Interstitial lung disease (ILD) - Symptoms, Causes, Complications, Treatment and Prevention
Definition of interstitial lung disease
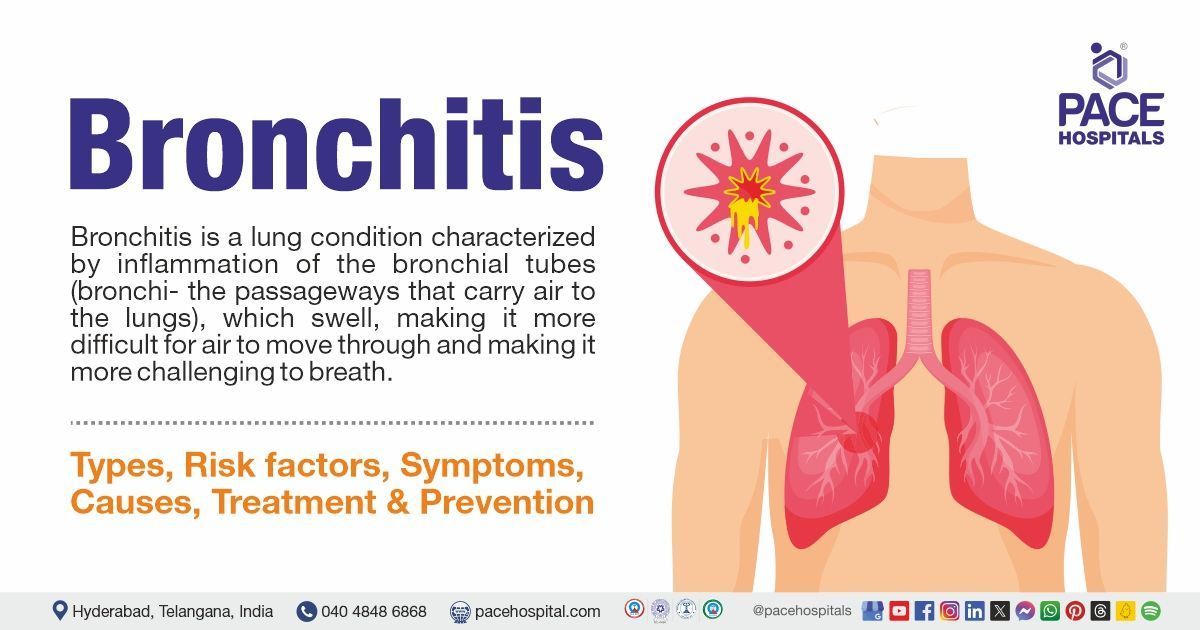
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) or Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia (IIP) is an umbrella term for a large group of diseases that cause scarring (fibrosis) of the lungs. This results in increased stiffness and loss of usual lung elasticity, a decrease in the oxygenation process, and resulting breathlessness and cough, leading to a poor quality of life. ILDs are usually treated by specialized pulmonologists.
History of interstitial lung disease
In 1872, a German physician, Von Buhl, described some cases of desquamative pneumonia in his letters to a friend, which may be the first description of pulmonary fibrosis. In 1892, William Osler (regarded as the father of modern medicine), in his medical textbook, coined the term Cirrhosis of the Lung. Following the above two physicians, many terms were used for these diseases, including Hamman-Rich syndrome, cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis and muscular cirrhosis of the lung, etc.
Prevalence of interstitial lung disease
Worldwide
According to a recent study using Global Burden of Disease data, the global incidence of ILDs has increased by 51% over the last decade, from 313.2 cases in 1990 to 207.2 cases per 100,000 cases in 2019. These published estimates show a noticeable variance in ILD epidemiology between countries.
India
According to a study of 3,089 participants, the prevalence of interstitial lung disease (ILD) in India ranges from 49.0 to 98.1 per 100,000 persons, with an annual incidence of 10.1 to 20.2 per 100,000 people. Another study indicated that the incidence of ILD in India rose from 24.7 to 33.6 per 100,000 individuals between 2005 and 2020.
Nomenclature and classification of interstitial lung disease
Idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (IIP) is a diverse collection of non-neoplastic illnesses that cause lung parenchymal damage through various patterns of inflammation and fibrosis. The interstitium, which comprises the space between the epithelial and endothelial basement membranes, is the major site of damage in IIPs. However, these illnesses typically affect not only the interstitium but also the airspaces, peripheral airways, arteries, and epithelial and endothelial linings.
The new ATS/ERS classification comprises the following clinicopathologic entities in order of relative frequency:
- Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF)
- Non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP)
- Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP)
- Acute interstitial pneumonia (AIP)
- Respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease (RB-ILD)
- Desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP)
- Lymphoid interstitial pneumonia (LIP)
Interstitial lung disease symptoms
Some people may not experience any symptoms at first, but as the disease progresses, symptoms may appear. Although the symptoms of interstitial lung disease might vary from person to person, the following are the most common ones:
- Shortness of breath: It may initially start during exertion and later may progress to present at rest.
- Dry cough: It may become wet when there is any secondary infection.
- Chest discomfort: Tightness or heaviness in the chest region
- Labored breathing: Difficulty or impairment in breathing
- Clubbing: A downward sloping of the nails and a broadening and rounding of the tips of the toes and fingers
- Fatigue: Extreme weakness and tiredness
- Weight loss: It may be due to the inability to consume food due to severe breathlessness.
These symptoms may be present along with the symptoms of underlying disease, such as joint pains in rheumatoid arthritis. In the late stages, patients may develop symptoms due to failure of other organs, the most common being heart failure.
Interstitial lung disease causes and risk factors
Anyone can get ILD, including children. Many things can cause or increase the risk of developing ILD, including:
- Family history: If a close relative has an ILD, the likelihood of developing an ILD in an individual increases. People may be more susceptible to developing lung scar tissue if they have genetic mutations.
- Occupation and Environment: Exposure to hazardous materials (grain dust, silica dust, indoor hot tubs, asbestos fibers, radiation treatments) accidentally or in the workplace, such as Occupational Lung Diseases (asbestosis and hypersensitivity pneumonitis), may increase the risk of developing ILD.
- Certain medications: Exposure to certain medications or therapies, such as chemotherapy or radiotherapy, may increase the risk of developing ILD.
- Autoimmune diseases: Some autoimmune diseases, such as scleroderma, sarcoidosis, rheumatoid Arthritis, mixed connective tissue disease, dermatomyositis, polymyositis, and Sjogren's syndrome, are also causes of ILD.
- Smoking: It is the most common cause of respiratory complaints worldwide. It not only causes ILD but also aggravates pre-existing disease.
- Gender: Certain interstitial lung diseases (ILDs) are more prevalent in either gender. Men are more likely to get idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and experience more severe symptoms from it. Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) is more prevalent in females. In addition, women are more likely to suffer from various autoimmune illnesses and connective tissue disorders that lead to ILDs.
Unfortunately, in most cases, the ultimate cause may not be known, such as in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF), which is the most severe type of lung fibrosis or scarring.
Interstitial lung disease complications
Without proper treatment, interstitial lung disease (ILD) can lead to the following complications:
- Pneumothorax: It is also known as a collapsed lung and happens when air escapes from the lungs. The space between the lung and the chest wall is then filled with air. This buildup of air puts pressure on the lung, preventing it from expanding as much as it would when one takes a breath.
- Pulmonary hypertension: It is a condition that affects the blood vessels of the lungs. It occurs when the blood pressure in the lungs exceeds normal levels.
- Respiratory failure: It is a life-threatening (severe) condition which causes difficulty breathing on one's own. Respiratory failure occurs when the lungs are not able to get enough oxygen into the blood.
- Lung cancer: It is a form of cancer that occurs when abnormal cells grow aberrant (uncontrollably) in the lungs. It is a significant health problem that can result in severe injury or death.
- Venous thromboembolism: Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a medical condition that occurs when a blood clot forms within a vein. VTE comprises of both deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE).
- Right-sided heart failure: Right heart failure (RHF) is a clinical syndrome associated with symptoms and signs caused by dysfunction and/or overload of the right heart structures, primarily the right ventricle (RV). This results in systemic venous hypertension, peripheral oedema, and, ultimately, the right heart's impaired ability to provide tissue perfusion.
Interstitial lung disease diagnosis
As the symptoms of ILD are not much different from other pulmonary diseases, a high index of suspicion during the patient's initial visit following thorough history taking and physical examination is the cornerstone for early diagnosis. The diagnosis of ILD involves the following:
- Medical history
- Family history
- Physical examination
- Blood tests
- Arterial blood gas
- Complete blood count
- Urea and electrolytes
- Liver function tests
- Calcium
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- C reactive protein
- Sputum analysis
- Imaging tests
- Chest X-rays
- Computed tomography (CT) scan
- High Resolution Computed Tomography (HRCT)
- Pulmonary function tests
- Spirometry
- Peak flow monitoring
- Bronchoscopy
- Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL)
- Lung biopsy
Interstitial lung disease treatment
Treatment for ILDs depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the symptoms. Treatment for ILDs does not cure lung damage but may prevent it from worsening and allow one to breathe more easily. Below are the treatment options for interstitial lung disease (ILD):
- Nonpharmacological therapy
- Cessation of smoking
- Avoiding exposure to harmful particles
- Pharmacological therapy
- Bronchodilators
- Corticosteroids
- Antifibrotics
- Oxygen therapy
- Pulmonary rehabilitation
- Lung transplant
Interstitial lung disease prevention
There is no way to prevent interstitial lung disease (ILD) caused by the genes in the body. Some ILDs can be prevented in the following ways:
- Avoiding smoking
- Avoiding toxins that can harm the lungs in the surroundings or workplace.
- Patients may need to have additional lung tests to see whether their lung damage is worsening.
- Getting Pneumococcal, influenza, and COVID-19 vaccinations can help avoid lung infections that can cause further lung damage.
Difference between ILD and COPD
Interstitial lung disease vs COPD
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) and
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are chronic lung conditions that can make it difficult to breathe. The illnesses, however, differ in terms of their underlying causes and the areas of the lungs affected. Below are some of the parameters that help in differentiating ILD and COPD:
| Parameters | ILD | COPD |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | It is an umbrella term used for a large group of diseases that develops scarring (fibrosis) of the lungs, resulting in increased stiffness and loss of usual lung elasticity, a decrease in the oxygenation process, and resulting in breathlessness and cough, leading to poor quality of life. | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a frequent lung condition caused by damage to the lung's airways or other parts. This damage restricts airflow and makes breathing difficult. |
| Symptoms | Shortness of breath, dry cough, chest discomfort, labored breathing, clubbing, fatigue and weight loss | Shortness of breath, a long-term cough with phlegm that does not go away, fatigue (feeling of tiredness), repeated chest infections, chest heaviness or tightness, and persistent wheezing or whistling are common symptoms of COPD. |
| Causes and risk factors | Family history, occupation and environment, certain medications, autoimmune diseases, smoking, gender | Age, genetics, air pollution, tobacco smoking, occupational exposure |
| Treatment | Bronchodilators, corticosteroids, antifibrotics, oxygen therapy, pulmonary rehabilitation, lung transplant | Bronchodilators, steroids, antibiotics, vaccines, oxygen therapy, pulmonary rehabilitation program, surgery, lung transplant |
Outcome
The overall outcome in ILDs depends on various factors, such as age at onset of symptoms, underlying other co-morbidities, the stage of fibrosis and lung function at the time of diagnosis, and the progression of symptoms despite possible the best treatment. As ILD causes and treatments are still under constant research, patients should never undermine the importance of constant vigilance of their symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Interstitial lung disease
What is the most common type of interstitial lung disease (ILD)?
Smoking-related ILD, followed by sarcoidosis and ILD associated with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and other connective tissue disorders, are the most common ILDs. The most common and severe form of ILD is Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, where the cause is not known.
Is interstitial lung disease genetic or hereditary?
The causes of Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) are vast, but very few diseases are genetic, such as Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis. Most causes are secondary to occupational/ autoimmune/ connective tissue disorders. Genetic causes will only be suspected if all other causes are ruled out and a familial history of the symptoms or disease exists.
Can interstitial lung disease be fatal or cause death?
Any part of the human body, once permanently damaged, can lead to death. The Lungs, the most important organs for respiration and breathing, can cause death as they fail to transport oxygen and remove carbon dioxide in the late stages of ILD, during where the lungs look like a beehive.
What is the difference between COPD and interstitial lung disease (ILD)?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is caused by smoking and other factors, wherein lungs lose their elastic nature and become permanently expanded. Interstitial lung disease (ILD), on the other hand, is a result of permanent damage to lung tissue and resulting scarring. Although, as with other chronic lung diseases, the endpoint regarding symptoms and pathology is the same in both diseases, COPD can be better controlled and even cured if smoking is stopped, but that is not the case with ILD, where the prognosis is comparatively poor.
Is interstitial lung disease curable or reversible, and how to cure it?
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a result of several conditions leading to permanent damage to the lung tissue. Lung tissue/parenchyma, once damaged, cannot regenerate, but it can heal only by scar formation, which is called fibrosis and is irreversible. However, in a handful of diseases like hypersensitivity pneumonitis, if we remove or treat the cause, the lung changes can be reversed. In all other cases, early detection of lung changes through clinical and radiological evaluation can help control the progression of the disease, but it can't stop the disease entirely through medications like antifibrotics (e.g., Pirfenidone).
Related articles
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868
Appointment request - health articles
Thank you for contacting us. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Oops, there was an error sending your message. Please try again later. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Our Locations – Find the Best Hospital Near You
Metro Pillar Number C1772, Beside Avasa Hotel, Hitech City Road, Near HITEC City Metro Station, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Mythri Nagar, Beside South India Shopping Mall, Hafeezpet, Madeenaguda, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
040 4848 6868
Payment in advance for treatment at PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, Telangana, India (Pay in INR ₹)
For Bank Transfer:-
- Bank Name: HDFC
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.50200028705218
IFSC Code: HDFC0000545 - Bank Name: STATE BANK OF INDIA
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.62206858997
IFSC Code: SBIN0020299
Scan QR Code by Any Payment App (GPay, Paytm, Phonepe, BHIM, Bank Apps, Amazon, Airtel, Truecaller, Idea, Whatsapp etc).

CONTACT US
Call: +914048486868
WhatsApp: +918977889778
Email: info@pacehospitals.in
FOLLOW US
SUBSCRIBE
Subscribe to our newsletter and stay updated with the latest health information.
Subscribe to PACE Hospitals' Public Newsletter
Thank you for subscribing to PACE Hospitals' Newsletter. Stay updated with the latest health information.
Oops, there was an error. Please try again submitting your details.
ABOUT US
QUICK LINKS
Disclaimer
General information on healthcare issues is made available by PACE Hospitals through this website (www.pacehospital.com), as well as its other websites and branded social media pages. The text, videos, illustrations, photographs, quoted information, and other materials found on these websites (here by collectively referred to as "Content") are offered for informational purposes only and is neither exhaustive nor complete. Prior to forming a decision in regard to your health, consult your doctor or any another healthcare professional. PACE Hospitals does not have an obligation to update or modify the "Content" or to explain or resolve any inconsistencies therein.
The "Content" from the website of PACE Hospitals or from its branded social media pages might include any adult explicit "Content" which is deemed exclusively medical or health-related and not otherwise. Publishing material or making references to specific sources, such as to any particular therapies, goods, drugs, practises, doctors, nurses, other healthcare professionals, diagnoses or procedures is done purely for informational purposes and does not reflect any endorsement by PACE Hospitals – your trusted hospital near me.