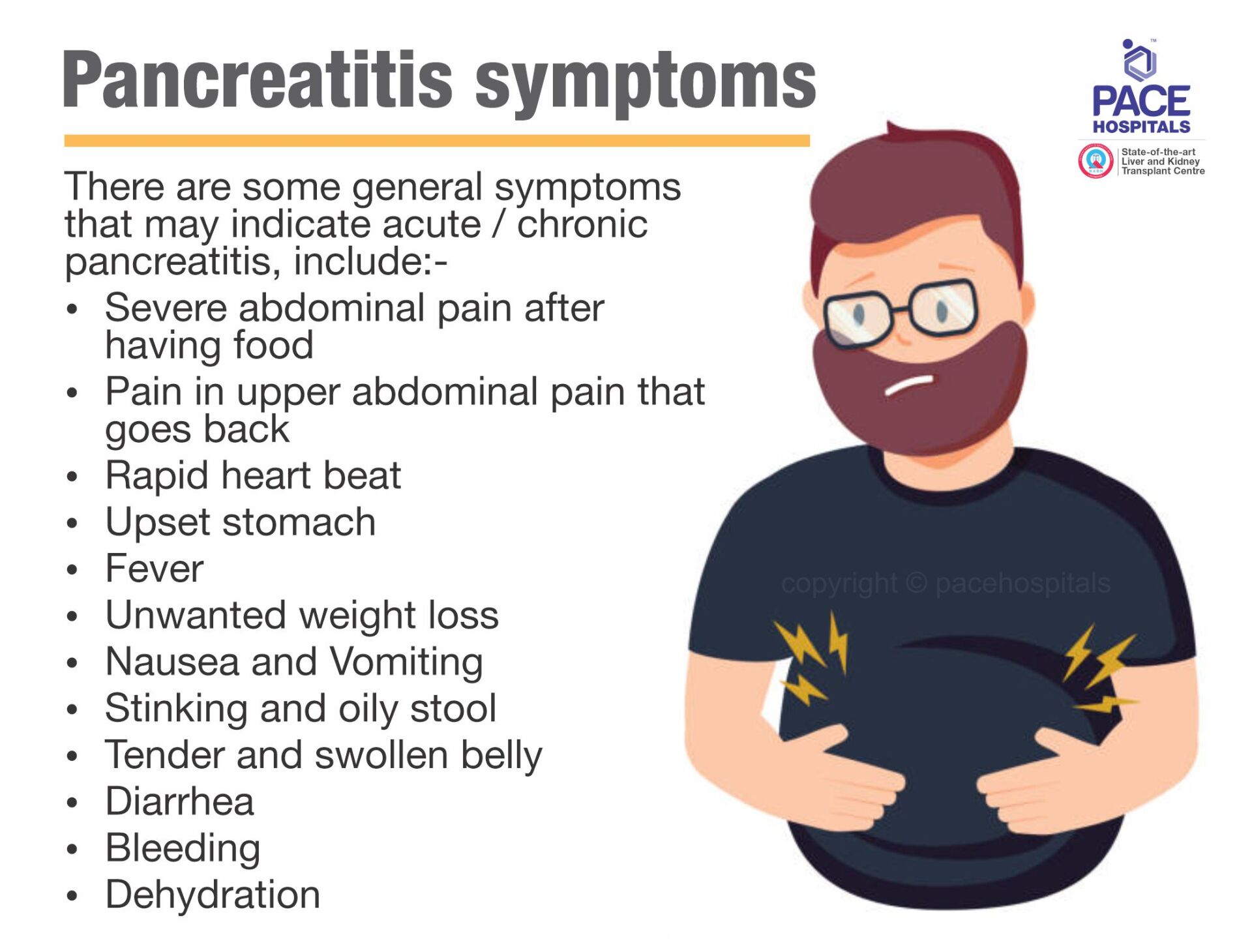
Pancreatitis symptoms
Signs and symptoms of pancreatitis depends on its type, there are some general symptoms that may indicate acute / chronic pancreatitis, include:-
- Severe abdominal pain after having food
- Pain in upper abdominal pain that goes back
- Rapid heart beat
- Upset stomach
- Fever
- Unwanted weight loss
- Nausea and Vomiting
- Stinking and oily stool
- Tender and swollen belly
- Diarrhea
- Bleeding
- Dehydration
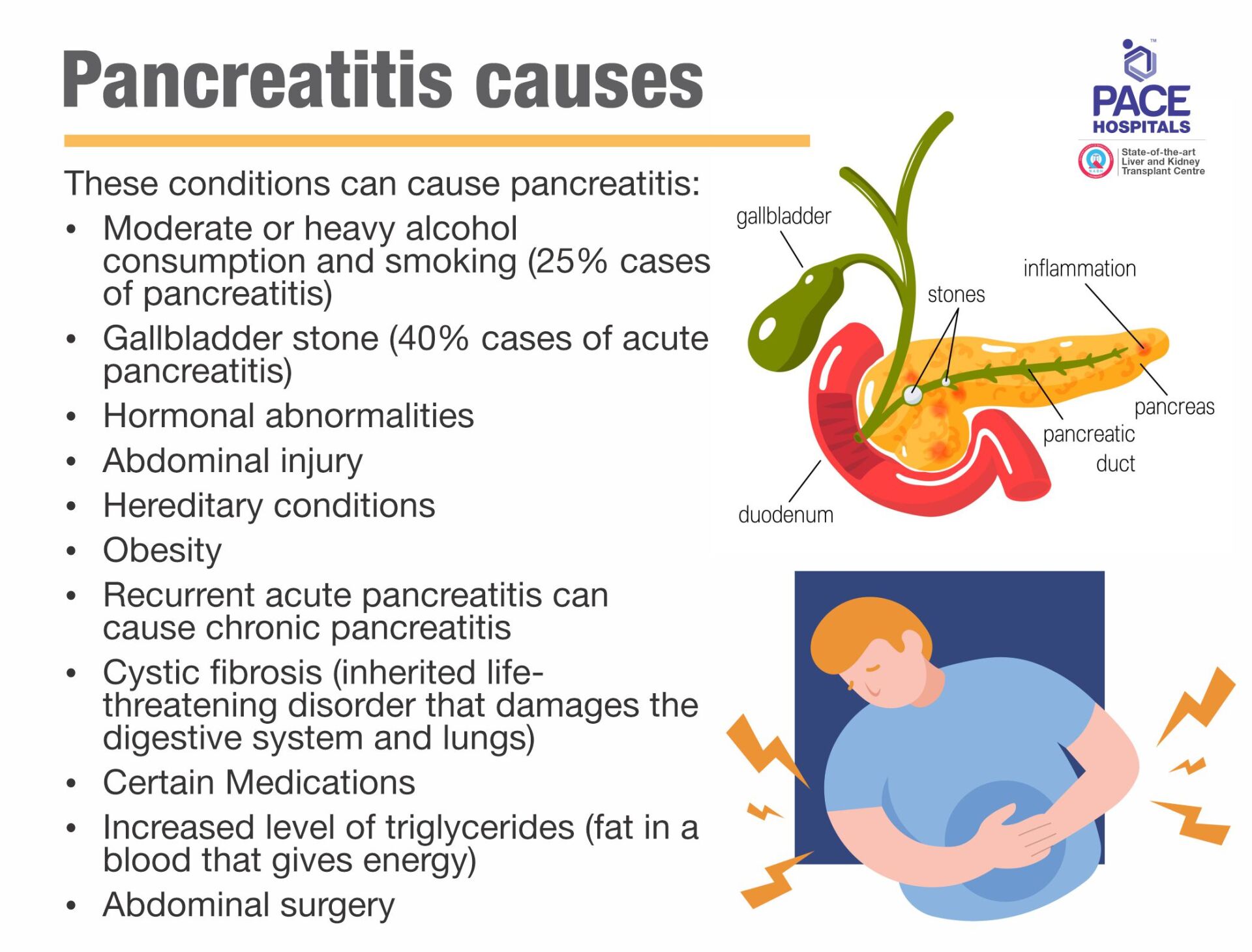
Pancreatitis causes
Pancreatitis, an inflammation of the pancreas occurs when digestive enzymes become activated while still in the pancreas, irritating the cells of your pancreas. These conditions can cause acute or chronic pancreatitis:
- Moderate or heavy alcohol consumption and smoking (25% cases of pancreatitis)
- Gallbladder stone (40% cases of acute pancreatitis)
- Hormonal abnormalities
- Abdominal injury
- Hereditary conditions
- Obesity
- Recurrent acute pancreatitis can cause chronic pancreatitis
- Cystic fibrosis (inherited life-threatening disorder that damages the digestive system and lungs)
- Certain Medications
- Increased level of triglycerides (fat in a blood that gives energy)
- Abdominal surgery
Pancreatitis risk factors
These following risk factors can increase risk of pancreatitis –
- Obesity
- Heavy alcohol consumption
- Cigarettes smoking
- Hereditary conditions or genetics
Men are at high risk compared to women. Combination of any of the above risk factors can increase the chances of getting acute or chronic pancreatitis, for example obese people consuming excess alcohol or a person is smoking cigarettes and consuming alcohol may increase the risk of acute or chronic pancreatitis.
Pancreatitis complications
Pancreatitis can cause severe complications that require immediate attention:
- Malnutrition, due to lack of digestive enzymes
- Diabetes, due to insulin mismanagement
- Pancreas infection
- Kidney problem / failure
- Pancreatic cancer
- Fatigue and dehydration due to diarrhea
- Necrotizing pancreatitis (tissues death inside the pancreas due to limited blood supply)
- Pancreatic pseudocyst (fluid collection in pancreas)
- Lungs problem such as difficult in breathing
Pancreatitis diagnosis
Pancreatitis has physical findings that affect body systems and can be diagnosed through blood test, imaging test and intervention procedure advised by doctor.
Depending on symptoms, the Gastroenterologist will ask about medical history, any family history of pancreatitis, eating and drinking habits, taking any prescription or over-the-counter medications, including vitamins and supplements.
To diagnose pancreatitis, a gastroenterologist may recommend:
- Blood and Stool tests: Amylase or lipase blood test and Stool routine test for digestive enzymes of the pancreas. It will be elevated 3 times in pancreatitis from its normal range. If blood test is showing normal ranges then we need to go to further evaluation.
- Imaging tests:
To understand pancreatitis and figure out what’s the cause. Doctor may recommend X-rays with a barium meal and Ultrasound imaging: specifically evaluate the gallbladder for stones
- Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS): Endoscopic examination to evaluate pancreatic masses and tumors, pancreatic cysts, small stone in bile duct and gall bladder not identified during ultrasound. This procedure is performed to collect small tissues of pancreas using FNA needle through the wall of the stomach or intestine directly into the pancreas.
- CT Scan, Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP), or PET scans: Non-invasive tests for detailed imaging of the pancreas and the surrounding. CT scans expose the patient to some amount of radiation. Furthermore, some patients are unable to receive IV contrast for their CT scans (due to allergies or kidney problems), and thus the quality of the pictures will be sub-optimal. A special kind of MRI called an MRCP can give high-quality pictures of the pancreas, the pancreas duct, and the bile ducts. However, some patients who are claustrophobic may decide against having an MRI performed.
- Biopsy or Tissue analysis: a tissue sample (biopsy) from pancreas may help diagnose pancreatitis and further look for signs of pancreatitis.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): to view the bile duct and pancreatic duct. It helps to remove gallstones from the bile duct gallstones that are causing a blockage.
Pancreatitis treatment
Pancreatitis treatment depends upon its type, cause, and stags. It’s very important to find the cause and extent of pancreas damage in guiding treatment.
Pancreatitis treatment usually require short-term or long-term hospitalization to initiate the aggressive treatment. In general the following treatment will be initiated for the treatment of pancreatitis -
- Pain medicine and antibiotics to lower down the infection.
- Intravenous (IV) fluids, it helps to prevent dehydration so that the rest of the organs of the body get adequate blood flow to support the healing process.
- Low-fat diet or fasting, to stop eating so your pancreas can recover. In this case, nutrition will be given through a feeding tube.
- Gallbladder surgery (cholecystectomy) if gallstones caused your pancreatitis.
- Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): to take out gallstones if they’re blocking your bile or pancreatic ducts. There different procedures that can be performed using ERCP like:
- Gallstone removal
- Sphincterotomy for pseudocyst drainage
- Balloon dilatation: to dilate, or stretch, a narrowed pancreatic or bile duct to keep the duct open
- Stent placement: placing a tiny piece of plastic or metal that looks like a straw into a narrowed pancreatic or bile duct to keep it open.
- Pancreas surgery such as
- Distal pancreatectomy
- Pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple procedure)
- Total pancreatectomy to clean out fluid or dead or diseased tissue a liver transplant.
Pancreatitis Prevention
Alcohol consumption and smoking cigarettes can increase the risk of pancreatitis. It is strongly recommended quitting smoking cigarettes and drinking alcohol to prevent pancreatitis. A healthy diet rich in high fiber, maintaining healthy weight, limiting intake of sugars and regular exercise can protect you against any non-communicable disease such as pancreatitis.
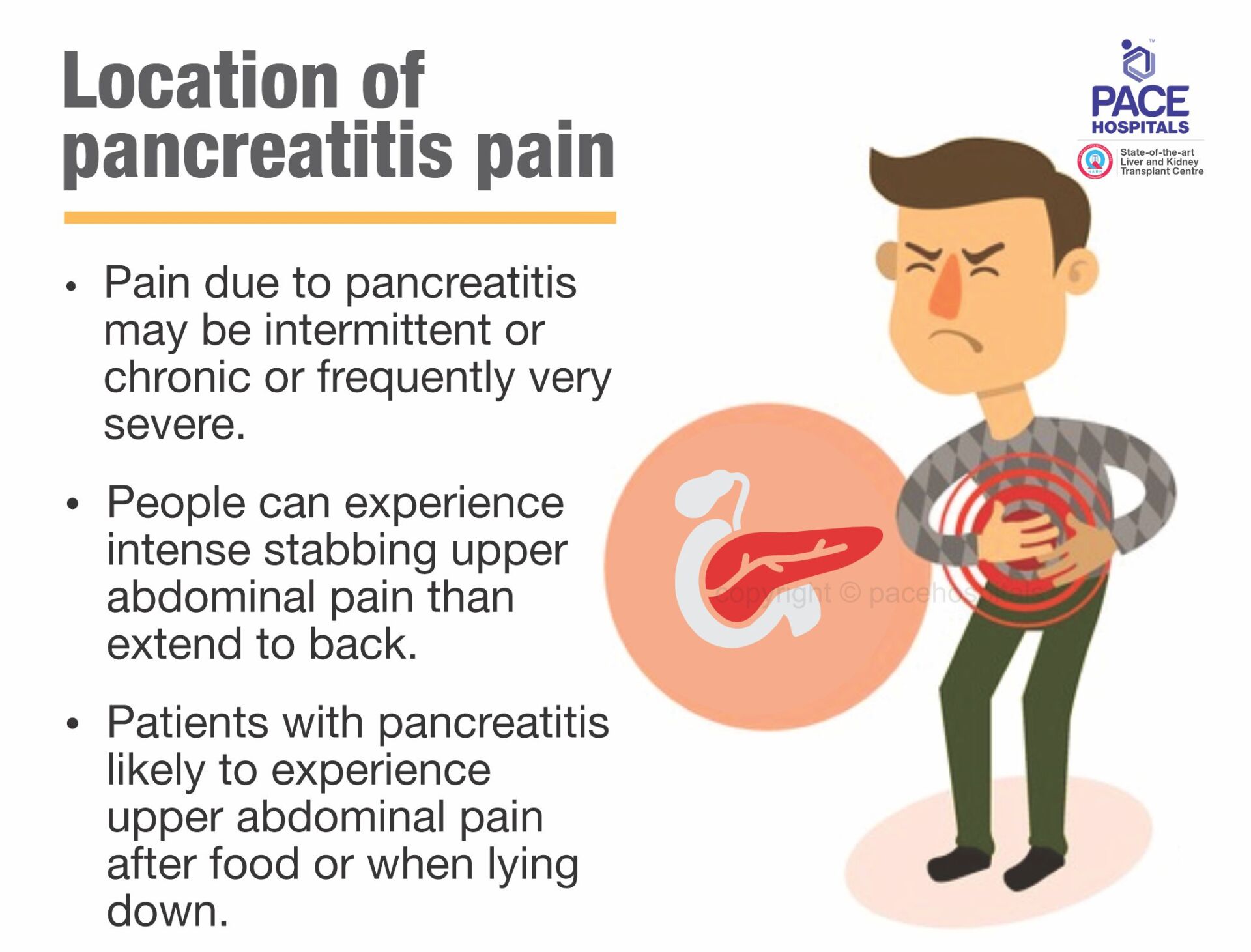
Location of pancreatitis pain
Pain due to pancreatitis may be intermittent or chronic or frequently very severe sometimes people can experience intense stabbing upper abdominal pain than extend to the back. In mild cases affected from acute conditions, pain may present for few minutes and can last for several hours whereas in severe cases affected from chronic conditions, pain may become constant for years together.
Patients with pancreatitis likely to experience upper abdominal pain after food or when lying down. Treatment at early stage can help in reliving symptoms and fast recovery from it.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Pancreatitis
When is pancreatitis fatal?
Pancreatic necrosis is a fatal condition that occurs due to increased levels of
inflammation, resulting in blockage of blood supply to the pancreas and
formation of necrosis (death) of pancreatic tissue, leading to infection from bacteria. This infection quickly spreads to the other organ resulting in multiple organ failure.
Is pancreatitis very serious?
The severity of pancreatitis depends on various factors. About 4/5 cases of acute pancreatitis demonstrate a quick improvement without any serious further problems. Nevertheless, 1 in 5 cases of pancreatitis are severe which may result in serious life-threatening complications, such as multiple organ failure. In severe cases with the development of complications there's a high risk of fatality.
Can pancreatic cancer be cured?
Yes, both types of pancreatic cancer – acute and chronic can be cured. treatment usually require short-term or long-term hospitalization to initiate the aggressive treatment.
How long does pancreatitis take to heal?
The healing time for pancreatitis can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Mild cases of acute pancreatitis may resolve within a few days to a couple of weeks, while severe cases or cases with complications may take several weeks or even months to heal. Chronic pancreatitis may require ongoing management and can take months to years to stabilize.
Which pancreatic enzyme is effective in digesting proteins?
The pancreatic enzyme trypsin is effective in digesting proteins. Trypsin is produced by the pancreas and plays a crucial role in breaking down proteins into smaller peptides and amino acids, which can be absorbed by the small intestine.
What is acute pancreatitis?
If the pancreatitis is temporary, it is called acute pancreatitis and usually resolves on its own without any intervention.
How to test for pancreatitis at home?
There is no test for pancreatitis at home. The abdominal pain caused by pancreatitis can be distinguished with other types of pain abdominal which can help in alerting the patients to consult doctors.
What is pancreatic juice?
Pancreatic juice is a fluid secreted by the pancreas playing a crucial role in digestion, helping in the breakdown of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. The pancreatic juice contains various enzymes, such as amylase, lipase, and proteases which help not only in digestion but also in the maintenance of an optimal pH environment for the enzymes to function.
How long can you live with chronic pancreatitis?
The natural history of chronic pancreatitis is poorly well defined. Mortality ratio is higher than that of the general population, survival at 10 years after the onset of the disease being estimated at 69-80%. Pancreatic cancer is one of the important causes of death but the extra pancreatic malignancies in chronic pancreatitis it is only known that they have common risk factors such as alcohol, smoking etc.
What is a pancreatic attack?
Acute pancreatitis is defined as an acute inflammatory attack of the pancreas with a sudden onset of symptoms. The commonest causes for acute pancreatitis are gallstones (40–65%) and alcohol (25–40%), and the remainder (10–30%) are due to a variety of causes including autoimmune and genetic risk factors.
How does hyperparathyroidism cause pancreatitis?
Acute and chronic pancreatitis has been commonly reported in association with primary hyperparathyroidism. Some authors have raised some doubt on the cause and effect relationship between the two diseases, because less than 1% of the patients with pancreatitis are affected by hyperparathyroidism and less than 4% of the patients with hyperparathyroidism develop a pancreatic inflammatory disease. Persistent hypercalcemia increases the calcium content of pancreatic juice and resulted in the accelerated conversion of trypsinogen to trypsin. This in turn triggered the pancreatic inflammation.
How gallstones cause pancreatitis?
Gallstones are hard, pebble-like deposits that form in the gallbladder which are typically composed of cholesterol or bilirubin. Gallstones can cause pancreatitis by blocking the duct that connects the gallbladder to the small intestines, known as the common bile duct. When a gallstone gets stuck in this duct, it can cause a backup of digestive enzymes into the pancreas, leading to inflammation and damage.
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868
Appointment request - health articles
Thank you for contacting us. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Oops, there was an error sending your message. Please try again later. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Our Locations – Find the Best Hospital Near You
Metro Pillar Number C1772, Beside Avasa Hotel, Hitech City Road, Near HITEC City Metro Station, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Mythri Nagar, Beside South India Shopping Mall, Hafeezpet, Madeenaguda, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
040 4848 6868
Payment in advance for treatment at PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, Telangana, India (Pay in INR ₹)
For Bank Transfer:-
- Bank Name: HDFC
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.50200028705218
IFSC Code: HDFC0000545 - Bank Name: STATE BANK OF INDIA
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.62206858997
IFSC Code: SBIN0020299
Scan QR Code by Any Payment App (GPay, Paytm, Phonepe, BHIM, Bank Apps, Amazon, Airtel, Truecaller, Idea, Whatsapp etc).

CONTACT US
Call: +914048486868
WhatsApp: +918977889778
Email: info@pacehospitals.in
FOLLOW US
SUBSCRIBE
Subscribe to our newsletter and stay updated with the latest health information.
Subscribe to PACE Hospitals' Public Newsletter
Thank you for subscribing to PACE Hospitals' Newsletter. Stay updated with the latest health information.
Oops, there was an error. Please try again submitting your details.
ABOUT US
QUICK LINKS
Disclaimer
General information on healthcare issues is made available by PACE Hospitals through this website (www.pacehospital.com), as well as its other websites and branded social media pages. The text, videos, illustrations, photographs, quoted information, and other materials found on these websites (here by collectively referred to as "Content") are offered for informational purposes only and is neither exhaustive nor complete. Prior to forming a decision in regard to your health, consult your doctor or any another healthcare professional. PACE Hospitals does not have an obligation to update or modify the "Content" or to explain or resolve any inconsistencies therein.
The "Content" from the website of PACE Hospitals or from its branded social media pages might include any adult explicit "Content" which is deemed exclusively medical or health-related and not otherwise. Publishing material or making references to specific sources, such as to any particular therapies, goods, drugs, practises, doctors, nurses, other healthcare professionals, diagnoses or procedures is done purely for informational purposes and does not reflect any endorsement by PACE Hospitals – your trusted hospital near me.