Uterine Cancer – Symptoms, Causes, Types, Diagnosis and Treatment
PACE Hospitals
Uterine cancer definition
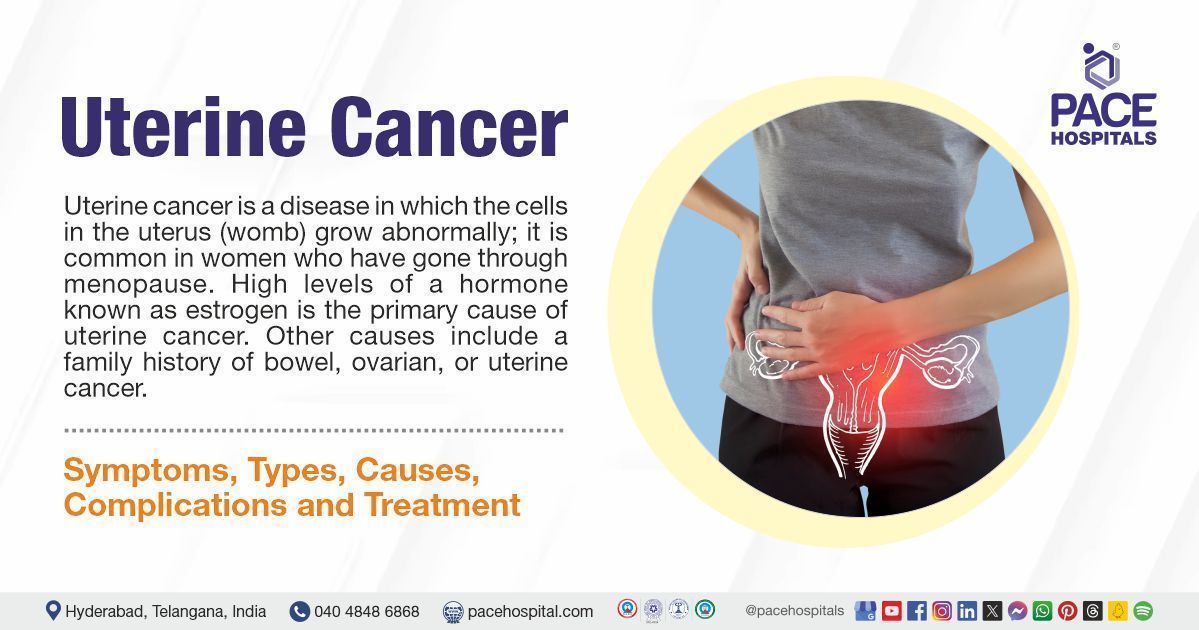
Uterine cancer is a disease in which the cells in the uterus (womb) grow abnormally; it is common in women who have gone through menopause. High levels of a hormone known as estrogen is the primary cause of uterine cancer. Other causes include a family history of bowel, ovarian, or uterine cancer. It is of two types: endometrial cancer (cancer that begins or develops in the lining of the uterus) and uterine sarcoma (a rare type of cancer that develops in other tissues or muscles of the uterus). The evaluation of cancer requires understanding the indications for biopsy, different sampling techniques, and the role of imaging studies in staging and assessing metastases. A gynecologic oncologist can successfully treat uterine cancer.
Uterine cancer meaning
In the year 1610, the word “uterine” was derived from the French word “uterin” meaning pertaining to the womb. From late Latin “uterinus” was derived meaning pertaining to the womb and Latin derived the word “uterus” meaning womb. Cancer was derived from the Greek language “karkinos” which has three English meanings: a crab, a tumor, and a zodiac constellation that represents a crab.
Uterine Cancer Statistics
Incidence of uterine cancer worldwide
Uterine cancer ranks fourth among the most frequently diagnosed cancers in the US, with estimates of 63,230 cases diagnoses in the year 2018. It was ranked as the sixth most common cancer worldwide in the year 2012 with an estimated 319,600 cases. Many studies indicated that endometrial cancers comprise approximately 90 percent of all uterine cancers. This disease is rare before the age of 45 years, but the risk rises among women in their late 40s to middle 60s of all races.
Incidence of uterine cancer in India
The incidence of uterine cancer in India is very low compared to developed countries. An incidence of 16,413 cases was reported in the year 2020, and GLOBOCON reported 6385 mortality cases.

Types of Uterine Cancer
Uterine cancer, which begins or develops in the uterus, is the most common type of cancer affecting the female reproductive system. There are two different types of uterine cancer, and they are listed below:
- Endometrial cancer - This cancer develops or grows in the endometrium (lining of the uterus), and it is the most common type of uterine cancer that accounts for more than 90 percent of cases. Endometrial cancer is referred to as uterine cancer as endometrium is a part of the uterus. More than 80 percent of all endometrial cancers are adenocarcinomas of the endometrium. These cancers develop when cells in the endometrium grow abnormally. Other types of endometrial cancers include:
- Serous adenocarcinoma: This carcinoma is more likely to spread or proliferate to the lymph nodes and various other parts of the body.
- Adenosquamous carcinoma: This carcinoma is similar to adenocarcinoma and carcinoma of squamous cells that line the outer layer of the uterus.
- Uterine carcinosarcoma: This is a rare type of cancer in which the cancer cells look like endometrial cancer and sarcoma. It has a higher risk of spreading to lymph nodes and other parts of the body.
- Primary pure squamous cell carcinoma of the endometrium: A rare form of uterine cancer that occurs so uncommonly that only about 70 cases have been diagnosed worldwide.
- Uterine clear cell carcinoma: A rare form of endometrial cancer that accounts for fewer than 5 percent of all uterine cancers.
- Uterine sarcoma - This type of cancer develops in the muscle wall of the uterus, accounting for 4 percent of all uterine cancers. Each subtype of uterine sarcoma differs in the way it develops and how it is treated. They are classified based on the type of cells in which they develop. Following are some of the types of uterine sarcoma:
- Uterine leiomyosarcoma: This is the most common type of uterine sarcoma which forms in the muscular wall of the uterus called the myometrium and accounts for about 2 percent of uterine cancers.
- Endometrial stromal sarcomas: This type of cancer develops in the connective tissues that support endometrium and accounts for less than 1 percent of all uterine cancers.
- Undifferentiated sarcoma: It is similar to endometrial stromal sarcoma but it is a more aggressive form (as it grows and spreads rapidly). It accounts for less than 1 percent of all uterine cancers.

Uterine Cancer Causes
There is no exact known cause of uterine cancer. However, there are a few factors that contribute to the development of uterine cancer. They are as follows:
- Imbalance of hormones: Hormonal imbalance between estrogen and progesterone is an etiologic factor in the development of uterine cancer. The interaction between the receptors of this hormone causes increased growth of the endometrium leading to cancer.
- Inflammation: Inflammation causes uterine cancer by inducing rapid cell division, increasing the possibility of replication errors and resulting in subsequent mutations.
- Genetic factors: Non endometrioid cancer pathogenesis is related to genetic factors and certain somatic mutations.

Uterine Cancer Symptoms
Unusual vaginal bleeding, particularly bleeding after menopause, is the most common symptom of uterine cancer. Other common signs and symptoms of uterine cancer include:
- Periods that are heavier than usual
- Vaginal bleeding between periods
- Continuous periods with no break
Less common signs and symptoms include:
- Unpleasant watery discharge
- Unexplained weight loss
- Difficulty in urinating or change in bowel habits
- Abdominal pain
Uterine Cancer Risk Factors
A risk factor can be anything that can increase the chance of developing a disease. There are different risk factors for different cancers. Various factors can increase the risk of developing endometrial cancer, but having these is not always a cause. Some women may develop endometrial cancer even without any known risk factors.
Following are some of the factors that can increase the risk of uterine cancer:
- Endometrial hyperplasia (thickened endometrium wall): Atypical hyperplasia may develop into cancer in about 8 percent of cases if left untreated.
- Postmenopausal or reaching menopause at the age of 45: In post-menopausal women, there is an increased risk of uterine cancer.
- Early Menstruation (before the age of 12 years): Menstrual periods starting at an early age increase the risk of uterine cancer.
- High blood pressure (hypertension) and diabetes: Hypertension and diabetes can increase the risk of endometrial cancer.
- Never having children: The balance of hormones shifts more towards progesterone during pregnancy. Those who were never pregnant or women who were infertile have a higher risk of developing uterine cancer.
- Obesity or being overweight: This is a major risk factor for uterine cancer. Obese women are 3 times more likely to develop endometrial cancer compared to women with normal weight.
- Family history of bowel, ovarian, or uterine cancer: Individuals with a family history of bowel, ovarian, or uterine cancer are at an increased risk of uterine cancer.
- Genetic conditions such as Cowden syndrome or Lynch syndrome: There is an increased risk of developing uterine cancer associated with genetic conditions like Cowden syndrome or Lynch syndrome.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or previous ovarian tumors: Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have a higher level of androgen & estrogen levels, and decreased levels of progesterone. The higher levels of estrogen compared to progesterone increase the risk of uterine cancer.
- Fertility treatment or using estrogen-only hormone replacement therapy: Estrogen therapy for fertility in the long term increases the risk of uterine cancer.
- Previous radiation therapy in the pelvic region: Radiation therapy damages DNA and can increase the risk of developing uterine cancer.
- History of intake of tamoxifen drug to treat breast cancer: Taking the drug tamoxifen for the long term increases the risk of uterine cancer.

Complications of Uterine Cancer
Complications of uterine cancer may include the following:
- Anemia: Heavy vaginal bleeding can cause chronic blood loss resulting in anemia.
- Perforation of the uterus, which may occur during dilation and curettage
- Problems arising after surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy.
Uterine cancer surgery complications
After any surgical procedure is performed, there is a risk of developing complications. Following are some of the complications that are seen after surgical treatment of uterine cancer:
- Infections – There is a risk of infection after any surgical treatment. Symptoms of infection may include high temperature or fever, shivering, cough, and sickness.
- Vaginal bleeding - Bleeding may occur, which may be similar to periods.
- Blood clots – These are possible complications as the patient does not usually move after surgery. As a result, blood may clot and cause thrombosis due to no movement and physical activity.
- Bowel or bladder problems – After surgery, there is a risk of damage to the bladder and uterus that may disturb the normal pathways.
- Swelling or edema – After surgery, swelling may occur.
Uterine Cancer Diagnosis
Early diagnosis and treatment of uterine cancer is necessary to prevent the progression and spread of cancer to other parts of the body. Gynecologic oncologists develop a definitive diagnosis. Below are some of the steps followed to diagnose uterine cancer:
Initial evaluation
- Review of Medical history
- Physical examination
Diagnostic tests
- Laboratory examination
- Blood tests
- Genomic testing
- Imaging studies
- Pelvic ultrasound
- Abdominal ultrasound
- Transvaginal ultrasound
- Biopsy techniques
- Endometrial biopsy
- Hysteroscopy and biopsy
Uterine Cancer Treatment
Uterine cancer is usually treatable when it is diagnosed early and the treatment depends on the size of the cancer, its area, how far it has spread, and the general health of the patient. Treatment includes surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and targeted drug therapy may also be included. In most women, when cancer has not spread, surgery is considered as the primary treatment.
Treatment of uterine cancer includes the following:
- Surgery (hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy)
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Hormone therapy
- Immunotherapy
- Targeted therapy
Expert Super Specialist Doctors
Advanced Diagnostics & Treatment
Affordable & Transparent Care
24x7 Emergency & ICU Support
Uterine Cancer Prevention
There are no definitive prevention measures for uterine cancer. However, there are a few measures that can help decrease the risk of developing uterine cancer.
- Maintaining healthy body weight: Women who are obese are 3 times more at risk of developing uterine cancer. Maintaining an ideal body weight reduces the risk of developing cancer.
- Being physically active: Regular physical exercise lowers the risk of endometrial cancer.
An ideal and active lifestyle with normal body weight lowers the risk of high blood pressure and diabetes, which are also major risk factors for uterine cancer.
Difference between Uterine fibroid and Uterine cancer
uterine fibroid vs uterine cancer
Uterine cancer and uterine fibroids both affect the uterus. Uterine cancer is cancer that develops in the lining of the uterus whereas uterine fibroids are non-cancerous and develop in the uterine wall. Following are the parameters that differentiate uterine cancer and uterine fibroid.
| Parameters | Uterine fibroid | Uterine cancer |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | These are tumors that grow in the wall of the uterus. These tumors are not cancerous. | It is a disease in which the cells in the uterus (womb) grow abnormally, it is common in women who have gone through menopause. |
| Symptoms | Heavy bleeding, frequent urination, pain during intercourse, lower back pain, and reproductive problems. | Unusual vaginal bleeding, particularly bleeding after menopause, is the most common symptom of uterine cancer. |
| Causes | There is a known cause of uterine fibroids but factors like genetics and hormonal imbalance plays role in etiology. | There is no known cause of uterine cancer but factors like obesity, conditions like diabetes, and high blood pressure can increase the risk of uterine cancer. |
| Treatment | The majority of women with uterine fibroids do not develop symptoms, those who show symptoms are treated with over-the-counter medications and with surgical procedures. These procedures include hysterectomy, myomectomy, endometrial ablation, and uterine fibroid embolization. | Treatment includes surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted drug therapy. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Uterine cancer
Is uterine cancer curable?
Yes, uterine cancer is curable when it is detected early. Treatment usually involves surgery, chemotherapy, or radiotherapy; targeted drug therapy may also include to treat cancer. Depending on factors like the size of the cancer, location, and how far it has spread, the treatment is decided.
Is uterine cancer and endometrial cancer the same thing?
Yes, uterine cancer and endometrial cancer are the same in most cases. Endometrial cancer is often called uterine cancer as it begins in the lining of the uterus (endometrium) and accounts for about 90 percent of all uterine cancers.
Can uterine cancer spread to the cervix?
Yes, uterine cancer can spread to the cervix. In stage II of endometrial cancer, the cancer spreads from the body of the uterus and starts growing in the supportive connective tissue of the cervix. In stage III, it may spread beyond the uterus and cervix. Uterine cancer spreads to nearby areas such as the cervix, ovaries, and bladder.
What is the survival rate of uterine cancer?
Survival rates of uterine cancer vary greatly depending on the stage and cell type. The relative survival rate of 5-year uterine cancer for localized cancer (stage 1 and stage 2) is 95 percent, for stage 3 cancer the five-year survival rate is 70 percent and the 5-year survival rate for stage 4 cancers is 18 percent.
What is the first sign of uterine cancer?
Unusual Vaginal bleeding is the most common and the first sign of uterine cancer. This vaginal bleeding must be after menopause or bleeding that is not related to periods. Other symptoms include unexplained weight loss, abdominal pain, and difficulty in urinating.
Can uterine cancer be detected by ultrasound?
Yes, uterine cancer can be detected by ultrasound; ultrasound is generally the first test to detect possible gynecologic problems. It can be used to look for endometrial polyps, and thickness of endometrium and to also detect the growth of cancer into the muscle layer of the endometrium. Pelvic ultrasound and transvaginal ultrasound are commonly used in the diagnosis of uterine cancer.
What is the CA 125 test for uterine cancer?
Many but not all endometrial and ovarian cancers release a substance called CA 125 into the bloodstream. In patients with endometrial cancers, very high levels of CA 125 may indicate that cancer has spread beyond the uterus. Physicians usually check the levels of CA 125 before the surgery.
Does a pap smear detect uterine cancer?
Pap smears cannot be used to screen uterine cancers. It is a procedure to collect cells from the surface of the cervix and vagina. These cells are viewed under a microscope to find out if these cells are abnormal. However, these test results sometimes show abnormal endometrium.
What is the treatment of stage 1 endometrial cancer?
Stage I and stage II endometrial cancers are considered low risk cancers as they do not spread to other parts of the body. Treatment of low-risk stage I endometrial cancer include the following:
- Surgery (Total hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo – oophorectomy) – The lymph nodes that are present in the pelvis and abdomen are removed and to look for cancer cells they are viewed under a microscope.
- Total hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo – oophorectomy with or without removal of lymph nodes present in pelvis and abdomen and surgery is followed by internal radiation therapy. External radiation therapy in the pelvic region may also be performed in certain cases.
- Radiation therapy in patients who cannot undergo surgery.
What are the symptoms of uterine fibroids?
These are tumors that grow in the uterus, however these tumors are not cancerous. Few common symptoms of
uterine fibroids are heavy bleeding between periods, bleeding with blood clots sometimes, frequent urination, cramping during periods, and pain during intercourse.
What is the difference between cervical cancer and uterine cancer?
Uterine cancer and cervical cancer are two different cancers that develop in the female reproductive system. Uterine cancer is a type of cancer in which the cells of the uterus grow abnormally whereas cervical cancer develops in the cervix. Uterine cancer can be treated if diagnosed early and treatment includes surgery, radiation therapy, and targeted drug therapy whereas cervical cancer is treated with surgery (hysterectomy), radiation therapy, immunotherapy, etc.
When to Consult a Doctor for Uterine Cancer?
Many women are unaware of the subtle changes that may precede uterine cancer. Even though you could experience sporadic anomalies in your menstrual cycle, you should never disregard symptoms that are odd, persistent, or inexplicable.
Key Warning Symptoms:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding, especially after menopause or between periods
- Heavy periods
- Pelvic pain, pressure, or a persistent feeling of fullness
- Watery, foul-smelling, or blood-colored vaginal discharge that cannot be described
- Pain during intercourse
- Weight loss, fatigue, or loss of appetite
- Frequent urination
It is essential to persist with a gynaecologist or gynecologic oncologist if these symptoms persist, feel out of the ordinary for your body. Early diagnosis helps maintain long-term health and well-being in addition to improving treatment outcomes.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868