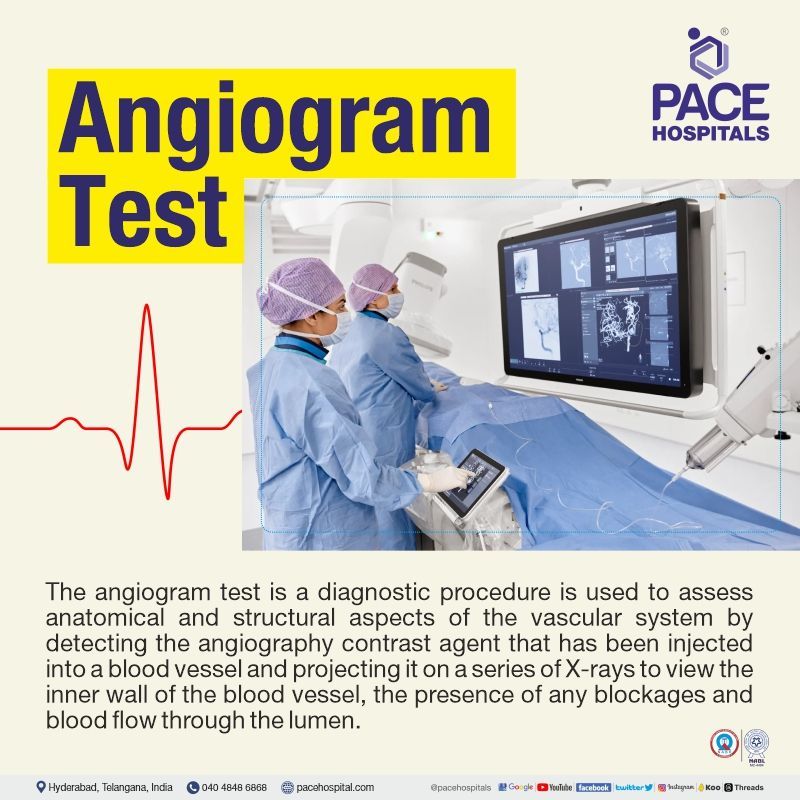
Angiogram Test - Uses, Procedure Indications & Cost
PACE Hospitals is one of the best hospital in Hyderabad for angiogram test. The Department of Cardiology is equipped with The next generation image-guided therapy platform - a Philips Azurion Cath Lab for outstanding interventional cardiac, electrophysiology, neuro and vascular performance for precise diagnostic results with delivering evidence based treatment.
Our team of best cardiologist and interventional radiologists in Hyderabad, Telangana, India are having extensive experience in performing angiography procedure.
Request an appointment for Angiogram test / procedure
Angiogram/Angiography - appointment
Why choose us?
State-of-the-art facility with Philips Azurion Cath Lab
Team of the best cardiologist with 15+ years of expertise
Cost-effective treatment with 99.9% success rate
All insurance accepted with No-cost EMI option
What is an Angiogram Procedure?
Angiogram meaning
The angiogram test is a diagnostic procedure, used to assess anatomical and structural aspects of the vascular system by detecting the angiography contrast agent that has been injected into a blood vessel and projecting it on a series of X-rays to view the inner wall of the blood vessel, the presence of any blockages and blood flow through the lumen.
Angiography test provides therapeutic choices during initial diagnosis and enables real-time, dynamic imaging through conventional imaging technologies that include non-invasive techniques, such as X-rays, computed tomography (CT angiogram) and Magnetic resonance (MR angiography). Invasive angiography is typical, and it is the gold standard for identifying the majority of intravascular diseases and offers treatment alternatives.
Types of Angiogram Test
There are different types of angiography, depending on the anatomical location or area of the body being examined.
- Neuroangiography or Cerebral Angiography
- Coronary angiography
- Pulmonary angiography
- Abdominal angiography
- Renal angiography
- Radionuclide angiography
- Lymphangiography
- Peripheral angiography or Extremity angiography
- Retinal angiography
- Arotography
- Trauma angiography
- Neuroangiography or Cerebral Angiography: It is the examination of cerebral blood vessels for abnormalities like aneurysms and diseases like atherosclerosis with the help of X-ray imaging guidance and administration of contrast dye.
- Coronary angiography:
It is a diagnostic test that employs X-rays to visualise the blood vessels in the heart. This test is used to determine the presence of blockages in the blood vessels that supply blood to the heart.
- Pulmonary angiography: It involves the administration of a contrast agent into the pulmonary blood vessels, followed by an X-ray imaging study. This is used to detect the presence of thrombus or blood clots in the pulmonary blood vessels.
- Abdominal angiography: It is used to examine the flow of abdominal blood vessels. This diagnostic test is used to check for any abnormality in abdominal blood flow to organs like the liver and spleen with the help of a contrast agent and X-ray imaging study.
- Renal angiography: It is a diagnostic procedure that uses imaging technology (X-ray) and contrast dye to examine the blood vessels in the kidneys. It is used to detect the presence of an aneurysm, stenosis, or a blockage in a renal blood vessel.
- Lymphangiography: It is a diagnostic test used to detect the presence of lymphatic diseases such as Lymphedema, Hodgkin lymphoma, and Lymphatic injury. Lipoidal dye is injected lymphatic vessels as a part of the test to visualise the lymphatic structures with the help of MRI or X-ray.
- Peripheral angiography or Extremity angiography: This test is used to identify the presence of any stenosis or blockage of blood vessels (arteries) that supply blood to the peripheral extremities, such as feet and legs and, in few cases in hands and arms, with the help of an X-ray imaging study and administration of contrast dye into the blood vessels.
- Retinal angiography: It is a diagnostic test where an ophthalmologist administers a yellowish colour dye into the arm blood vessels, which might take a few seconds to reach the blood vessels of the eyes and pass through the retina. The ophthalmologist observes the blood vessels (eye) and takes pictures of the retina with the help of a special camera. It is used to diagnose diabetic retinopathy, ocular melanoma, macular oedema, etc.
- Radionuclide angiography:
Radionuclide angiography (RNA) is a nuclear medicine test where a small amount of radioactive substance (radionuclide) will be inserted through arm blood vessels to track the blood cells' progress through an organ (heart) with the help of a scanner. A gamma camera is used to record the muscle at work which is further mapped with the electrocardiogram recordings. RNA is used to detect the heart muscles injuries, aneurysm, heart failure etc.
- Aortography: It is used as a standard procedure for the evaluation of peripheral vascular disease with the help of contrast dye and X-ray imaging study. It provides a clear picture of the obstruction in the aorta (main artery) that carry oxygenated blood to the lower body.
- Trauma angiography: It is used to detect the presence of traumatic arterial injuries with the help of an X-ray imaging study and administration of contrast dye into the blood vessels.
Angiogram Methods
Depending on the technique used to diagnose the blockage, there are three different methods of angiograms or angiography tests.
- Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA)
- Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA)
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA)
Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) test: A CT angiography is a medical test that combines a computed tomography scan (CT scan) with an injection of a specialised dye to create images of the tissues and blood vessels in a specific area of the body. An intravenous line will be inserted in the patient’s peripheral blood vessels, and the angiogram dye will be injected. The dye used in angiography (CT angiography) is known as a contrast substance because it "lights up" the blood vessels and tissues being investigated.
Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) test: It provides a picture of the brain's blood vessels in order to detect problems with blood flow. The technique involves inserting a catheter, a tiny, thin tube, into the brain blood vessels through an artery in the leg. The catheter is used to administer a contrast dye, and the blood vessels are imaged using X-ray technology.
Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) test:
Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is a non-invasive diagnostic procedure that combines MRI technology with intravenous (IV) contrast dye to examine blood vessels. The contrast dye makes blood vessels on the MRI picture seem opaque, allowing the interventional radiologist to see the blood vessels being assessed. Blood flow is frequently evaluated, and the heart and other soft tissues are examined with an MRA.
Angiogram vs Angiography | Differences between Angiogram and Angiography
A diagnostic approach used to diagnose flow abnormalities in the blood vessels.
| Angiography | Angiogram |
|---|---|
| It is a diagnostic procedure that is used to examine blood vessels with the help of a special dye known as a contrast agent, which will be injected into the blood vessels on standard X-rays. | It is a diagnostic image of an X-ray that depicts the blood flow in the blood vessels (arteries/arteriogram or veins/venogram) that produce through an angiography procedure. |
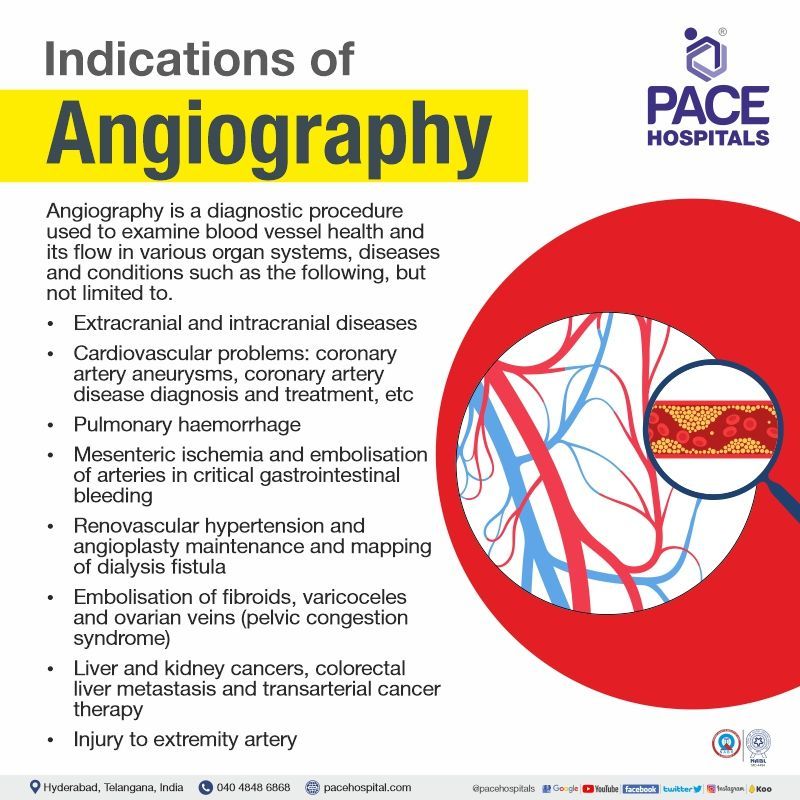
Angiography indications, Angiogram uses
Angiography is a diagnostic procedure used to observe blood vessel health and its flow in various organ systems, diseases, and conditions such as the following:
Brain
- Extracranial disease, including subclavian steal syndrome, extracranial carotid stenosis, cavernous-carotid fistula, and epistaxis.
- Intracranial disease includes cerebral vasospasm, acute stroke, cerebral arteriovenous malformations and aneurysms, subarachnoid haemorrhage without a history of trauma and WADA test.
Cardiovascular
- Peripheral vascular disease
- Thoracic and abdominal aortic aneurysm and dissection
- Coronary artery aneurysms
- Vascular malformations
- Coronary artery disease diagnosis and treatment
Gastrointestinal:
- Embolisation of arteries in critical gastrointestinal bleeding
- Mesenteric ischemia (sudden decline in blood flow through mesenteric vessels)
Pulmonary
- Pulmonary haemorrhage
Renal:
- Angioplasty maintenance and mapping of dialysis fistula
- Renovascular hypertension
Reproductive
- Ovarian veins embolisation in patients with pelvic congestion syndrome
- Embolisation of fibroids
- Varicoceles embolisation
Oncology
- Carcinoid tumours
- Hepatoma (liver cancer)
- Kidney cell cancer
- Colorectal liver metastases
- Transarterial cancer therapy (e.g., radiofrequency ablation and chemotherapy)
Trauma
- Injury to extremity artery; internal bleeding due to visceral injury and pelvic trauma
Angiography contraindications
Though the angiography procedure is safe and effective, it is not indicated for everyone. The following are the contraindications of angiography.
Absolute contraindications
Morbidly obese patients with weights exceeding 158.7 kilograms.
Relative contraindications in
- Patients with a history of allergic responses (mild) to angiography can be pretreated with corticosteroids and antihistamines.
- Patients with underlying renal dysfunction or dehydration have a considerable chance of acquiring renal function after contrasting medium administration. For this subset of patients, ultra-low contrast or zero contrast procedures have been proposed.
- Patients with a history of severe iodinated contrast medium allergy, cardiovascular system collapse, bronchospasm, angioedema, and laryngospasm. When accessible, carbon dioxide angiography could be performed on these individuals.
- Patients with pregnancy, unless there is a risk of maternal (mother/women) mortality due to uncontrollable internal bleeding.
- Patients with coagulopathy, International normalised ratio (INR) greater than 2, and platelet count lesser than 50,000/microliter are at high risk of bleeding.
- Diabetic patients on biguanides therapy might have the risk of developing lactic acidosis and worsening renal function, especially if they already have renal impairment.
- For patients who exhibit severe anxiety or are unable to lie motionless, conscious sedation may be necessary for such.
In patients with kidney, liver, or thyroid problems, cerebral angiography is contraindicated.
Preparation for the Angiogram Procedure
The patient preparation for angiography includes the following.
- An angiography eligibility evaluation may necessitate a hospital visit. Angiography is performed in the X-ray or radiology department of a hospital.
- On visiting the centre, the interventional radiologists or vascular surgeons would like to know more about the patient's medical, pregnancy and medication history, which includes the usage of over-the-counter and herbal supplements.
- People on oral hypoglycaemic agents for diabetes, antiplatelet or anticoagulant medicines, and patients with a history of hypersensitivity to iodinated angiography contrast agents should all be carefully examined before initiation of angiography test to prevent complications.
- The physician would suggest stopping certain medications before the test, which might cause procedure problems.
- The physician would perform a physical examination and prescribe blood tests (that also reveal the function of kidneys, which helps in the excretion of contrast dye) to know the patient's physical status.
- The entire procedure and risk (if any) involved will be explained clearly to the patient, and the patient will be provided with a consent form to sign, which permits the interventional radiologists or vascular surgeons to do the procedure. It is important for the patient to read the consent document carefully and ask any questions they may have before signing.
- The patient should not consume anything by mouth for eight hours prior to the angiography. A person should accompany the patient as the patient might feel drowsy for the first 24 hours post angiogram test.
- Patients undergoing conventional angiography should drink plenty of water before the procedure to lessen the likelihood of contrast medium-induced nephrotoxicity.
- The patient will be provided with a surgical gown, and their vitals, such as blood pressure, blood sugar levels (if diabetic), and electrocardiogram, will be checked before inserting the intravenous line.
Depending on the type of angiography being performed, access may be achieved through a large or medium-sized artery or veins in various different locations.
- When working on the iliac arteries, the abdominal and thoracic aorta, the upper limbs, the head, and the neck, the femoral (inserting contrast media through groin/thigh vessels) method is typically used as a retrograde approach. Its big diameter makes it suitable for the insertion of stents or occlusive aortic balloons.
- For the coronary angiogram test, the radial (inserting contrast media through forearm vessels) method has largely replaced the femoral and brachial approaches because of its lower risk of complications. The femoral approach allows for the use of larger sheaths, as well as percutaneous suture devices and collagen plugs.
- Both the antegrade femoral approach and the popliteal route are used for limb angiography.
During the Angiogram procedure
The angiogram procedure steps are as follows.
- The patient will be administered general anaesthetics, and a small incision will be made, also called an access site. Local anaesthetic is used to numb the area before an incision is made in the skin over one of the blood vessels (often in the groin or the wrist).
- In the catheter angiography procedure, a suitable long thin, flexible tube (catheter) is introduced via the access site and guided to the desired vessel via a guide wire. The patient might feel a pushing sensation during this process.
- A special dye (angiography contrast agent) will be injected through the catheter. The patient might experience transient feelings of heat, flushing, and the urge to urinate for a few seconds after the insertion of contrast dye.
- In the case of the computerised tomography technique, a cut will be placed on the blood vessel (mostly in the wrist), and an angiography contrast agent will be injected.
- Still or fluoroscopic X-ray images can be captured with the digital subtraction angiography (DSA) technique, with a frame rate of between 2 and 3 frames per second (FPS). Visual inspection can detect moderate to severe stenosis and other problems.
- In some cases, treatment can be administered simultaneously, such as the insertion of a balloon or thin tube used to dilate a constricted artery, termed angioplasty. After the angiogram procedure, the catheter will be removed (in case of catheter angiography procedure), and any bleeding will be staunched by applying pressure to the wound.
Post angiogram care
- If the patient had any cuts during the procedure, the patient would be kept for a few hours in a recovery room until the bleeding stopped.
- While withdrawing the catheter that is placed into the patient’s groin, if there is any bleeding, pressure may apply by the health care staff or nurse for up to 10 minutes to stop the bleeding.
- If the catheter was introduced into the patient's arm, a little pressurised cuff may be wrapped around the patient’s arm. Over the course of several hours, the pressure is lowered gradually.
- The patient might receive the results on the same day.
- Having a support person nearby for at least 24 hours is advisable in case of any complications.
- Drinking plenty of water is recommended, as the injected angiogram contrast dye leaves the patient’s body through urine.
- The health care staff will provide the counselling with respect to diet, follow-ups, and when to resume withdrawal medication (stopped prior to the procedure).
Recovery from angiogram procedure
- The patient might go home on the same day or the following day based on the patient's condition.
- The patient can go to regular activities the following day of discharge; however, lifting heavy objects and doing severe exercise for a few days should be avoided.
Angiogram side effects - After Angiogram complications
Even though overall angiography-related complications / side effects are uncommon, angiogram complication risks are higher in patients with elderly age, renal disease, calcified non-compliant arteries, reduced cardiac reserve, and patients with multiple comorbidities. The angiogram complications / side effects can be minor or major, such as:
Minor Side effects / Complications
- Bruising (rupture of small blood vessels)
- Vomiting sensation
- Burning sensation or hot flushes at the site of the cut
- Pain at the site of puncture
- Allergic reactions (minor) such as rashes or hives to contrast agent.
- Decline in renal function (short time/ transient)
Major Complications (Rare)
- Acute renal failure
- Anaphylactoid reaction (allergy reaction) to contrast agent causing loss of consciousness, difficulty in breathing, and dizziness
- Hematoma, or false aneurysm, significant bleeding occurs in less than 5% of angiogram tests.
Cerebral angiography complications
The following are rare significant blood vessel and brain complications such as:
- Loss of consciousness
- Hemiplegia (one side of the body paralysed)
- Bleeding or bruising at the site of the puncture.
- Transient ischemic attack
- Infection
- Loss of speech ability
Complications of coronary angiography
The following are some of the potential problems of coronary angiography:
- Heart attack
- Increased heartbeat
- Stroke
- Bleeding from the wound
- Allergic reactions to contrast dye.
Angiogram vs Angioplasty | Difference between Angiogram and Angioplasty
Angiography procedure is a method that uses X-rays to examine the blockage of blood vessels. If the cardiologist or interventional radiologist detects any blockage (stenosis) of a blood vessel, an angioplasty procedure will be used in order to widen the blood vessel and restore the blood flow.
| Angiogram | Angioplasty |
|---|---|
| It is a diagnostic tool to visualise blood vessels | It is an interventional procedure used in the treatment of blocked vessels |
| It can be performed on various parts of the body, such as the heart, brain, lungs etc. | It can be performed on the heart and peripheral arteries. |
| Used to detect the location, extent, and severity of blockages in blood vessels. | Used to widen narrowed or blocked blood vessels in addition to location, extent, and severity. |
| Risks of Bruising, soreness, and transient renal impairment. | Risks of Bleeding, blood clots, and blood vessel damage. |
CT angiography vs angiography (CT angiogram vs angiography)
Angiography is a traditional way of finding out the blocked blood vessels, where a catheter is used to insert the contrast media into the blood vessels, whereas, in CT angiography, contrast is inserted directly into the blood vessel. However, the following are the differences between CT angiogram and angiography.
| CT angiography | Angiography |
|---|---|
| It is less invasive procedure, during this contrast media inserted directly through a blood vessel. | Comparatively it is more invasive procedure, during this contrast media inserted through the artery via a catheter. |
| Less Bleeding, as it involves a vein puncture, and the contrast medium is directly injected without any catheter. | More bleeding, as it involves artery puncture and catheter insertion |
| Less accurate and liable compared to traditional angiography | More accurate and liable than CT angiography |
| 100 to 150 ml of contrast reagent use | 10 to 20 ml of contrast reagent use |
| It takes less time (20 minutes to an hour) | Comparatively it takes more time (3 to 7 hours). |
| Preferably, in younger patients with no risk factors and mild positive treadmill test. | Preferably, in patients with high-risk factors and with associated comorbidities. |
Differences between Angiogram, Arteriogram and Venogram
All these are diagnostic images that provide the visualisation of blood flow through blood vessels using X-ray technology and contrast dye; however, the differences between them are as follows:
| Angiogram | Arteriogram | Venogram |
|---|---|---|
| It depicts the blood flow in both arteries and veins | It depicts the blood flow of arteries. | It depicts the blood flow of veins. |
| It can detect blockages in both arteries and veins. | It can detect only aneurysm (Ballooning of a blood vessel), stenosis (narrowing of a blood vessel) and other blockages in arteries. | It can detect only deep vein thrombosis and other vein abnormalities. |
Differences between Arteriogram and Arteriography
These are diagnostic approaches that provide the presence of any abnormality in the blood flow of the arteries in various parts of the body; however, there is a minute difference between them.
- Arteriogram: It is an image that provides a picture of the arterial blood vessels with the help of an X-ray when a special dye is inserted in the arteries. It is obtained after arteriography.
- Arteriography: It is an invasive test that is used for the evaluation of arteries or the presence of any blockages in the arteries.
Differences between Venogram and Venography
These are diagnostic approaches that provide the presence of any venous blood flow abnormality in various parts of the body; however, there is a precise difference between them.
- Venogram: It is an image that provides a picture of the venous blood vessels with the help of an X-ray when a special dye is inserted in the veins. It is obtained after venography.
- Venography: It is an invasive test that is used for the evaluation of veins or the presence of any blockages in the veins.
Frequently asked questions:
How much does an angiogram cost in Hyderabad, Telangana?
Coronary angiogram cost in Hyderabad ranges varies from ₹ 15,000 to ₹ 20,000 (INR fifteen thousand to twenty thousand). However, price of angiogram/ angiography test in Hyderabad depends upon the multiple factors such as patient age, condition, and CGHS, ESI, EHS, insurance or corporate approvals for cashless facility.
- CT angiogram cost in Hyderabad, Telangana ranges vary from ₹ 10,000 to ₹ 15,000 (INR ten thousand to fifteen thousand).
- CT Pulmonary Angiogram cost in Hyderabad, Telangana ranges vary from ₹ 5,500 to ₹ 8,000 (INR five thousand five hundred to eight thousand).
How much does an angiography cost in India?
Coronary angiography cost in India, ranges vary from ₹ 12,000 to ₹ 22,000 (INR twelve thousand to twenty-two thousand). However, price of angiogram / angiography test in India vary in different private hospitals in different cities.
- CT angiography price in India ranges varies from ₹ 8,000 to ₹ 14,000 (INR eight thousand to fourteen thousand).
- CT pulmonary angiography cost in India ranges varies from ₹ 5,000 to ₹ 8,500 (INR five thousand to eight thousand five hundred).