Successful ERCP with PD Stenting and Sphincterotomy for Acute on Chronic Pancreatitis
The Gastroenterology team at PACE Hospitals successfully performed Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) and ERCP with pancreatic duct (PD) stenting and sphincterotomy in a 34-year-old male diagnosed with acute on chronic calculous pancreatitis, complicated by a dilated PD syndrome. Imaging revealed walled-off necrosis in the pancreatic tail, splenic vein thrombosis, and a left pleural effusion. To aid drainage and nutritional support, a percutaneous catheter drainage (PCD) procedure and nasojejunal (NJ) tube placement were also performed.
Chief Complaints
A 34-year-old male patient from Godavarikhani, with a
BMI of 19 kg/m², presented to the Gastroenterology Department at
PACE Hospitals, Hitech City, Hyderabad, with complaints of shortness of breath and abdominal pain persisting for the past one day, seeking further management.
Past History
The patient had a known history of chronic pancreatitis and Type 3c diabetes mellitus, for which he was on medication. He also had a history of left-sided pleural effusion, which was managed previously with intercostal drain (ICD) placement.
Additionally, he was an active smoker and alcoholic, with his most recent alcohol consumption occurring one day prior to presentation. There was no history of associated fever.
General Examination
Upon admission to PACE Hospitals, the patient's vital signs were stable. On general examination, the patient was conscious, responsive, and obeying commands. There was noticeable pallor, but no icterus. Physical examination revealed tenderness in the epigastric region. The respiratory examination revealed absent breath sounds on the left side, which is indicative of a possible pleural effusion or lung collapse, where fluid or air accumulates in the pleural space. The cardiovascular examination was normal, with S1 and S2 heart sounds present, suggesting no abnormal heart sounds or signs of heart failure. The neurological examination indicated no apparent deficits.
Diagnosis
After being admitted to PACE Hospitals, the patient underwent a thorough review of her medical history and a detailed clinical examination by the gastroenterology team, which led to the suspicion of Acute to Chronic Calculous Pancreatitis. This was identified as the primary diagnosis, as it was the underlying cause of many of the patient's complications. The acute flare-up on top of the chronic pancreatitis resulted in critical issues such as:
- Walled-Off Necrosis (WON) in the pancreatic tail, raising the risk of infection and further tissue damage.
- Pancreatico-pleural effusion, contributing to respiratory distress.
- Splenic and inferior mesenteric vein thrombosis, with potential for portal hypertension and collateral vessel formation.
- Type 3c Diabetes Mellitus, secondary to pancreatic endocrine dysfunction.
A comprehensive set of investigations was carried out by the gastroenterologist/gastroenterology doctor to confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of complications:
- Serum amylase and lipase levels were significantly elevated, consistent with active pancreatic inflammation.
- Chest X-ray revealed a left-sided pleural effusion.
- Pleural fluid analysis showed high amylase and lipase levels, indicative of a pancreatico-pleural fistula.
- Contrast-Enhanced CT (CECT) of the abdomen demonstrated chronic calcific pancreatitis, a multiloculated pseudocyst, massive pleural effusion, and mild hepatosplenomegaly.
- Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) provided detailed imaging of a dilated and irregular pancreatic duct, intrapancreatic necrosis, parenchymal atrophy, and T2 hypointense calculi.
- Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) confirmed <25% WON in the tail and splenic vein thrombosis.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) showed mild anaemia.
- Serum albumin levels were low, indicating hypoalbuminemia.
- Blood glucose levels supported the diagnosis of Type 3c diabetes mellitus.
- An endocrinology consult was sought to manage glycaemic control.
Based on the confirmed diagnosis, the patient was advised to undergo Acute on Chronic Pancreatitis Treatment in Hyderabad, India, under the expert care of the Gastroenterology Department.
Medical Decision Making (MDM)
After a thorough consultation with the consultant gastroenterologists, Dr. Govind R Verma, Dr. Sudhir, Dr. Padma Priya, and other specialists, including Dr. Tripti, a comprehensive evaluation was carried out to determine the most appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic approach for the patient.
Based on their expert assessment, it was concluded that ERCP with PD stenting and PD sphincterotomy would be the most effective procedure to address the patient's condition of acute on chronic calculous pancreatitis and its associated complications, including Walled-Off Necrosis, pancreatico-pleural effusion, and splenic vein thrombosis.
Surgical Procedure
Following the decision, the patient was scheduled for an ERCP with PD stenting and PD sphincterotomy procedure in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals, under the expert care of the Gastroenterology Department, to manage the acute on chronic calculous pancreatitis and its complications including pancreatic tissue damage, pleural effusion, and vascular complications, which were contributing to the patient's deteriorating condition.
As planned, the patient was admitted to the Medical Intensive Care Unit (MICU) for close monitoring and comprehensive supportive care. Initial management focused on controlling infection, reducing pancreatic inflammation, and ensuring adequate nutritional support. This included the administration of intravenous antibiotics and antifungals, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), thiamine, pancreatic enzyme supplementation (Creon), and diuretics. A nasojejunal (NJ) tube was also inserted to facilitate enteral nutrition, given the patient’s compromised oral intake.
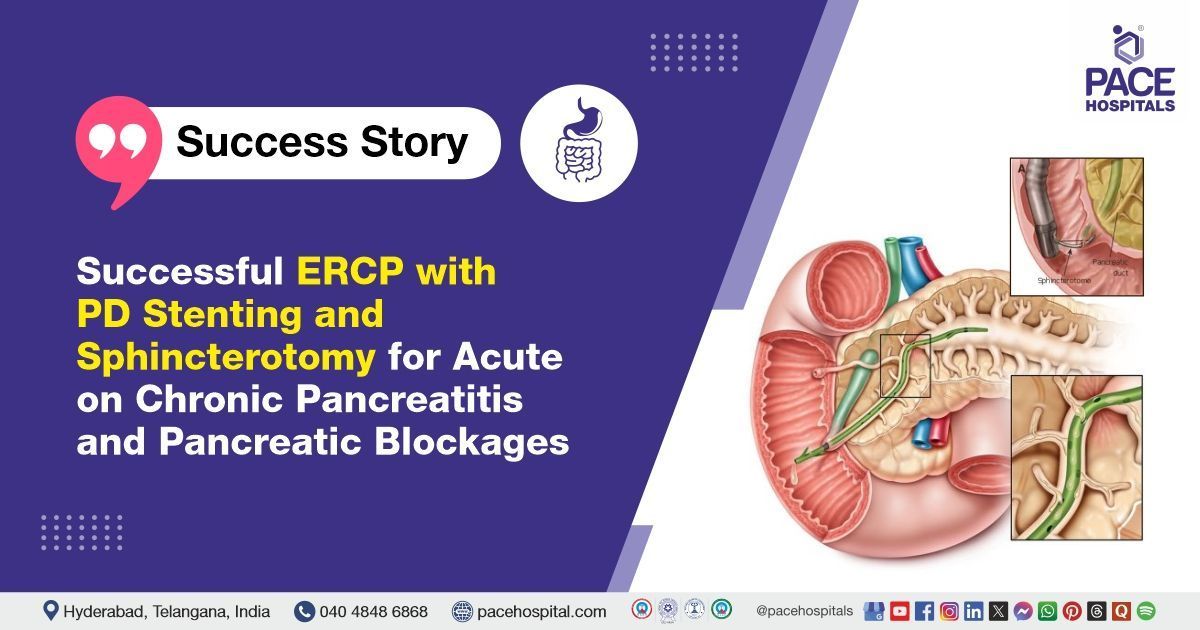
Following stabilization and preparatory management, the patient underwent Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) with pancreatic duct (PD) stenting and PD sphincterotomy under the expert care of the Gastroenterologists in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals. The procedure played a crucial role in relieving ductal obstruction, reducing complications, and significantly contributing to the overall stabilization and ongoing recovery of the patient.
ERCP with pancreatic duct (PD) stenting and sphincterotomy is a minimally invasive endoscopic procedure used to diagnose and treat disorders affecting the pancreatic duct. The procedure involves advancing an endoscope through the mouth into the duodenum, where a stent is placed to relieve ductal obstruction and facilitate improved drainage of pancreatic fluids. Additionally, a small incision is made in the sphincter muscle (sphincterotomy) to further ease fluid outflow. This combined technique is especially beneficial in managing conditions such as chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic duct strictures, and fistulas, often reducing the need for more extensive surgical interventions.
Postoperative Care
The patient’s postoperative recovery had been smooth and uneventful. However, during the hospital stay, the patient developed a fever spike, which prompted an escalation in antibiotic therapy. Following the adjustment in treatment, the patient had responded well, with noticeable symptomatic improvement. With clinical stability achieved, the patient was discharged with appropriate medical advice and follow-up instructions.
Discharge Medications
Upon discharge, the patient was prescribed a combination of medications including antibiotics, enzyme supplements, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), non-opioid analgesics, and nutritional supplements to support pancreatic healing, control any residual infection, reduce gastric acid secretion, manage pain effectively, and enhance nutritional recovery.
Dietary
The patient was also advised to follow a high-protein diet to promote nutritional recovery, and was strongly instructed to maintain strict abstinence from alcohol to prevent further pancreatic injury and related complications.
Emergency Care
The patient was informed to contact the Emergency ward at PACE Hospitals in case of any emergency or development of symptoms like fever, abdominal pain, or vomiting.
Review and Follow-up Notes
The patient was advised to return for a follow-up appointment with the endocrinologist in the OPD at PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, one week after discharge, with a prior appointment. A subsequent follow-up with the consultant gastroenterologist was scheduled for three weeks later, also in the OPD, with a prior appointment.
Conclusion
This case highlights how effective advanced procedures like ERCP with PD stenting and PD sphincterotomy are in treating pancreatic blockages. It emphasizes the importance of such advanced techniques in addressing complex pancreatic conditions, demonstrating their value in providing effective treatment for challenging cases.
Dual Intervention for Pancreatic Duct Obstruction: The Role of PD Sphincterotomy and Stenting
PD sphincterotomy is performed along with PD stenting to enhance the effectiveness of the treatment for pancreatic duct obstruction. The pancreatic duct (PD) sphincter, located at the junction of the pancreatic duct and the duodenum, can become constricted or narrowed due to chronic inflammation, stone formation, or scarring in chronic pancreatitis. Performing a sphincterotomy, which involves making a small incision in the sphincter muscle, allows for easier passage of pancreatic juices, reduces ductal pressure, and facilitates better drainage of pancreatic fluid. When combined with PD stenting, which involves placing a tube to maintain ductal patency, it ensures long-term relief from obstruction and prevents recurrence. Together, these procedures help reduce symptoms, such as pain and fluid buildup, and prevent further complications like pancreatic pseudocysts or infections.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868