Liver Cancer: Risks, Prevention and Screening to Protect Liver Health
PACE Hospitals
Written by: Editorial Team
Medically reviewed by: Dr. Govind Verma - Senior Consultant Gastroenterologist & Hepatologist
Liver cancer is one of the most preventable yet fatal forms of cancer worldwide. Nearly up to 80 percent of primary liver cancers are because of chronic viral hepatitis B or C, conditions that inflame and scar the liver over years. Understanding your risk factors, adopting preventive lifestyle changes, and getting regular screenings can help detect liver cancer early, when it’s most treatable.
Understanding Liver Cancer
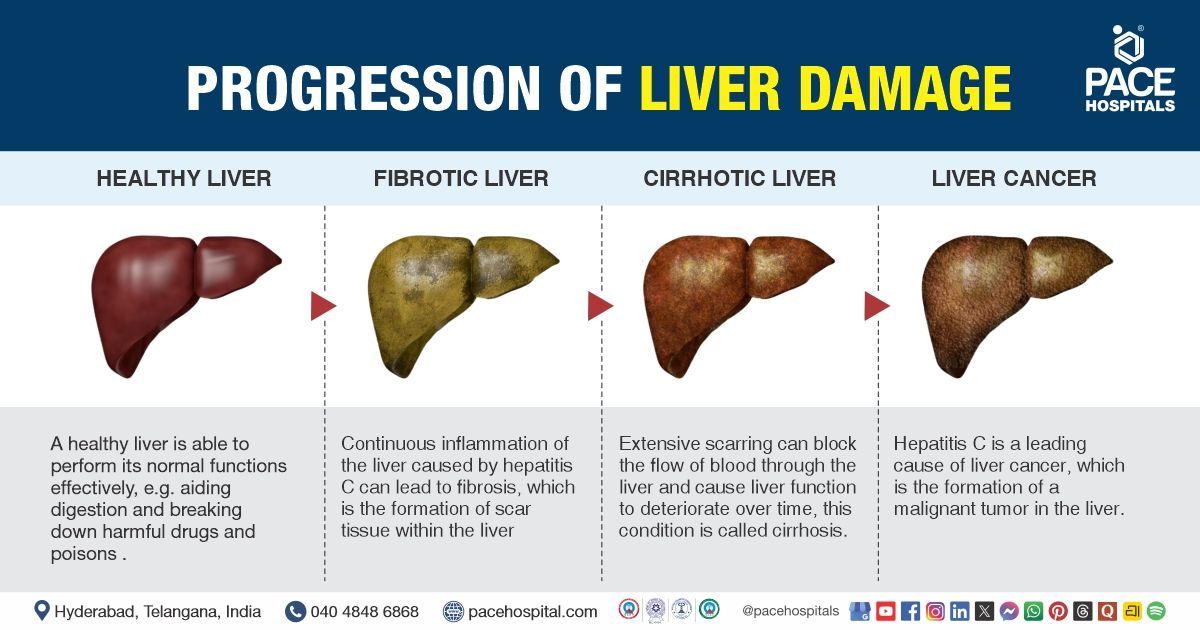
The liver is a vital organ responsible for detoxifying harmful substances, aiding digestion, and regulating metabolism. When its cells undergo genetic mutations, they may grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors.
There are two main categories:
- Primary liver cancer: Starts in the liver (most commonly hepatocellular carcinoma [HCC]).
- Secondary/metastatic liver cancer: Spreads to the liver from other organs (such as colon, lung, or breast).
Worldwide, hepatocellular carcinoma remains the most frequent type and is commonly associated with hepatitis B, hepatitis C, fatty liver disease or cirrhosis.
Major Risk Factors for Liver Cancer
While anyone can develop liver cancer, certain conditions significantly raise the risk.
Chronic Hepatitis B and C Infections
Up to 4 in 5 cases of liver cancer stem from hepatitis B or C infections.
- Hepatitis B (HBV): Transmitted through blood, unprotected sex, or from mother to child during childbirth. Vaccination can prevent it.
- Hepatitis C (HCV): Spread mainly via infected blood, shared needles, or unscreened transfusions (especially before 1994). There’s no vaccine yet, but it’s curable with antiviral drugs.
Both viruses can silently damage the liver over 20–30 years, leading to cirrhosis and eventually cancer.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
A rapidly growing epidemic in India and worldwide, NAFLD occurs when excess fat (triglycerides) accumulates in liver cells.
It is most common among people who are:
- Overweight or obese
- Diabetic or insulin-resistant
- Living a sedentary lifestyle
When untreated, NAFLD can progress to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer.
Alcoholic Liver Disease
- Excessive alcohol consumption remains a leading cause of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Those who consume alcohol and also have hepatitis B or C face a multiplied risk of liver cancer.
- Avoiding or limiting alcohol is crucial for individuals with any liver condition.
Genetic Disorders – Hemochromatosis
This uncommon hereditary condition leads to the body absorbing too much iron, which builds up in the liver and other organs and ultimately results in cancer and fibrosis. Damage can be avoided with early diagnosis via blood tests.
Environmental Exposures
- Aflatoxins: Produced by molds on improperly stored grains, nuts, and spices, especially in warm, humid regions.
- Arsenic: Sometimes found in contaminated groundwater.
- Vinyl chloride: A chemical used in plastics manufacturing.
- Anabolic steroids: Long-term use can elevate risk.
Prevention of Liver Cancer
The good news is that most causes of liver cancer are preventable. Simple but consistent lifestyle choices and medical precautions can drastically reduce your risk.
Prevent Hepatitis B and C Infections
Vaccination for Hepatitis B
- The hepatitis B vaccine is safe, effective, and provides > 95 % protection.
- It’s included in most childhood immunization schedules.
- Adults who haven’t received it, especially healthcare workers or those at higher risk, should get vaccinated.
Prevent Hepatitis C Transmission
- Avoid sharing needles or razors.
- Ensure all blood transfusions are from screened donors.
- Use barrier protection during sexual activity.
- Verify sterilization for tattoos, piercings, and dental tools.
If you test positive for hepatitis B or C, early antiviral treatment can stop liver scarring and significantly lower your cancer risk.
Limit Alcohol Consumption
- Alcohol damages liver cells, causing inflammation and fibrosis.
- Combining alcohol with viral hepatitis or obesity accelerates damage.
- If you drink, stay within safe limits or ideally, avoid it entirely.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Obesity increases liver fat, insulin resistance, and inflammation.
Adopt a lifestyle that includes:
- Regular exercise (at least 30 minutes daily)
- A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Limited processed foods, sugar, and saturated fats
These habits help prevent NAFLD and other metabolic conditions linked to liver cancer.
Eat Smart to Protect Your Liver
- Avoid moldy or improperly stored grains and nuts to prevent aflatoxin exposure.
- Eat fresh, balanced meals with high fiber content.
- Stay hydrated.
- Limit red meat and refined carbohydrates.
- Choose lean proteins and heart-healthy fats (olive oil, avocados, nuts in moderation).
Treat Chronic Liver Diseases Promptly
- People diagnosed with hepatitis B or C should remain under regular medical supervision.
- Antiviral therapies can reduce viral load, prevent cirrhosis, and lower cancer risk.
- Manage diabetes, high cholesterol, or thyroid issues early, they can worsen NAFLD progression.
Liver Cancer Screening and Early Detection
Liver cancer develops slowly, often over two to three decades. In its early stages, symptoms are minimal or absent, which makes routine screening essential, especially for those at higher risk.
Who Should Be Screened?
You should consider regular screening if you:
- Have chronic hepatitis B or C
- Have cirrhosis from any cause
- Are overweight, diabetic, or have NAFLD
- Have a family history of liver disease
Recommended Screening Methods
A simple, non-invasive imaging test to detect liver nodules or abnormalities. It is recommended every 6 months for high-risk individuals.
Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP) Blood Test
Liver cells produce a protein called AFP. Increased levels could be a sign of cancer or liver damage. For better accuracy, it is frequently used in combination with ultrasound.
CT scan or MRI
If ultrasound or AFP results are suspicious, advanced imaging can provide detailed visualization and guide further management.
Regular screening allows for early diagnosis, when curative treatments like surgery, ablation, or transplantation are still possible.
Healthy Lifestyle and Dietary Recommendations
- Eat a diet rich in antioxidants (berries, leafy greens, turmeric).
- Avoid crash diets and fad cleanses that stress the liver.
- Get adequate sleep and manage stress to maintain immune balance.
- Avoid unnecessary medications or supplements that can harm the liver.
- Quit smoking, it’s an independent risk factor for liver cancer.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention if you experience:
- Persistent fatigue or weakness
- Pain in the right upper abdomen
- Jaundice (yellowing of eyes/skin)
- Unexplained weight loss
- Swelling of the abdomen (ascites)
- Loss of appetite
These could indicate advanced liver disease or developing cancer. Early intervention can save lives.
Summary at a Glance
| Risk Factor | How to Prevent It | How to Prevent It |
|---|---|---|
| Hepatitis B / C | Vaccination & safe practices | Every 6 months (ultrasound + AFP) |
| Alcohol | Limit / avoid | Annual liver function test |
| NAFLD / Obesity | Weight control, exercise | Every 6–12 months |
| Aflatoxin Exposure | Proper food storage | As needed |
| Genetic / Hereditary | Family screening & tests | Every year |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the main cause of liver cancer?
The leading causes are chronic hepatitis B and C infections, followed by alcohol abuse, obesity, and fatty liver disease.
Is liver cancer preventable?
Yes. Up to 70–80 % of cases can be prevented through hepatitis B vaccination, early treatment of hepatitis C, healthy lifestyle choices, and alcohol control.
What are the early signs of liver cancer?
Early stages are often silent. Later symptoms include abdominal pain, fatigue, jaundice, weight loss, and a swollen abdomen.
Does fatty liver increase liver cancer risk?
Yes. NAFLD and its severe form (NASH) can lead to cirrhosis and significantly elevate cancer risk.
Is liver cancer hereditary?
Not usually, but genetic conditions like hemochromatosis can raise risk. Family members may benefit from periodic screening.
Can liver cancer be cured?
If detected early, it may be completely curable through surgery or liver transplantation. Advanced cases can still be managed effectively with targeted therapies.
Who should get screened for liver cancer?
Anyone with chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, viral hepatitis, or NAFLD should undergo screening every 6 months using ultrasound ± AFP.
Can hepatitis C be cured?
Yes. Modern antiviral medications can eliminate the hepatitis C virus in 80–95 % of cases, reducing the risk of cirrhosis and cancer.
How effective is the hepatitis B vaccine?
The vaccine provides over 95 % protection when the full three-dose schedule is completed.
How can diet help prevent liver cancer?
A balanced diet with fiber, antioxidants, and limited fat helps maintain liver health. Avoid junk foods, alcohol, and moldy grains.
What role does exercise play in liver health?
Frequent exercise lowers body fat, speeds up metabolism, and guards against liver damage caused by obesity.
How often should people with hepatitis B or C be screened?
Every 6 months, with ultrasound and AFP testing—even if you feel healthy.
Conclusion
Liver cancer doesn’t appear overnight—it’s the result of years of silent liver damage. But it’s also one of the most preventable cancers when risk factors are managed early.
Through vaccination, lifestyle modification, regular screening, and timely treatment of liver diseases, individuals can safeguard their liver and dramatically reduce cancer risk.
Remember: Prevention begins with awareness. Your liver works tirelessly for you—protect it before it’s too late.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868
Appointment request - health articles
Recent Articles