Best Diabetes Doctor in Hyderabad for Comprehensive Diabetes Care
✅ Recommended by 8,925 Happy Patients. Get hassle-free appointments with diabetes specialist doctor.
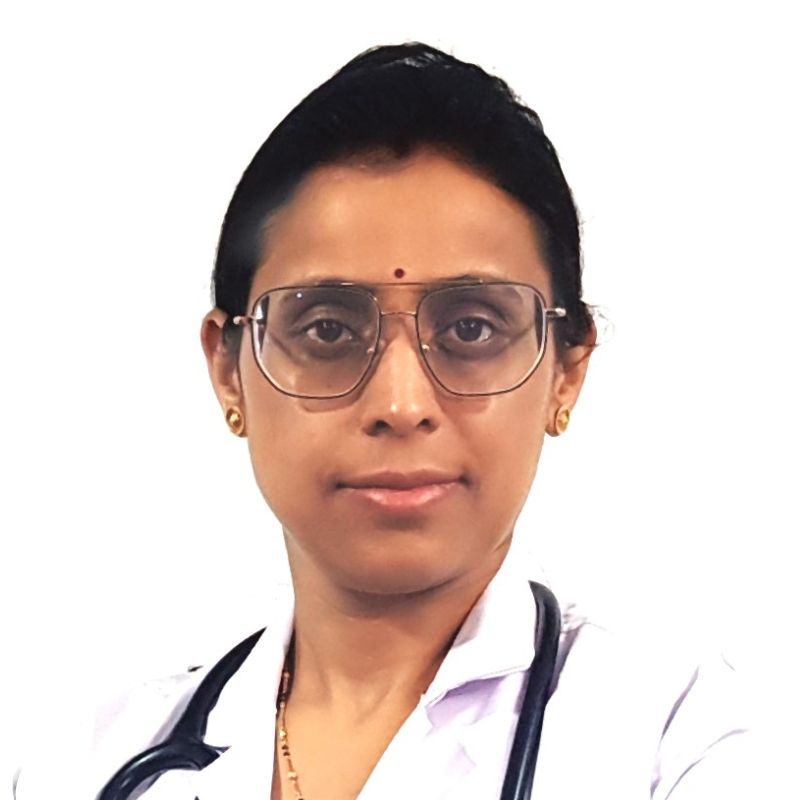
Dr. Tripti Sharma
MBBS, MD (General Medicine), DM (Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism)
Experience : 14+ years
Endocrinologist (Adult & Paediatric), Physician & Diabetologist
Specialist
Diagnosing and treating various endocrinology-related health conditions such as thyroid disorders (hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and goitre), diabetes (type 1 diabetes mellitus, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and gestational diabetes), adrenal disorders (Cushing’s syndrome and Addison’s disease), pituitary gland disorders (acromegaly, prolactinoma, growth hormone deficiency, etc.), infertility (male and female), hypertension, obesity, dyslipidaemia, osteoporosis, puberty and growth disorders, polycystic ovary syndrome, hypogonadism, menstrual and other hormonal disorders.
Expertise
Management of Fever of unknown origin, Management of Sepsis & Multiorgan failure, Diabetes mellitus, Hypertension, Thyroid Disorder, Pregnancy Induced Hypertension, Dyslipidemia & hyperlipidemia, Anaemia management, Weight loss & Fatigue Syndromes, HIV treatment, Lung diseases (Asthma, Empyemathorasis, Bronchiectasis Treatment, Interstitial Lung Disease Treatment), Allergy and Immunological Disorders, Anaemia and Blood Disorders, Rheumatology and Joint Related Disorders, COVID-19 / Swine Flu, Endocrinological Disorders, Cardiac problems, Liver & Kidney disorders, Infectious disease, Autoimmune disease, Haematological disorders, Malabsorption syndromes, Weight Reduction management, Diagnostic Dilemmas, Pyrexia of unknown origin (PUO)
Consultation Timing:
Mon to Sat - 9 am to 5 pm
Location:
PACE Hospitals, Hitech City
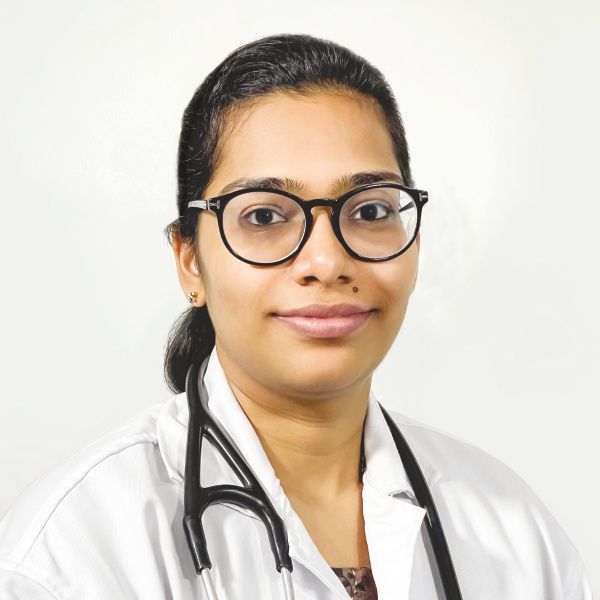
Dr. Kaku Madhurya
MBBS, MD (General Medicine), MRCP (UK)
Experience : 11+ years
Consultant General Physician and Diabetologist
Specialist
Hypertension, Diabetes, Thyroid Disorders (hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and goitre), Weight loss, Weight gain, Autoimmune diseases and Infectious diseases.
Expertise
Management of diabetes and its complications, fever of unknown origin, thyroid disorders, HIV and Its management, tuberculosis, dyslipidemia, anaemia, asthma, COPD, obesity and lifestyle disorders.
Consultation Timing:
Mon to Sat - 9 am to 6 pm
Location:
PACE Hospitals, Hitech City
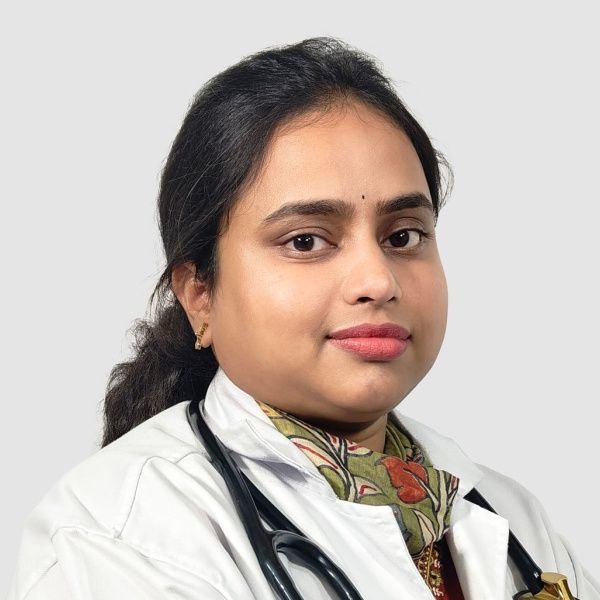
Dr. Mounika Jetti
MBBS, MD (General Medicine)
Experience : 9+ years
Consultant General Physician and Diabetologist
Specialist
Diabetes, Hypertension, Thyroid disorders, Obesity, Weight loss, Infectious diseases, Autoimmune diseases, Immunisation protocols, Anaemia, Cardiac and Renal issues and many other general conditions.
Expertise
Chronic disease management, Treatment of diabetes and its complications, Fever of unknown origin (FUO), thyroid disorders, dyslipidemia, tuberculosis, anaemia, asthma, obesity, COPD, lifestyle disorders, HIV and Its management, innovative treatment approaches and preventive healthcare strategies.
Consultation Timing:
Mon to Sat - 11 am to 8 pm
Location:
PACE Hospitals, Hitech City
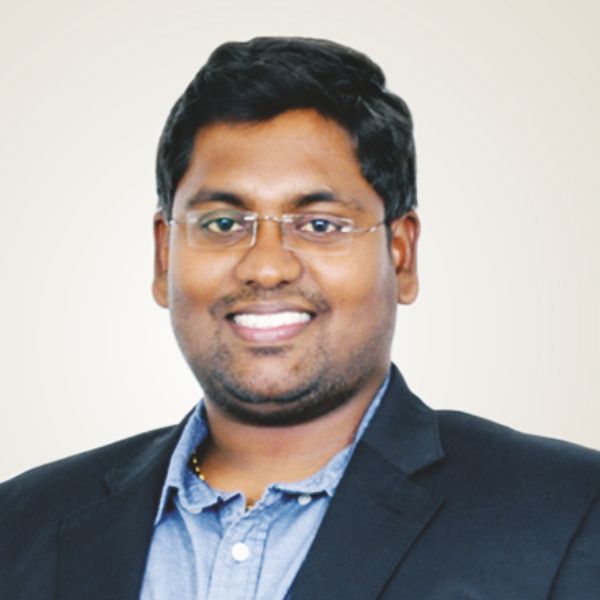
Dr. Sai Ramakrishna O
MBBS, MD (General Medicine)
Consultant General Physician & Diabetologist
Specialist
Diabetes, Hypertension, Thyroid Disorders, Fever management, Malabsorption syndromes, Headache & Migraines, Obesity, Autoimmune diseases, Anaemia and Blood Disorders, and Infectious diseases
Expertise
Management of Fever of unknown origin, Management of Diabetes mellitus, Hypertension, Sepsis & Multiorgan failure, Thyroid Disorder, Pregnancy Induced Hypertension, Anaemia management, Weight loss & Fatigue Syndromes, Dyslipidemia & hyperlipidemia, HIV treatment, Lung diseases (Asthma, Empyemathorasis, Bronchiectasis Treatment, Interstitial Lung Disease Treatment), Allergy and Immunological Disorders, Anaemia and Blood Disorders, Rheumatology and Joint Related Disorders, COVID-19 / Swine Flu, Endocrinological Disorders, Cardiac problems, Liver & Kidney disorders, Infectious disease, Autoimmune disease, Haematological disorders, Malabsorption syndromes, Weight Reduction management, Diagnostic Dilemmas, Pyrexia of unknown origin (PUO)
Consultation Timing:
Mon to Sat - 9 am to 6 pm
Location:
PACE Hospitals, Madinaguda
Diabetes Specialist in Hyderabad for Effective Diabetes Management
PACE Hospitals is having some of the best diabetes doctor in Hyderabad, they are committed to delivering world-class care for patients living with diabetes mellitus. We offer a multidisciplinary approach to managing and treating all forms of diabetes, including Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabetes. Our team of highly experienced diabetes specialist in Hyderabad, are equipped with extensive experience and advanced knowledge, ensuring that each patient receives personalized care tailored to their unique condition and lifestyle.
From accurate diagnosis to cutting-edge treatments and continuous monitoring, we focus on controlling blood sugar levels, preventing complications, and improving overall quality of life. Our diabetologists adopt a holistic approach, addressing not only the medical aspects of diabetes but also providing nutritional guidance, lifestyle modification support, and patient education to empower individuals in managing their condition effectively. At PACE Hospitals, patients can be assured of compassionate care and expert treatment, making a trusted choice for diabetes management in Hyderabad.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Diabetes
Who is at higher risk for developing diabetes?
Individuals who are obese, aged above 45 years, with a family history of diabetes, hypertension, not being physically active, or with medical history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease are at higher risk of developing diabetes. Natives of Hispano, American Indian, African are also at high risk for developing diabetes.
What are the common signs of diabetes in children and adolescents?
Following are the classical and common signs and symptoms observed in children and adolescents with type I diabetes:
- Extreme thirst (polydipsia), frequent urination (polyuria), extreme hunger (polyphagia), blurred vision, fatigue and weakness.
Are there any specific symptoms that might indicate uncontrolled diabetes?
Alarming symptoms such as drastic weight loss, fatigue all the time, irritability, recurrent infection (in areas of genitals, urinary tract, skin, oral cavity), dry mouth, itching, decreased vision and impotence indicate diabetes.
What are the potential long-term complications of diabetes?
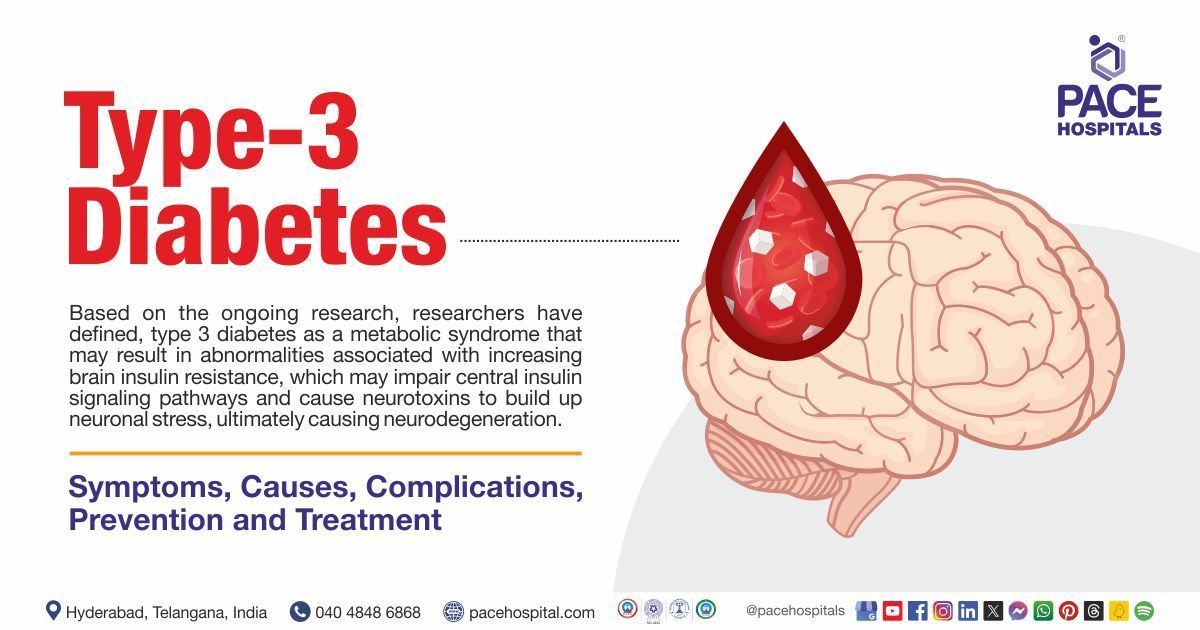
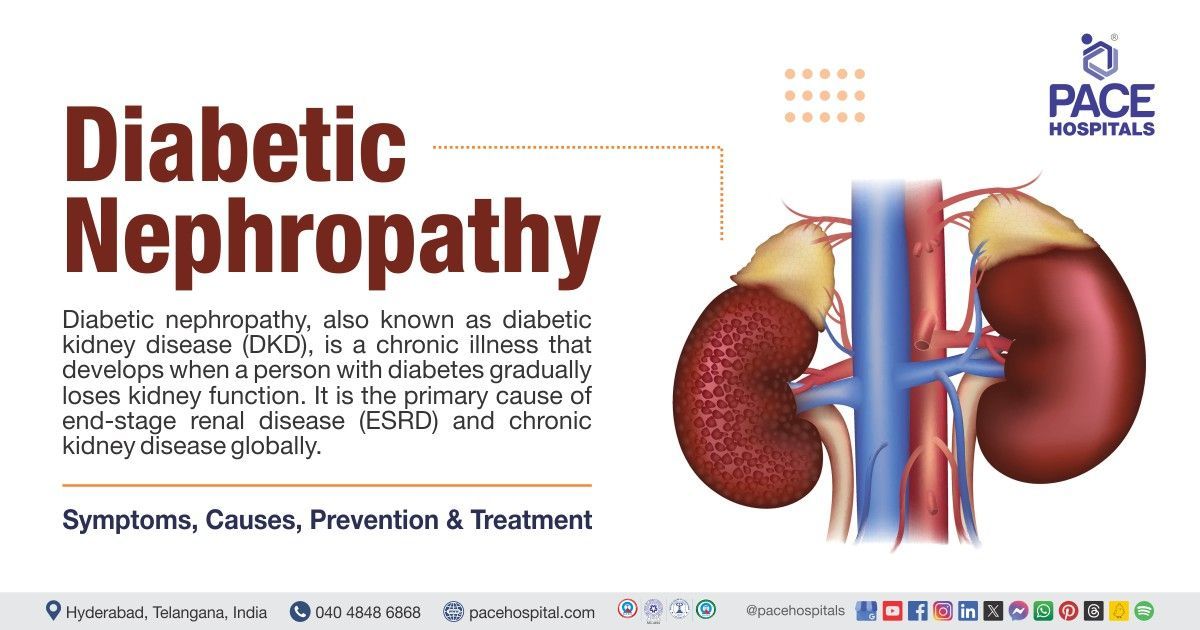
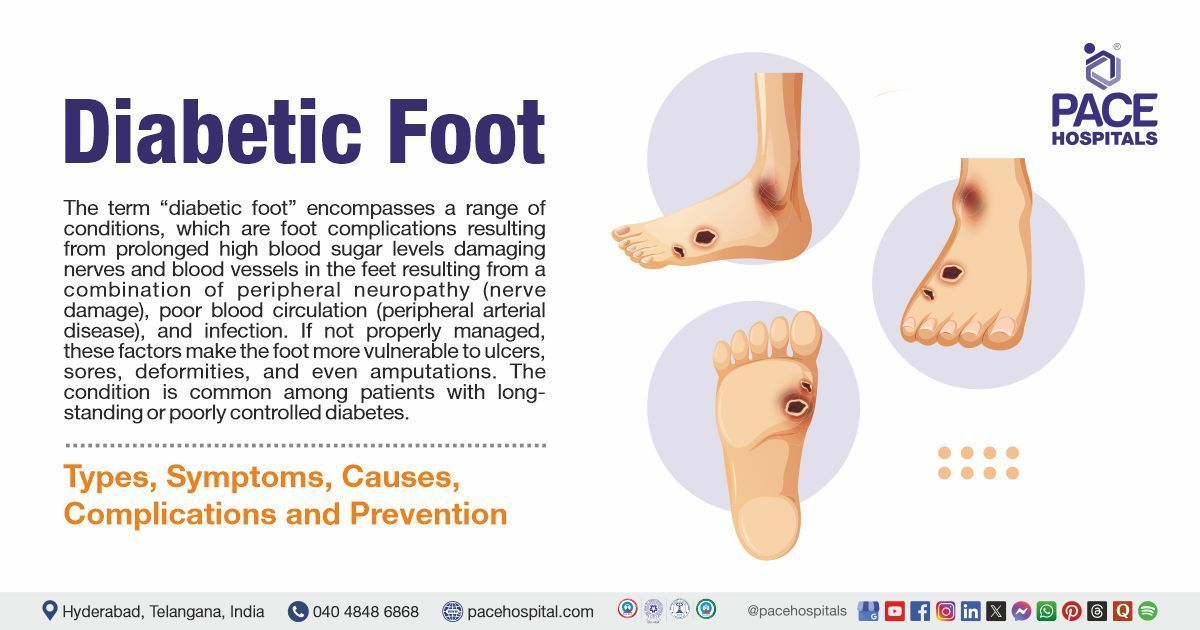
Long term complications of diabetes include retinopathy (damage to retina), diabetic foot, nephropathy (damage to the kidneys), neuropathy (damage to nerves) heart attack, stroke, gum diseases and impotence in men.
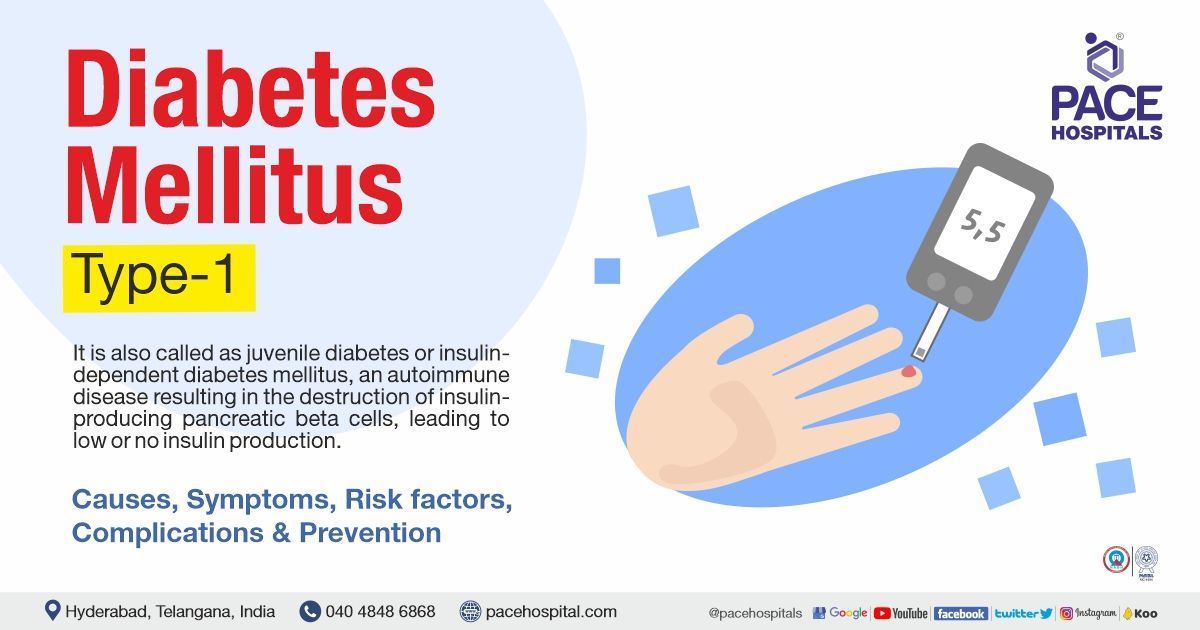
Different types of diabetes?
Diabetes is generally of three types which includes type I, type II and gestational diabetes.
- Type I Diabetes: This is an autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system attacks pancreatic beat cells which produce insulin, ultimately resulting in absolute deficiency of insulin. Due to insufficient insulin glucose accumulates instead of moving to the cells. This accumulation or buildup is known as hyperglycemia.
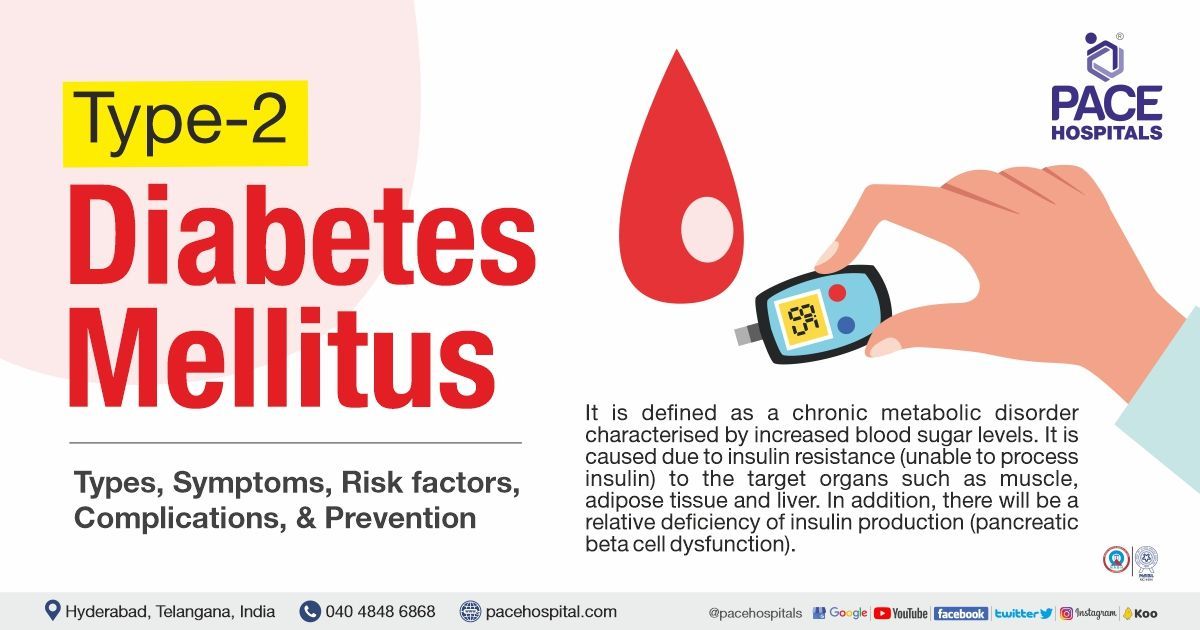
- Type II Diabetes: This is the most common type of diabetes and accounts for about 90 percent of all the cases. Initially with increased production of insulin, homeostasis of glucose was maintained gradually insulin production is decreased and response to insulin is also diminished resulting in increased serum glucose levels.
- Gestational Diabetes:
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a condition characterized by hyperglycemia the increased blood glucose levels during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes can occur at any time of pregnancy but usually affects during the second and third trimester.
What is the difference between type I and type II diabetes?
Type I diabetes, caused by an autoimmune genetic disorder where the pancreas does not produce insulin. The body’s immune system attacks islets cells of pancreas that make insulin whereas in Type II diabetes the pancreatic cells produce insulin, but the cells do not respond to insulin, the body becomes resistant to insulin. Both Type I and type II diabetes releases high glucose levels in blood.
Can gestational diabetes lead to Type II Diabetes later?
Gestational diabetes mellitus occurs due to pancreatic beta cell dysfunction with preexisting insulin response, this can increase a women’s risk of developing type 2 diabetes after pregnancy. Meta analysis reports estimated that risk for
type II diabetes among women with gestational diabetes was 10 times more compared to women with normoglycemic pathways.
What are the primary symptoms of type I diabetes?
Hyperglycemic symptoms such as extreme thirst (polydipsia), extreme hunger (polyphagia), fatigue, numbness or tingling in feet, weight loss, frequent urination (polyuria), weakness are the early and primary symptoms of type I diabetes.
What specific symptoms should prompt one to seek medical attention?
Symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis which include fruity odor breath, nausea, vomiting, rapid breathing, blurred vision, confusion, weakness requires immediate medical attention as it leads to severe complications.
What are the primary risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes?
Obesity, age greater than 40 years, family history of diabetes, hypertension, low density lipoprotein(LDL) less than 35mg/dL, triglycerides greater than 250mg/dL, smoking, not being physically active are the primary risk factors for developing type II diabetes.
Does being overweight or obese increase the risk of diabetes?
Excess body fat when accumulated causes a set of metabolic abnormalities which includes insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, non-alcoholic fatty liver, prediabetes and type II diabetes. Increase in body mass index is correlated with a progressive increase in risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
How can early screening help in identifying risk factors for diabetes?
Screening of diabetes includes some diagnostic tests such as fasting blood sugar (FBS), glucose tolerance testing, random plasma sugar (RBS), glycated hemoglobin (HbA1C). The test results give estimates and based upon the reference values the patient is considered as prediabetic or diabetic.
Screening for diabetes is recommended by the US Preventive Service Task Force, it is suggested that screening can be done between the age of 40 to 70 years, who are overweight and obese and if results are normal retesting is done every 3 years. Patients who are obese and with other major risk factors are screened at short intervals of time. Thereby early screening aims for identifying risk factors that develop diabetes, early diagnosis and preventing progression of disease.
Is there any genetic test available to assess the risk for diabetes?
Genetic testing is performed to diagnose monogenic diabetes. It is recommended for adults and children having a family history of diabetes or having any risk factor like
obesity. This test involves giving a sample of blood or saliva, DNA is isolated from this sample and analyzed for mutations in genes causing monogenic diabetes.
Does diabetes increase the risk of heart disease and stroke?
In type I and type II diabetes, the high blood glucose levels cause buildup or accumulation of glucose in oxygen, blood and nutrients carrying arteries in the body. Accumulation of glucose in arteries leads to narrowing and thickening of walls of the arteries. Overtime, this damage to arteries carrying blood to the heart causes heart disease and arteries carrying blood to the brain causes stroke.
What impact does diabetes have on vision and eye health?
Diabetes leads to diabetic retinopathy where the high blood glucose levels destroy the retina and causes damage to the eyes, and this can affect vision and in some severe cases cause blindness. Diabetes causes diabetic eye disease which includes conditions such as cataracts, diabetic macular edema, neovascular glaucoma.
Can diabetes cause kidney damage?
Yes, diabetes can cause kidney damage. Diabetic kidney disease or diabetic nephropathy which is a microvascular complication of type I and type II diabetes develops due to genetic reasons, autoimmune process, resistance to insulin and increased blood glucose levels.
Are people with diabetes more prone to infections?
Diabetes presents notable risk factors for all kinds of infection. Both type I and II are correlated with higher risk of infection. Retrospective studies revealed that diabetes accounts for about 6 percent of infection related hospitalizations and 12 percent of infection related deaths. Deficits in immune system, changes in innate immunity causes infections particularly bone and joint infections, sepsis and cellulitis.
What tests are used to diagnose diabetes?
Based on the symptoms observed following, test are performed to diagnose diabetes:
HbA1c: HbA1c test which is also known as glycated hemoglobin test measures blood sugar levels for the past 2 to 3 months.
- Normal: Below 5.7 %
- Prediabetes: 5.7 % to 6.4%
- Diabetes: 6.5 % or above
Fasting Blood Glucose: This diagnostic test is performed after an overnight fast.
- Normal: 99mg/dL or above
- Prediabetes: 100 to 125mg/dL
- Diabetes: 126mg/dL and above.
Random Blood Glucose: As the name suggests, this test can be performed at any random time without any overnight fast. Serum value 240mg/dL or more indicates that the patient is diabetic.
Glucose Tolerance test: Overnight fasting is required; fasting blood glucose level is monitored then a glucose containing fluid is given to the patient and after 2 hours of fluid intake blood glucose levels are monitored.
- Normal: 140mg/dl
- Prediabetes: 140 – 199 mg/dL
- Diabetes: 200 mg/dL or more.
What is the difference between fasting blood glucose and hemoglobin A1c test?
HbA1c test is conducted to measure blood sugar levels of past 2 to 3 months while fasting blood sugar measures blood glucose levels and the results show glucose levels at the time of blood withdrawn. Fasting blood glucose requires keeping patients to fast for about 8 hours and this test is not applicable in the afternoon, whereas HbA1c test does not require any kind of fast and can be performed at any specific time.
What are the normal ranges for blood glucose and HbA1C tests?
Following are the normal reference ranges for fasting blood glucose and glycated hemoglobin test:
- HbA1c: HbA1c test, which is also known as glycated hemoglobin test, measures blood sugar levels for the past 2 to 3 months. If blood glucose values are below 5.7 percent the patient is considered to be normal or non-diabetic, values between 5.7 to 6.4 it comes under prediabetic, if the values exceed 6.5 percent, then the patient is considered to be diabetic.
- Fasting Blood Glucose: This diagnostic test is performed after an overnight fast. For blood glucose to be considered normal, the value must be below 99 mg/dL. A value of 100 to 125mg/dL is considered to be prediabetic, whereas value above 126mg/dL is considered diabetic.
What are the possible reasons for a false positive or false negative result in diabetes testing?
Possible reasons for false negative HbA1c include high altitude, hemorrhage, pregnancy, blood transfusion, hemolytic anemia, chronic kidney failure, administration of erythropoietin, sickle cell anemia.
The test shows elevated levels of blood glucose if the patient did not fast before the test is conducted. This is a false positive result which involves unnecessary treatment as the patient is non-diabetic. Factors like anxiety, stress, improper technique are other factors that cause false positive results in diabetic testing.
How often should one get tested if at risk for diabetes?
Children and teens who are obese and with other risk factors like family history of diabetes should get tested every 3 years. Adults and children who are diagnosed with prediabetes should retest every year for type 2 diabetes.
Pregnant women should get tested in the 15th week of their gestation if they have any of the risk factors for diabetes mellitus, and those who have no prior diagnosis or history of diabetes should get tested between 24th and 28th week of gestation to prevent gestational diabetes.
What are the different treatment options for diabetes?
Type I diabetes, also termed as Insulin dependent diabetes, occurs due to insufficient or lack of insulin. Therefore, treatment of type I diabetes includes daily administration of insulin injections.
Initial treatment of type 2 diabetes involves reduction of blood glucose levels through diet and physical exercise. Diet must include fruits, vegetables, low glycemic index food like pasta, brown rice etc. Avoid sugary items and opt for high protein rich foods. Moderate exercise is also recommended. Other therapies include drugs from specific classes.
What is Insulin dependance, how does it affect Type I diabetes?
Type I diabetes leads to destruction of pancreatic beta cells that produce insulin; this destruction leads to deficiency of insulin. To treat type I diabetes, it requires lifelong replacement of insulin by administration of insulin injections daily or with use of automated insulin delivery system. As treatment of type I diabetes requires necessity of insulin, type I diabetes is also termed as Insulin dependent diabetes.
Is it safe for type 2 diabetic patients to take insulin?
Yes, Insulin is safe in type 2 diabetic patients. Following are the specific times when Insulin is advised as a treatment regimen for type II diabetic patients:
- When blood glucose levels are very high
- During pregnancy or severe illness or after a surgical procedure.
- Insulin can be used as a treatment option when drug therapy is not effective or when the high blood glucose levels are harder to manage by drug therapy.
How is gestational diabetes treated during pregnancy?
Treatment of gestational diabetes includes a healthy diet, regular exercise and use of certain medications. Diet must include fruits, vegetables, food rich in starch and low glycemic index like pasta, brown rice, pulses. Avoid sugar in diet and increase proteins.
Physical activity lowers the blood glucose levels therefore moderate exercise for 10 to 15 min is recommended. Treatment also includes medications such as biguanides and metformin. Insulin is recommended in certain conditions when blood glucose levels are very high.
What is continuous glucose monitoring and how does it help?
Continuous glucose monitoring means measuring or monitoring blood glucose levels at any time of the day and night using an electronic device. This electronic device has three parts. First one is a sensor which is inserted under skin, this sensor estimates glucose levels within the cells, second one is a transmitter that sends information to the third part which is a software program or to a receiver.
What are some common myths about diabetes?
There are many myths and misconceptions surrounding diabetes, which can lead to confusion and fear among those who have been diagnosed with the condition. Here are some common myths about diabetes:
- Eating too much sugar causes diabetes: While consuming large amounts of sugar can lead to weight gain and other health problems, it is not the direct cause of diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is caused by genetics and other unknown factors, while Type 2 diabetes is caused by a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors.
- People with diabetes can't eat sweets or desserts: People with diabetes can still enjoy sweets and desserts, but they need to do so in moderation and as part of a balanced diet. It's important for people with diabetes to monitor their blood sugar levels and adjust their insulin or medication doses as needed.
- Diabetes is not a serious condition: Diabetes is a serious, chronic condition that can lead to complications such as heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and blindness if left untreated. It's important for people with diabetes to manage their blood sugar levels and receive regular medical care to prevent these complications.
- Only overweight or obese people can get diabetes: While being overweight or obese is a risk factor for Type 2 diabetes, it's not the only factor. People who are of normal weight can still develop Type 2 diabetes, and some people with Type 1 diabetes are at a healthy weight.
- A person can get diabetes by touching someone else: Diabetes mellitus is not contagious. It's a chronic condition that affects how your body regulates blood sugar levels, and it's not something that can be passed from person to person.
It's important to educate yourself about diabetes and separate fact from fiction. By understanding the truth about diabetes, you can better manage the condition and live a healthy, fulfilling life.
What our patients have to say
Experts perspective
Related articles



Why choose PACE Hospitals?
- A Multi-Super Speciality Hospital.
- NABH, NABL, NBE & NABH - Nursing Excellence accreditation.
- State-of-the-art Liver and Kidney transplant centre.
- Empanelled with all TPA’s for smooth cashless benefits.
- Centralized HIMS (Hospital Information System).
- Computerized health records available via website.
- Minimum waiting time for Inpatient and Outpatient.
- Round-the-clock guidance from highly qualified diabetologists, endocrinologists & general physicians.
- Standardization of ethical medical care.
- 24X7 Outpatient & Inpatient Pharmacy Services.
- State-of-the-art operation theaters.
- Intensive Care Units (Surgical and Medical) with ISO-9001 accreditation.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868