Whipple procedure for Solid Pseudopapillary Epithelial Neoplasm (SPEN)
PACE Hospitals
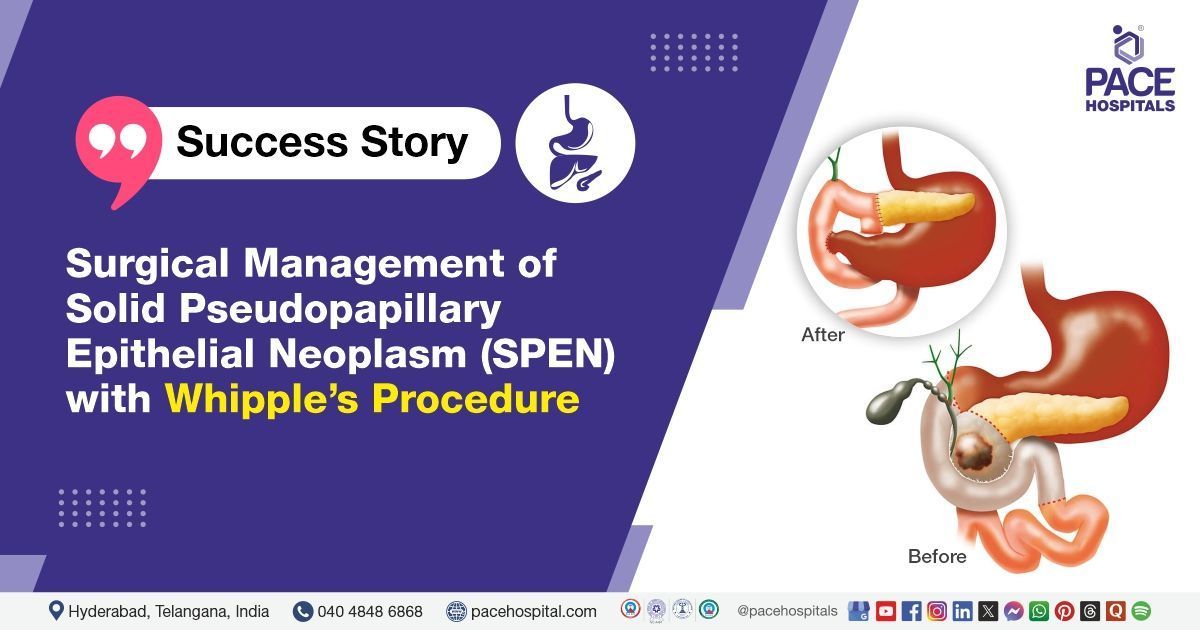
PACE Hospitals’ Surgical Gastroenterology team successfully performed the Whipple's Procedure (Pancreaticoduodenectomy) for a young child suffering from Solid Pseudopapillary Epithelial Neoplasm (SPEN) associated with jaundice and severe biliary obstruction.
Chief Complaints
A 9-Year-Old Male patient presented to the Surgical Gastroenterology Department, at
PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, with complaints of jaundice persisting for three weeks, along with intermittent epigastric pain. The jaundice was associated with generalized itching. There was no history of fever, nausea, vomiting, or significant weight loss.
Medical History
The patient had no history of significant medical conditions, abdominal surgeries, or chronic illnesses. There was no known history of similar complaints in the past. The family history was non-contributory.
Diagnosis
The patient was initially evaluated at an external hospital, where an ultrasound (USG) showed a 47x45x39 mm well-defined, heterogeneous, predominantly solid echogenic lesion in the pancreatic head, externally indenting the common bile duct (CBD), leading to upstream biliary dilatation.
PET-CT confirmed the presence of a mildly hypermetabolic, well-defined, heterogeneously enhancing soft tissue density lesion in the pancreatic head, indenting the ampulla of Vater and CBD, causing dilatation of the cystic duct, common hepatic duct (CHD), and bilateral intrahepatic biliary radical dilatation (IHBRD).
Based on these findings, the diagnosis of
Solid Pseudopapillary Epithelial Neoplasm (SPEN) of the pancreas was established.
Medical Decision Making
Given the presence of a pancreatic head mass causing biliary obstruction, surgical intervention was deemed necessary. After detailed discussion with the patient's guardians and obtaining informed consent, Surgical Gastroenterologist, Bariatric and Metabolic Surgeon, GI and HPB Oncologist, Liver Transplant Surgeon
Dr. Suresh Kumar S has decided to proceed with
Whipple's surgery (Pancreaticoduodenectomy). The decision was based on the need for complete tumor resection to prevent complications such as biliary obstruction, further tumor progression, and possible malignant transformation.
Surgical Procedure
The patient was admitted for further evaluation and optimization before surgery. The preoperative workup included complete blood counts, liver function tests, coagulation profile, and imaging studies. With adequate preoperative preparation, Whipple's surgery (Pancreaticoduodenectomy) was performed on the patient.
The stomach was transected just proximally to the pylorus, and the jejunum was excised 10 cm distal to the specimen. Pancreaticojejunostomy (PJ) was performed using 5-0 Prolene with the Blumgart technique.
Hepaticojejunostomy (HJ) was done with 4-0 Vicryl in an interrupted anterior and posterior pattern. Gastrojejunostomy (GJ) was performed in a two-layer, end-to-side fashion. A 26 Fr drain was placed in the subhepatic space to monitor postoperative drainage.
Intraoperative Findings
During the surgical procedure, a 4x5 cm mass was found involving the head of the pancreas. A small, posteriorly placed main pancreatic duct measuring approximately 3 mm was noted. The pancreas was firm in texture, with normal vasculo-biliary anatomy.
Postoperative Care
The patient was under observation in the postoperative period. Intravenous (IV) fluids, antibiotics, and supportive medications were administered. He started on an oral liquid diet once bowel function resumed and tolerated it well. Subsequently, he progressed to a soft diet without complications.
Serial ultrasound screenings showed no intra-abdominal collections or gastric distension. However, increased drain fluid amylase levels required careful supervision.
Discharge Notes
The patient showed a satisfactory postoperative recovery and was hemodynamically stable at discharge. The abdominal drain was left in situ for continued monitoring.
He was advised on wound care and drain care, including regular cleaning and monitoring for signs of infection.
Emergency Care
The Patient’s guardians were instructed to admit the patient to the Emergency department of PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad in case of any symptoms such as fever, worsening abdominal pain, vomiting, or any abnormal drainage from the surgical site.
Dietary Recommendations
A low-residue diet was recommended to facilitate easy digestion and prevent strain on the gastrointestinal system. The patient was advised to avoid fatty, fried, and spicy foods. A balanced diet with adequate protein and fluids was encouraged to promote healing and recovery.
Review and Follow-up Notes
The patient was instructed for a follow-up visit after one week in the Surgical Gastroenterology OPD at PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad. He was advised to bring the histopathology examination (HPE) report for further evaluation and guidance on adjuvant therapy if required.
Solid Pseudopapillary Epithelial Neoplasm in Pediatric Patients
Solid Pseudopapillary Epithelial Neoplasm (SPEN) is a rare pancreatic tumor, constituting 15–20% of pediatric pancreatic tumors. It predominantly affects females (~90%), but cases in young males have been reported. SPEN can occur in children as young as 5 years old, commonly presenting with abdominal pain, jaundice, or a palpable mass.
The tumor is usually large (>5 cm) but slow-growing, primarily affecting the pancreatic head or body. Though it has a low malignant potential, it may cause biliary obstruction or local invasion. Metastases are rare, with the liver and peritoneum being the most common sites.
In such cases, complete surgical resection is the treatment of choice, with >95% survival rates. Chemotherapy and radiotherapy are rarely required. Early diagnosis and surgical intervention ensure curative outcomes in pediatric patients.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868