Chronic Pancreatitis: Types, Symptoms, Causes, Risk Factors, Treatment & Prevention
Chronic pancreatitis definition
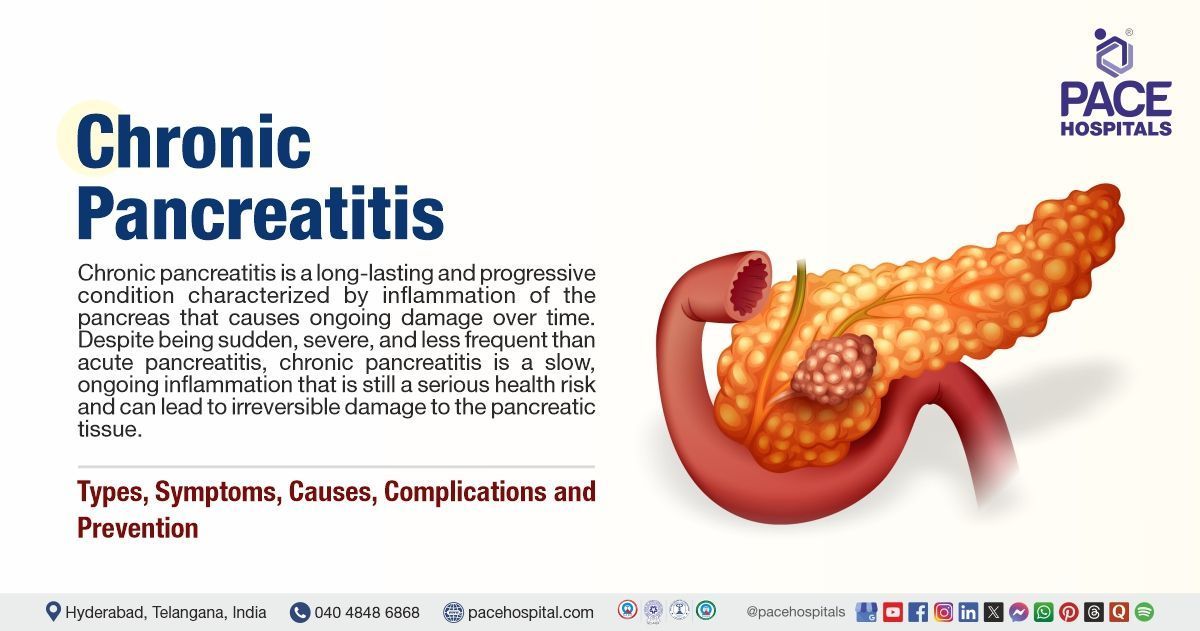
Chronic pancreatitis is a long-lasting and progressive condition characterised by inflammation of the pancreas that causes ongoing damage over time.
Despite being sudden, severe and less frequent than acute pancreatitis, chronic pancreatitis is a slow, ongoing inflammation that is still a serious health risk and can lead to irreversible damage to the pancreatic tissue.
Over time, the pancreas becomes scarred and may no longer be able to produce important digestive enzymes and insulin, leading to complications such as malabsorption, diabetes, and chronic pain.
Chronic pancreatitis meaning
- Chronic: Long term
- Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas
Incidence of Chronic Pancreatitis
Although chronic pancreatitis is less common than acute pancreatitis, it is still a serious health issue because it raises the risk of pancreatic cancer and other complications.
Globally, a small percentage of people are suffering from chronic pancreatitis, as studies show that there are between 50 and 100 cases per 100,000 people each year.
As people age, the prevalence rises, especially in those over 40. Additionally, it usually affects people who have a history of alcohol consumption and is more prevalent in men.
Approximately between 3% - 35% of people who experience acute pancreatitis for the first time can develop chronic pancreatitis over the course of three to eight years.
Estimates of the prevalence of chronic pancreatitis (CP) in South India are high, ranging from 114 to 200 cases per year.
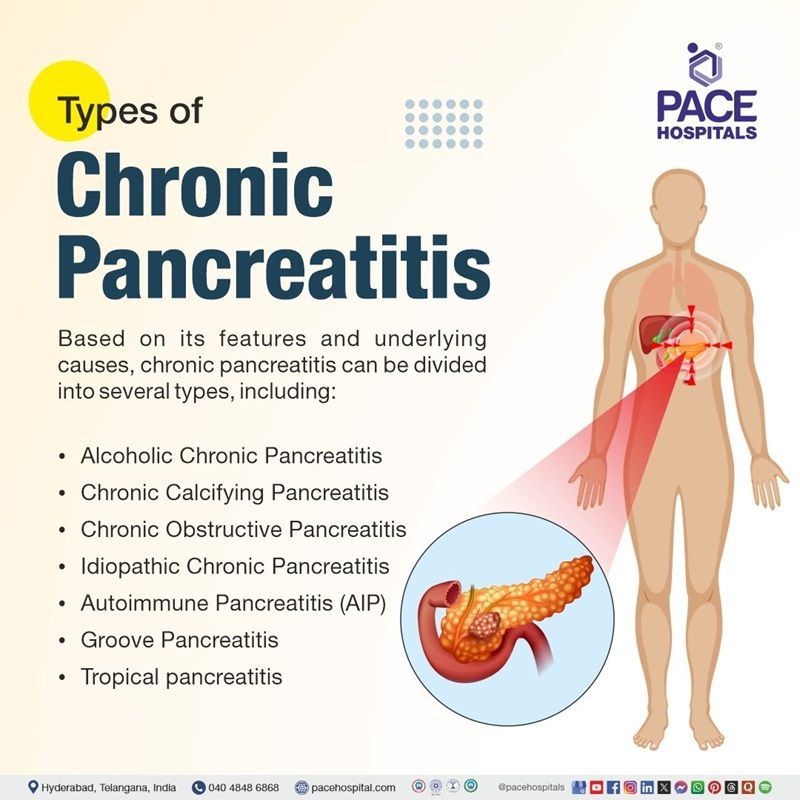
Chronic Pancreatitis Types
Based on its features and underlying causes, chronic pancreatitis can be divided into several types. A more thorough explanation of the different forms of chronic pancreatitis are mentioned here:
- Alcoholic Chronic Pancreatitis: It is the most common type of chronic pancreatitis, resulting from repeated episodes of acute pancreatitis, often caused by heavy alcohol consumption, leading to irreversible pancreatic damage.
- Chronic Calcifying Pancreatitis: The hallmarks of chronic calcific pancreatitis include extensive pancreatic calcification and fibrosis.
- Chronic Obstructive Pancreatitis: This type is caused by stenosis or blockage of the main pancreatic duct, often due to stones or cancer.
- Idiopathic Chronic Pancreatitis: In many cases, the exact cause of chronic pancreatitis remains unknown (idiopathic). Genetic factors, including mutations in the CFTR (Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator) gene, have been identified in some cases.
- Autoimmune Pancreatitis (AIP): This type is an autoimmune condition where the body's immune system attacks the pancreas.
- Type 1 AIP: A manifestation of immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD), often affecting multiple organs.
- Type 2 AIP: It is also known as idiopathic duct-centric chronic pancreatitis, and it is associated with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) but is limited to the pancreas.
- Groove Pancreatitis: This rare type primarily affects the pancreatic duodenal groove and can mimic or mask pancreatic cancer.
- Tropical pancreatitis: Diabetes mellitus, pancreatic calculi, and recurrent abdominal pain are the hallmarks of tropical pancreatitis, which is prevalent in tropical areas.
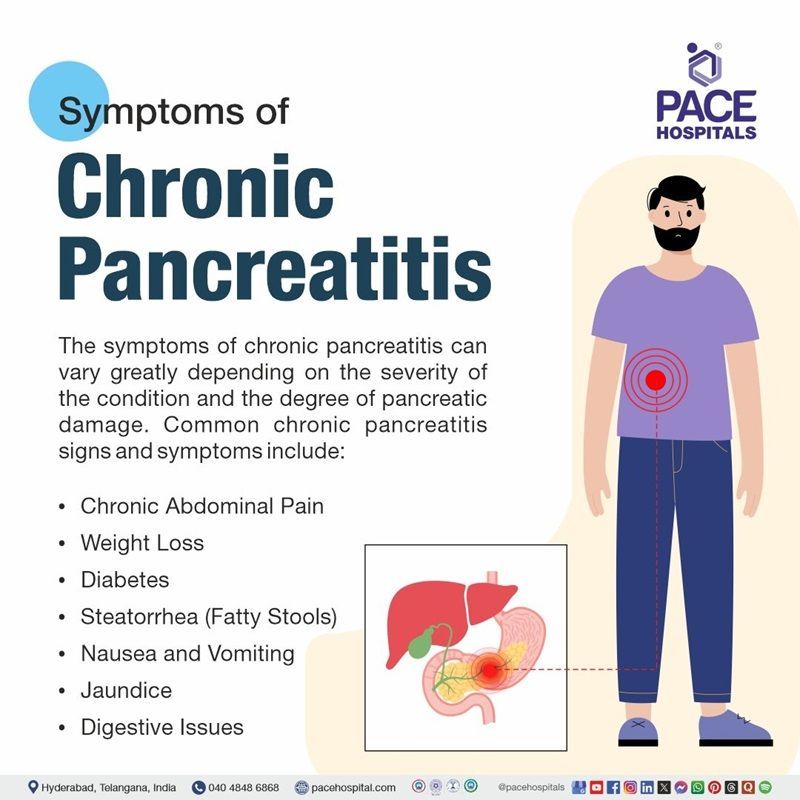
Chronic Pancreatitis Symptoms
The symptoms of chronic pancreatitis can vary greatly depending on the severity of the condition and the degree of pancreatic damage. Common chronic pancreatitis signs and symptoms include:
- Chronic Abdominal Pain: In chronic pancreatitis, abdominal pain, often described as dull, sharp, or nagging, is a primary symptom, typically occurring in the upper abdomen and radiating to the back, and can be intermittent or constant.
- Weight Loss: Weight loss is often due to impaired digestion and absorption of nutrients. The pancreas fails to produce enough digestive enzymes, leading to malabsorption, diarrhoea, and weight loss.
- Diabetes: Chronic pancreatitis can damage the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas, leading to insulin resistance or diabetes. This is particularly common in advanced cases.
- Steatorrhea (Fatty Stools): The inability to digest fats properly leads to the presence of fat in the stool, which becomes bulky, foul-smelling, and difficult to flush.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Chronic inflammation and scarring in the pancreas can lead to nausea and vomiting, especially after eating fatty or rich foods.
- Jaundice: When the bile duct becomes obstructed, it can lead to jaundice, which is characterized by yellowing of the skin and eyes.
- Digestive Issues: In some cases, chronic pancreatitis can lead to digestive problems such as indigestion, bloating, and loss of appetite.

Chronic Pancreatitis Causes
The exact cause of chronic pancreatic disease can vary, but it is often linked to one or more of the following factors:
- Heavy Alcohol Use: Excessive alcohol consumption is the leading cause of chronic pancreatitis. Alcohol can damage the pancreatic cells, causing them to become inflamed and eventually leading to scarring.
- Genetic Factors: Certain inherited genetic mutations can increase the risk of chronic pancreatitis. For example, mutations in the PRSS1, CFTR, and SPINK1 genes have been associated with hereditary pancreatitis.
- Gallstones: Gallstones can block the pancreatic duct, preventing the proper drainage of digestive enzymes, leading to inflammation and scarring of the pancreas.
- Obstruction of the Pancreatic Duct: Conditions such as tumors, cysts, or strictures in the pancreatic duct can lead to chronic inflammation and damage to the pancreas.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the pancreas, such as autoimmune pancreatitis, can lead to chronic pancreatitis.
- High Blood Lipids (Hyperlipidemia): Elevated levels of fat in the blood can damage the pancreas and lead to the development of chronic pancreatitis.
- Smoking: Smoking is another risk factor that increases the risk of chronic pancreatitis. Studies suggest that smoking combined with alcohol use significantly increases the risk of developing this condition.
- Trauma or Surgery: Injury to the pancreas or surgical procedures involving the pancreas can increase the risk of developing chronic pancreatitis.
Risk Factors of Chronic Pancreatitis
Several environmental and genetic factors can contribute to an increasing risk of chronic pancreatitis, such as:
- Excess alcohol consumption: Alcohol abuse is the most common cause associated with chronic pancreatitis, which accounts for approximately 65% of all cases. Research shows that the risk of pancreatitis increases with having four or five drinks of alcohol per day. Alcohol abuse raises the risk of progression from acute to chronic pancreatitis.
- Age: Chronic pancreatitis can occur at any age. However, the risk increases as the person ages due to the changes in the pancreas, including a reduction in blood flow to the pancreatic tissue.
- Family History: Some people experience chronic pancreatitis not due to alcohol abuse; instead, factors such as a family history of chronic pancreatitis or pancreatic cancer can increase the risk.
- Smoking: It poses a significant contribution to the development of multiple long-term conditions, including pancreatitis, by promoting inflammation and oxidative stress, leading to further damage and the onset of chronic pancreatitis.
- Obesity and poor diet: The obesity pandemic poses a unique set of problems for pancreatitis, both by increasing pancreatitis incidence and acute pancreatitis severity. A diet high in fats and low in nutrients can increase the risk of chronic pancreatitis. A healthy diet may help prevent the condition.
- Genetic Predisposition: Inherited genetic conditions such as cystic fibrosis or mutations in the PRSS1 gene may increase the likelihood of chronic pancreatitis.

Chronic Pancreatitis Complications
Over time, chronic inflammation due to chronic pancreatitis leads to the development of parenchymal fibrosis, progressing to end-stage pancreatitis, characterized by complications such as:
- Pancreatic Cancer: CP can increase the risk of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC: a common type of pancreatic cancer) due to chronic inflammation, as it further causes scar tissues and damages the pancreas.
- Diabetes: Endocrine dysfunction and the subsequent insufficiency (failure of the endocrine system) associated with chronic pancreatitis lead to the development of diabetes mellitus (DM) due to the damage to the insulin-producing cells, requiring lifelong insulin therapy.
- Metabolic Bone Disease: It is another common complication in chronic pancreatitis, which is occasionally termed CP-associated osteopathy. About 66% of people have this condition, which includes both osteopenia and osteoporosis. Similarly, many studies have demonstrated an increased risk of low-trauma fractures in patients with CP.
- Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency (EPI): It develops due to inadequate production or secretion of pancreatic enzymes. Symptoms of mild EPI are mostly related to fat malabsorption and include abdominal bloating, cramping, and gas, while symptoms of severe EPI include unexplained weight loss and steatorrhea (Fatty stool).
- Splenic Vein Thrombosis (SVT): The splenic vein is more commonly affected than the portal or superior mesenteric veins due to the lower levels of inflammation in CP. It is estimated that (SVT) develops in approximately 10–20% of patients with CP.
- Pseudocysts: Pancreatic Pseudocyst prevalence in CP patients has been reported to be between 20 and 40 percent; however, this may be overstated because peripancreatic fluid collections have been reclassified under different terminology.
- Duodenal Obstruction: It is another local complication associated with CP. Among hospitalized patients with acute or chronic pancreatitis, the incidence of duodenal obstruction is approximately 1%.
Chronic Pancreatitis Diagnosis
The diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis is often challenging as it requires a combination of clinical, laboratory, and imaging studies:
Blood Tests
- Amylase and Lipase
- Trypsinogen
- Faecal Fat Test
- Stool Elastase Test
Imaging Studies
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)
Minimally invasive tests
- Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
- Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
Other Tests
- Bentiromide Test
- Pancreatic Function Test (PFT)
Chronic Pancreatitis Treatment
Treatment of chronic pancreatitis aims to relieve symptoms, manage complications, and prevent further damage to the pancreas. Treatment options include:
- Pain Management
- Pain relief
- Analgesics
- Nerve Blocks
- Pancreatic Enzyme Replacement
- Pancreatic enzyme supplements
- Surgical Interventions
- Drainage Procedures
- Pancreatectomy and Auto Islet Transplantation
- Whipple Procedure (Pancreaticoduodenectomy)
- Puestow Procedure (Longitudinal Pancreaticojejunostomy)
- Frey Procedure
- Insulin Therapy
- Insulin therapy (If diabetes develops)

Chronic Pancreatitis Prevention
While chronic pancreatitis cannot always be prevented, specific lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk:
- Avoid Excessive Alcohol Consumption
- Quitting Smoking
- Maintaining a Healthy Diet
- Exercising Regularly
- Addressing underlying conditions
Difference between Acute Pancreatitis and Chronic pancreatitis
Acute vs chronic pancreatitis
Pancreatitis refers to the inflammation of the pancreas, and it can occur in two distinct forms: acute and chronic. While both conditions involve inflammation, they differ in their onset, duration, causes, and long-term effects, such as:
| Elements | Acute pancreatitis | Chronic pancreatitis |
|---|---|---|
| What it is | Sudden inflammation of the pancreas | Long-term, progressive inflammation of the pancreas |
| Causes | Gallstones, alcohol use, high triglycerides, infections, trauma | Chronic alcohol abuse, genetic factors, autoimmune conditions, ductal obstructions |
| Duration | Short-term (days to weeks) | Long-term (months to years) |
| Onset | Sudden, rapid onset | Gradual onset with periods of exacerbation |
| Symptoms | Severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever | Persistent abdominal pain, weight loss, malabsorption, steatorrhea |
| Pancreatic Function | Normal pancreatic function post-recovery | Impaired pancreatic function (e.g., insulin and digestive enzyme deficiency) |
| Complications | Pancreatic necrosis, pseudocysts, organ failure | Diabetes, pancreatic cancer, malnutrition, pancreatic insufficiency |
| Treatment | Supportive care (hydration, pain control, treating underlying cause) | Lifestyle changes (avoid alcohol), pain management, enzyme replacement therapy |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Chronic Pancreatitis (CP)
How long does chronic pancreatitis last?
Chronic pancreatitis is a long-term condition that lasts for years and often progresses over time. It typically does not resolve on its own, and the symptoms can be managed but may persist or worsen, leading to complications such as diabetes or pancreatic insufficiency. The duration depends on the severity, underlying causes, and management strategies.
Can chronic pancreatitis be reversed?
Unlike acute pancreatitis, it cannot be fully reversed as it causes permanent damage to the pancreas. However, treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing further damage.
Is chronic pancreatitis life-threatening?
Chronic pancreatitis itself is not typically outright life-threatening but may cause grave complications like pancreatic cancer, diabetes, malnutrition, and failure of organs, which would be life-threatening if untreated.
Can chronic pancreatitis be confused with cancer?
Yes, chronic pancreatitis can be mistaken for pancreatic cancer due to similar symptoms, such as weight loss, jaundice, and abdominal pain. Imaging tests are crucial to differentiate the two conditions.
Can chronic pancreatitis be cured?
Chronic pancreatitis is not curable, but symptoms can be managed through lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes surgery.
What is chronic calcific pancreatitis?
Chronic calcific pancreatitis is a particular form of chronic pancreatitis in which calcium deposits (pancreatic stones) develop within the pancreas as a result of chronic inflammation and injury. The repetitive insult over time leads to fibrosis, and this impairs the function of the pancreas as well as forming further stones, which causes gastrointestinal problems and possible complications like diabetes.
When does acute pancreatitis become chronic?
Acute pancreatitis becomes chronic when repeated episodes of inflammation cause irreversible damage to the pancreas, leading to scarring, loss of function, and ongoing symptoms over time.
Can I gain weight with chronic pancreatitis?
Weight gain in chronic pancreatitis is uncommon. Most individuals experience weight loss due to malabsorption, pancreatic enzyme deficiency, and decreased appetite, although weight gain can occur if the condition is well-managed.
Can a healthy diet help with chronic pancreatitis?
Yes, a healthy, balanced diet can decrease the workload on the pancreas, enhance digestion, and helps avoid malnutrition in patients with chronic pancreatitis.
Can I live a long life with chronic pancreatitis?
The long-term survival of chronic pancreatitis patients shows a mortality rate of around 80% after 20 years in smokers and after 30 years in non-smokers. While chronic pancreatitis is a serious condition that can impact life expectancy, with proper management and lifestyle changes, many people can live long and relatively normal lives.
What disease is the highest rate associated with chronic pancreatitis?
Diabetes (26.32%) was the most common comorbidity in chronic pancreatic patients. Approximately 26.32% of patients with chronic pancreatitis develop diabetes, which can lead to further complications and a decreased quality of life. In addition to diabetes, CP patients face an increased risk of pancreatic cancer, which is a serious concern as it accounts for a substantial portion of cancer-related mortality in these individuals.
What is the average age for chronic pancreatitis?
Chronic pancreatitis is a progressive disorder associated with the destruction of the pancreas, which is more common in men and usually develops in individuals between 30 and 40 years of age.
What test confirms chronic pancreatitis?
ERCP is a sensitive and specific test for diagnosing chronic pancreatitis. However, no single test definitively confirms chronic pancreatitis; a combination of imaging studies (CT, ERCP, EUS, MRCP) and functional tests are utilized to diagnose the condition.
What are 10 amazing foods to heal your pancreas?
To support a healthy pancreas, incorporating certain foods can help, such as whole grains (e.g., quinoa and brown rice), lean proteins (e.g., fish and chicken), leafy greens (e.g., kale and spinach), berries, avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, sweet potatoes, and turmeric.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868