Mini Gastric Bypass: Effective Revision Surgery for Weight Regain in Morbid Obesity
PACE Hospitals
An adult male patient with morbid obesity (BMI of 40.04 kg/m²) presented to PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, seeking revision metabolic surgery. The patient underwent
laparoscopic sleeve conversion to mini gastric bypass (MGB), Which was a successful procedure without any significant complications.
Medical History
A 36-year-old male patient was presented to the Surgical Gastroenterology Department of PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, with a medical history of morbid obesity, initially managed with a sleeve gastrectomy performed in 2016. Despite significant initial weight loss following the procedure, the patient experienced weight regain over the past two years. His body mass index (BMI) was 40.04 kg/m² at the time of presentation, categorizing him as severely obese. This prompted the need for revision metabolic surgery.
The patient had no known allergies, and his medical history did not indicate any significant comorbidities such as
diabetes,
hypertension, or cardiovascular disease. There were no prior complications with his sleeve gastrectomy procedure, and he had a generally healthy recovery. However, the weight regain prompted him to seek further surgical intervention, particularly to address the metabolic challenges posed by obesity.
Diagnosis
Upon presentation, the primary diagnosis was morbid obesity, specifically with a BMI of 40.04 kg/m². The patient had previously undergone a sleeve gastrectomy but was experiencing weight regain over the past two years, likely due to insufficient long-term weight loss or other factors related to the stomach's anatomy after the initial surgery.
Medical Decision Making
Given the patient's BMI and the history of weight regain, the Surgical Gastroenterologist, Bariatric and Metabolic Surgeon, GI and HPB Oncologist, and Liver Transplant Surgeon, Dr. Suresh Kumar S decided to perform a laparoscopic sleeve conversion to mini gastric bypass (MGB).
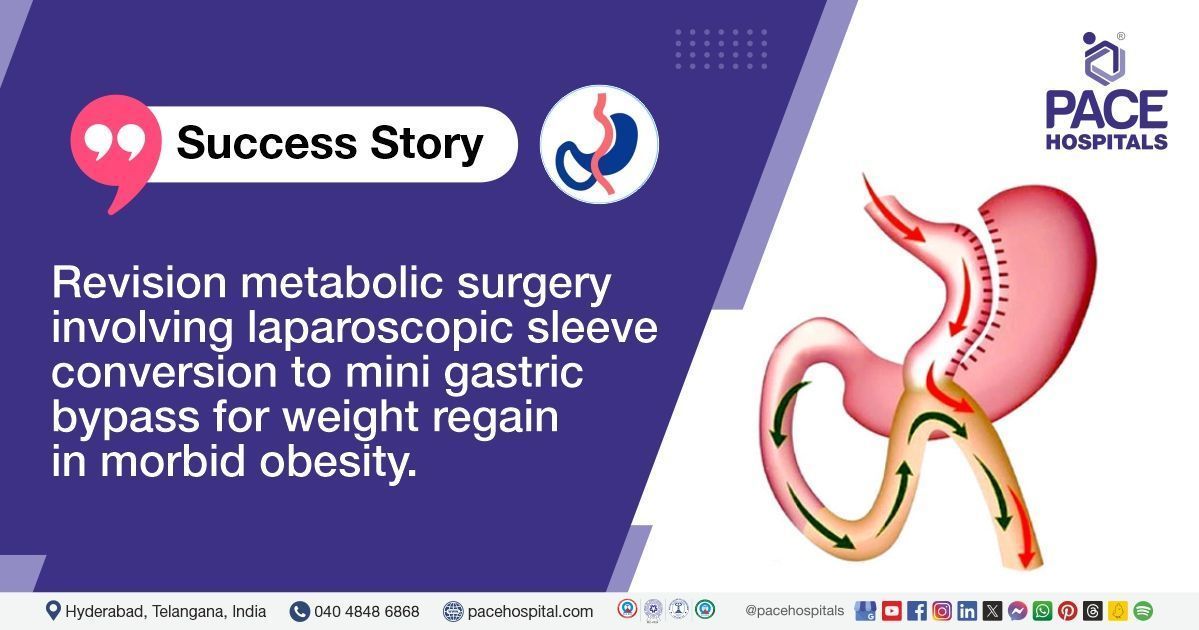
MGB offers better long-term weight loss and metabolic benefits for patients who have not achieved adequate results with previous bariatric procedures. It involves creating a smaller stomach pouch and rerouting a portion of the small intestine to enhance weight loss and metabolic function.
Surgical Procedure
Preoperative assessment and PAC clearance were done to ensure the patient's fitness for surgery. The patient was informed of the potential risks and benefits of the procedure, and informed consent was obtained. The decision to proceed with the conversion was made with the understanding that this approach would offer better results for weight loss and metabolic control than revising the sleeve gastrectomy alone.
The patient underwent a laparoscopic sleeve conversion to a mini gastric bypass. This procedure is minimally invasive and involves creating a small gastric pouch, followed by rerouting a portion of the small intestine. The surgery was successful, and the patient showed no signs of intraoperative complications.
Postoperative Care
After the surgery, the patient’s vital signs were stable, and he was monitored closely for any complications such as infection, bleeding, or anastomotic leaks. The patient was ambulated as soon as feasible to reduce the risk of thromboembolic complications.
- Post surgery, the patient was given a few medications to manage the complications and pain.
- Intravenous (IV) Antibiotics: The patient was administered IV antibiotics to prevent postoperative infections.
- Antacids: IV antacids were given to prevent gastric irritation and to help protect the newly created gastric pouch.
- Analgesics: Pain control was managed with analgesics post-surgery to ensure the patient's comfort.
- IV Fluids: IV fluids were administered to maintain hydration and support overall recovery.
The patient developed urinary retention postoperatively, a common complication of abdominal surgeries. The patient’s urinary retention was managed with catheterization, and the Foley catheter remained in place at the time of discharge.
Dietary Management
The patient was initiated on a liquid diet on post-operative day (POD) 2 to ensure gradual and safe introduction of nutrition. The diet was planned in phases, starting with clear liquids, then progressing to full liquids, and later to soft foods as tolerated. A liquid diet was recommended for 10 days, followed by a soft diet to promote proper healing and weight loss.
Discharge and Recovery
The patient tolerated the oral intake of fluids well and was in a stable condition at the time of discharge. The Foley catheter was left in situ at discharge, with instructions for follow-up care to ensure its removal once urinary function returned to normal. Ambulation was encouraged to aid in recovery, and the patient was advised to refrain from strenuous activities for two months. A period of bed rest for two weeks was recommended to allow the body to heal after the surgical procedure.
Discharge medications
The patient was prescribed with few a medications to manage pain, and supplement nutrition
absorption.
- PPIs (Proton Pump Inhibitors): To protect the gastric mucosa and reduce acid secretion.
- Analgesics: Pain management was continued with analgesics as needed.
- Multivitamin Tablets: To ensure proper nutrition, especially after bariatric surgery.
- Opioids: For pain relief, prescribed cautiously to avoid dependence.
- Anticoagulants: To prevent
deep vein thrombosis (DVT), considering the patient’s immobility in the immediate postoperative period.
Follow-Up notes
The patient was instructed to follow up in the outpatient department (OPD) after one week with Dr. Suresh Kumar S to monitor progress, remove the Foley catheter, and assess the weight loss trajectory. Advised to report any adverse symptoms like vomiting, abdominal pain, or fever. In such cases, the patient was informed that he could be admitted to the
emergency ward for further evaluation and management.
Case discussion: Laparoscopic sleeve conversion to mini gastric bypass in morbid obesity
Revision metabolic surgery, involving laparoscopic sleeve conversion to mini gastric bypass (MGB) is a surgical approach designed to address weight regain in patients who have previously undergone bariatric procedures, such as sleeve gastrectomy. This procedure is particularly beneficial for individuals who have experienced insufficient long-term weight loss or have regained weight after the initial surgery. In this case, a 36-year-old male patient with morbid obesity and a BMI of 40.04 kg/m² sought surgical intervention after experiencing weight regain following a sleeve gastrectomy performed in 2016. Despite initial success, the patient’s weight had gradually increased over two years, prompting the need for a revision procedure.
The laparoscopic sleeve conversion to MGB involves creating a smaller gastric pouch and rerouting a portion of the small intestine, which helps enhance weight loss and improves metabolic function. The procedure is minimally invasive, reducing the risk of complications and ensuring quicker recovery times. Postoperatively, the patient was monitored for complications such as infection or bleeding, and he received medications for pain management and infection prevention. He was also started on a phased diet to support healing and weight loss. This approach not only aids in significant weight reduction but also improves long-term metabolic health. Proper follow-up care is crucial to ensure proper recovery, monitor weight loss progress, and address any potential complications.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868