Thyroid Disease: Types, Causes, Symptoms, Complications, Treatment & Prevention
Thyroid disease definition
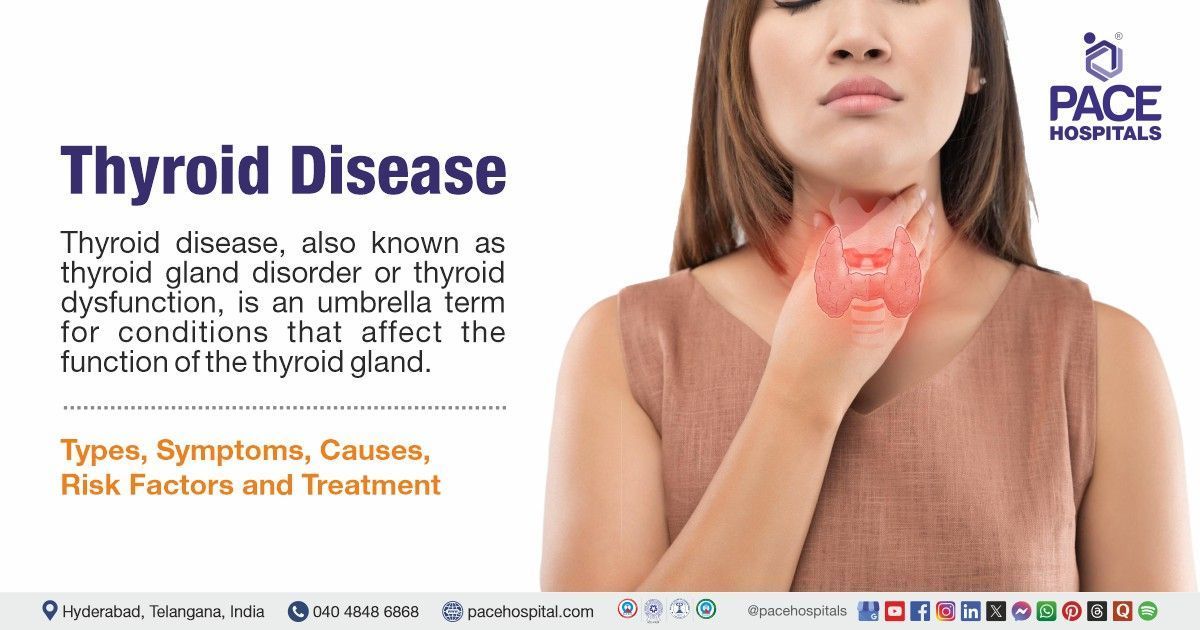
Thyroid disease, also known as thyroid gland disorder or thyroid dysfunction, is an umbrella term for conditions that affect the function of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland (a butterfly-shaped, two-lobed endocrine gland located in the front of the neck) produces hormones (t3: triiodothyronine and t4: tetraiodothyronine), to regulate various functions in the body, including metabolism, breathing, digestion etc. Any abnormalities (either too much or too little) in the production of thyroid hormones lead to thyroid diseases, which are caused mainly by autoimmune conditions or deficiency of iodine.
Heart disease, osteoporosis, and infertility are some complications that could arise if a patient with thyroid disorders goes undiagnosed. Thyroid disease treatment includes pharmacological therapy (Such as thyroid medications) and surgical interventions (like thyroidectomy). Depending on the type of thyroid disorder, the endocrinologists will opt for either.
Prevalence of Thyroid Disease
Global prevalence of thyroid disease
Across the world, thyroid diseases are one of the most prevalent endocrinopathies. It is estimated that about 20 crore people globally are diagnosed with thyroid disease, with hypothyroidism (1-2%) and hyperthyroidism (0.2-1.3%) being common, and autoimmune thyroid diseases, like Hashimoto's and Graves' disease, frequently being the causes.
Prevalence of thyroid disease in India
According to epidemiological studies, thyroid nodules are clinically found in 1% of men and 5% of women, and their frequency rises with age and in iodine-deficient populations.
In India, about 4.2 crore people suffer from thyroid disease, making it the most common endocrine disorder. As per an Indian research study (a population-based study done in Cochin), the prevalence of hypothyroidism and subclinical hypothyroidism was reported as 3.9% and 9.4%, respectively. The prevalence in women (11.4%) is higher than in men (6.2%). In the iodine-sufficient areas, congenital hypothyroidism affects about one newborn in every 3500–4000 births.
It is well-understood that thyroid disease is not a major cause of mortality. However, it does cause significant complications which lead to disability.
Thyroid disease in women
People of all ages are prone to have thyroid disorders. Thyroid disease in more frequently affected in women than men. The thyroid's functioning greatly influences a woman's reproductive, menopause, pregnancy, post-partum, puberty, and menstruation. The types of thyroid disorder in females are similar to those in males, such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism.

Types of Thyroid Disease
In general, there are 2 types of thyroid disease, which are as follows.
As per a few research reports, there are different types of thyroid gland diseases, including Hyperthyroidism, Hypothyroidism, Hashimoto's thyroiditis (An autoimmune disease), goiter, thyroid nodules, and thyroid cancer.
Hyperthyroidism
It occurs when the thyroid gland releases an excessive thyroid hormone into the bloodstream.
Hypothyroidism
It occurs when the thyroid gland fails to release the required hormones into the bloodstream.
Hashimoto's thyroiditis
It is an autoimmune disease where the thyroid cells are attacked by the immune system, resulting in an insufficient amount of thyroid hormone production.
Goiter
It is a thyroid disease characterized by enlargement of the thyroid gland, which is caused by iodine deficiency.
Thyroid nodules
It is an abnormal growth (Usually non-cancerous) of thyroid gland cells, which are often asymptomatic.
Thyroid cancer
It is a cancerous condition of the thyroid where the thyroid cells mutate and multiply, resulting in the formation of a tumor.
Cretinism
A condition caused by decreased activity of the thyroid gland at birth (congenital hypothyroidism), resulting in developmental delay, growth retardation, and other abnormal features.
Thyroid Disease Causes
The causes of thyroid gland disorders vary based on several factors. The common causes of thyroid disease are autoimmune diseases such as Hashimoto's disease and Graves' disease, which attack the thyroid gland and can cause glandular destruction, leading to hormone imbalance (hypothyroidism/hyperthyroidism) or thyroid hormone overproduction (thyrotoxicosis).
Other common causes of thyroid disease include:
- Radiation Therapy
- Drug-induced
- Congenital hypothyroidism
- Infiltrative disorders
- Post-partum thyroiditis
- Subacute thyroiditis
- Thyroidectomy
- Toxic adenoma, toxic multinodular Goiter, or Plummer's disease
- Thyroiditis
- Iodine induces hyperthyroidism
- Hypothalamic disease
Rare causes such as:
- Isolated TSH deficiency
- Hypopituitarism
- Radiation Therapy: Exposure to radiation (as a part of treatment) increases the risk of hypothyroidism and benign thyroid nodules.
- Drug-induced thyroid dysfunction: Intake of certain drugs (as a part of treatment), such as glucocorticoids, anticancer agents, and antiarrhythmics, can alter the production and secretion of thyrotrophin (thyroid-stimulating hormone), resulting in a decrease in the production of thyroid hormone.
- Congenital hypothyroidism: This is a thyroid hormone deficiency that occurs at birth, which is mostly caused by an abnormality in thyroid gland development or thyroid hormone biosynthesis disorder, resulting in hypothyroidism.
- Infiltrative disorders: These are caused by the deposition of abnormal substances in the thyroid, hypothalamus, or pituitary, resulting in damage to these organs and leading to infiltrative diseases. For instance, scleroderma can induce hypothyroidism, as it results in fibrosis of the thyroid gland.
- Post-partum thyroiditis: It is the condition where a woman's thyroid gland is swollen after giving birth to a child, resulting in an overactive thyroid or hyperthyroidism. The exact cause of this condition is idiopathic (unknown); however, this condition affects a small percentage of pregnant women.
- Subacute thyroiditis: It is a condition where the body's immune system attacks the thyroid gland, which is often followed by upper respiratory tract infection. It occurs due to viral infection of the throat and ear, flu, or common cold. The subacute thyroiditis occurs after a few weeks of infection.
- Thyroidectomy: It is the surgical removal of the thyroid gland, used to treat hormonal diseases, cancers, and benign diseases that do not respond to medical management. This procedure leads to low or absence of thyroid hormone production, resulting in hypothyroidism.
- Toxic adenoma, toxic multinodular Goitre, or Plummer's disease: It is an active multinodular goitre that contains one or more autonomously functioning nodules, which results in hyperthyroidism.
- Thyroiditis: It is the group of conditions that results in inflammation of the thyroid gland, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, leading to underactive thyroid or hypothyroidism.
- Iodine induces hyperthyroidism: It is caused by sudden exposure to excess iodine, resulting in the synthesis and release of excess thyroid hormones.
- Hypothalamic disease: The hypothalamus is a gland that controls the hormone system that releases hormones to the pituitary gland, which controls the release of thyroid-stimulating hormones (TSH). Diseases that occur in the hypothalamus can lead to abnormal release of TSH, resulting in thyroid diseases.
- Isolated TSH deficiency: It is a rare type of congenital hypothyroidism (central), an autosomal recessive disease characterized by decreased levels of thyroid hormones (hypothyroidism) due to a deficiency in TSH synthesis. This results in severe mental and growth retardations.
- Hypopituitarism: It is an inactive condition of the pituitary gland, where it doesn’t make enough hormones, resulting in hypothyroidism. Hypopituitarism is caused by autoimmune diseases, pituitary tumors, low blood supply to the pituitary gland, sarcoidosis, amyloidosis, genetic diseases, etc.
Causes of thyroid disease in females
The thyroid causes in females are mainly due to the presence of autoimmune conditions, which might occur due to the effects of sex steroids on the immune system. Several research studies have demonstrated the exacerbation of autoimmune conditions during pregnancy (due to high oestrogen and progesterone levels) and post-partum (after childbirth) period, resulting in thyroid gland problems.
In addition, few studies estimated the immune inhibitory cytokines that are produced by the mother, placenta, or foetus inhibit the immune response during pregnancy. Decrease in these inhibitors after childbirth results in the beginning or exacerbation of autoimmune diseases.

Thyroid Disease Symptoms
Persons with thyroid disease can experience a variety of symptoms. Unfortunately, thyroid disease symptoms closely resemble the signs of other medical conditions and stages of life, which makes it difficult to identify whether these symptoms are related to thyroid disease or other conditions. The following are the common thyroid disease symptoms:
Hyperthyroid Symptoms (high thyroid symptoms/ overactive thyroid symptoms)
- Increased sweating
- Heat sensitivity
- Hyperactivity
- Feeling tensed
- Increased heart rate
- Increase in systolic blood pressure
- Decrease in menstrual flow
- Eyelid lag (higher upper eyelid than normal)
- Tremor in the hands
- Weakness in muscles
- Decrease in weight
Hypothyroid Symptoms (low thyroid symptoms/ underactive thyroid symptoms)
- Feeling cold
- Voice changes (hoarse)
- Difficulty in passing stool
- Mild weight gain
- Difficulty in concentrating
- Diffuse alopecia (loss of hair)
- Feeling sleepy for a long time
- Muscle and joint pain
- Hearing problem
- Depression
- Dry skin
- Dyspnoea (shortness of breath)
- Menorrhagia (heavy periods)
- Fluid accumulation in hands and feet
- Cold peripheral extremities
- Cavity effusions
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Late tendon reflex relaxation
- Bradycardia (slow heart rate)
- Puffiness around the face, feet, and hands
Symptoms of thyroid disease in females
The thyroid disease symptoms in women might include tiredness, difficulty passing the stools, menstrual irregularities, infertility, muscle cramps, weight gain, cold intolerance, depression, brittle nails, and difficulty concentrating in patients suffering from primary and central hypothyroidism.
Complications of Thyroid Disease
Untreated or poorly managed thyroid disease, whether hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) or hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid), can lead to many serious health complications, including heart problems, bone issues, fertility problems, and in severe cases, life-threatening conditions.
Complications of Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid)
- Heart problems
- Bone issues
- Eye problems (Graves' Ophthalmopathy)
- Thyrotoxic crisis (Thyroid Storm)
- Skin problems (Graves' Dermopathy)
Complications of Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid)
- Heart problems
- Nerve damage (Peripheral Neuropathy)
- Infertility
- Mental health issues
- Goiter
Thyroid Disease Diagnosis
Thyroid disease diagnosis can be challenging for an endocrinologist, as the symptoms resemble those of other conditions. The following are the diagnostic tests that are used to detect thyroid problems, including:
- Physical examination
- Thyroid blood test
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
- Total T4 (Tetraiodothyronine)
- Free T4 (Tetraiodothyronine)
- Total T3 (Triiodothyronine)
- Free T3 (Triiodothyronine)
- Radioactive iodine uptake test
- Thyroid peroxidase antibodies
- Thyroglobulin antibodies
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) receptor antibodies
- Calcitonin
- Thyroid imaging tests
- Ultrasound
- Thyroid scan
Thyroid Disease Treatment
The primary goal of thyroid disease treatment is to normalize the abnormal thyroid levels, and this can be done through either thyroid medications (pharmacological) or thyroid surgery.
If the patient has high levels of thyroid hormones (hyperthyroidism)
- Thyroid medications (pharmacological management):
- Anti-thyroid drugs
- Radioactive iodine
- Beta-blockers
- Thyroid surgery:
- Thyroidectomy
If the patient has low levels of thyroid hormones (hypothyroidism) and Hashimoto's thyroiditis:
- Thyroid replacement medication or hormone replacement therapy

Prevention of Thyroid Disease
The prevention of thyroid disease is not possible as autoimmune diseases are the major cause. However, the following measures can aid in minimizing the risk of developing thyroid diseases:
- Abstain smoking: Smoking can negatively impact thyroid function and increase the risk of thyroid disorders, so avoiding it is crucial for maintaining hormonal balance.
- Regular thyroid screening: Consistent thyroid screening helps detect any early signs of thyroid dysfunction, ensuring timely treatment and preventing complications.
- Limited soy intake: Soy contains compounds that may interfere with thyroid hormone production, so moderating its intake can help prevent potential thyroid issues.
- Avoiding processed food: Processed foods often contain unhealthy fats, excessive sugars, and artificial additives that can disrupt hormone balance, including thyroid function.
- Reducing stress: Chronic stress can impact thyroid health by increasing cortisol levels, which may interfere with thyroid hormone production and overall well-being.
- Intake of required iodized salt: Iodine is essential for thyroid hormone production, and consuming iodized salt ensures adequate iodine intake to support healthy thyroid function.
Thyroid prevention foods
The following are the foods to avoid for thyroid patients or supplements that aid in preventing thyroid inflammation or worsening the thyroid condition.
Hyperthyroidism
- Excess iodized salt
- Dairy products
- Iodine supplements
- Egg yolk
- Baked food items
- Gluten diet
- Caffeine
Hypothyroidism
- Large amount of goitrogens
- Soy products (soy milk, soy sauce, etc.)
- Gluten diet
- Ultra-processed foods and added sugars
Thyroid diet
A well-maintained thyroid diet plays a pivotal role in managing and reducing the risk of thyroid diseases. The thyroid diet plan should include micronutrients such as zinc, iodine, iron, selenium, and vitamins B12, D3, and A that consist of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, thereby reducing body fat, thyroid autoantibodies, and improving thyroid function.
Maintaining a high consumption of a Mediterranean diet (that consists of fruits, whole grains, vegetables, and healthy fats), low consumption of meat, and complete consumption of lactose and gluten aids in reducing thyroid symptoms.
Diet for People with Thyroid Issues
The following are the best foods for thyroid patients that aid in decreasing symptoms, such as
- Daily consumption of vegetables and fruits for a minimum of five servings
- Daily consumption of water and fluids in large volumes
- Daily consumption of a diet rich in whole grains, rice, and fiber
- Usage of unsaturated fats in cooking
- Intake of a diet rich in low-fat proteins such as beans, fish & legumes.
Differences between a Normal neck and an Enlarged thyroid
Normal neck vs Enlarged thyroid
The neck is a vital part of the body, supporting the head and facilitating essential functions like breathing, swallowing, and movement. However, variations in the neck’s appearance or size can sometimes signal different underlying health conditions or anatomical differences. Here are some variations of normal and enlarged necks:
| Elements | Normal neck | Enlarged thyroid |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Absence of bulge or swelling | The presence of a bulge or swelling at the front of the neck |
| Size of Thyroid Gland | Normal butterfly shape, absence of a lump | Enlarged thyroid gland with the presence of a lump or mass that can be sensed with touch. |
| Movement | Moves freely while swallowing | Less freely movable while swallowing |
| Thyroid levels | Normal levels | Abnormal levels |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Thyroid Disease
What are the long-term effects of thyroid disease?
The thyroid gland is the main organ responsible for producing hormones that affect various body functions. Long-term effects of thyroid disease include goitre, heart problems, peripheral nerve damage, depression, myxoedema, infertility, birth defects, obesity, joint pain, weak, brittle bones, and severe eye problems such as Graves' ophthalmopathy and Graves' dermopathy (redness and swelling in the skin).
Can thyroid problems cause kidney disease?
Yes, thyroid problems can cause kidney disease as thyroid hormones increase renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) through both pre-renal and intrinsic renal effects. Hyperthyroidism results in an increase in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone pathway and GFR, but hypothyroidism is associated with decreased GFR.
Does thyroid disease affect milk supply?
Yes, thyroid dysfunction is a leading cause of hormonal problems that impact milk production. Thyroid hormone levels in women may fluctuate during pregnancy and immediately after delivery, which might impact milk production. Because a small amount of thyroid hormone reaches the baby through breast milk, the baby's thyroid levels may also need to be checked regularly after birth, depending on the mother’s medication intake.
Is thyroid curable?
Thyroid diseases are generally manageable with lifelong hormone treatments, medications, radioiodine therapies, or surgeries, but they are not always curable. Proper treatment helps manage symptoms and prevent complications, though ongoing care is often necessary.
Does thyroid disease cause hives?
Yes, patients suffering from thyroid autoimmunity can have hives. As per the research study,4.3% to 57.4% of patients had shown chronic spontaneous hives (symptoms that persist for more than six weeks) that are associated with autoimmune thyroid disease.
Is thyroid a communicable disease?
No, thyroid hormone secretion abnormalities are not contagious and cannot be spread through bodily fluids, insect bites, or inhaled viruses. It can be passed down only through genetic transmission (parent to child).
What is thyroid disease in females?
Thyroid disease in women can affect women of any age. Overactive or underactive thyroid gland has a major impact on a woman's reproductive system.
Too low or high thyroid hormone levels can cause:
- Very light or very heavy periods, irregular or absent menstrual periods.
- Ovulation may also be affected. Women with an underactive thyroid have a higher risk of developing cysts in their ovaries. Extreme hypothyroidism has been linked to breast milk production while preventing ovulation.
- Miscarriages, premature births, stillbirths, and post-partum bleeding have all been associated with a deficiency of thyroid hormone. Pregnant women with an overactive thyroid are more likely to experience severe morning sickness.
- May cause the early onset of menopause (in the early 40s).
Does Graves' disease go away after the thyroid is removed?
Yes, in the majority of cases, total thyroidectomy (removal of the thyroid gland) is the optimal treatment for hyperthyroidism caused by Graves' disease, and it has the added benefits such as:
- Reducing the risk of disease recurrence
- Discontinuation of anti-thyroid drugs (ATD) and radioactive iodine (RAI), thus avoiding RAI and ATD-associated side effects.
How is autoimmune thyroid disease treated?
Graves' disease and Hashimoto's disease are the autoimmune disorders that cause the occurrence of thyroid disease. Anti-thyroid medications, beta-blockers, radioiodine therapy, and thyroid surgery are the treatment options for Graves' disease. T4 and T3, hormone replacement therapy, are the treatment options for Hashimoto's disease.
How is thyroid eye disease treated?
Thyroid eye disease (TED), an autoimmune condition and eye disorder, causes inflammation (swelling) and damage to the fatty tissue, muscles, and connective tissue around the eye. The endocrinologist will try to treat the thyroid condition if the patient has it.
In addition to that, the endocrinologist may prescribe anti-inflammatory medications, other systemic steroids to reduce inflammation, and eye drops to relieve irritation and dryness. Eyelid, eye muscle, and orbital decompression surgery are options for treating thyroid eye disease. In some cases, the endocrinologist might opt for radiation therapy.
Which symptoms of thyroid disease are seen in older adults?
The common symptoms of hypothyroidism in elderly patients include fatigue, increased weight, cold intolerance, change in voice (hoarse), difficulty in passing stool, and myalgias. Hyperthyroidism includes a decrease in weight, sweating or heat intolerance, feeling tensed, tiredness, muscle weakness, and shortness of breath.
Does thyroid disease run in families?
Yes, thyroid disease runs in families because genetics plays a role in determining thyroid hormone and thyrotropin (TSH) concentrations, as well as susceptibility to autoimmune thyroid disease.
Does thyroid eye disease cause headaches?
Yes, swelling and inflammation are the characteristic features of Graves’ eye disease, also termed thyroid eye disease.
Progressive swelling may cause:
- Increased pressure inside the eye socket
- Headache or pressure pain that gets worse with eye movements.
- Reduced vision occurs when swollen tissues press against the optic nerve.
Does thyroid disease cause high blood pressure?
Yes, hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can both increase the risk of high blood pressure (Hypertension). Lipid abnormalities are found in patients with thyroid dysfunction, which can cause atherosclerotic changes (the accumulation of fat, cholesterol and other substances accumulate in the blood artery walls) in the blood vessels, leading to a rise in blood pressure.
Can you have Hashimoto's disease without a thyroid?
No, a person cannot have Hashimoto's disease without a thyroid gland, as it is an autoimmune disorder, where the immune system makes antibodies that attack thyroid cells, causing hyperthyroidism.
What is polycystic thyroid disease?
Polycystic thyroid disease is a rare cause of hypothyroidism characterised by multiple thyroid cysts that are detected through ultrasonography. High iodine consumption increases the risk of developing polycystic thyroid disease, leading to hypothyroidism.
How to treat thyroid disease naturally?
To support thyroid health naturally, focus on a balanced diet rich in iodine, selenium, and zinc, as these nutrients are vital for thyroid function. Additionally, manage stress through relaxation techniques, regular exercise, and adequate sleep. Always consult a healthcare professional before making significant changes.
How to avoid thyroid disease?
Thyroid diseases can be prevented by
- Avoiding processed foods, as many chemicals can alter thyroid hormone production.
- Quitting smoking
- By practicing meditation or any changes in lifestyle in order to reduce stress.
- Avoiding foods rich in soy and gluten.
- An appropriate amount of iodine intake.
As per the WHO recommendations, the daily intake of iodine is as follows.
| Group | µg per day |
|---|---|
| Infants (0‐59 months) | 90 µg/day |
| School children (6‐12 years) | 120 µg/day |
| Adolescents | 150 µg/day |
| Pregnant and lactating women | 200 µg/day |
Related Articles



Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868