Dyssynergic Defecation - Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
Patient Education Series
WHAT IS CONSTIPATION?
Constipation is one of the most common gastrointestinal complaints in the general population, and more so in females and the elderly.
It is not a disease, but a symptom of various diseases/disorders of mixed etiologies and mechanisms.
Constipation is defined as the occurrence of 2 or more of the following symptoms in the previous 12 months (without the use of laxatives):
- Fewer than 3 bowel movements per week,
- Excessive straining during at least 25 % of bowel movements,
- A feeling of incomplete evacuation after at least 25 % of bowel movements, and
- Passage of hard or pellet‐like stool during at least 25 % of bowel movements.
- Severe straining during defecation,
- A sensation of a “blockage”,
- Digital manipulation during defecation and
- A sensation of incomplete evacuation.
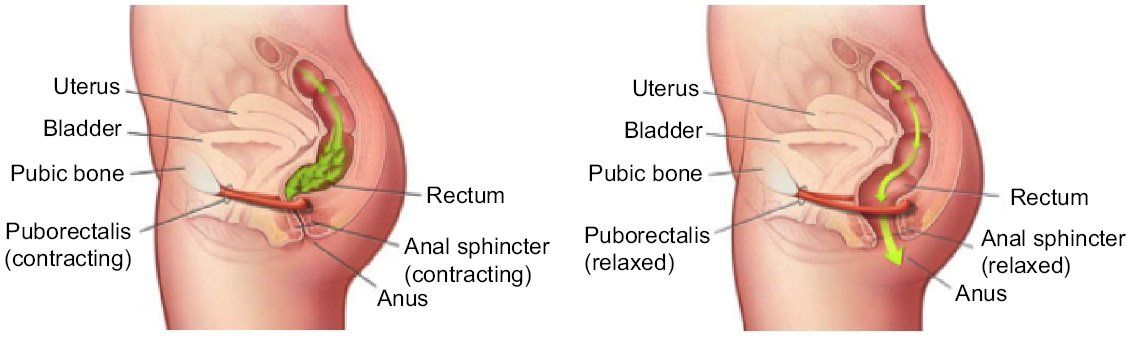
The intergrity and proper functioning of the internal and the external anal sphincters along with the pubo-rectalis muscle is essential for the process of defecation.
The physiological mechanisms of DD include inability to coordinate abdominal, rectoanal, and pelvic floor muscles during defecation because of causes such as:
- Inadequate rectal and/or abdominal propulsive force,
- Impaired anal relaxation or
- Increased anal outlet resistance as a result of paradoxical external anal sphincter or puborectalis contraction (muscles in the pelvis).
PSYCHOLOGICAL DISTRESS AND QUALITY OF LIFE
In the past the understanding of DD was poor. However, in the last decade there has been compelling evidence of significant psychological distress in patients with dyssynergia and that DD greatly impacts quality of life of the patient.This has been the driving force that had lead to the recent developments in diagnosis and management of DD.
DIAGNOSIS
The first step in making a diagnosis of DD is to exclude an underlying metabolic or pathological disorder.
When it comes to tests and investigations, a good digital rectal examination
is the first step in the cascade. It is useful to assess the resting and squeeze tone of the anal sphincter and puborectalis muscle by asking the subject to squeeze.
Slow transit constipation may co-exist in up to two thirds of patients with DD and hence, an assessment of colonic transit is useful.
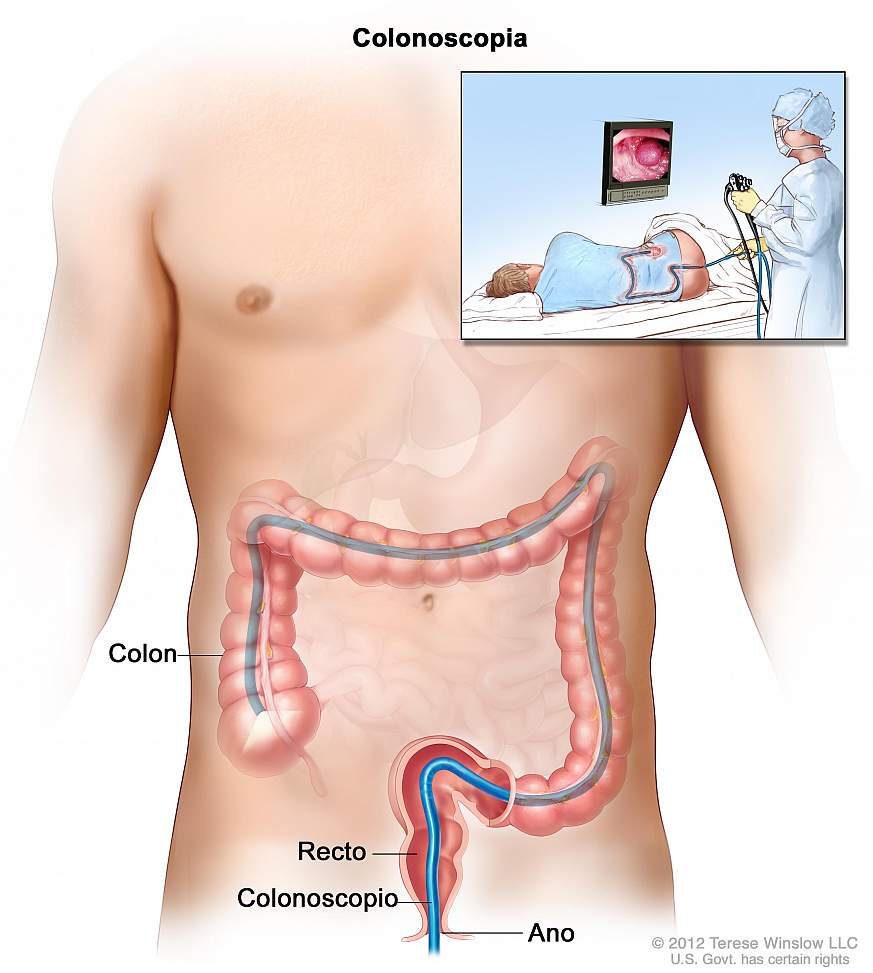
An evaluation using flexible sigmoidoscopy
will provide evidence other mucosal lesions such as solitary ulcer syndrome, inflammation or malignancy if present.
An MRI defecogram
evaluates pelvic floor anatomy and provides information on structural pathology such as rectocele, intussusception, rectal prolapse etc.
Anorectal manometry
provides assessment of dyssynergia and its subtypes together with an assessment of rectal sensation, reflexes, and compliance. It is essential for a diagnosis of DD. It detects abnormalities during attempted defecation. Normally, when a subject bears down or attempts to defecate, there is a rise in rectal pressure, which is synchronized with a relaxation of the external anal sphincter. This maneuver is under voluntary control and is primarily a learned response. The inability to perform this coordinated movement represents the key pathophysiologic abnormality in dyssynergic defecation. This may be due to inadequate pushing force, paradoxical anal sphincter contraction, impaired anal sphincter relaxation, or a combination of these mechanisms. Based on these features, at least four types of dyssynergic defecation have been recognized.
MANAGEMENT
The treatment should be customized for each individual, taking into consideration patient’s symptoms, underlying pathophysiology, age, co-morbid conditions, patient’s concerns and expectations. Treatment consists of :
- Standard treatment for constipation,
- Biofeedback therapy, and
- Other measures including colectomy and ileostomy.
Biofeedback therapy is the mainstay for treatment of DD. It is an instrument-based “operant conditioning” technique. The goals are
- To correct the dyssynergia or incoordination of abdominal and pelvic floor muscles during evacuation, and
- To improve perception of rectal filling in patients with impaired rectal sensation.
For further details and treatment contact us:
Gastroenterology Dept
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
T: 04048486868
E: info@pacehospitals.in
For Appointment, Visit: https://www.pacehospital.com/book-appointment
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868