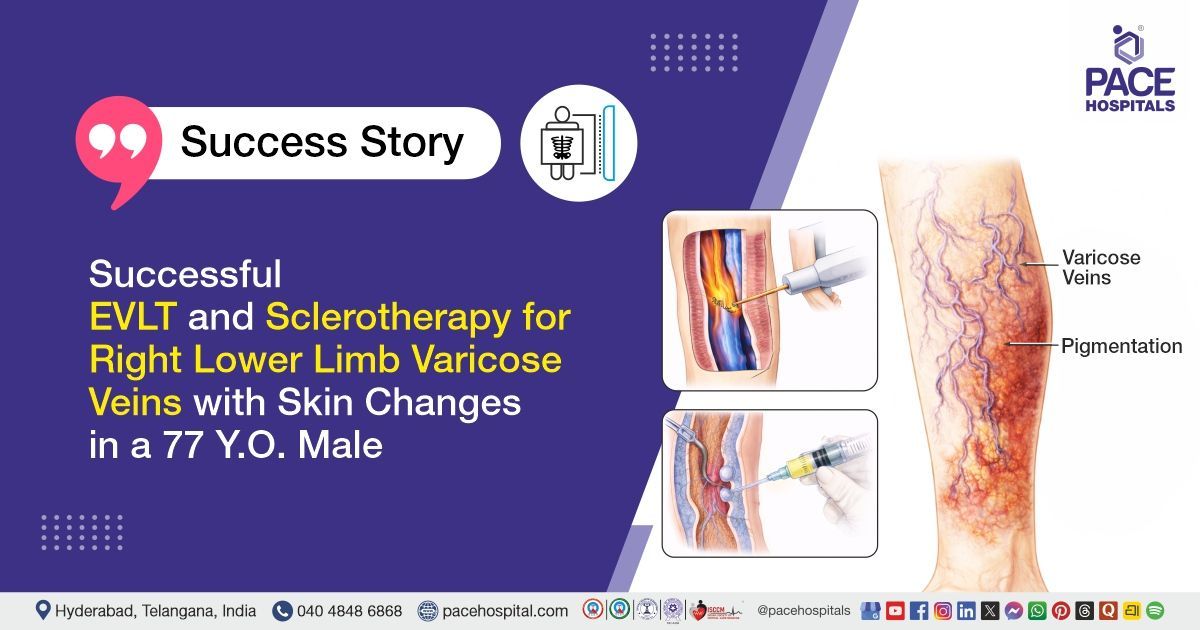
POEM Procedure Successfully Improves Eating and Swallowing ability in a 37-Year-Old female with achalasia cardia | Case study
PACE Hospitals
PACE Hospitals' Gastroenterology team successfully performed a POEM (PER ORAL ENDOSCOPIC MYOTOMY) procedure on a 37-year-old female with achalasia cardia (Eckardt’s score: 5), improving her ability to eat and swallow comfortably.
A 37-year-old female patient with complaints of difficulty in swallowing since 9 years, mainly for solids more since one year with a history of regurgitation (backflow of digestive fluids and undigested food into the mouth) was admitted to PACE Hospitals for further treatment.
Medical History
Delving deeper, it was understood that the patient had been experiencing difficulty in swallowing for 9 years, mainly for solids more since one year with a history of regurgitation (bringing swallowed food back into the mouth) which led to her admission to PACE Hospitals for additional care and management.
Diagnosis
Upon being admitted to PACE Hospitals and understanding the history and physical examination, the patient was subjected to an Endoscopy and barium swallow investigations. Evaluating the diagnostic investigations, the patient was diagnosed with:
Achalasia cardia (Eckardt's score: 5), a condition in which the muscles in the lower part of the oesophagus fail to relax properly, causing difficulty swallowing. The Eckardt's score evaluates the severity of Achalasia by assigning points for symptoms such as difficulty swallowing, chest pain, weight loss, and regurgitation.
The healthcare team collectively agreed that pursuing a POEM procedure could effectively address the diagnosed conditions and contribute to the patient's treatment plan.
POEM is an endoscopic therapy for Achalasia that uses upper endoscopy rather than conventional surgery, which involves an incision in the skin. In patients with Achalasia, the lower oesophageal sphincter is too tight. The goal of treatment for Achalasia is to loosen the lower oesophageal sphincter and open up the narrowed areas of the oesophagus.
It is performed with an endoscope, a narrow flexible tube with a camera inserted through the mouth (peroral) to cut muscles in the oesophagus (myotomy) to treat swallowing disorders caused by muscle problems such as spasms. Cutting the muscles loosens them and prevents them from tightening and interfering with swallowing.
Treatment
After consultations with the team of therapeutic endoscopists - Dr. Govind Verma, Dr. Raya Venkatesh Reddy, and consultant gastroenterologist Dr. M Sudhir, it was determined that a peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) procedure was the most effective method of treating the patient.
After the necessary investigations were done and clearances were obtained, the patient was administered intravenous antibiotics, and later, the POEM procedure was performed.
An upper gastrointestinal endoscopy was performed well to look inside the oesophagus and stomach. The fundus (upper part of the stomach) appeared normal, but there was moderate resistance at the area where the oesophagus meets the stomach (GE junction), about 40 cm from the mouth. Carbon dioxide monitoring was done throughout the procedure. At 9 cm above the GE junction, at a 6’o clock position, mucosa infiltrated with diluted methylene blue. Dye was used to highlight tissues, and a small incision was made with a T knife to create a tunnel beneath the mucosa. Blood vessels were cauterized (sealed), and the circular muscle was cut with a hybrid knife. The tunnel was closed with clips, and a post-procedure scope passed easily through the GE junction. The procedure went smoothly without any issues.
The aftermath
Post-surgery, the patient was kept on NBM (nil by mouth-without food or drink) for two days. The necessary medicines were given as supportive care.
The oral gastrograffin test was completed, and it indicated a smooth passage of gastrograffin across the gastroesophageal junction with minimal retention of contrast seen in the lower esophagus, which resulted in a successful procedure outcome. The patient began to experience symptom improvement gradually, and a liquid diet was started.
The patient was sent home with follow-up instructions and advised to follow a liquid diet for five days, followed by a soft diet for the next five days. Advised to avoid cool liquids. The patient was also instructed to contact PACE Hospitals at once in case of fever, abdominal pain, or vomiting.
After one week, the patient was asked to get a review by Dr. Govind Verma about her status.
Evaluating Severity of Achalasia: The ESS Scale and Its Clinical Implications
Achalasia is a chronic condition of the esophagus characterized by dysphagia, chest discomfort, regurgitation, and malnutrition. Achalasia is caused by improper lower esophageal sphincter relaxation and a lack of peristalsis in the absence of obstructive disease. Currently, upper endoscopy, timed barium esophagram (TBE), and esophageal high-resolution manometry (HRM) are commonly used to diagnose achalasia and assess treatment outcomes. While these tests are also used to evaluate therapy response, a self-reported measure of the severity of symptoms is often the major endpoint in clinical trials and the main component that determines clinical management decisions. Despite other achalasia-symptom scoring tools exist, such as the Achalasia Severity Score, Vantrappen Dysphagia Score, and Watson Dysphagia Score, the Eckardt Symptom Score (ESS) is a simpler and more widely used measure for grading symptom severity in achalasia patients in both clinical and research settings. However, a rigorous validation study to evaluate whether the ESS is the best way to assess achalasia symptoms has not yet been carried out.
The Eckardt Symptom Score (ESS) is the gold standard assessment for achalasia, having been developed prior to the current criteria for developing patient-reported outcome measures. The main achalasia symptoms, weight loss, dysphagia, chest pain, and regurgitation, are scored from 0 (no symptoms) to 3 (severe). These are added up to get a maximum score of 12.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868