Type 3 diabetes - Symptoms, Causes, Complications and Treatment
PACE Hospitals
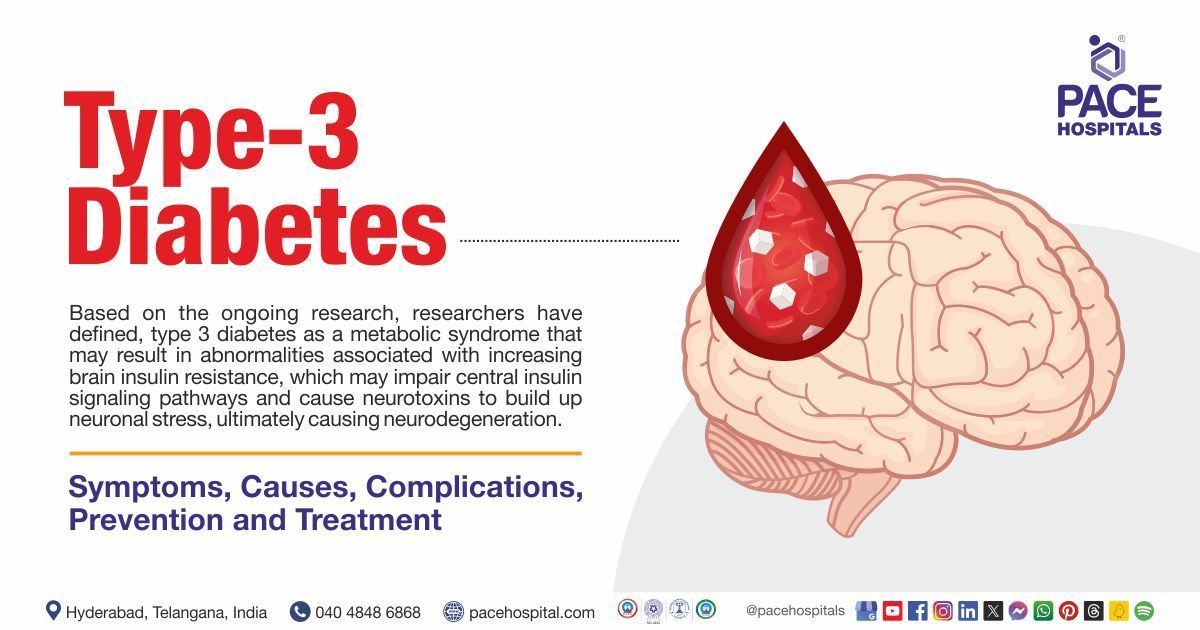
Type 3 diabetes definition
Based on the ongoing research, researchers have defined, type 3 diabetes as a metabolic syndrome that may result in abnormalities associated with increasing brain insulin resistance, which may impair central insulin signalling pathways and cause neurotoxins to build up neuronal stress, ultimately causing neurodegeneration.
Nowadays, most people are aware of type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus; however, type 3 diabetes (T3DM), another type of diabetes, has just recently been identified.
This uncommon type of diabetes presents symptoms of insulin resistance in the brain, and it may significantly affect neurocognition (brain function) and play a crucial role in the development of Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, one of the most modifiable risk factors for the onset of Alzheimer's disease (AD) remains to be type 2 diabetes.

Type 3 diabetes symptoms
The symptoms of dementia, similar to those associated with early Alzheimer's disease, may be seen in the proposed type 3 diabetes disease. Below are the proposed symptoms of type 3 diabetes (T3D):
- Brain insulin resistance: It is the inability of brain cells to respond to the insulin and the insulin receptor substrates (IRS) that are associated with it. It is a symptom of type 3 diabetes (T3D), sometimes referred to as "insulin resistance of the brain".
- Memory processing (recognition and retrieval): Type 3 diabetes (T3D) is caused by an impairment in the brain's neurons' ability to respond to insulin, which is necessary for basic functions, including memory and learning.
- Brain atrophy: Brain atrophy (BA), sometimes referred to as cerebral atrophy (CA), is a condition in which the loss of brain cells and neural connections causes the brain's tissues to shrink.
- Cognitive decline or impairment: Numerous hallmark symptoms of Alzheimer's disease (AD) have been linked to insulin insensitivity, including memory impairments and cognitive decline.
- Alteration in brain metabolism: Peripheral insulin resistance causes changes in brain metabolism by reducing insulin signalling in the central nervous system.
- Impaired glucose metabolism: Memory impairment and hippocampal shrinkage have been associated with impairments in glucose metabolism. Nevertheless, it is still unknown exactly which molecular pathways link the development of Alzheimer's disease (AD) to changes in the metabolism of glucose and insulin.
- Oxidative stress: It is an imbalance between the production and accumulation of oxygen-reactive species (ROS) in cells and tissues and the biological system's ability to detoxify these reactive products results in oxidative stress.

Type 3 diabetes risk factors
A more recent study, however, indicates that an enzyme that breaks down insulin via changing metabolic pathways may convert type 2 diabetes to type 3 diabetes. Both oxidative stress and beta-amyloid buildup in the brain are potential outcomes of this process, and these conditions are hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease. The possible risk factors for type 3 diabetes are listed in a 2020 study. They consist of:
- Diet: A 2020 study identified a low-fiber diet combined with a high-calorie, sugar, and fat intake as a possible risk factor for type 3 diabetes.
- Lack of physical activity: A sedentary lifestyle or low physical activity (PA) contributes to the development of numerous long-term illnesses such as diabetes.
- Family history: According to studies, people's assessment of their risk of disease can be influenced by their family history, and people with a family history of diabetes are more likely to have a higher risk of diabetes.
- Genetics: A person's interaction with the surrounding environment can also be affected by their genes, which may impact the risk of diabetes in addition to directly affecting insulin action or secretion.
- Exposure to stress: Prolonged stress could be a significant factor in the development of type 3 diabetes, neurological morbidity, and the risk of ischemic stroke.
- Low socioeconomic status: Diabetes risk was higher in people with a lower socioeconomic status than in those with a higher socioeconomic status.
- Birth weight: Low birth weight has been connected with adult chronic conditions such as obesity, diabetes mellitus, and hypertension.
- Race and ethnicity: Research has shown that compared to non-minority people, members of race and ethnic minorities are more likely to have diabetes.
Type 3 diabetes pathophysiology and causes
Studies conducted in animals and in vitro suggested that insulin resistance can contribute to the pathophysiology of Alzheimer's disease (AD) through a variety of pathways. The pathophysiology of type 3 diabetes includes:
- Alzheimer's disease (AD) is also considered to be a type of diabetes due to the prevalence of endocrine disorders, particularly diabetes.
- Diabetes has been shown to be a risk factor that affects the pathology of Alzheimer's disease (AD) by affecting synaptic communication, brain morphology (brain shrinkage), and memory processing (recognition and recall).
- Also, irrespective of genotype, the hyperinsulinemia-related degradation of insulin signalling, and insulin resistance are the important factors that support the reasons for maintaining insulin at the centre of both diseases.
- Several recent studies have shown that poor hippocampus insulin signalling causes insulin signalling decline and the concurrent development of insulin resistance, which also negatively affects memory and other executive functions.
- This discussion supports the strong connection between hyperinsulinemia, insulin resistance, and diseases like type 3 diabetes (T3D) and Alzheimer's disease (AD) that develop due to it.

Type 3 diabetes complications
All diabetic complications can be seen in diabetes type 3. However, there appears to be a rise in severity. Long-term diabetes mellitus leads to complications that develop slowly. The long-term effects of diabetes can be life-threatening which include microvascular and macrovascular complications such as:
- Diabetic nephropathy (kidney damage): Diabetes is a chronic condition that leads to a gradual decrease in kidney function in individuals with diabetic nephropathy, commonly referred to as diabetic kidney disease.
- Diabetic retinopathy (eye damage): A complication of diabetes called diabetic retinopathy is caused by elevated blood sugar levels that damage the retina or back of the eye. If left untreated and undetected, it may result in blindness.
- Diabetic neuropathy (nerve damage): Diabetes may cause diabetic neuropathy, a type of nerve disease that affects nerves involved in sensation, movement, and other body functions.
- Skin infections: Skin conditions, some of which result from reduced circulation and modifications to the small blood vessels. Infections, especially skin infections, are also more common in people with diabetes.
- Cardiovascular diseases: Blood vessel damage and damage to the nerves that maintain the heart and blood vessels results in heart disease and stroke.
- Depression: It is a type of mood illness that results in a persistently sad and uninterested feeling.
- Gum disease and other dental problems: A high blood sugar level in saliva stimulates the growth of harmful microbes in the mouth, leading to gum disease and other dental problems.
Differences between type 1, type 2, and type 3 diabetes (Alzheimer's disease)
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes are the two common types of diabetes. Type 3 is an uncommon type of diabetes. Below are some parameters that help differentiate type 1, type 2, and type 3 diabetes.
| Parameters | Type 1 diabetes | Type 2 diabetes | Type 3 diabetes (Alzheimer’s disease) |
|---|---|---|---|
| How it occurs? | When insulin production in the pancreatic cells stops, type 1 diabetes develops. Without insulin, muscle cells cannot use glucose as an energy source. Rather, blood glucose levels rise, which makes a person very sick. | When the pancreas produces insufficient insulin or insulin that functions improperly, type 2 diabetes (also known as insulin resistance) develops. The blood's glucose levels, therefore, start to rise above normal. | These researchers have tried to define it as a metabolic syndrome that may result in abnormalities associated with increasing brain insulin resistance, which may impair central insulin signalling pathways and cause neurotoxins to build up neuronal stress, ultimately causing neurodegeneration. |
| Risk factors | Although the exact cause of this condition is not known, studies indicate that an individual with a genetic predisposition may be susceptible to environmental triggers. | Type 2 diabetes is regarded as a lifestyle condition since it is more likely to develop in people who are overweight and do not exercise regularly. | Genes, ethnicity, inactivity, obesity, type 2 diabetes, poor diet, and high blood pressure are all potential risk factors for type 3 diabetes. |
| Management | Insulin medications are used in the management of type 1 diabetes. | People with type 2 diabetes may benefit from medication, nutrition, and exercise. | Alzheimer's disease management involves both medication and support. Blood sugar can be controlled by lifestyle choices and diet. |
| Prevention | Although there is no known cure, medicines can help control the condition. Research on prevention is still being done. | Type 2 diabetes can be treated and avoided with dietary and lifestyle modifications. | Although there is no cure, insulin resistance may be avoided with moderate exercise, a good diet, and a healthy weight. |

Type 3 diabetes prevention
A few lifestyle modifications can help delay or avoid the onset of Alzheimer's disease, commonly known as type 3 diabetes. Below are some of the preventive measures for type 3 diabetes:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Obese or overweight people are at high risk of diabetes and heart disease. Maintaining a healthy weight decreases this risk.
- Controlling blood pressure: The risk of stroke increases with increased blood pressure. Lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise and cessation of smoking can reduce the risk of Alzheimer's.
- Diet: Curcumin, a ketogenic diet, and antioxidants were all researched as possible therapeutic agents; however, the results of these studies have not been clear.
- Keeping physically active: According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, maintaining a moderate body weight and getting enough exercise can help avoid insulin resistance and prediabetes.
- Controlling blood sugar levels: Abnormal blood sugar levels lead to diabetes, which can increase the chances of stroke, heart disease, and dementia; hence, blood sugar levels must be controlled.
- Staying mentally active: Activities that keep one mentally stable, such as playing games and socializing, must be followed.
- Avoiding alcohol: Drinking too much alcohol leads to the risk of diabetes, hypertension, and stroke. Limiting alcohol consumption can help.
Type 3 diabetes diagnosis
Some researchers suggested that type 3 diabetes, which is characterized by impaired insulin signalling in the brain, is connected to Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathology. There are no specific tests for diabetes type 3, as many healthcare professionals do not officially accept it as a diagnostic term. However, Alzheimer's disease (AD) can be diagnosed using the following tests:
- Medical history
- Cognitive and neurological tests
- Lab investigations: Blood tests, lumbar puncture (To test for specific proteins in the spinal fluid)
- Imaging tests:
- Computed Tomography (CT) scan
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)
- Positron emission tomography (PET) scans.
- Psychiatric evaluation
- Genetic tests
- Vascular tests such as head and neck magnetic resonance angiogram (MRA) or computed tomography angiogram (CTA)
- Brain tests include electroencephalogram (EEG), Cardiac tests such as electrocardiogram [ECG], echocardiography, and ambulatory cardiac rhythm monitoring.
- Beta-amyloid low levels in the (CSF) cerebrospinal fluid
- Deposits of beta-amyloid in the brain were detected by positron emission tomography (PET) scan.
Type 3 diabetes treatment
A poorly managed blood sugar level may raise the chance of Alzheimer's. Because of this close connection, Alzheimer's disease has been termed "diabetes of the brain" or "type 3 diabetes (T3D)" by some researchers. Since type 3 diabetes is not an accepted diagnosis, there is no single type of treatment for it. Different treatment options are available for prediabetes, type 2 diabetes, and Alzheimer’s disease. The treatment options for Alzheimer’s disease include the following:
There is no cure for Alzheimer's, but the goal of therapy is only to improve the function.
Lifestyle modifications:
- Lifestyle modifications include proper sleep, adequate exercise, taking an anti-inflammatory diet, and avoiding stress-related activities .
- Regular exercise may benefit patients with cognitive dysfunction and older adults.
- Regular aerobic exercise (30 mins/day), along with strength training, may improve behaviour and functioning and reduce depression in Alzheimer's disease.
Nonpharmacological management of Alzheimer’s:
- Cognitive training, aromatherapy, music therapy, and massage help maintain a healthy environment.
- Behavioural techniques that can manage agitation and anxiety .
- Socialization, such as family gatherings, may be helpful in Alzheimer’s patients.
Medical management of Alzheimer’s: Alzheimer’s medications include:
- Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
- Selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitors
- NMDA antagonists
- Antipsychotics
- Vitamin deficiencies, hypothyroidism, and depression need to be treated appropriately at therapeutic dosing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Type 3 diabetes
What are the 3 types of diabetes?
Type 1, type 2, and gestational type of diabetes are the three most common types of diabetes. In type 1 diabetes, the body produces little amount or no insulin. In type 2 type of diabetes, the body's cells cannot use insulin properly. One type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy is called gestational diabetes.
Is there a type 3 diabetes?
Nowadays, most people are aware of type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus; however, type 3 diabetes (T3DM), another type of diabetes that may affect neurocognition (brain function), has just recently been identified and proposed by researchers.
Why is Alzheimer’s called type 3 diabetes?
 Button
ButtonAlzheimer's is also called type 3 diabetes. The less common form of diabetes, known as type 3, causes insulin resistance in the brain and may have a significant effect on neurocognition and also play a role in the development of Alzheimer's disease (AD).
What is type 3 diabetes?
Researchers have tried to define type 3 diabetes as a metabolic syndrome that may result in abnormalities associated with increasing brain insulin resistance, which may impair central insulin signalling pathways and cause neurotoxins to build up neuronal stress, ultimately causing neurodegeneration.
How to test for type 3 diabetes?
A specific test cannot diagnose type 3 diabetes. To identify Alzheimer's disease, a neurological examination, a patient's medical history, and neurophysiological tests are used.
Related articles

Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868