Lung Cancer: Types, Causes, Symptoms, Complications, Prevention
PACE Hospitals
Overview | Prevalence | Types | Causes | Symptoms | Complications | Diagnosis | Treatment | Prevention | FAQs | When to consult a Doctor
Lung cancer definition
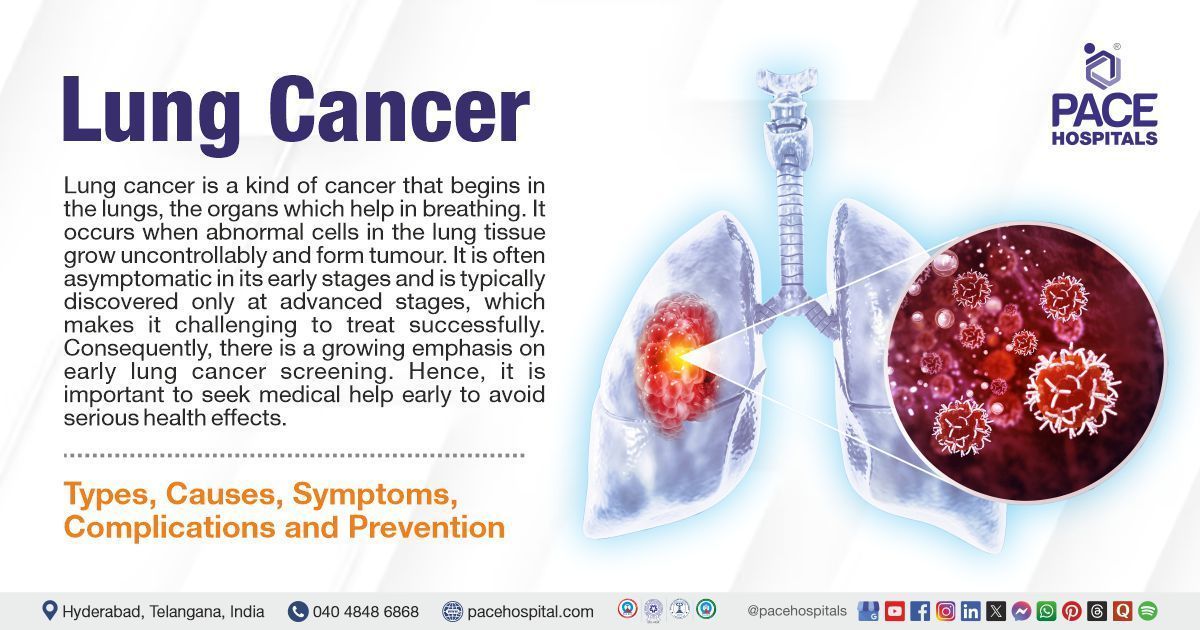
Lung cancer is a kind of cancer that begins in the lungs, the organs which help in breathing. It occurs when abnormal cells in the lung tissue grow uncontrollably and form tumors. Lung cancer is one of the most common and dangerous types of cancer, affecting both smokers and non-smokers alike.
It is often asymptomatic in its early stages and is typically discovered only at advanced stages, which makes it challenging to treat successfully. Consequently, there is a growing emphasis on early lung cancer screening. Therefore, it is important to seek medical help early to avoid serious health effects.
Lung Cancer Meaning
The term "lung" is derived from the Old English word "lunge," which refers to the organ responsible for respiration. The word "cancer" is derived from the Greek word "karkinos," which means a crab, representing the shape of the tumours. The term symbolizes the disease's ability to spread to different body parts, like a crab's legs extending outward.
Lung Cancer Prevalence
Lung cancer prevalence worldwide
Globally, lung cancer is one of the most often diagnosed cancers. As per the World Health Organization (WHO), in 2020, there were approximately 22 lakh new lung cancer cases, making it the second most prevalent cancer globally after breast cancer. This type of cancer is considered the leading cause of cancer-related fatalities, with an estimated 18 lakh deaths occurring annually.
Lung cancer prevalence in India
In India, lung cancer rates are on the rise, with an estimated 78,000 new cases reported in 2020. The incidence of lung cancer in India is high and varies by state. In 2021, the incidence of lung cancer in India was 67,795 cases, which was 5.9% of all cancer cases. It has become a major public health concern, particularly in urban areas, due to rising tobacco use and air pollution. The disease is also diagnosed more frequently in men than in women, reflecting the higher incidence of smoking.
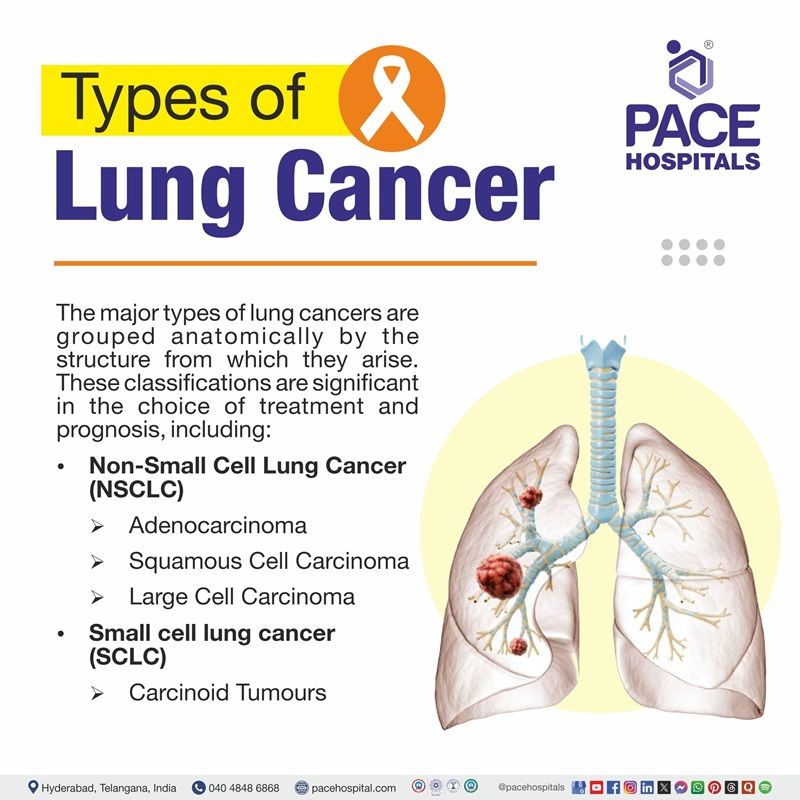
Types of Lung Cancer
The major types of lung cancers are grouped anatomically by the structure from which they arise. These classifications are significant for the choice of treatment and prognosis.
Lung cancer classification: Different categories of lung cancer include:
- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC):
- Adenocarcinoma
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Large Cell Carcinoma
- Small cell lung cancer (SCLC)
- Carcinoid Tumors
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
It accounts for 80% to 85% of lung cancer cases. Non-small cell lung cancer includes several subtypes, each of which has its own unique histological features. The most common subtypes are:
- Adenocarcinoma: The most common type of NSCLC, adenocarcinomas are lung cancers that develop from glandular cells. They are found more frequently in women and those who do not smoke. These tumors are often seen as masses in the lungs' outer sections and can sometimes secrete mucus.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: This cancer develops from squamous cells lining the airways. It is usually located in the centre of the lungs and has strong connections with smoking. These tumours often appear in the lungs as central masses with hollow spaces.
- Large Cell Carcinoma: This type is known for its large, undifferentiated cells and can occur in any part of the lung. It is generally a fast grower and spreader, making it hard to treat.
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC)
It accounts for about 10% to 15% of lung cancers. This is a highly aggressive type of lung cancer that begins in the neuroendocrine cells of the lungs. Like most forms of lung cancer, SCLC is significantly connected to smoking. Most SCLC patients usually have a history of smoking, which is the reason for concern, given the casual relationship between the two entities. SCLC is characterized by small, round cells with scant cytoplasm and a high nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio.
- Carcinoid Tumours: These are rare tumors that originate in the neuroendocrine cells of the lungs. They are slow growing by nature, account for fewer than lung tumours, and are usually less aggressive than other types.
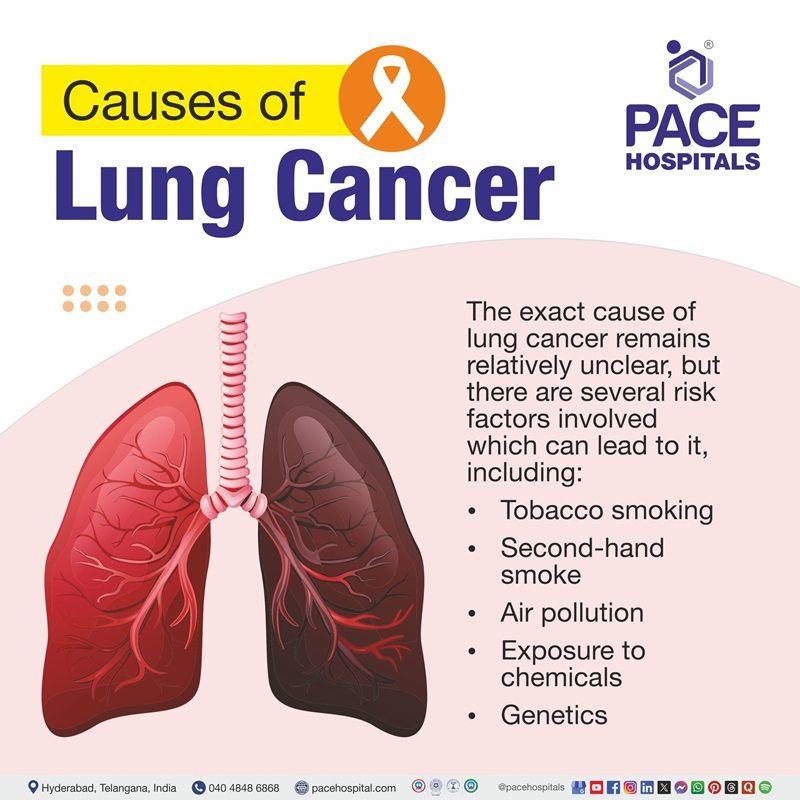
Lung Cancer Causes
The exact cause of lung cancer remains relatively unclear, but there are several risk factors which can lead to it, including:
- Tobacco: Tobacco smoking is responsible for 85% of lung cancer cases, causing about 8 out of 10 cases of lung cancer in females and 9 out of 10 cases in males. The risk is high if the person smokes more cigarettes.
- Second-hand smoke: Second-hand smoke comes from the smoke of a burning cigarette and the smoke exhaled by a smoker. Breathing in second-hand smoke exposes individuals to cancer-causing agents, increasing the risk of related health conditions.
- Air pollution: As per some studies, living in areas with higher levels of air pollution can raises the risk of lung cancer.
- Exposure to chemicals: Being exposed to certain chemicals such as asbestos, arsenic, chromium, beryllium, nickel, soot, or tar in the workplace increases the chances of developing lung cancer.
- Genetics: A family history of cancer can leads to mutations that can increase the chances of lung cancer, although these cases are rare.
- Previous Lung Diseases: Other diseases, such as Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and even tuberculosis, can make a person more susceptible to lung cancer.
- HIV infection: The risk is higher if the person has HIV. People with HIV have higher smoking rates, making it unclear whether the increased risk is due to HIV infection or smoking.

Lung Cancer Symptoms
Since signs of lung cancer may not show up until the disease has progressed, lung cancer frequently goes undetected in its early stages. However, early diagnosis and treatment can be aided by identifying warning symptoms, including:
- A persistent cough: It persists for an extended period and either worsens or does not improve. It might produce strange phlegm or blood.
- Shortness of Breath: Breathing difficulties can occur during everyday routines, often because of tumour growth obstructing the airways.
- Chest discomfort: Patients with lung cancer experience sharp or dull pain or severe discomfort in the chest region that worsens with deep breathing, laughing, or coughing.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Significant weight loss without dietary or exercise modifications frequently indicates cancer-related metabolic changes.
- Fatigue: Patients experience continuous weakness or tiredness that interferes with routine activities, does not improve with rest, and affects daily activities.
- Hoarseness: A voice change resulting from nerve involvement or pressure on the vocal cords, making it sound strained or raspy.
- Haemoptysis, or coughing up blood: For those with lung cancer, haemoptysis occurs because of tumour growth within the lungs, damaging blood vessels and creating bleeding within the airways. This symptom is one of the leading indicators of lung cancer.
- Facial or neck swelling: The tumor pressing up against major veins can blocks blood flow, resulting in noticeable swelling.
Symptoms of lung cancer in females are generally similar to those in males, including persistent cough, chest pain, and shortness of breath.
Complications of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer complications can occur as the disease advances, spreads to other organs, or as a result of treatment side effects. The following lung cancer complications impact a person's general health and quality of life:
- Breathing Problems: Lung tumours can block or narrow the airways, causing severe dyspnoea (breathing difficult) and decreased lung function.
- Pleural Effusion: Lung cancer can cause pleural effusion by spreading to the pleura, leading to increased fluid production due to inflammation or obstruction of lymphatic flow.
- Metastatic lung cancer (Metastasis: cancer spread): Lung cancer commonly spreads to other organs, such as the brain, liver, or bones, leading to additional complications and symptoms.
- Respiratory Infections: Weakened lung function due to lung cancer makes patients more prone to recurrent infections, including pneumonia and bronchitis.
- Blood Clots: Lung cancer can cause blood clots in the lungs by triggering a hypercoagulable state and tumour-related vessel compression, leading to pulmonary embolism.
- Pain Management Issues: As the cancer progresses, it can cause severe pain, mainly if it spreads to the bones or nerves.
- Superior Vena Cava Syndrome: A tumour pressing on the superior vena cava (a major vein in the chest) can cause facial, neck, and upper body swelling.
- Psychological Impact: A lung cancer diagnosis can lead to mental and emotional health challenges such as anxiety, depression, and stress.
Lung Cancer Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of lung cancer is vital for effective treatment. Various methods are employed to confirm the diagnosis, including:
- Medical history and physical examination
- Blood Tests
- Imaging Tests
- Chest X-ray
- CT scan
- PET Scan
- Biopsy
- Bronchoscopy
- Endobronchial Ultrasound (EBUS)
- CT-guided Core biopsy
- Sputum Cytology
- Other tests
- Lung Function Test
- Mediastinoscopy
- Thoracoscopy
Lung Cancer Treatment
Lung cancer treatments vary based on the type, stage, and tumor location and the patient's overall health, including:
- Surgery (Lung cancer surgery)
- Radiation Therapy
- Chemotherapy (Lung cancer medications)
- Targeted Therapy
- Immunotherapy
- Palliative Care
Why Choose PACE Hospitals?
Expert Super Specialist Doctors
Advanced Diagnostics & Treatment
Affordable & Transparent Care
24x7 Emergency & ICU Support

Lung Cancer Prevention
While it may not be possible to prevent lung cancer completely, individuals can take steps to reduce their risk through lifestyle changes and by avoiding risk factors that contribute to its development. Here are some key preventive measures:
- Quitting smoking: It is the leading cause of lung cancer. The most effective way to reduce the risk of lung cancer is to quit smoking and avoid exposure to second-hand smoke.
- Minimizing the exposure to carcinogenic chemicals: Reducing exposure to workplace chemicals such as asbestos and radon gas. Ensuring proper ventilation and safety measures in high-risk environments can help to avoid exposure.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity improves lung function and overall health. Regularly exercising can help reduce inflammation and enhance immunity.
- Avoiding air pollution: Reducing exposure to outdoor and indoor pollutants like smoke and chemicals. Using air purifiers and maintaining clean indoor air quality can help to prevent air pollution.
- Maintaining a Healthy Diet: A diet rich in vegetables, fruits, and whole grains boosts immunity. Antioxidants in healthy foods may help protect against cancer cell formation.
- Vaccination: Chronic infections can lead to inflammation, increasing cancer risk. Protecting against infections through vaccination for flu and pneumonia can help prevent lung infections.
- Getting regular screenings: High-risk individuals should undergo regular lung cancer screenings. Early detection through low-dose CT scans can improve treatment outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Lung cancer
Is lung cancer curable?
It is curable if detected early, especially in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) stages I and II. Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, and targeted therapies. However, in advanced stages, treatment focuses more on managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
Is lung cancer hereditary?
Although there is no direct genetic component to lung cancer, a family history of the condition may raise the risk. It develops due to a combination of certain genetic factors and lifestyle decisions, including smoking and exposure to toxic substances.
What are the leading causes of lung cancer?
The main reason for lung cancer is smoking, which is responsible for about 85% of cases. Other causes include exposure to second-hand smoke, air pollution, asbestos, radon, and certain genetic factors. Non-smokers can also develop lung cancer, which is often linked to environmental factors or genetic predispositions.
Can lung cancer occur in non-smokers?
Yes, lung cancer can occur in non-smokers. Factors like exposure to second-hand smoke, radon, air pollution, and certain genetic conditions can contribute to the development of lung cancer in non-smokers.
What are the early symptoms of lung cancer?
Common symptoms of this cancer include persistent cough, chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, wheezing, coughing up blood or rust-coloured sputum, loss of appetite, fatigue and unexplained weight loss.
What is lung cancer?
It is a type of cancer that begins in the lungs, an organ responsible for breathing. It occurs when abnormal cells in the lung tissue grow uncontrollably and form tumors. It is one of the most common and deadliest cancers globally.
Can X-rays detect lung cancer?
Yes, a chest X-ray can help detect lung cancer. However, it can't provide a definitive diagnosis. X-rays can show white-grey masses that may be tumours, but they can't distinguish between cancer and other conditions. More advanced imaging techniques, like CT scans, can provide more detailed images of the lungs.
Can lung cancer be treated?
Lung cancer is treatable, especially when it is detected early. Chemotherapy can be performed to destroy or shrink tumors, radiation therapy can kill cancer cells, surgery can remove the entire tumour or a portion of the lung, targeted therapy can attack specific cancer cells, and immunotherapy can boost the body's immune system to combat cancer. The patient's health and the type and stage of the cancer determine the available therapy options.
Is lung cancer preventable?
While it may not be possible to prevent lung cancer entirely, specific lifestyle changes can reduce the risk by quitting smoking or never starting smoking, avoiding exposure to second-hand smoke and carcinogens like radon and asbestos, maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular physical activity, undergoing regular screening if the person is at high risk (e.g., long-term smoker).
What are the survival rates for lung cancer?
The type of lung cancer, the patient's general condition, and the stage at diagnosis all affect survival rates. Generally, lung cancer has a five-year overall survival rate of about 19%. However, the survival percentage can be significantly higher if the diagnosis is early. Screening for early detection greatly improves results.
Can lung cancer recur after treatment?
Yes, lung cancer can recur even after successful treatment. The risk of recurrence depends on multiple factors, including the stage of cancer at diagnosis, the treatment received, and how well the cancer responded to the treatment.
How did I know I had lung cancer?
Coughing up blood, chest pain, breathing difficulties, prolonged coughing, and unexplained weight loss are all signs of lung cancer. Imaging studies such as PET Scans, CT scans or X-rays are typically used for diagnosis, and a biopsy is performed for confirmation.
Is lung cancer contagious?
No, lung cancer is not contagious. It cannot spread from person to person through physical contact, air, or sharing personal items. It develops due to genetic changes and environmental factors, not through infection.
Does lung cancer affect my voice?
Yes, lung cancer can cause a tumor to press on the vocal cords or a nerve, leading to hoarseness or a raspy voice. Consulting a healthcare professional is recommended if a person experiences unexplained and prolonged hoarseness.
How to survive stage 4 lung cancer?
While there is currently no cure for stage 4 lung cancer, the focus is on managing symptoms, improving quality of life through palliative care, and extending life expectancy by utilizing treatment options like chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapies, often in combination with regular monitoring and close communication with healthcare team; this includes discussing the needs and goals for treatment to ensure the best possible care.
Who treats lung cancer?
Lung cancer is treated by a team of specialists, including
oncologists,
pulmonologists, radiation oncologists, and thoracic surgeons. The type of treatment you receive depends on the stage of cancer and treatment options.
When to consult a doctor for lung cancer?
Consult a doctor for lung cancer if you’ve been having ongoing breathing problems or other symptoms that don’t seem to go away, such as:
- A cough that lasts for weeks or gets worse over time
- Coughing up blood or rust-colored mucus
- Shortness of breath or chest pain
- Hoarseness or wheezing
- Unexplained weight loss or constant tiredness
If these symptoms persist, it’s advisable to consult a lung cancer specialist, such as a pulmonologist or oncologist. Early detection provides better treatment options and improves recovery chances.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868